Biology Unit 1 Biochemistry
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What is metabolism

What are intramolecular bonds? What are they?

what are ionic bonds

what are non covalent bonds

what are polar covalent bonds

What are intermolecular bonds? What are the different types?

What are london dispersion forces

What are dipole-dipole forces?
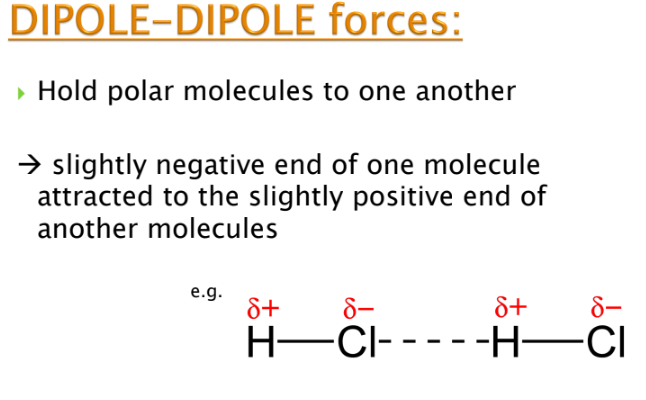
What are hydrogen bonds


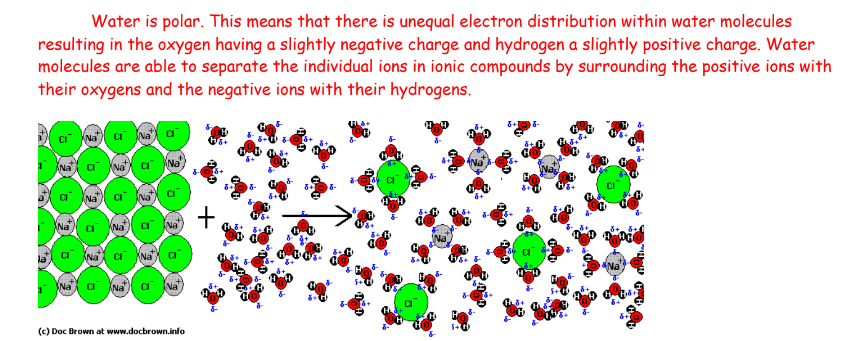



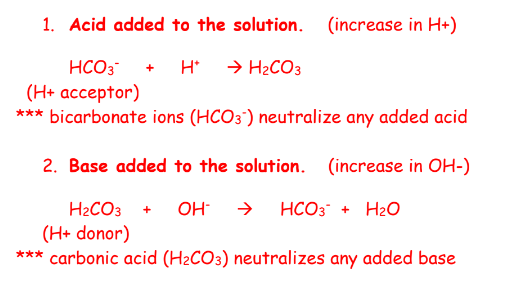


what is the role of an acid
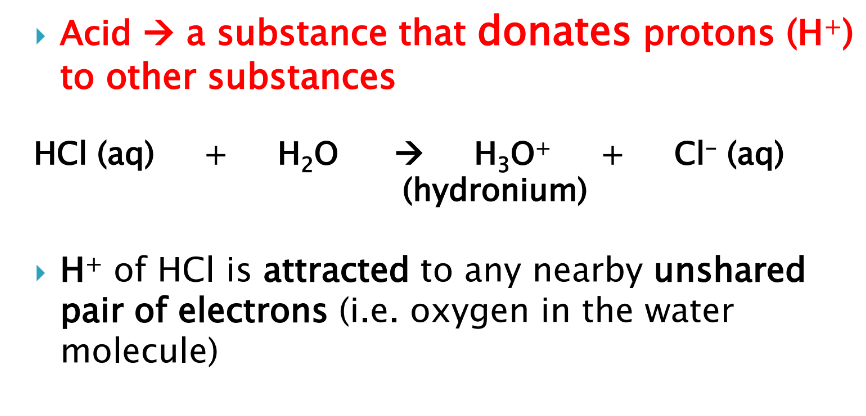
what is the role of a base

