Principles of Anatomy: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
spinal cord segments
31 segments, each segment = one spinal nerve
cervical spinal nerves
8 segments = 8 pairs
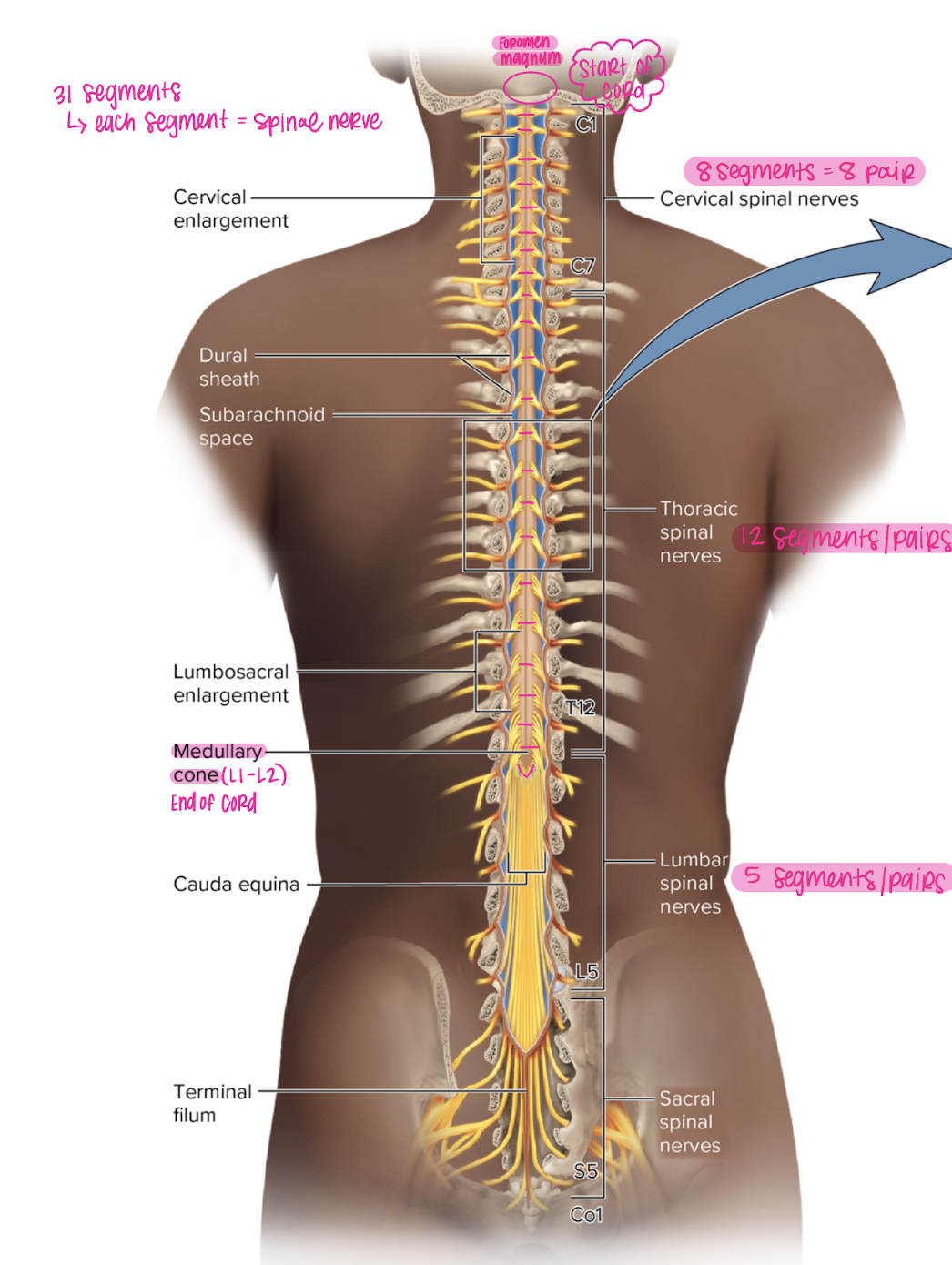
Thoracic spinal nerves
12 segments, pairs
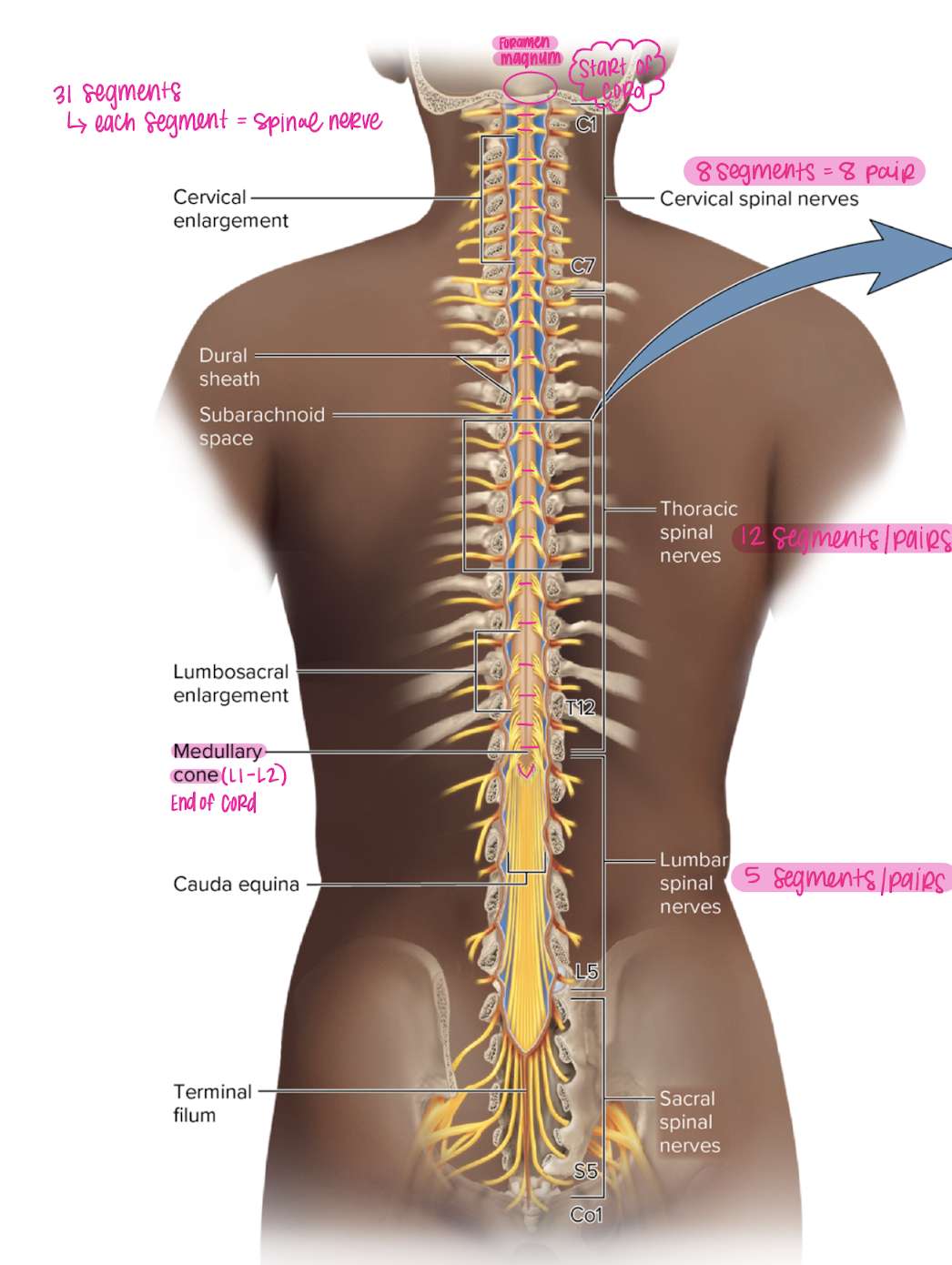
lumbar spinal nerves
5 segments, pairs
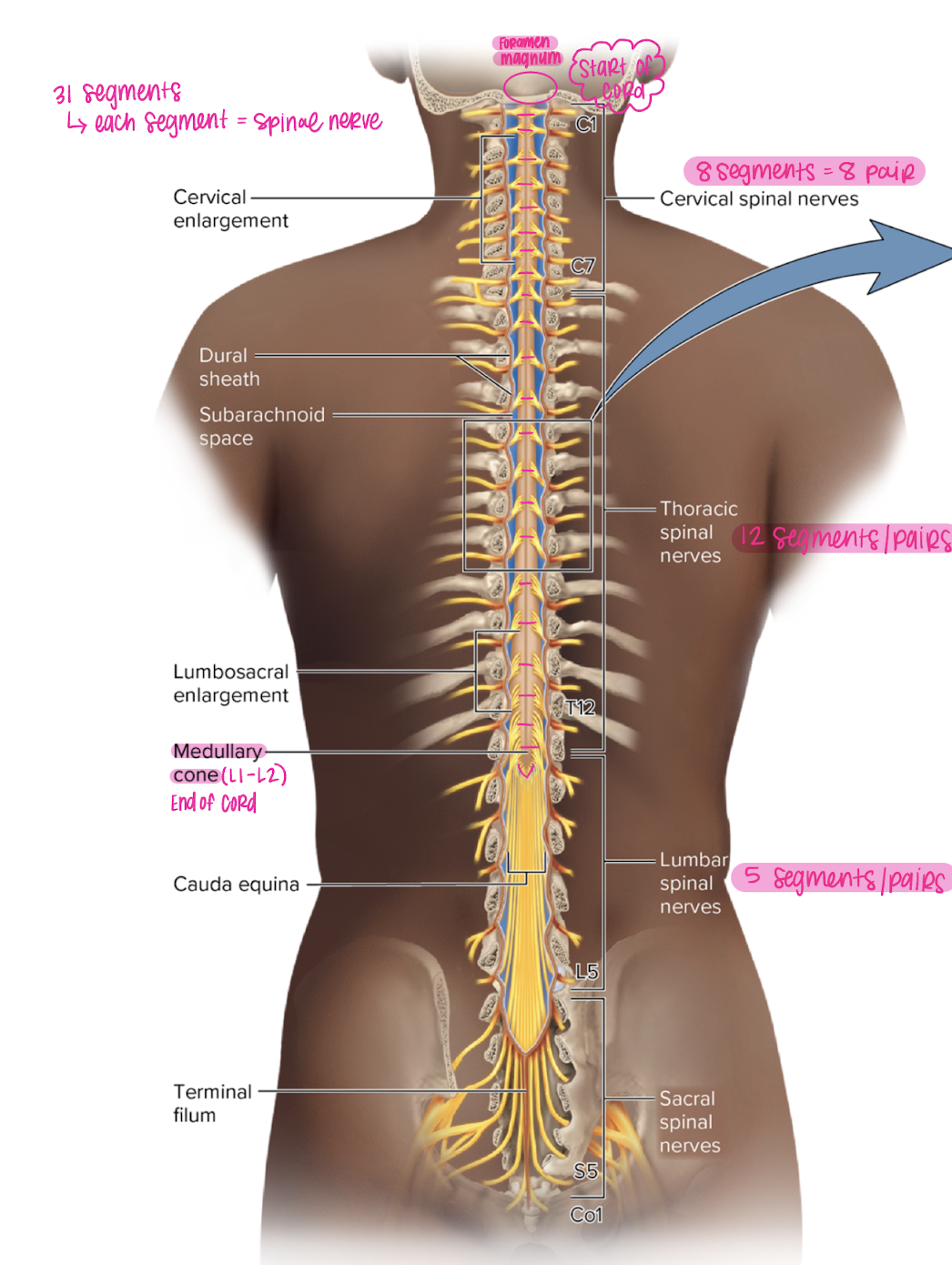
conus medullaris
end of the spinal cord (L1-L2)
cauda equina
“horse tail” region distal to the medullary cone
pia mater
layer of meninges closest to the cord
