Unit 9 - Meiosis, Cell Cycle, Plants
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/65
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
1
New cards
Why is interphase necessary for Meiosis?
It prepares the cell to split.
2
New cards
Meiosis I
pairs of homologous chromosomes are separated from each other
results in random chromosome combinations in gametes
results in random chromosome combinations in gametes
3
New cards
Steps of Meiosis I
Prophase I; Metaphase I; Anaphase I; Telophase I
4
New cards
Prophase I
Homologous chromosomes cluster together
crossing over occurs
crossing over occurs
5
New cards
Crossing Over
segments of DNA exchanged between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes
6
New cards
Metaphase I
homologous chromosomes line up in middle
attachment to spindle is random
attachment to spindle is random
7
New cards
Anaphase I
homologous chromosomes separated
move to opposite sides (poles) of cell
move to opposite sides (poles) of cell
8
New cards
Telophase I
Spindle fibers dissolve
no form new nuclear envelope
will immediately divide again
no DNA replication between meiosis I and II
cell divides in cytokinesis
no form new nuclear envelope
will immediately divide again
no DNA replication between meiosis I and II
cell divides in cytokinesis
9
New cards
Meiosis II
sister chromatids separated; gametes generated; similar to mitosis
results in 4 genetically unique haploid daughter cells
results in 4 genetically unique haploid daughter cells
10
New cards
sister chromatids
identical copies of chromatids
11
New cards
Prophase II
chromoesomes condense
12
New cards
Metaphase II
chromosomes line up on top of each other in middle of cell
spindle attached to centromere of each chromosome
spindle attached to centromere of each chromosome
13
New cards
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate
spindle shortens and moves to opposite ends of cell
spindle shortens and moves to opposite ends of cell
14
New cards
Telophase II
nuclear envelope forms around chromosomes in all four cells
cytokinesis
cytokinesis
15
New cards
How does Meiosis lead to variation in gametes, why is is important?
Gametes will have different DNA which is important for evolution
16
New cards
How does crossing over lead to more variation in gametes
It mixes parts of the chromosomes which allows for gametes to have different DNA
17
New cards
Gametogenesis
Development of Haploid cells into gametes
18
New cards
Male Gametes
Sperm
19
New cards
Female Gametes
Egg
20
New cards
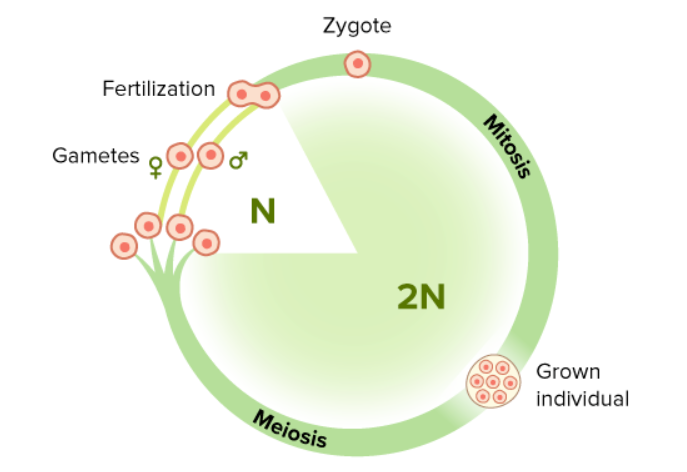
Diploid Life Cycle
majority of life spend as diploid adults
meiosis produces haploid gametes
fertilization forms diploid zygote
mitosis and cytokinesis produce two diploid cells
meiosis produces haploid gametes
fertilization forms diploid zygote
mitosis and cytokinesis produce two diploid cells
21
New cards
Haploid Life Cycle
life cycle with majority of time spend as haploid organisms
fuse to form diploid zygote
meiosis produces more haploid gametes
fuse to form diploid zygote
meiosis produces more haploid gametes
22
New cards
Nondisjunction disorders
failure of replicated chromosomes to separate during anaphase II
Most human abnormal chromosome numbers result in death of developing embryo
Most human abnormal chromosome numbers result in death of developing embryo
23
New cards
Monosomy
when humans only have one autsome
24
New cards
Trisomy
When humans have an extra autosome
25
New cards
Chromosomal Abnormality
A mutation in the chromosome
26
New cards
Inversion
chromosome being flipped upside down
27
New cards
Deletion
removal of a part of a chromosome
28
New cards
Duplication
an addition of a chromosome
29
New cards
Translocation
a piece of a chomosome being transferred to another chromosome
30
New cards
Plant
Eukaryotic Organism that produces its own food
31
New cards
Why are Plants Essential for Humans?
