18A - Benzene
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the difference between an aliphatic and aromatic compound?
Aliphatic - Straight/branched chain organic susbstance
Aromatic - 1+ rings of 6 carbon atoms with delocalised bonding electrons
What are some uses of aromatic compounds?
Fragrances
Drugs - antibiotic, pain relief
Plastics
Pigment
What are some properties of benzene?
Planar structure - so flat
Cyclic - 6 carbon atoms bonded
Delocalised pi electrons - make it stable
High mp bc stable
low bp bc non- polar, hard to dissolve in water
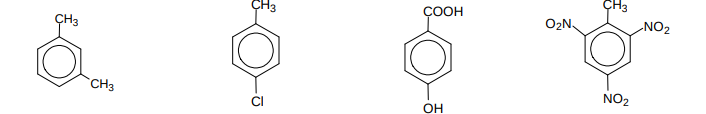
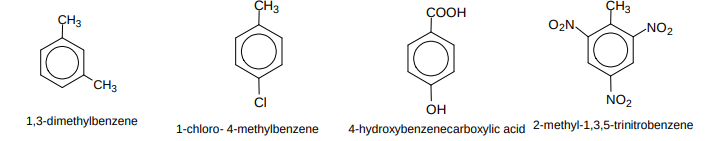
Name these compounds?
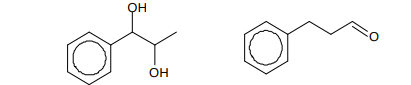
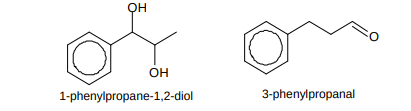
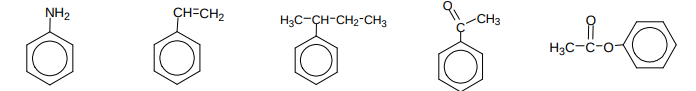
Name these compounds
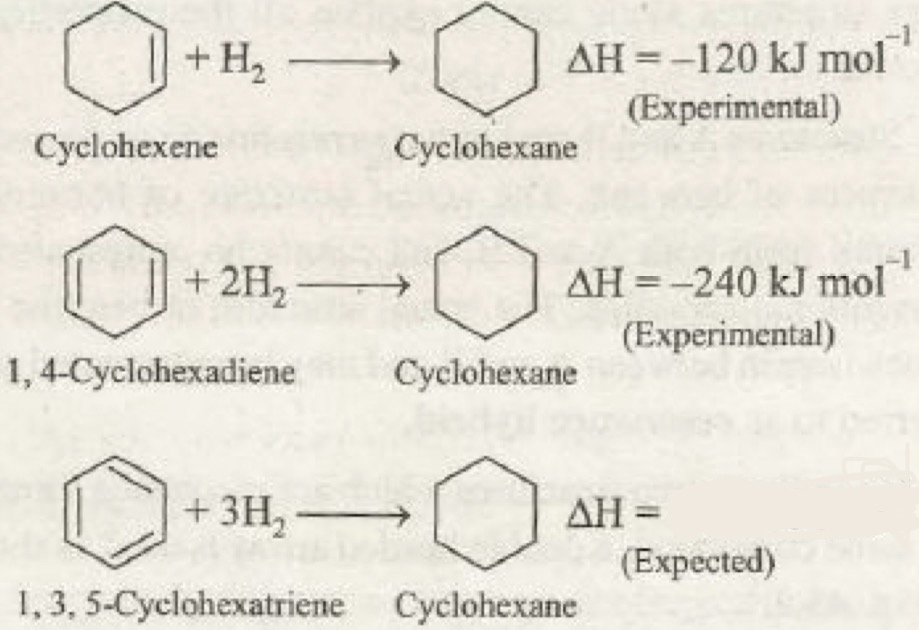
What is the expected value for benzene and what does it show about benzene
-360
Benzene is more stable than the proposed structure of cyclohexan 1,3,5 triene (benzene has less energy)
What are the 2 electrophillic addition reactions benzene can undergo?
Nitration
Freidal - crafts acylation
What are the conditions and reagant for the nitration reaction of benzene and what is the electrophle?
Nitric acid (HNO3)
conc sulfuric acid
warm
Electrophile - NO2
In nitration of benzene why shouldn’t the temperature go above 55 degress?
Multiple substitution reactions occur which wont produce arenes
What is the combustion reaction of benzene?
C6H6 + 7.5 O2 → 6CO2 + 3H2O
What are the reagents for halogenation of benzene?
X (halogen) and FeX catalyst
What are the reagent and conditions of freidal crafts actuation and alkylation
Alkylation : haloalkane and AlCl3 catalyst, reflux
Acylation : Acyl chloride, AlCl3 catalyst, reflux
What is the formula for phenols?
C6H5OH
What is the reaction of phenol with bromine water? (what does it produce and observations)
Produce 2,4,6 tribromophenol
white preciptate, antisepctic smell
Brown to colourless
What is the difference between bromination of phenols compared to benzene?
Phenol doesn’t need catalyst
Undergoes multiple substitution reactions
Why is the reaction of bromine water more reactive with phenols than benzene?
In phenols the lp of e- in the oxygen atom is partially delocalised into the benzene ring structure, so e- density increases
bromine is more polarised
What can phenoles be used to make?
plastics
Antiseptics
Disinfectant
Resin for plants
Why is phenol more like to react with a haloalkane than benzene?
Bc of lone pair on oxygen delocalises into benzene ring
Which increases electron density
Making phenol more susceptible to electrophillic attack