What functional group do bases and acid contain?
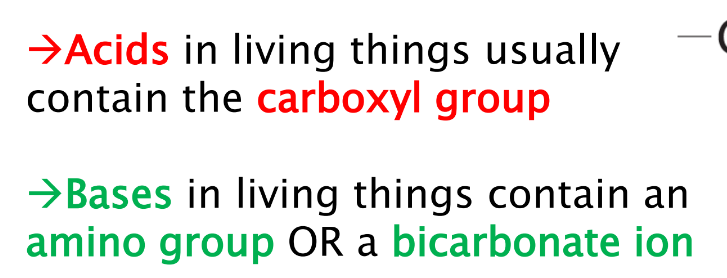
what is acidosis
ph below 7.35
what alkalosis

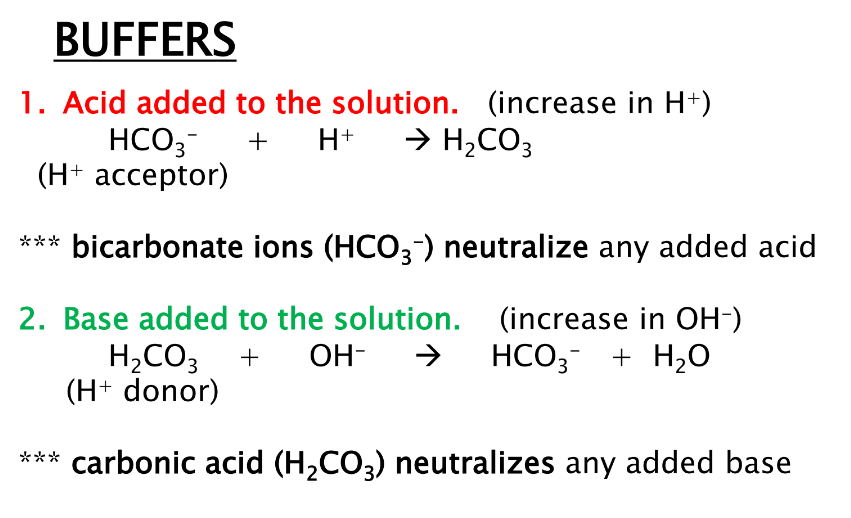
why is buffering important

what is the equation for a bicarbonate buffer for
1.acid
2.base
what is an example structure for hydroxyl
what is an example structure for carbonyl
what is an example structure for carboxyl
what is an example structure for amino
what is an example structure for sulfhydryl
what is an example structure for phosphate
what is an example structure for methyl
what are carbons

