Product Costing
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is the risk of not costing a product in the right manner including everything that is relevant?
There is going to be this risk that you may sell a product for less than its actually worth not allowing you to recover all your costs and this means we turn into a loss making entity which is worst scenario for business
How much does something cost to manufacture?
Point at which all the fixed , variable costs and costs associated with running of organisation have been covered
What are the costs while manufacturing
Materials- raw materials bought in physically used for manufacturing process
Labours -employing a workforce to physically operate the machinery and physically manufacture
overheads-always exist in product costing such as rent and electricity
Example of overheads
Rent and electricity
What are the different service firms?
Professional service and manufacturing services
What is an example of a professional service firm
Accountancy firm
What are costs for a professional service firm?
The labour costs and how does the workforce operate and engage which is normally through computer
Overhead cost for accountancy firm which use computers and travel to clients
Computer depreciation and travel getting too and from clients but we don't need to consider anything in production
What is direct labour?
Labour costs associated with pulling all those parts together which includes direct materials being the materials to manufacture the product
Can we monitor indirect materials?
No
Why is total product cost useful?
Amount we can use to ensure that we effectively price our products going into the market.
Why do we include indirect materials in any organisation?
The costs must be shared which we need to recover to ensure that we are profitable
What is prime cost?
Cost of any direct cost associated with the manufacturing of a product( Direct materials, direct labour etc)
What do we need to do with overhead costs
Allocate and apportion them to each product to ensure that the costs are what is happening in the organisation
What is included in labour cost?
Hourly cost multiplied by the number of hours worked + pension contribution + national insurance
How can labour costs be split into?
Salaries so monthly, weekly and annual basis as long as they are directly related to the production of the material
Which costs are not related to production of material?
Overhead costs
What is piecework?
Contractual commitment therefore depends on how effective and efficient the employee is as how much they earn( The more products manufactures more money)
Do all businesses offer the same benefit in kind?
No
Examples of benefit in kind?
Car allowance
Characteristics of direct costing
Always attributable ands traceable to the product and it generally will be variable(more they work the more the labour is going to cost)
Indirect element examples
Pension contributions and national insurance
Purpose of keeping time records?
To make sure we are accurately going to cost something and time efficiently and effectively
Show how a salary payable is split into direct and indirect costs
-Direct: Labour time spent on each product
-Indirect: Work spread over a range of jobs and activities
Direct labour cost attributable to employee is example of variable or fixed costs?
Variable costs
What do materials include
All material required for manufacturing a product then we use these to come up with our material cost and job cart and materials are a direct cost
What are production overheads?
All of our additional expenses that we are going to have in the organisation that we need production to continue but they aren't going to be traceable or related to anything which keep the business operational
Example of production overheads?
Physically repairing machinery, safety procedures and rent of factory buildings
Service Business Production Overheads
-Cost of transport to jobs
-Replacement of tools
-Protective Clothing
Production Overheads: Traditional Approach step by step method
-Allocate(Allocate means assign a whole item of cost to single cost unit) indirect costs to cost centres
-Apportion(Apportion means spread costs over two or more cost units) service cost centre costs to production cost centres
-Absorb overhead costs into product costing in a manner that is reasonable
Formula for production Overheads?
Indirect materials plus indirect labour plus other indirect costs
What is the purpose of absorbing costs?
They can be assigned to products
Methods of absorbing Overheads
-Cost per direct labour hour( direct labor/
-Cost per machine hour
-Cost per $ of labour cost
-Cost per unit
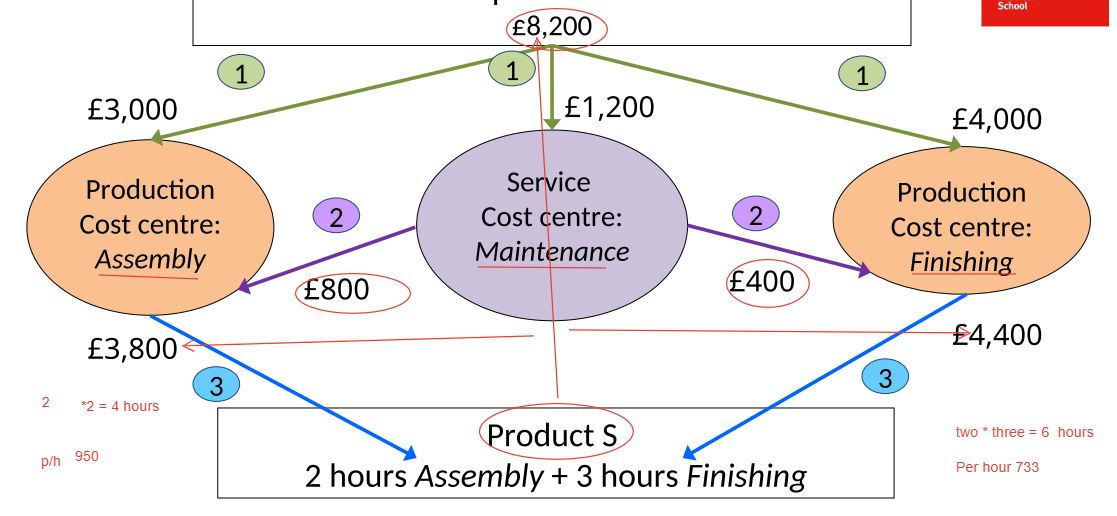
In this example What do we need to do to maintenance department and why?