* provide food
* produce oxygen
* material for manmade things
* produce oxygen
* material for manmade things
32
New cards
Why are Plants Important for Nature?
* provide food
* maintain atmosphere
* recycle matter
* provide materials for manmade things
* create habitats for many organisms
* maintain atmosphere
* recycle matter
* provide materials for manmade things
* create habitats for many organisms
33
New cards
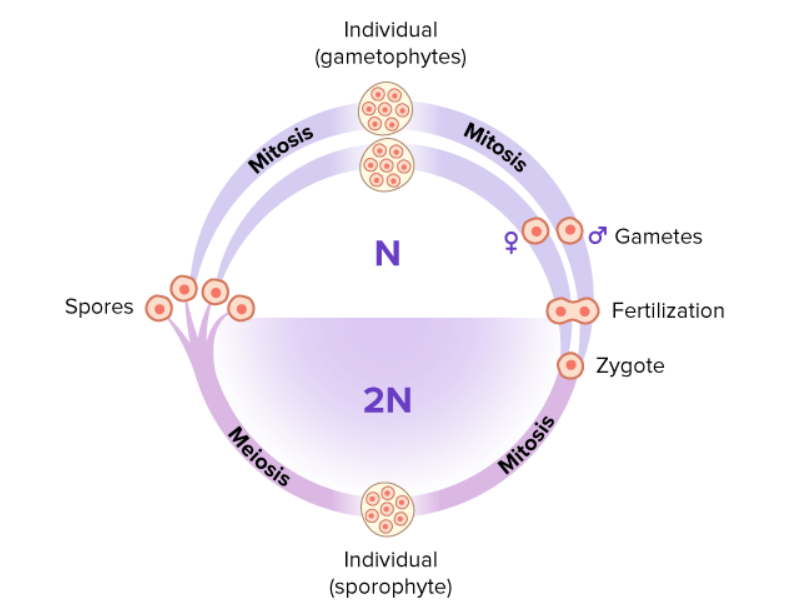
Alternation of Generations
Life cycle that alternates between haploid and diploid phases
34
New cards
Mosses (Bryophyte)
Non-Vascular plants with spores
Doesn’t have roots, vascular tissues, leaves, seeds, flowers
inefficient at absorbing water
Reproduce through moisture and spores
Doesn’t have roots, vascular tissues, leaves, seeds, flowers
inefficient at absorbing water
Reproduce through moisture and spores
35
New cards
Ferns (and friends)
Vascular plants with spores
Has Xylem and Phloem
developed roots, stems, and sunlight
grew tall for sunlight
Has Xylem and Phloem
developed roots, stems, and sunlight
grew tall for sunlight
36
New cards
Conifers (Gymnosperm)
Cone bearing seed plants with an open ovule
seeds and reproductive structure in cones
male gametes carried by wind to fertilize femal egametes in seed cones
seeds and reproductive structure in cones
male gametes carried by wind to fertilize femal egametes in seed cones
37
New cards
Flowering Plants
Seed bearing plants with a surrounded ovule
flowers contain reproductive organs
colors, designs, scents, nectars attract pollinators
flowers contain reproductive organs
colors, designs, scents, nectars attract pollinators
38
New cards
How have plants responded to their Enviroment?
They have evolved overtime to adapt to their surroundings such as developing vascular tissues, flowers, and more.