what are hydrocarbons

what are isomers
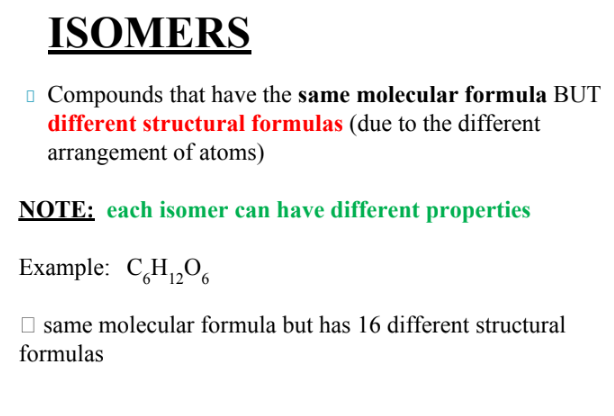
what are the different types of isomers
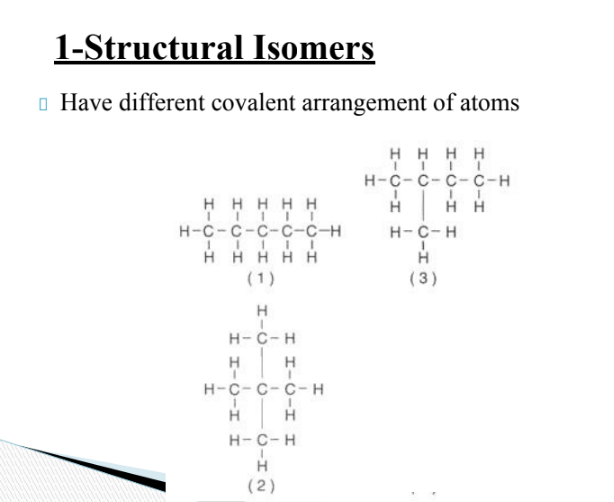
what are structural isomers
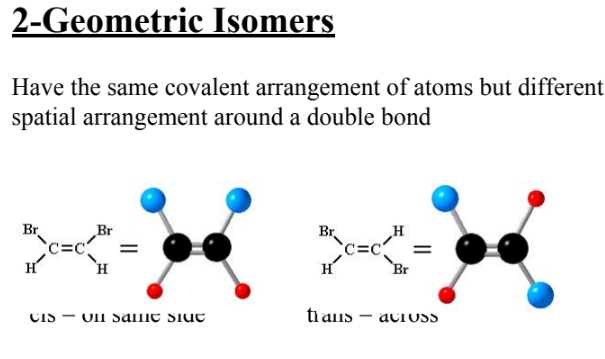
what are geometric isomers
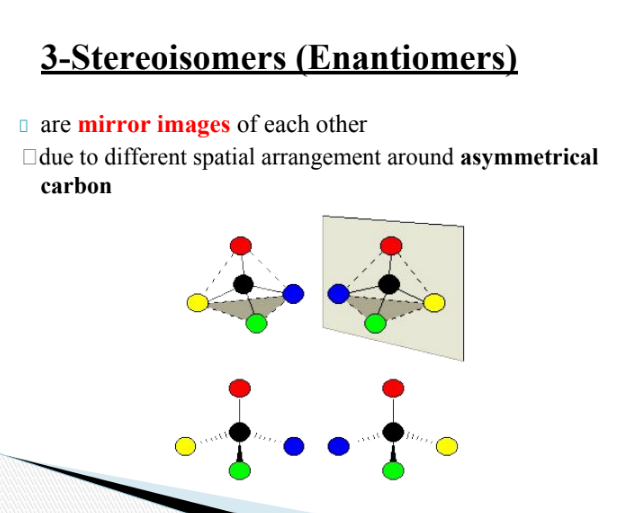
what are stereoisomers
why are functional groups important

what are the 4 types of macromolecules

what are macromolecules made from
polymers
How are polymers broken down and made
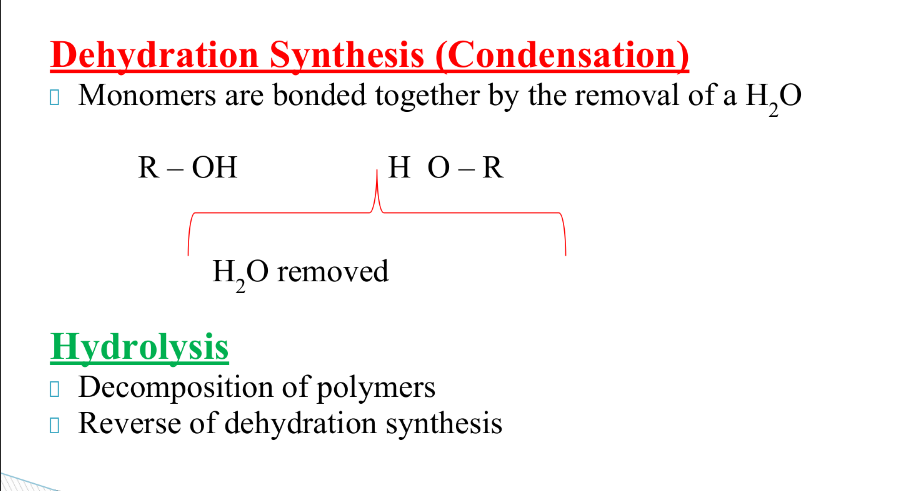
What are linkages, what are the different types and what type of reaction forms them?
Ether, Peptide, ester, phosphodiester

