Exploring Creation with Biology Module 14 Study Guide
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
2. If a portion of a plant is producing new cells, what type of plant tissue will be in that region?
Meristematic tissue will be anywhere that mitosis is going on. The cells that perform mitosis are a part of the meristematic tissue.
3. What do we call the structure that attaches the blade of the leaf to the stem?
The petiole attaches the leaf blade to the stem.
4. Identify the leaf mosaics in the pictures below:
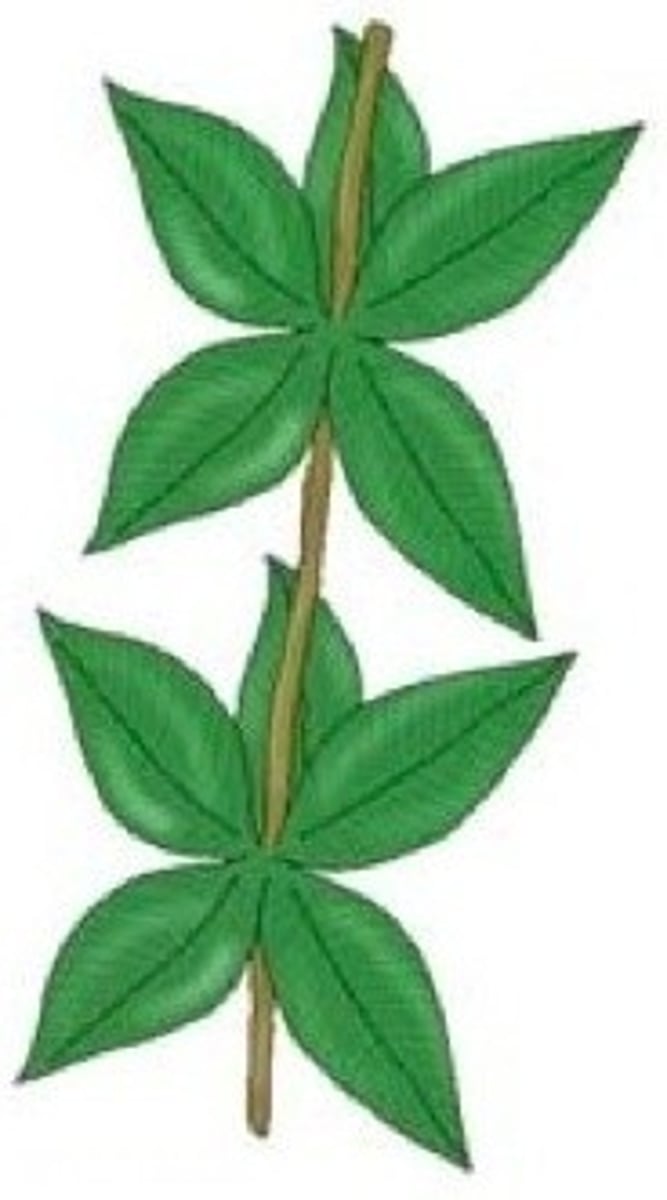
a.
Whorled
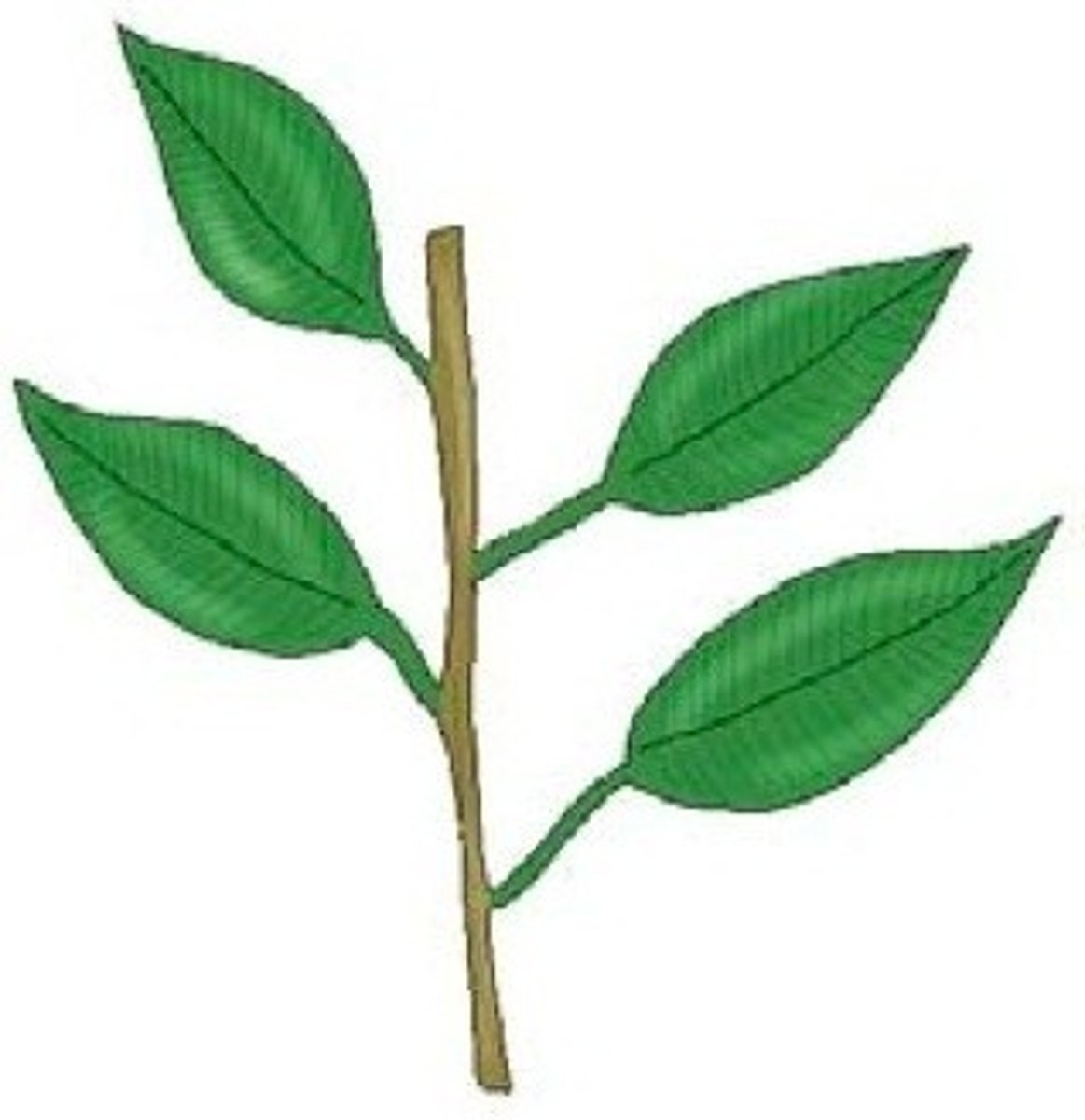
4. Identify the leaf mosaics in the pictures below:
b.
Alternate

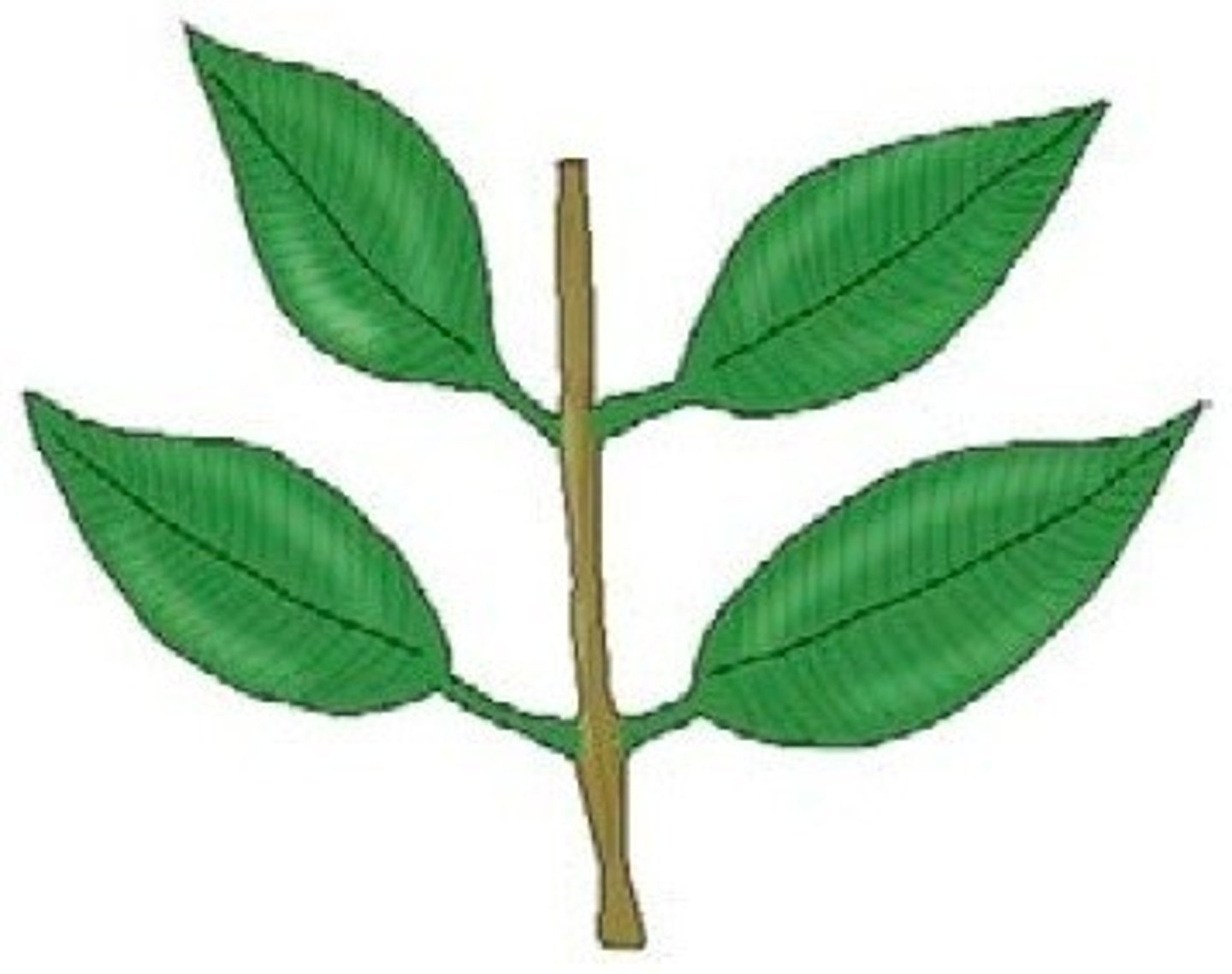
4. Identify the leaf mosaics in the pictures below:
c.