39
New cards
xylem
vascular tissue that transports water and dissolved minerals from roots to stems and leaves
40
New cards
phloem
vascular tissue that transports food from photosynthetic cells to other parts of the plant for growth or storage
41
New cards
Roots
made of vascular tissues
anchor plants securely in the ground
anchor plants securely in the ground
42
New cards
Stems
made of vascular tissues and lignin
allows plants to grow higher and supply water to plant
allows plants to grow higher and supply water to plant
43
New cards
Leaves
collect sunlight, CO2
reduce water loss
reduce water loss
44
New cards
Flowers
Reproductive organs of flowering plants
45
New cards
Sepal
Protect developing flower while it is a bud
46
New cards
Petal
Attracts animals to the flower by being brightly colored
47
New cards
Stamen
Made of Anther and Filament
Male reproductive structure of a flower
helps pollen be more likely carried away
Male reproductive structure of a flower
helps pollen be more likely carried away
48
New cards
Carpel/Pistil
Made of Stigma, Style, Ovary, Ovule
Female reproductive structure of a flower
sticky to help catch pollen
Female reproductive structure of a flower
sticky to help catch pollen
49
New cards
Photosynthesis Formula
Light Energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6+ 6O2
50
New cards
Photosynthesis reactants
Light Energy + Water + Carbon Dioxide
51
New cards
Photosynthesis Products
Oxygen + Glucose
52
New cards
Cellular Respiration Formula
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
53
New cards