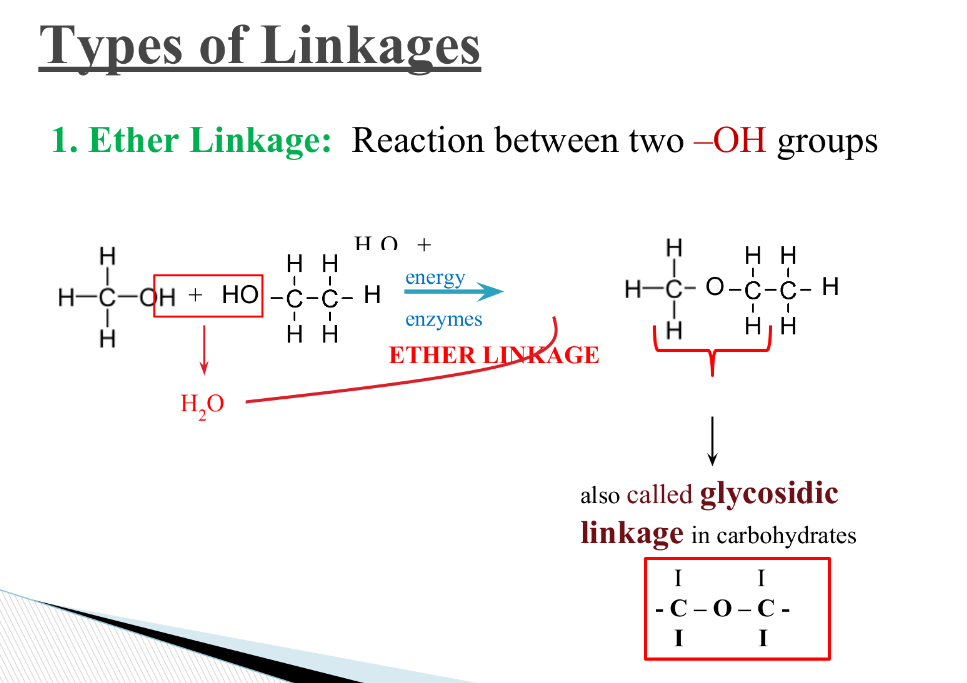
what is a ether linkage? Where is it found?
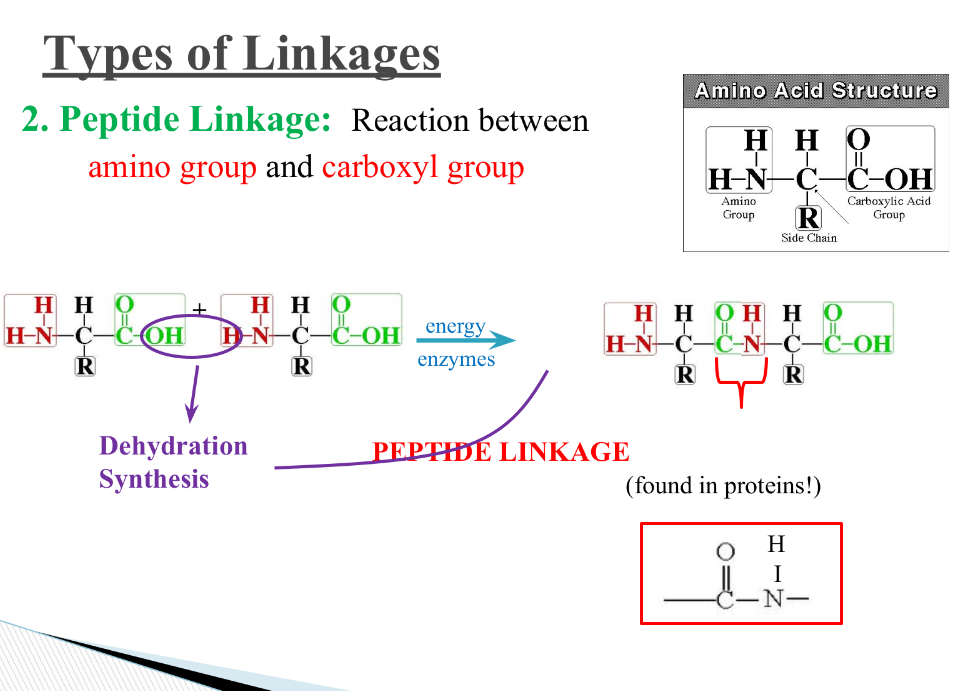
What is a peptide linkage? Where is it found?
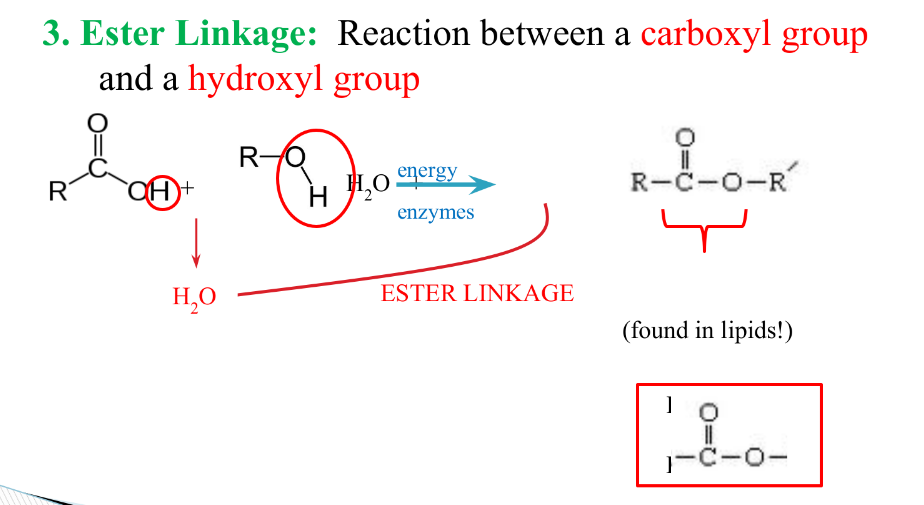
What is a ester linkage? Where is it found?
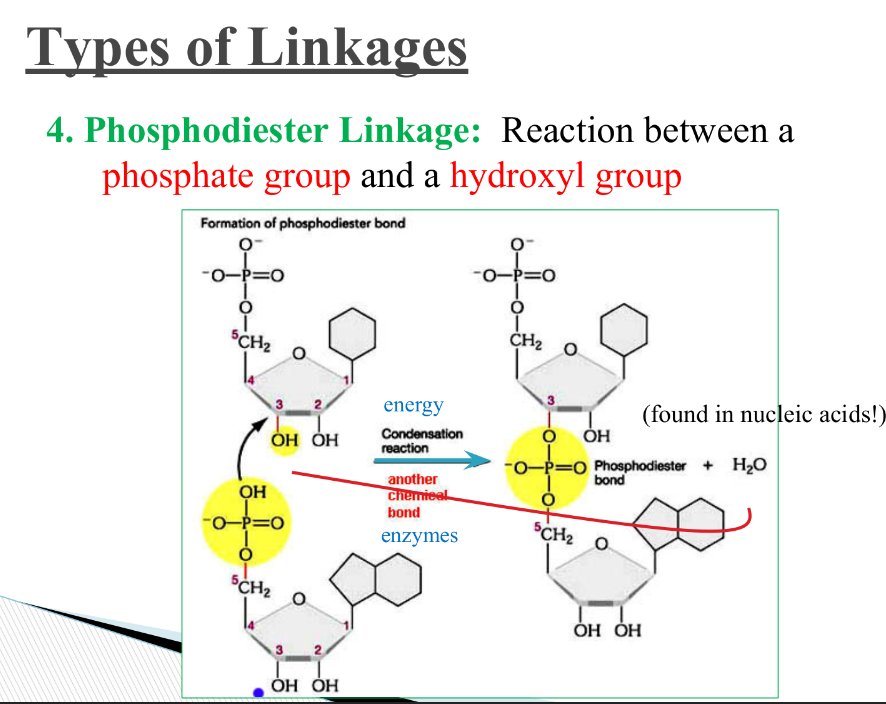