-The maintenance department will not manufacture a product so we have 1200 worth of costs that have not been allocated to a product.
-We need to think of additional cost of allocation to remove that cost from maintenance and move it to the finishing and assembly departments.
-We will allocate based on reasonable method which could be value of machines we need maintenance department to maintain the machines so the higher the value of machines you hold the more likely you are to require the maintenance department.
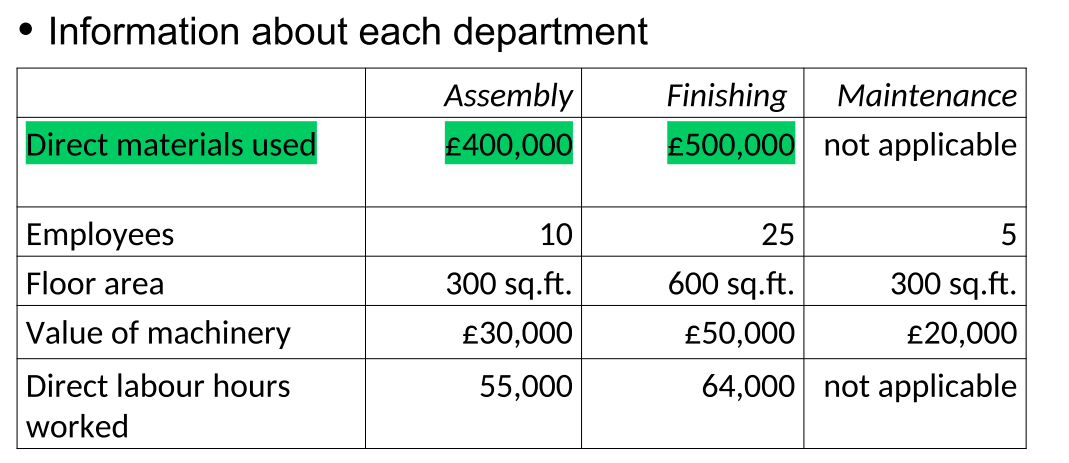
How do we apportion indirect materials used based on direct materials
Use the same ratio that has given in question
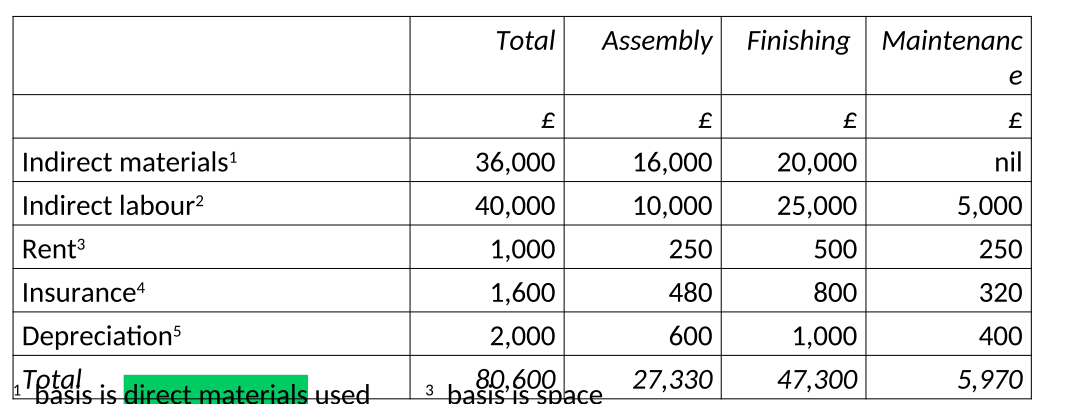
Why do we remove maintenance costs while apportioning costs over department?
As they don’t contribute to the direct production and they do not generate a product
How do you calculate Overhead per direct labour hour?
Total cost per dept./ No of direct labour hours
Predetermined Overhead Cost Rates
-Estimated at the start of a reporting period based on: Overhead costs of previous periods and Best guess for the forecast period
-Adjusted to actual at the end of the period
Predetermined overhead cost rate
Estimated fixed overhead/Estimated labour hours
Is estimated and actual is not the same for costs applied to jobs what do you need to do?
Add Under-applied or over-applied fixed overheads
Formula for fixed overhead incurred
Actual Hours worked on jobs * Overhead costs applied to jobs
What is Activity-based costing?
-A methodology for more precisely allocating overhead to those items that actually use it.
-Allocating costs based on the activity that is driving them so we must think about what drives each individual element of a business
What drives depreciation?
The value of the number or the running time of machines.
Five stages in establishing an ABC system
-Identify activities
-Identify cost drivers that influence the cost of an activity
-Create a cost pool for each activity
-Calculate cost rate for each pool
-Allocate costs to products using drivers for each activity
Traditional based costing for overheads( simplified process)
-Cost centres, Overhead cost rate and Allocate cost using cost rate to measure consumption of cost
Activity based costing for overheads( simplified process)
-Cost pools, Cost driver rate and Allocation cost using cost driver rate and estimated demand for cost
Overhead cost rate for traditional or activity-based costing?
Traditional
Cost-driver rate for activity-based costing or traditional?
Activity-based
What is product costing?
The amount something costs to manufacture is the point where all of the fixed costs and variable costs have been covered as well as other costs
Total production cost formula
Prime cost + Production overhead costs
What is production overhead costs
Total of indirect materials , Indirect labour and other indirect costs in production
Are benefits in kind an indirect cost?
Yes