Cellular Respiration Reactants
Glucose + Oxygen
54
New cards
Cellular Respiration Products
Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP
55
New cards
Chloroplast Structure
(only need to know Thylakoids and Stroma)

56
New cards
Stroma
Fluid-filled internal space of the chloroplasts which encricle the grana and thylakoids containing chloroplast DNA, starch, and ribosomes laong with the enzymes needed for the Calvin Cycle
57
New cards
Thylakoids
Flattened sac of membrane inside of a chloroplast where the first stage of photosynthesis occurs
58
New cards
Chlorophyll
A green pigment which absorbs light to provide energy for photosynthesis
59
New cards
Photosynthesis
Process of plants using light energy to create glucose as nutrients
60
New cards
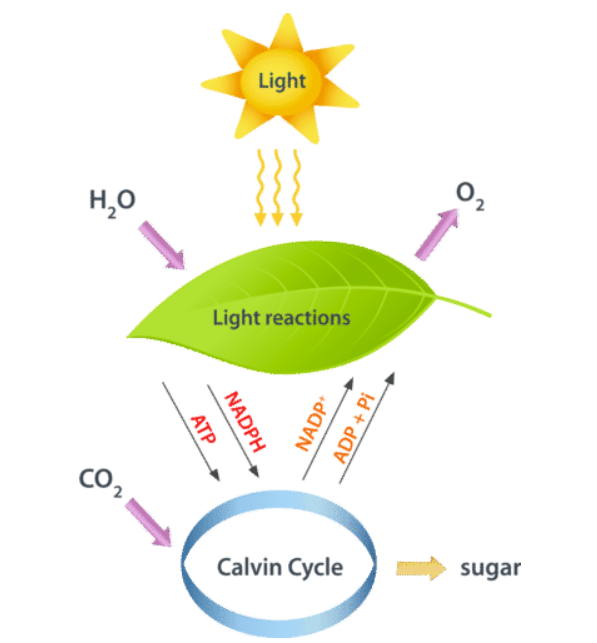
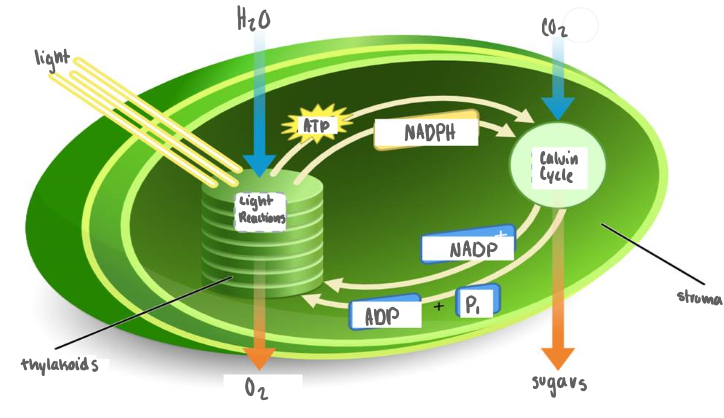
Model of Photosynthesis
Light and water goes into Light reactions in the Thylakoid which produces O2, NADPH, ATP
NADPH, ATP, and CO2 go into the Calvin Cycle which Produces NADP+, ADP + Pi + sugar
NADP+ and ADP+Pi go into light reactions
Sugar is distributed to the plant as nutrients
NADPH, ATP, and CO2 go into the Calvin Cycle which Produces NADP+, ADP + Pi + sugar
NADP+ and ADP+Pi go into light reactions
Sugar is distributed to the plant as nutrients
61
New cards
Light Reactions
First part of Photosynthesis
Light energizes electrons in chlorophyll and these electrons are used to make ATP and are stored in a coenzyme (NADPH)
water is used to replace the electrons in chlorophyll and oxygen gas is released into the air