Opposite

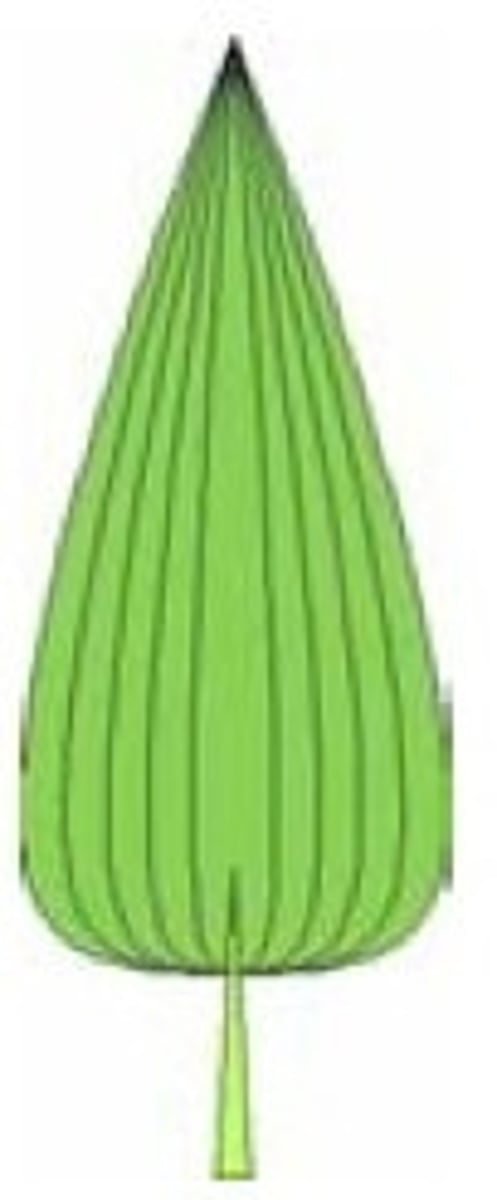
5. Determine the shape, margin, and venation of the following leaf:
Shape - Deltoid
Margin - Entire
Venation - Parallel

5. Determine the shape, margin, and venation of the following leaf:
Shape - Elliptocal
Margin - Serrate
Venation - Pinnate
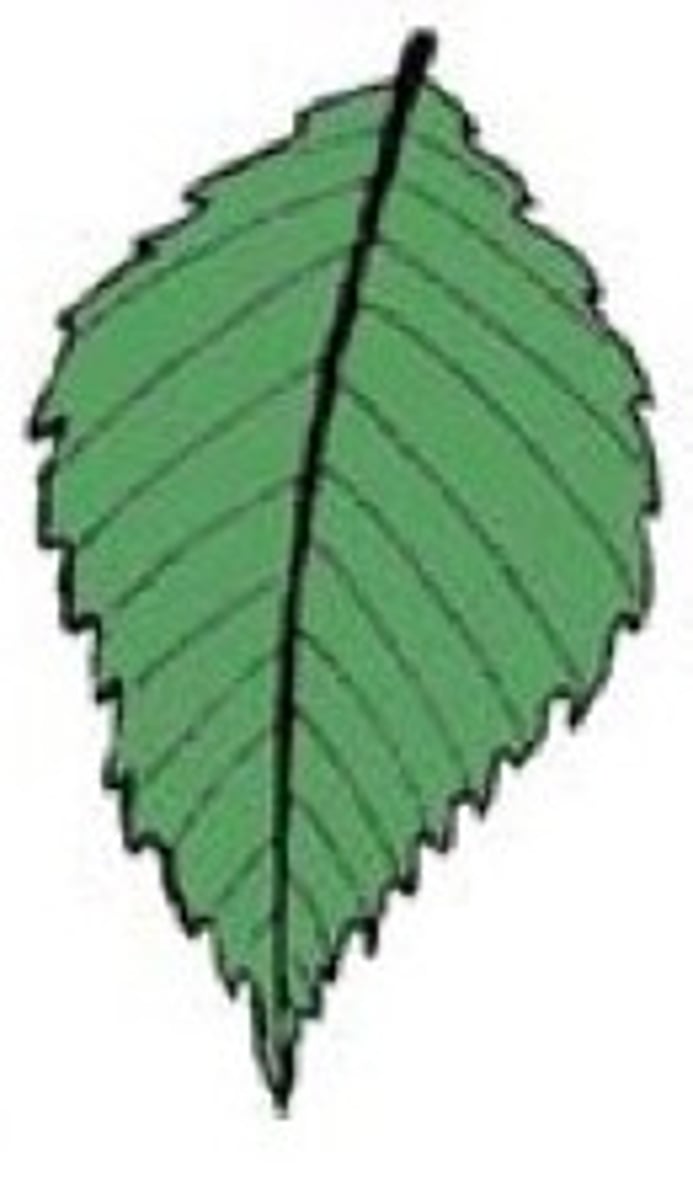

5. Determine the shape, margin, and venation of the following leaf:
Shape - Lobed
Margin - Entire
Venation - Pinnate