What is a phosphodiester linkage? Where is it found?
What does hydrate mean in regards to carbohydrates
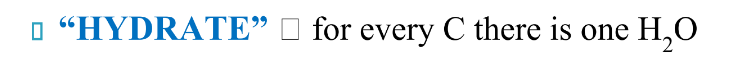
What are the different monosaccharide? Draw them
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
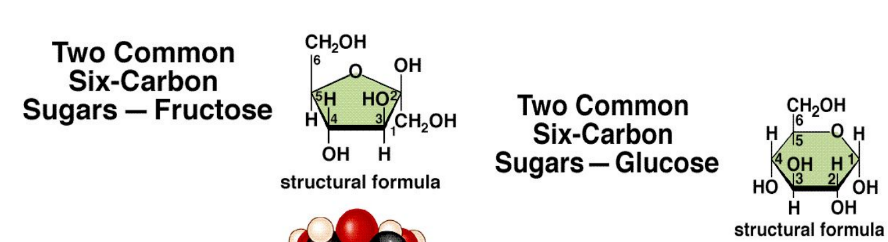
What are the different disaccharides
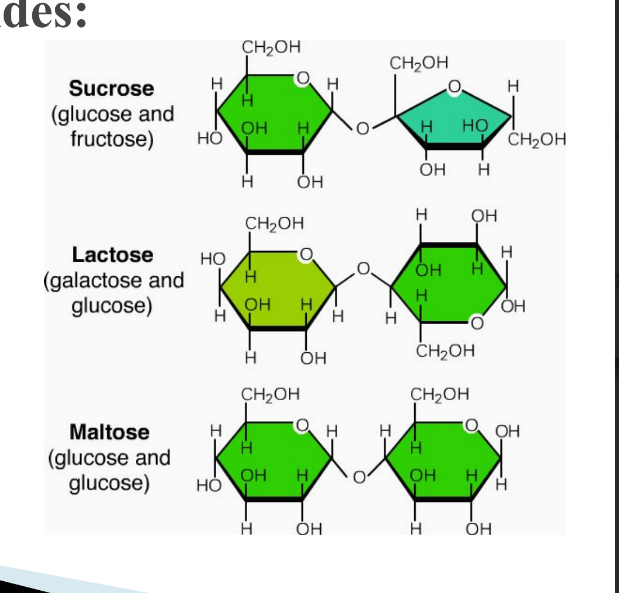
How are disaccharides formed
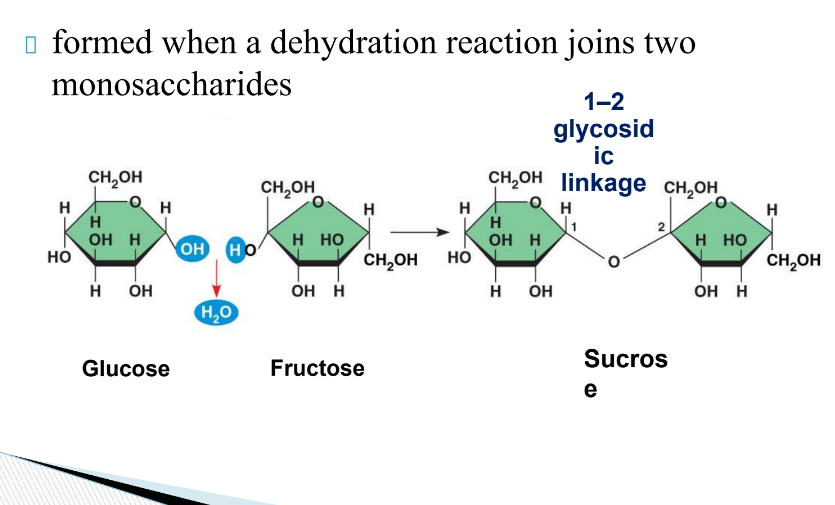
What are Polysaccharides?
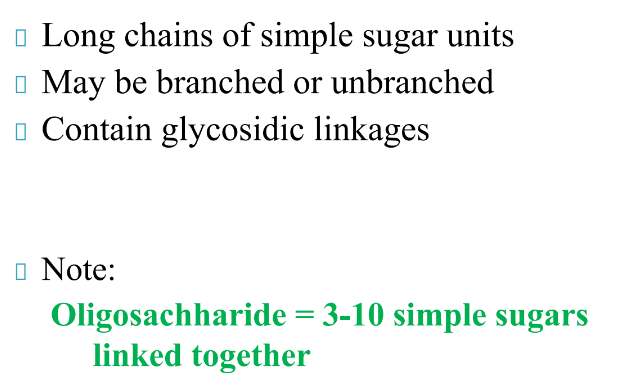
What are the different Polysaccharides?
Starch, Glycogen, Chitin, Cellulose
what is starch