Light energizes electrons in chlorophyll and these electrons are used to make ATP and are stored in a coenzyme (NADPH)
water is used to replace the electrons in chlorophyll and oxygen gas is released into the air
62
New cards
Calvin Cycle
Second Part of Photosynthesis
ATP and NADPH provide energy, hydrogen ion, and electrons
used to bind with CO2 to form sugar
ATP and NADPH provide energy, hydrogen ion, and electrons
used to bind with CO2 to form sugar
63
New cards
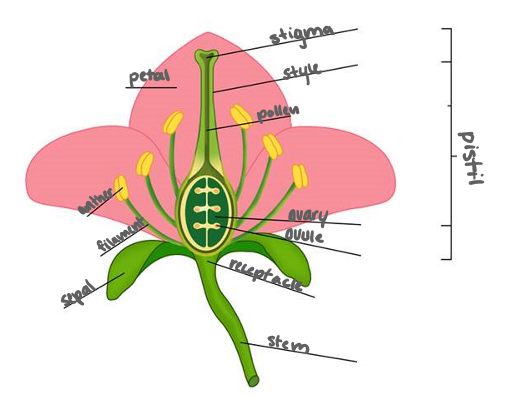
Model of a Flower
Pistil
Stigma, Style, Pollen
Petal
(Stamen) Anther, Filament
Ovary, Ovule
Stem
Stigma, Style, Pollen
Petal
(Stamen) Anther, Filament
Ovary, Ovule
Stem
64
New cards
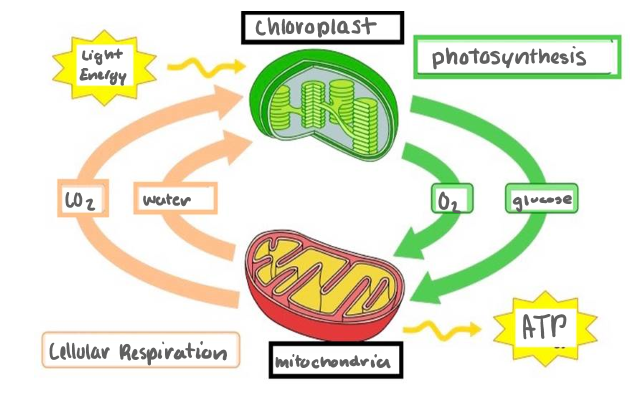
Connection between Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Diagram
Light Energy, Chloroplast, Photosynthesis
O2, Glucose
Mitochondria, Cellular Respiration, ATP
CO2, Water
O2, Glucose
Mitochondria, Cellular Respiration, ATP
CO2, Water
65
New cards
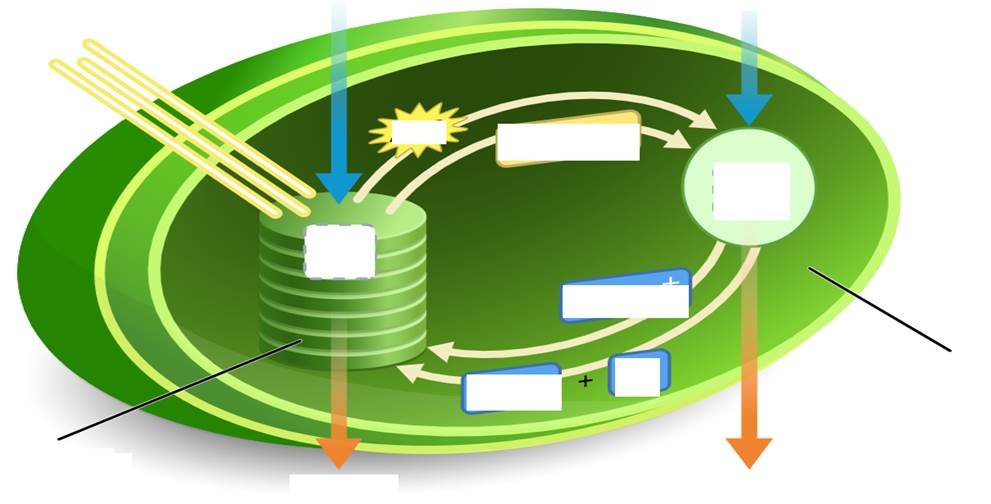
Photosynthesis Diagram
Light, H20
Light Reaction, Thylakoids
ATP, NADPH
C02
Calvin Cycle, Stroma
NADP+, ADP + P1
Sugars
Light Reaction, Thylakoids
ATP, NADPH
C02
Calvin Cycle, Stroma
NADP+, ADP + P1
Sugars
66
New cards
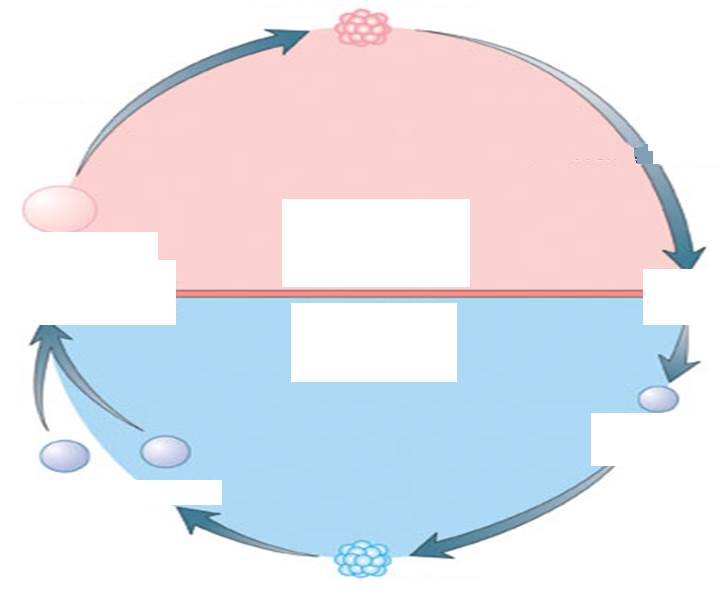
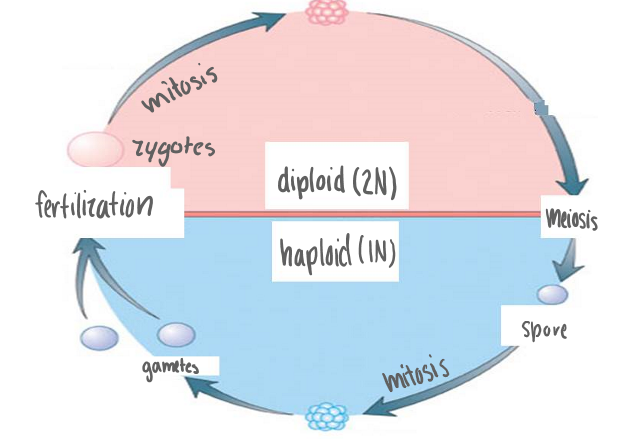
Alternation of Generations Diagram
Meiosis, Spore, Mitosis, Gametes (Egg, Sperm)
Fertilization, Zygotes, Mitotsis
Diploid (2N Plant)
Haploid (IN Plant)
Fertilization, Zygotes, Mitotsis
Diploid (2N Plant)
Haploid (IN Plant)