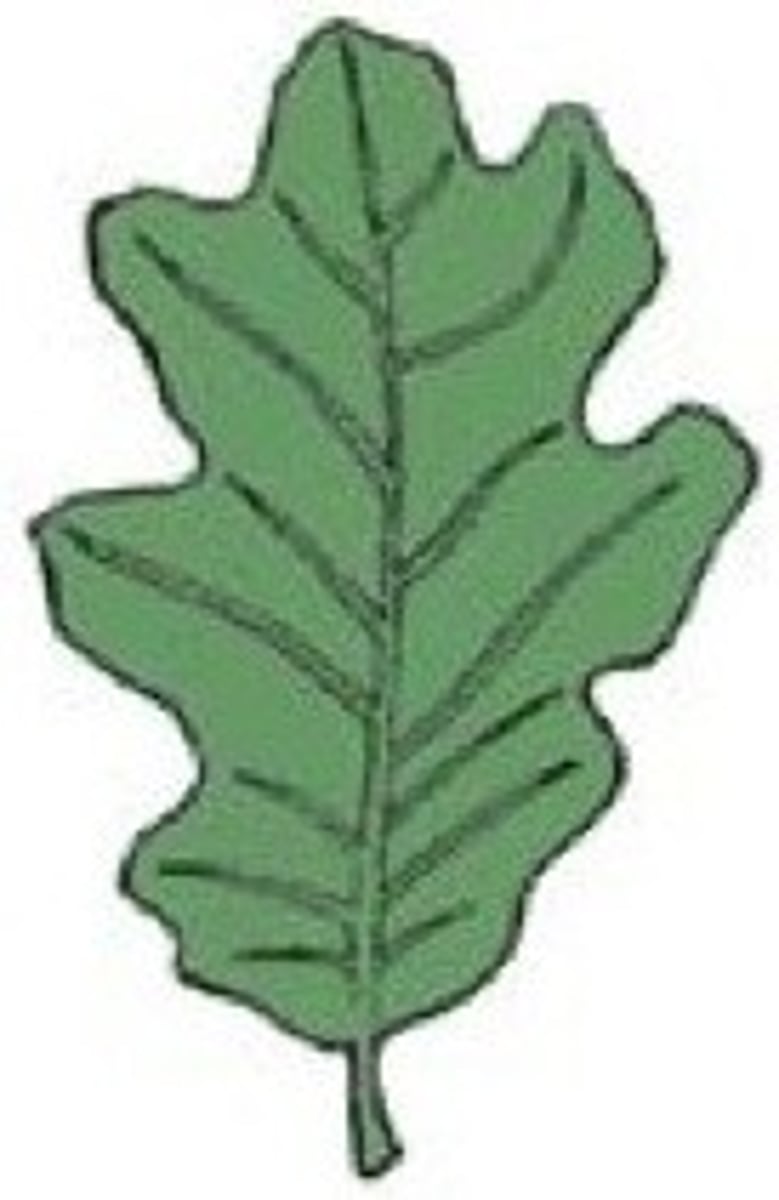

5. Determine the shape, margin, and venation of the following leaf:
Shape - Cleft
Margin - Dentate
Venation - Palmate
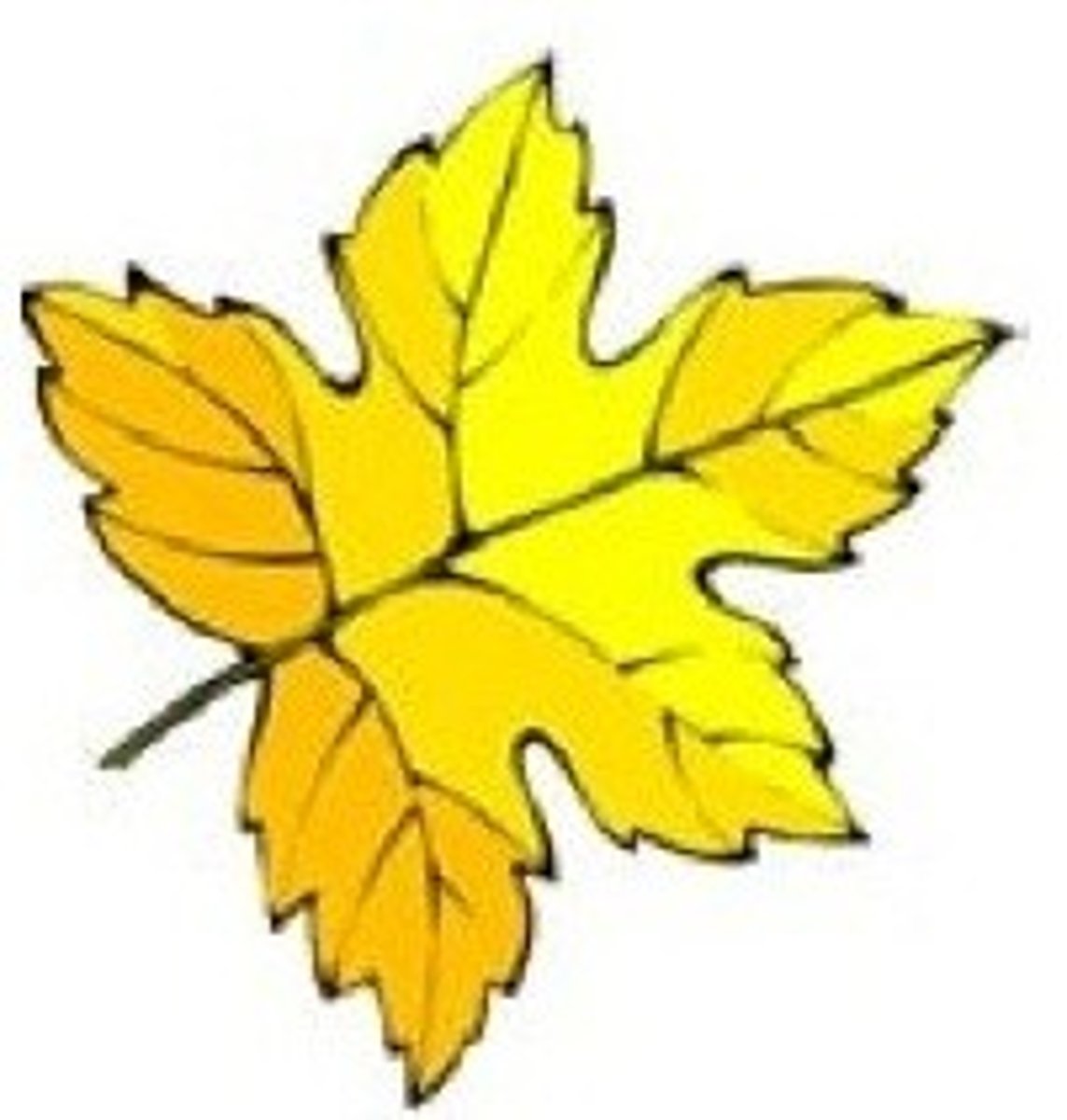

5. Determine the shape, margin, and venation of the following leaf:
Shape - Orbicular
Margin - Undulate
Venation - Pinnate (This is a tough one. You might think it's parallel, but there is actually a vein in the middle, from which the other veins sprout. )