What is glycogen

What is cellulose

What is chitin

What is the structure of Fats
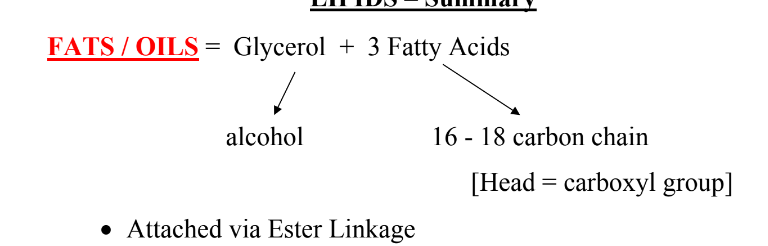
What are the different types of fatty acids

What are the functions of lipids

What is the structure and function of phospholipids?

What is the structure of steroids? Name two examples

What are the structures of waxes
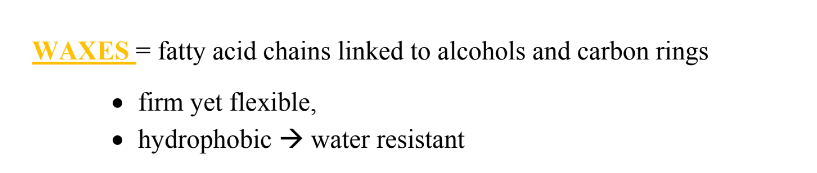
Why is cholesterol important

Where does cholesterol come from

What is the role of HDL

why is HDL important
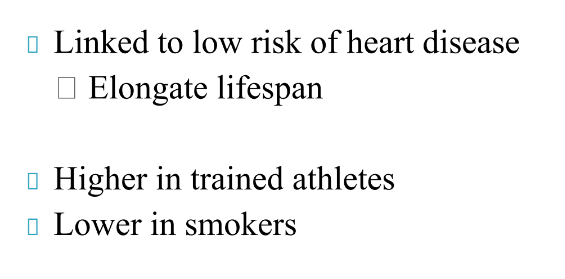
What is the role of LDL

What is the ratio of HDL to LDL that is recommended

What are statins

what are the functions of proteins

How many amino acids are there
20
The bond between 2 amino acids is called _____
peptide bond
What are the different structures of protein? What are the differences?

What are example of proteins with quaternary structure?
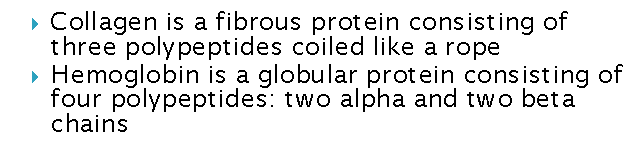
What is denaturation

What causes denaturation

explain what organic solvents are

Explain using a disease why consistent protein structure is important

what are chaperone proteins

what are nucleic acids

What are the roles of nucleic acid
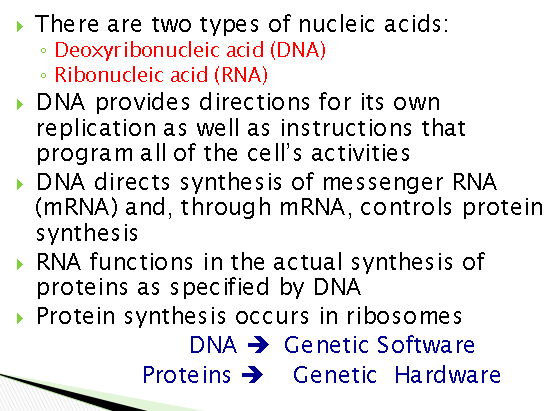
Describe the structure of nucleic acids

