Animals & the environment lecture content
1/112
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
What is the definition of Natural selection?
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than
other individuals because of those traits.
Describe what is meant by Overproduction?
Members of a population can produce more offspring than can survive and reproduce due to finite resources
Describe what is meant by Variation?
Members of the same population exhibit variable phenotypic traits, and some of this variation is heritable.
Describe what is meant by Competition?
Individuals compete for limited environmental resources
Describe what is meant by differential reproduction.
Some members of a population leave more offspring than other members of the same population.
In his work, On the Origin of Species by means of Natural Selection, Charles Darwin’s ideas can be distilled into for main tenets. What are they?
Overproduction, Variation, Competition, Differential reproduction
How many main tenets can Charles Darwin’s’ work be distilled into.
Four
Identify and describe the four main ideas of Charles Darwin’s work?
1) Overproduction: Members of a population can produce more offspring than can survive and reproduce due to finite resources
2) Variation: Members of the same population exhibit variable phenotypic traits, and some of this variation is heritable.
3) Competition: Individuals compete for limited environmental resources.
4) Differential reproduction: Some members of a population leave more offspring than other members of the same population.
Define the term Morphotype
A group of individuals of the same species that look the same.
What is a Mutation.
A change in the
nucleotide sequence of an organism’s DNA that can lead to variations in traits.
What are the three ways mutations can be categorized?
1) Adaptive: increases the chances of reproduction in the individual carrying it.
2) Maladaptive: decreases the chances of reproduction in the individual carrying it.
3) Neutral: does not affect the chances of reproduction in the individual carrying it.
What is meant by an adaptive mutation?
mutations that increases the chances of reproduction in the individual carrying it.
What is meant by a Maladaptive mutation?
Mutations that decreases the chances of reproduction in the individual carrying it.
What is meant by a neutral mutation?
A mutation that does not affect the chances of reproduction in the individual carrying it.
What is Differential Reproductive Success?
The concept that individuals with better adaptations have greater access to resources and chances of survival, leading to higher reproductive success, which results in more alleles being passed on to the gene pool and an increase in the frequency of favored alleles.
Define Evolution
The change in allele frequencies within a population from one generation to another.
Define relative fitness
The contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation relative to the contributions of other individuals.
Define the term Hypothesis
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find.
What is a null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis suggests that there is no effect or difference in a situation, and any observed changes are due to chance.
I.e the expectation, if no evolutionary mechanisms occurred and the allele frequency remained the same.
What is the importance of using a Null Hypothesis?
The null hypothesis allows for determining whether observed data deviates from what would be expected by chance alone. If results show a statistically significant difference, the null hypothesis can be rejected, leading to support for the alternative hypothesis.
What is the difference between a hypothesis and a null hypothesis?
A hypothesis proposes a testable prediction regarding a relationship or outcome, while a null hypothesis states that there is no significant effect or difference, serving as a baseline for comparison.
What does the selection coefficient represent?
A measure of selective pressure against a particular phenotype, relative to the others in the population.
What does the fitness coefficient (W) represent?
W measures an individual's reproductive success compared to the population average; a value of 1 indicates peak success.
( the adaptive value of a particular phenotype)
How is the selection coefficient(s) calculated?
It is calculated as 1 - W.
How is the fitness coefficient(W) calculated?
the phenotype/morphotype that produces the most offspring is said to have a fitness of 1.0 (100%). All other competing individuals' W are measured relative to the most successful genotype's W.
Calculate the fitness coefficients for mice with different fur coats if:
The white mice produced 3 offspring in a given generation, the black mice produced 2, and the brown produced 1.
White Mice: W = 1.0
Black Mice: W = 2/3 = 0.66 (The black mice are 66% as fit as the white mice)
Brown Mice: W = 1/3 = 0.33 (The brown mice are 33% as fit as the white mice)
A recent field experiment examined how the genotype at one locus affected the survival of sunflowers. 200 individuals with the AA, Aa, and aa genotypes were planted. Survival was surveyed at the time of flowering. AA :170, Aa:20, aa: 20
What are the relative fitnesses and selection coefficients for each genotype?
To calculate relative fitness, divide by the highest fitness (AA).
W: AA=1 Aa=0.12 aa=0.12
S: AA=0 Aa=0.88 aa=0.88
Which of these statements about Georges Cuvier (1769-1832) is not correct.
He recognised that extinction of species was common
He noticed that older strata had fossils very different from extant species
He suggested that boundaries between strata represent catastrophic events
He developed the field of Paleontology
He inferred that species must evolve
He inferred that species must evolve
Cuvier opposed the idea of evolution,
What were aristotle’s views on life?
Viewed species as fixed and unchanging
Arranged in a hierarchy of perfection = Scala Naturae “Great chain of being” •
Prevailing view for more than two millennia
What were the 18th century European views on life?
Species were individually designed by God and therefore perfect
Earth is young (<10,000 years old)
What were Carolus Linnaeus views on life?
Interpreted organismal adaptations as evidence each species was designed for a specific purpose by god.