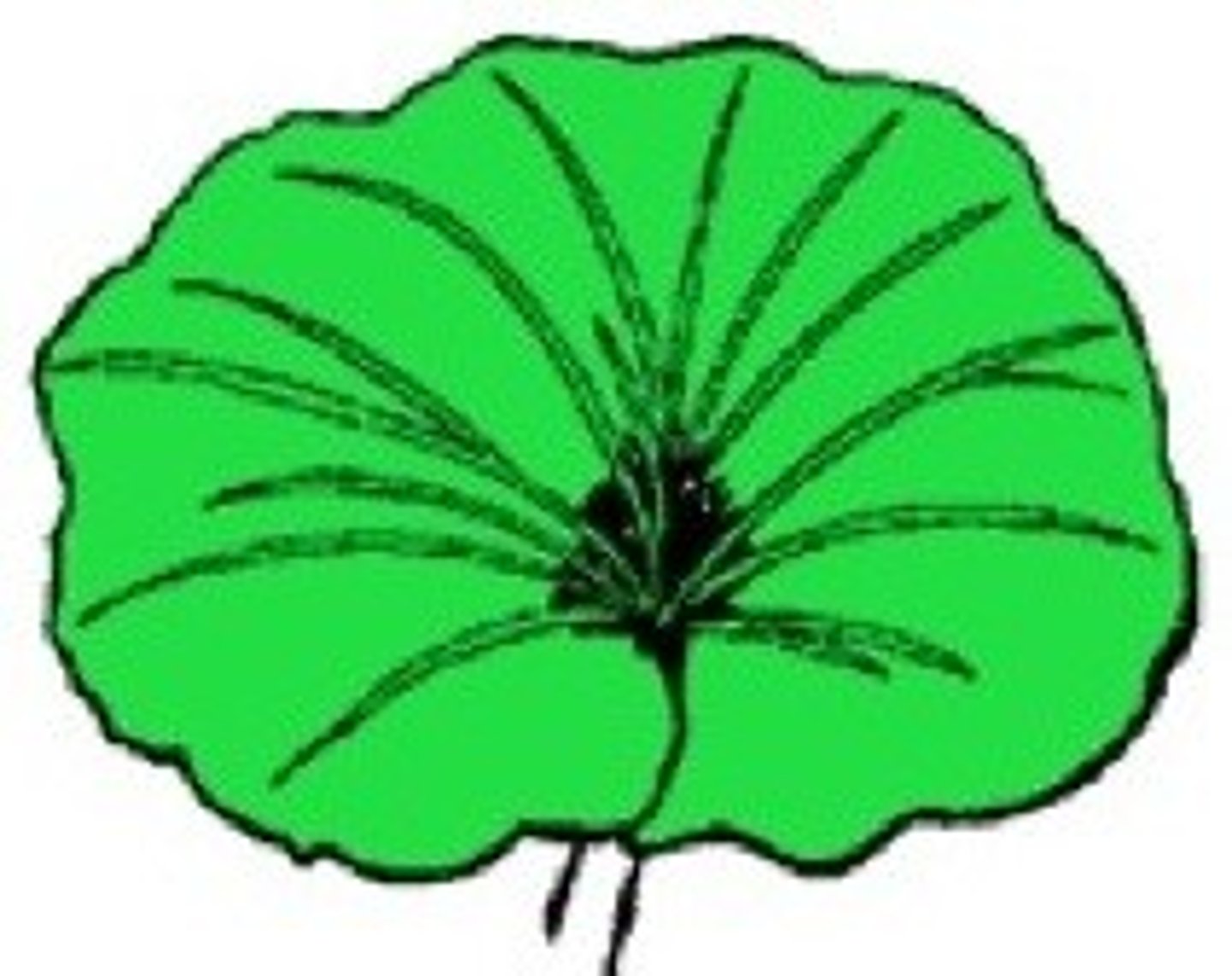
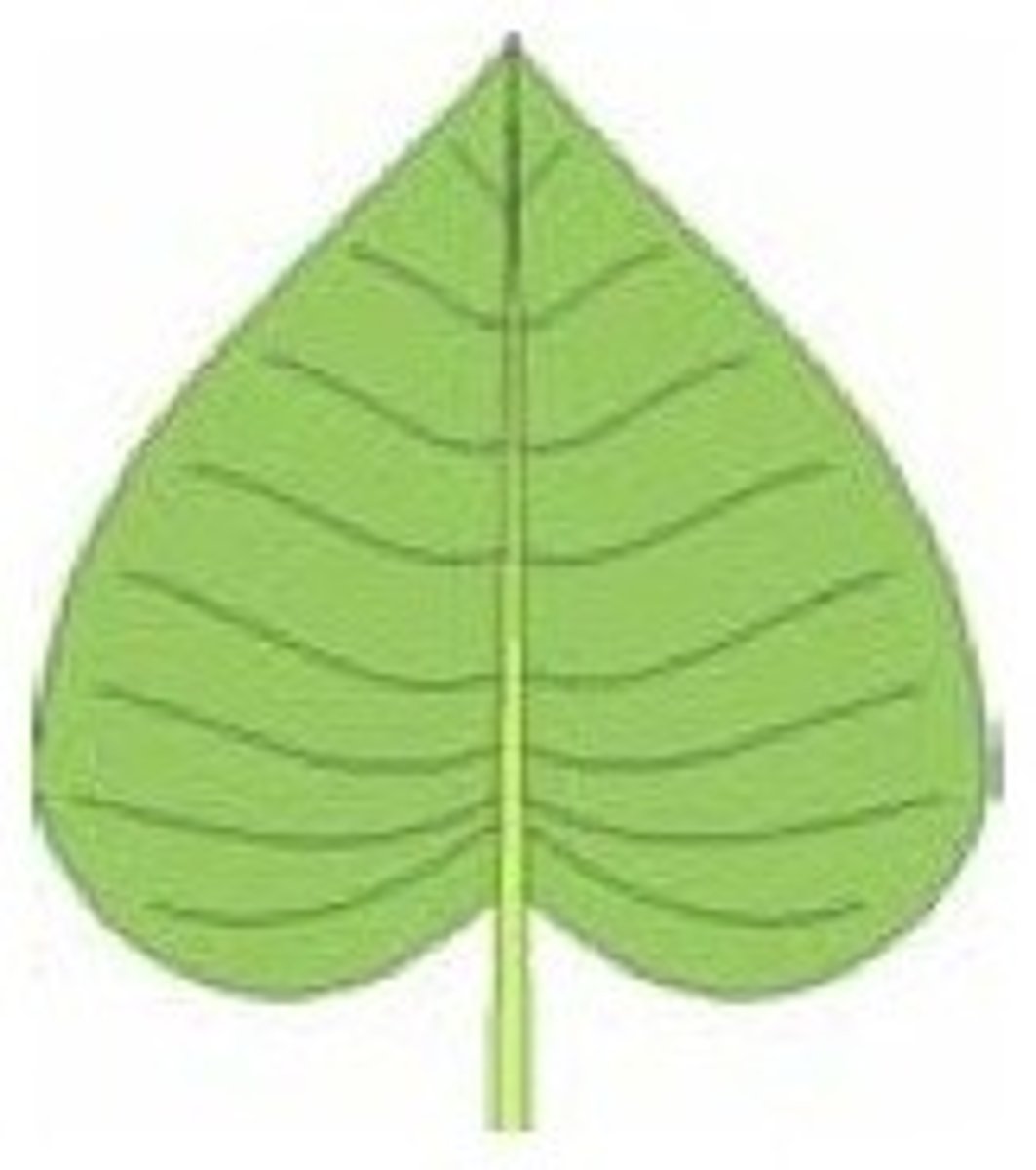
5. Determine the shape, margin, and venation of the following leaf:
Shape - Chordate
Margin - Entire
Venation - Pinnate

6. In a leaf, what is the function of the following tissue, palisade mesophyll?
photosynthesis
6. In a leaf, what is the function of the following tissue, spongy mesophyll?
photosynthesis
6. In a leaf, what is the function of the following tissue, epidermis?
protection
6. In a leaf, what is the function of the following tissue, xylem?
transports water and minerals
6. In a leaf, what is the function of the following tissue, phloem?
transports food and organic substances
6. In a leaf, what is the function of the following tissue, chollenchyma?
support
7. What controls the opening and closing of the stomata on a leaf?
The guard cells control the opening and closing of the stomata.
