One Shot—II
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Promotes Elongation of Cell in plants
Auxin
Promotes Seed Germination and Steam Elongation in plants
Gibberellin
Promotes Cell Division in plants
Cytokinins
Promotes Stress Responses and closing of Stomata in plants
Abscisic Acid
Promotes Fruit Ripening in plants
Ethylene
Function of Lymph
• Immunity: Fight infections with white blood cells[lymphocites]
• Cleaning: Collect extra fluid and waste from tissues, returns to blood
• Fat Absorption: Absorbs fat from small intestine during digestion and send it to blood
— Helper of the body: Cleans, Protects and Deliverys —
What helps Xylem in water transport
Transpiration Pull and Root Pressure
What helps phloem in Translocation
Requires energy in ATP form
Urine Formation Precess
• Filtration: Blood enter in Kidneys and filter out waste & extra water due to bomens capsule[Glomerulus].
• Reabsorption: Useful things like glucose, water and salts go back into the blood[Tubule].
• Secretion: Extra waste products are added into the Urine[Collecting duct].
• Remaining waste and water form Urine and leaves the body.
Total number of Nerves in our body
12 pairs of Cranial nerves and 31 pairs of Spinal nerves
Receptors of our body
• Photo Receptor
• Phono Receptor
• Thermo Receptor
• Olfactory Receptor
• Gustatory receptor
• Nociceptors
Functions and Parts of Neurons
Responsible for Transmission and sometimes it longest as 1m.
—Parts of Neurons—
• Dendrite
• Soma
• Nucleus
• Axon
• Axon Terminal
• Myellin Sealth
• Nodes
• Synapse
Types of Neurons
• Sensory Neurons [Receptor to CNS]
• Motor Neurons [CNS to muscle or glands]
• Interneurons [Connect Sensory to Motor]
Parts and Functions of Forebrain
• Cerebrum— Helps in thinking, reasoning, memory, emotions, perceptions and speech
• Thalamus— Helps in Transmission of Sensory information to the cerebrum
• Thalamus— It controls sleep, anger and thirst etc.
Function of Mid-Brain
Connects Forebrain to Hindbrain.
Process Sensory Signals and Controls Motor Function and also helps in Reflex Action
Parts and Functions of Hindbrain
• Cerebellum— Controls Balance Actions in body
• Medulla Oblongata— Controls entire Involuntary Actions, like breathing, heart rate, blood pressure and digestion
• Pons— Regulates Sleeping Cycle and Breathing
Protection of Brain
Cranium Box and 3 layers which is called meninges is filled with Cerebrospinal Fluid[CSF].
It absorbs shocks and prevent Brain from Shocks and Injuries.
Protection of Spinal Cord
Like Brain, is is also wrapped with spinal meninges which is filled with Cerebrospinal Fluid[CSF].
It is protected by Vertebral Column or Backbone, contains 33 individual bones called Vertebrae.
Human Endocrine System
• Pituitary Gland— Growth Hormone[excess–Gigantis][less–Dwarfism]
• Thyroid Gland— Thyroxine[less–Goitre]
• Pancreas— Insulin and Glycagon[less–Diabetes]
• Adrenal Gland— Adrenaline
• Testes[male]— Testesterone
• Ovaries[female]— Oestrogen and Progesterone
Types of Tropism
• Photo Tropism
• Geo Tropism
• Hydro Tropism
• Chemo Tropism
• Thigmo Tropism
Advantages of Variation
• Helps survival in Changing Environment
• Provides disease resistance, drives evolution
• Ensures species Continuity
• Increase Adaptinility
Types and Examples of Binary Fission
— Binary Fission —
• Longitudinal– Euglena
• Transverse– paramecium
• Irregular– Amoeba
Types and Examples of Asexual Reproduction
• Binary Fission— Euglena, Paramecium and Amoeba
• Multiple Fission— Plasmodium
• Budding— Hydra and Yeast
• Fragmentation— Spyrogyra
• Regeneration— Planaria
• Vegetative Propagation— Potato and Bryophyllum
Advantages of Vegetative Propagation
• Rapid Growth
• No Seed Needed
• Genetically Identical Plants
• Better Survival Rate
• No Pollination Required
Difference between Mitosis and Meosis
— Mitosis —
• 1 Division
• 2 Identical Cells
• Diploid
• Growth and RepairA
• Sexual Reproduction
— Mitosis —
• 2 Division
• 4 Identical Cells
• Haploid
• Gametes[sperm & egg]
• Sexual Reproduction
Parts of Flower
• Stamens[male]: Anther[produce pollen], Filament[support]
• pistil[female]: stigma[sticky], style[tube] and ovary[contain ovule]
• Petals[attractive part]
• Sepals[protect flower bud]
• Ovule[contain eggs to seeds]
Parts of Seeds
• Cotyledon [storage]
• Redical [root]
• plumule [shoot]
Sexual Transmitted Disease
• Viral Infection— HIV AIDS, Warts
• Bacterial Infection— Gonorrhea, Syphilis
Contraceptive Methods
• Physical Methods: Condoms, Diaphragm and Cervical Cap
• Surgical Methods: Vasectomy and Tuboctomy
• Chemical Method: OCs [phills]
• IUCD: Copper T
Scientific Name of Pea Plant
Pisum Sativum
Bacteria tha make it's food own with help of photosynthesis
Cyanobacteria
United Nation Environment Programme decode to Prevent Ozone layer on
1987
Parts of Male Reproduction System
• Testes: Sperm/Testesterone
• Epididymis: Sperm Nourishment
• Vas Defence: Tube
• Seminal Vesical: Fluid/ Nourishment
• Prostate Gland: Fluid/ Activate
• Urethra: Out Urine/ Sperm
• Penis: Transfer
Parts of Female Reproductive System
• Vegina: Entry
• Cervix: Uterus Opening
• Uterus: Push Towards Fallopian Tube
• Fallopian Tube: Fertilisation be here
Two Amylase that present in Buccal Cavity
• Salivary Amylase[starch]
• Lingual Lipase[fat]
Extraction of Metal from its Ore
• Step¹— Crushing and Grinding
• Step²— Concentration of Ore
• Step³— Extraction of Ore[Roasting or Calcination]
• Step⁴— Reduction
• Step⁵— Refining of Metal
Prevention from Corrosion
• Covering [Paint, Grease, Varnish, Enamel]
• Galvanising [Thin Coating of Zinc]
• Alloys
Prevention from Rancidity
• Using Air Tight Container
• Storing in Cool and Dark places
• Packing with Nitrogen
Types and Examples of Indicators
Natural Indicator: Litmus[R/B] and Turmeric[Y/R]
Synthetic Indicator: Phenopthalin[C/P] and Methyl Orange[R/Y]
Olfactory Indicator: Onion, Vanilla essence and Clove oil
PH in Everyday Life
• Our body works between pH 7–7.8.