Species fixed and unchanging
True or False: 18th and 19th Century France and Britain: Exerted a strong influence on Darwin.
True
How did 18th and 19th century France and Brittan influence Darwin
Darwin agreed that if geologic change results from slow, continuous actions rather than from sudden events, then Earth must be much older than the widely accepted age of a few thousand years.
Multiple Choice Darwin and Wallace were influenced by...
Traveling the world
geologists such as Hutton and Lyell
both
The correct answer is: both
Who is George Curvier?
• Largely developed paleontology, the study of fossils
• Recognized extinctions as common
•Opposed the idea of evolutionary change
•And instead advocated catastrophism, events in the past are different from present day
Who is associated with the theory of catastrophism?
Georges Cuvier
Define the term catastrophism.
the theory that the Earth's landscape and geological features were formed by sudden, catastrophic events, causing the extinction of some species, rather than gradual, uniform processes.
What does catastrophism suggest about species extinction?
Catastrophic events, such as a flood, would destroy many species living in a area, which were later repopulated by different species immigrating from other areas.
What is the concept of Gradualism?
The idea that profound change can take place through the cumulative effect of slow but continuous processes.
Who is associated with the concept of Gradualism?
James Hutton
What is the principle of Uniformitarianism?
Processes operating today are the same processes that operated in the past.
Who is associated with the concept of Uniformitarianism?
Charles Lyell
What concept is this an example of:
Processes operating today are the same process of the past, at the same rate.
I.e. if we can calculate how much silt is falling in a river, we can predict how much would have in the past.
Uniformitarianism (Lyell):
What is Lamarck's Theory of Evolution?
Lamarck's Theory of Evolution proposed that evolution occurred over many generations.
What mechanism did Lamarck propose for evolution that Darwin disagreed with?
Lamarck believed in ’Inheritance of acquired traits’
What are the two main points articulated in Darwin's The Origin of Species?
Descent by Modification and evolution by Natural Selection.
What does the phrase ‘descent with modification’ usually refer to in the context of evolution by natural selection?
Organisms presently inhabiting the Earth are descendants of an common ancestor.
and
As species adapt to different environments over time, they accumulate differences and diverge from one another.
how did Darwin perceive both unity and diversity in life?
Darwin thought of evolution as a process in which both descent (shared ancestry, resulting in shared characteristics) and modification (the accumulation of differences) can be observed.
How do descent by modification and natural selection relate?
Natural selection is the primary mechanism of descent with modification.
How did Darwin describe the process of natural selection?
Darwin inferred that that individuals with inherited traits that are better suited to the local environment are more likely to survive and reproduce than less well-suited individuals.
What happens to advantageous traits over many generations?
A higher proportion of individuals in a population will have the advantageous traits, increasing the allele frequency in the gene pool.
What did Darwin perceive about the unity of life?
He attributed it to the descent of all organisms from a common ancestor that lived in the remote past. (Descent)
What did Darwin perceive about the diversity of life?
He thought that as the descendants of that ancestral organism lived in various habitats, they gradually accumulated diverse modifications, or adaptations, that fit them to specific ways of life. (modification)
What key concept is fundamental to Lamarckian evolution, but is not a key
concept of Darwinian evolution by natural selection?
A. Phenotypes acquired during the life of an individual are passed directly to offspring.
B. Phenotypes vary between siblings.
C. Phenotypes must have a genetic component to be inherited.
D. Phenotypes that provide more opportunities for reproduction will be under positive
selection.
E. Phenotypes that provide survival advantages will be under positive selection.
A. Phenotypes acquired during the life of an individual are passed directly to offspring.
What is the smallest unit of evolution?
Population
Define the term population
a localized group of individuals of the same species and interbreed, producing fertile offspring.
True or False: A trait advantageous in current environment may be useless or detrimental in another
True
True or False: Natural Selection causes variation:
False-it only acts on variation that already exists within a population.
How can one test the theory of evolution?
observing changes in populations over time, looking at
comparative anatomy, analyzing the fossil record, comparing DNA sequences
What are Analogies?
Analogous structures are similar features in different species that evolved independently due to similar environmental pressures (convergent evolution), despite not sharing a common ancestor
What are Homologies?
Homologies refers to phenotypic and genetic similarities due to shared
ancestry.
What type of evolution do homologous structures arise from?
Divergent evolution
What type of evolution do analogous structures arise from?
Convergent evolution
Define convergent evolution:
Convergent evolution occurs when similar environmental pressures and natural selection produce similar (analogous) adaptations in organisms from different evolutionary lineages.
Define divergent evolution?
The evolutionary pattern in which species sharing a common ancestry become more distinct due to experiencing different selection pressures.