8. Why is the bottom of a leaf typically a lighter shade of green than the top of the leaf?
The spongy mesophyll is typically on the underside of the leaf, and it is usually a lighter shade of green due to the fact that the photosynthesis cells are not as tightly packed there.
9. Name two types of pigments that cause leaves to be a color other than green.
Carotenoids and anthocyanins.
10. If a tree has no abscission layer, will it be deciduous?
No, a tree without an abscission layer cannot be deciduous. Remember, the abscission layer cuts off the flow of nutrients to the leaves, which causes them to stop doing photosynthesis, causing them to die. With no abscission layer, that will not happen and the tree will not lose its leaves in the winter.
11. Where is the abscission layer?
The abscission layer is right between the stem and the petiole.
12. Name the four regions of a root. Which region contains undifferentiated cells?
The four regions of a root are: the root cap, the meristematic region, the elongation region, and the maturation region. The undifferentiated cells are in the meristematic region.
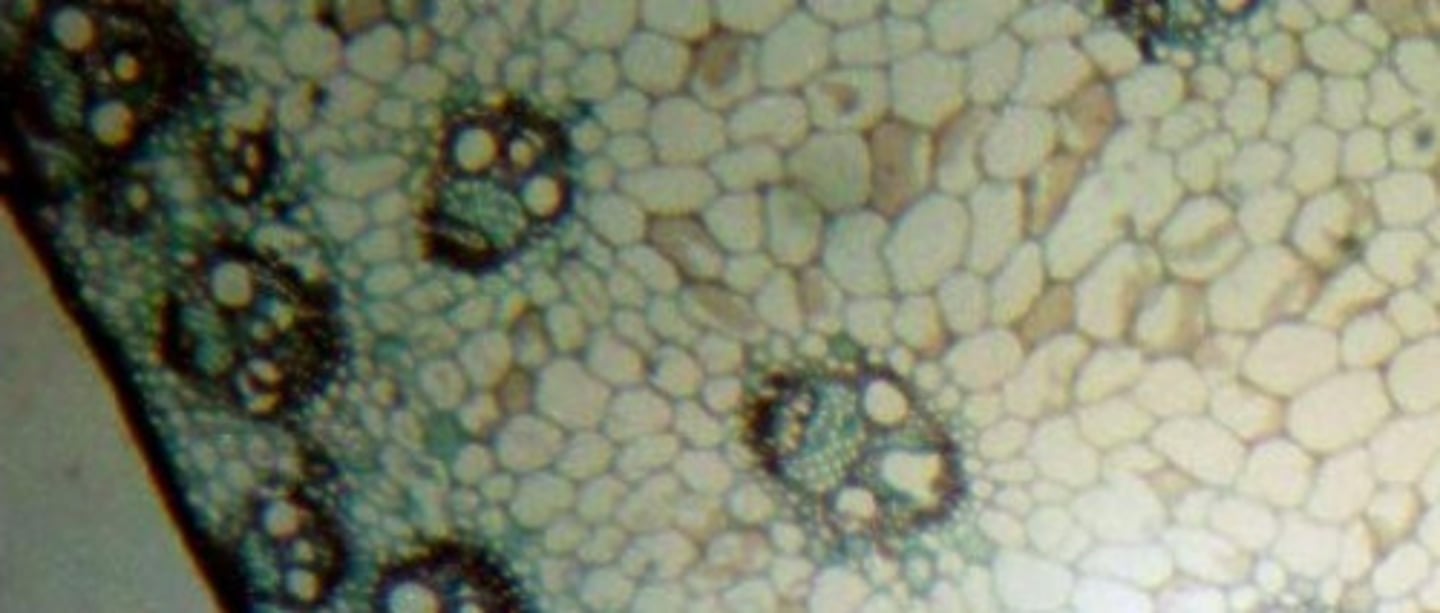
13A. Did the following stem cross section come from a monocot or a dicot?
dicot
14. What allows woody stems to have no limits to their growth, unlike herbaceous stems?
Woody stems have no limit to their growth because the cork cambium can always produce more bark. Thus, when the bark cracks, the inner parts of the stem are not exposed to the surroundings.
15. What is the function of vascular cambium?
The vascular cambium produces new vascular tissue.
16. If a stem has cork cambium, is it woody or herbaceous?
It is woody. The cork cambium appears only in woody stems. It makes new cork tissue for the outer bark.
17. What kind of vascular tissue makes up most of the wood in a woody stem? What kind of vascular tissue is found in the inner bark of a woody stem?
Xylem make up most of the wood in a woody stem, while phloem are found in the inner bark.
18. What is the dominant generation in the moss life cycle? Is it haploid or diploid?
The dominant generation in mosses is the gametophyte generation, and it is haploid.
19. A fern has antheridia and archegonia. Which part of the fern life cycle is it in? Is this the dominant generation?
If it has archegonia and antheridia, it produces gametes. Thus, it is in the gametophyte generation,
which is not the dominant generation for ferns.