• pH of Rain less then 5.6 called Acid Rain.
• Our stomach produce HCl [pH 1–1.5]
• Tooth Decay starts when pH of mouth less then 5.5.
• Plant needs specific pH for their growth [pH 6–8]
• Self defence by Animals [Honey bee–Methanoic Acid(2-3)]
Fullerance has
20 Hexagonal Rings and 12 Pentagonal Rings
Different between Breathing and Respiration
—Breathing—
¹Inhalation and Exhalation
²Physical Process
³Occurs in Nostrils, Lungs, Diaphragm
⁴No Energy Produced
⁵Voluntary and Involuntary
—Respiration—
¹Breaking down of Glucose to form ATP
²Chemical Process
³Occurs in Cells & Mitochondria
⁴ATP is Produced
⁵Only Involuntary
Fuse wire is formed with
Copper[Cu]–Nikkle[Ni] Alloy / Lead[Pb]–Tin[Sn] Alloy
Heat Element is formed with
Nickrome Alloy wire
Image Formation in Concave Mirror or Convex Lens
• At Infinity— At F/F²
• Beyond C/2F¹— Between C/2F² & F/F²
• At C/2F¹— At C/2F²
• Between C/2F¹ & F/F¹— Beyond C/2F²
• At F/F¹— At Infinity
• Between F/F¹ & P/O— Beyond Mirror/Lens
Image Formation in Convex Mirror or Concave lens
At Infinity— At F/F¹
Between ∞ & P/O— Between P/O & F/F¹
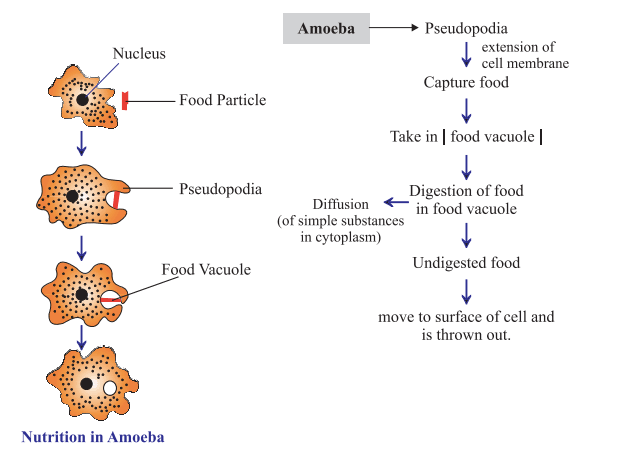
Respiratory System
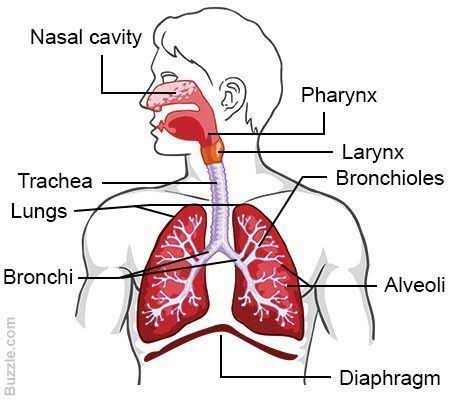
Human Eye Structure
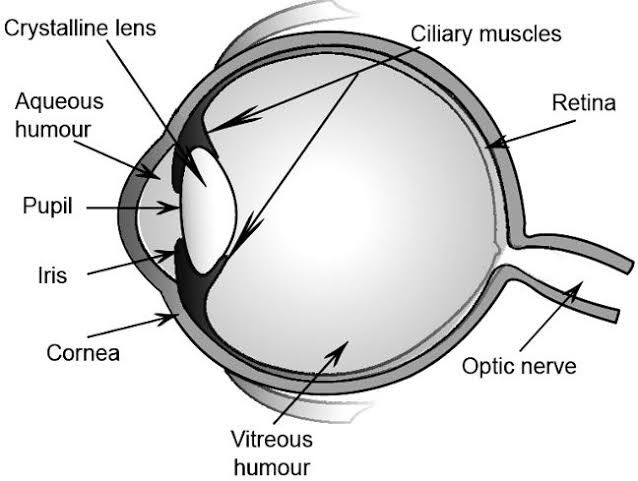
Nutrition in Amoeba