What are nucleotide monomers

what are the two nitrogenous bases? Draw them

What is ATP

What is metabolism
c

What is the first law and second law of thermodynamics
Entropy of the entire universe will always
increase with time
a measure of randomness or disorder in a
group of objects or energy
disorder is more likely than order

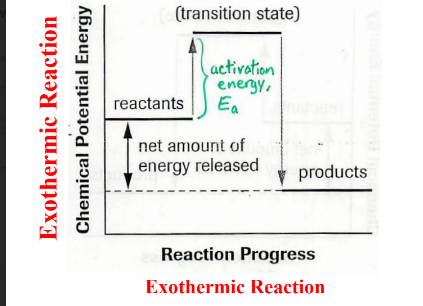
Draw a graph showing a exothermic reaction
Draw a graph showing a endothermic reaction
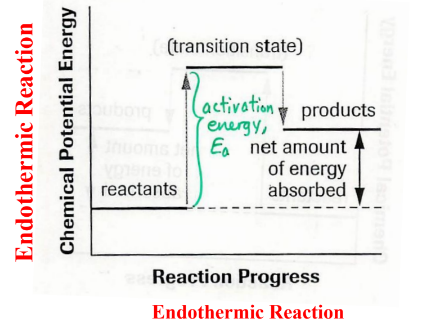
What is activiation energy
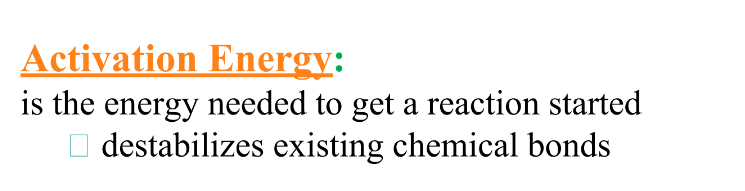
Know how to do energy bond calculations
What is an enzyme and substrate

What is an active site
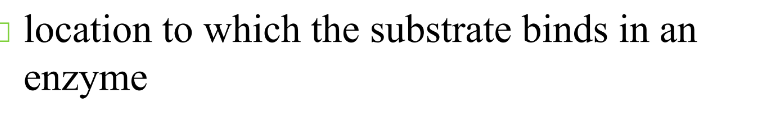
Describe the lock and key model and induced fit
How do enzymes enable
chemical reactions to take
place?
Help reduce the activation energy !
(less “extra”energy is needed)
Transition state can occur at lower temperature
How SPECIFICALLY do Enzymes
Lower Activation Energy?
1. Bring substrates together in the correct
orientation
The enzyme provides a template so they can
come together in the proper orientation (
LOWERS Activation energy)
2. Twisting and Stretching bonds
Active site can “stress” the substrate
( LOWERS Activation energy)
by bending or stretching critical chemical bonds
3. Creates a suitable microenvironment
The active site may contain:
Acidic side chains providing an area of
low pH OR basic side chains with a high
pH, etc.
The microenvironment makes it easier for
the reaction to proceed
(LOWERS Activation energy)
A SINGLE Enzyme catalyzes a
SINGLE Chemical Reaction
The active site is “shape specific” !
only ONE substrate can fit into an the active site of
ONE SPECIFIC enzyme for the chemical reaction to
occur
what are co factors

what are co enzymes

what are the two types of enzyme inhibition
competitive and non competitive
what happens during competitive inhibition
when a molecule, the inhibitor, competes with the substrate for the enzyme's active site. This means the inhibitor physically blocks the substrate from binding, effectively reducing the enzyme's activity.
what happens during non competitive inhibition