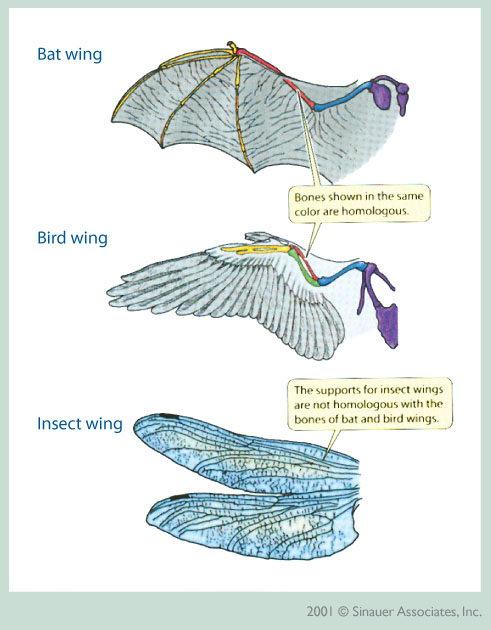
Are the wings of a bird and a dragonfly an example of analogous or homologous structures.
analogous structures
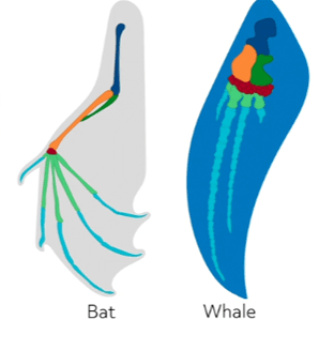
Are the wings of a bat and whale fins an example of convergent or divergent evolution?
Divergent Evolution.
What are the three types of homologies that can be used as evidence for evoution?
i. Anatomical homology(bone structure)
ii. Comparative embryology(Reveals additional anatomical homologies not visible in adult organisms)
iii. Vestigial structures(Remnants of features that served important functions in the ancestral species.)
Are the wings of a bird and a bat an example of analogous or homologous structures.
Homologous.
What are Vestigial structures?
Remnants of features that served important functions in the ancestral species.
Explain the difference between a homologous structure and an analogous structure?
Homologous structures are anatomical features in different species that are similar because they were inherited from a common ancestor.
Analogous structures, on the other hand, are features in different species that are similar because they evolved independently to serve similar functions, not because of a shared ancestry.
Define the term Phylogeny:
Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a species or group of related species
What does a phylogenic tree depict?
A branching diagram that represents a hypothesis about the evolutionary history of a group of organisms.
What is Systematics?
Scientific discipline that classifies organisms using their evolutionary relationships.
If you used a phylogeny diagram to classify species=> that would be systematics
Describe Binomial Nomenclature
When looking at binomial nomenclature what does the Genus represent?
Capitalized First part of binomial nomenclature that refers to the family the specie belongs to.
When looking at binomial nomenclature what does the Specific epithet represent?
The lowercase second part of the binomial nomenclature that is unique to each species within the genus.
Define the term taxon:
The taxonomic unit at any classification level.
What is the hierarchical Classification and describe the order of taxon.
Classification system from broad to narrow from
broad to narrow are domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
What is meant by the term Sister taxa?
groups that share an immediate common ancestor that is not shared by any other group.
True or false: The more morphological and molecular(DNA Sequence) similarities, the more likely the organisms are closely related.
True
What are Molecular homologies?
What are Molecular analogies?
What are Orthologous genes?
When looking at taxon how many Domains are there?
Two domains plus hybrid Eukaryotes
What is a rooted phylogenic tree?
A rooted tree includes a branch to represent the most recent common ancestor of all taxa in the tree.
True or False: Phylogenetic trees indicate
when species evolved or how much
change occurred in a lineage.
False.
Which of the following shows the correctly formatted taxonomic
name for the Wellington tree wētā?
A. Hemideina crassidens
B. Hemideina Crassidens
C. Hemideina Crassidens
D. hemideina crassidens
E. hemideina crassidens
A.Hemideina crassidens (Genus is capitalized and specific epithet is lower cased, and both are italicized.
What can phylogenetic history can be inferred from?
Morphological and molecular homologies among living and fossil organisms.
What are phenotypic and genetic similarities due to shared ancestry are called?
Homologies
Which of the following best explains why many birds such as weka, kiwi and
kakapo are flightless despite not being closely related?
A. Divergent evolution
B. Convergent evolution
C. Homology
D. Synapomorphy
E. Parsimony
B. Convergent evolution
What does the term clade refer too?
A group of taxa with shared common ancestor
What make a clade valid?
A valid clade is monophyletic; Signifying that it consists of the ancestor species and all its descendants (including any that are extinct).
A valid clade is monophyletic. What does the term Monophyletic mean?
That the clade consists of the ancestor species and all its descendants
True or False: A valid Clade share a more recent common ancestor with each other than with any other taxa.
True
Define shared ancestral characteristics:
A homologous structure that is older than the branching of a clade and thus is shared beyond the taxon we are trying to define.
e.g Vertebrae is not unique to mammals.
Define Shared derived characteristics;
An evolutionary novelty unique to a clade.
E.g Hair is unique to mammals.
What is the mutation gene duplication? Describe its characteristics;
One of the most important types of mutations in evolution. increases the number of genes in a genome creating paralogous genes (parlous). Duplicated genes can take on new functions by further mutations
Define Paralogous genes;
Genes that are copies of each other, resultant from gene duplication. They are free from constraints, and often add new functions.
How are paralogous genes formed?
Gene duplication.