20. Why are plants from phylum Bryophyta relatively small?
Since plants from phylum Bryophyta have no vascular tissue, there is no efficient way to transport nutrients throughout the plant. The plant must therefore stay small so that the nutrients need not
21. If a 15-foot tall plant has a root system that goes four feet deep, is it a fibrous or taproot system?
The plant must have a fibrous root system. If a root system does not go deeper than the height of a plant, it must spread out so that its total length is greater than that of the plant.
22. What are the male and female reproductive organs in a tree from phylum Coniferophyta?
The female reproductive organ is the seed cone, and the male is the pollen cone.
23. What is the fundamental difference between monocots and dicots?
The number of cotyledons produced in the seed is the fundamental difference between monocots and dicots. Monocots have one cotyledon in their seeds, dicots have two.
24. Name another difference between monocots and dicots.
In monocots, the venation is parallel, while it is netted (pinnate or palmate) in dicots. The fibrovascular bundles are packaged differently in monocots and dicots. Typically, monocots have fibrous root systems whereas dicots have taproot systems. Finally, monocots usually produce flowers in groups of three or six while dicots produce flowers in groups of four or five. The student need list only one of these.
25. A plant produces seed cones and pollen cones. Is it vascular? To what phylum (of the ones that we discussed) does it belong?
It belongs in phylum Coniferophyta, which contains the cone-making plants. It is vascular. Only the bryophytes are nonvascular.
26. A plant produces flowers. To what phylum does it belong?
It belongs in phylum Anthophyta.
a. Botany
The study of plants
b. Perennial plants
Plants that grow year after year
c. Annual plants
Plants that live for only one year
d. Biennial plants
Plants that live for two years
e. Vegetative organs
The parts of a plant (such as stems, roots, and leaves) that are not involved in reproduction
f. Reproductive plant organs
The parts of a plant (such as flowers, fruits, and seeds) involved in reproduction
g. Undifferentiated cells
Cells that have not specialized in any particular function
h. Xylem
Nonliving vascular tissue that carries water and dissolved minerals from the roots of a plant to its leaves
i. Phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant
j. Leaf mosaic
The arrangement of leaves on the stem of a plant
k. Leaf margin
The characteristics of the leaf edge
l. Deciduous plant
A plant that loses its leaves for winter
m. Girdling
The process of cutting away a ring of inner and outer bark all the way around a tree trunk
n. Alternation of generations
A life cycle in which there is both a muticellular diploid form and a multicellular haploid form
o. Dominant generation
In alternation of generations, the generation that occupies the largest portion of the life cycle
p. Pollen
A fine dust that contains the sperm of seed-producing plants
q. Cotyledon
A "seed leaf" which develops as a part of the seed - it provides nutrients to the developing seedling and eventually becomes the first leaf of the plant.
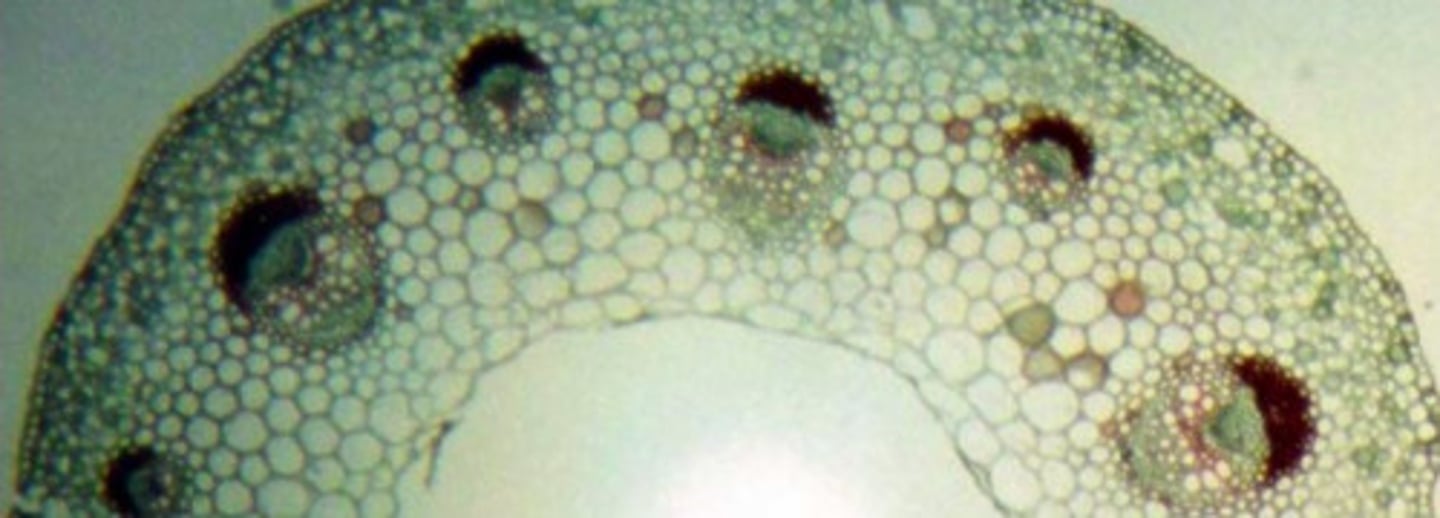
13B. Did the following stem cross section come from a monocot or a dicot?
monocot