subarachnoid space
space between arachnoid and pia where CSF flows
arachnoid mater
transparent and thin layer of meninges
subdural space
space between dura and arachnoid
dura mater
thick outer layer of the meninges
epidural space
space between dura (periosteal) and bone filled with fat tissue where epidural is placed
lumbar cistern and lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
largest collection of fluid in subarachnoid space at the bottom of spinal cord (L2-S2)
ideal space for needle to draw CSF, easy to avoid hitting the spinal cord
Needle is inserted between L3 and L4
Grey matter
divided into dorsal and ventral horns
cell body of motor neuron lives in ventral horn and axon leaves horn to form ventral root
white matter
Dorsal column, ventral column, lateral column
myelinated axons that run up and down cord carrying sensory (ascending) and motor (descending) info
Dorsal horn
found in the grey matter
central process of sensory neuron innervates
receives incoming sensory info from peripheral and central processes
ventral horn
found in grey matter
where cell body of the motor neuron lives (efferent pathway)
column
white matter tracts
lateral, dorsal, ventral
dorsal column
ascending spinal tract (red)
gracile fasciculus (medial)
cuneate fasciculus (lateral)
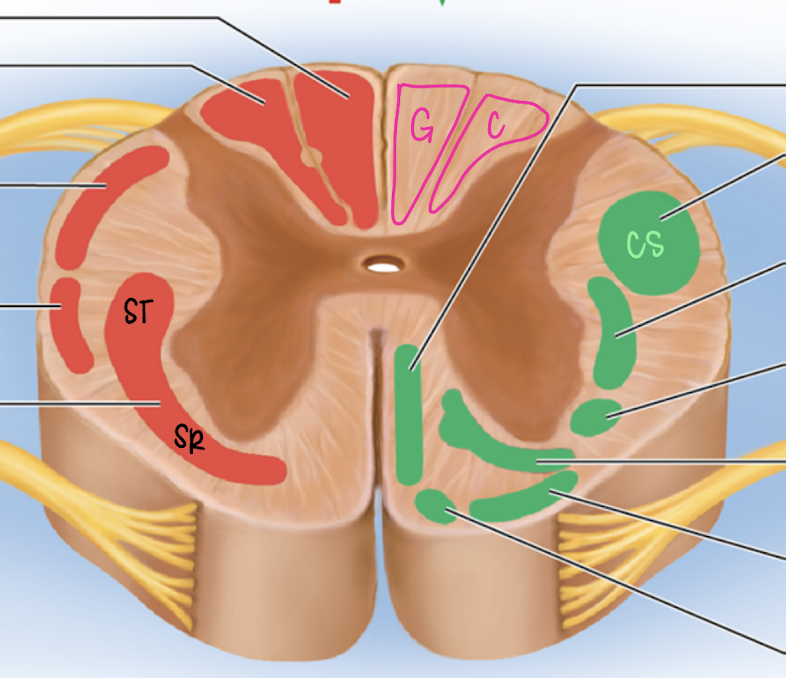
gracile fasciculus
dorsal column
medial
fine touch, proprioception for LOWER BODY
decussates at medulla oblongata
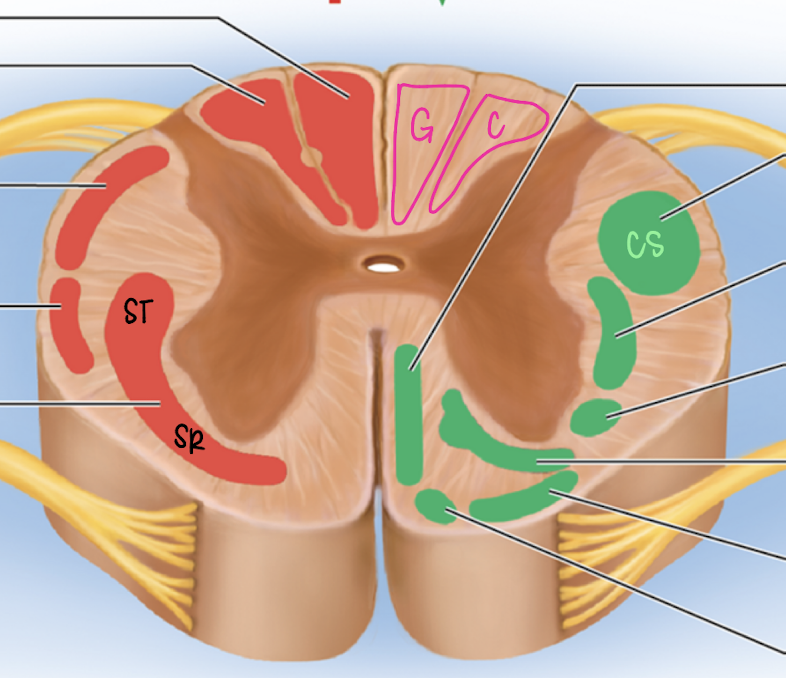
Fasciculus cuneatus
dorsal column
lateral
fine touch and proprioception for UPPER BODY
decussates at medulla oblongata
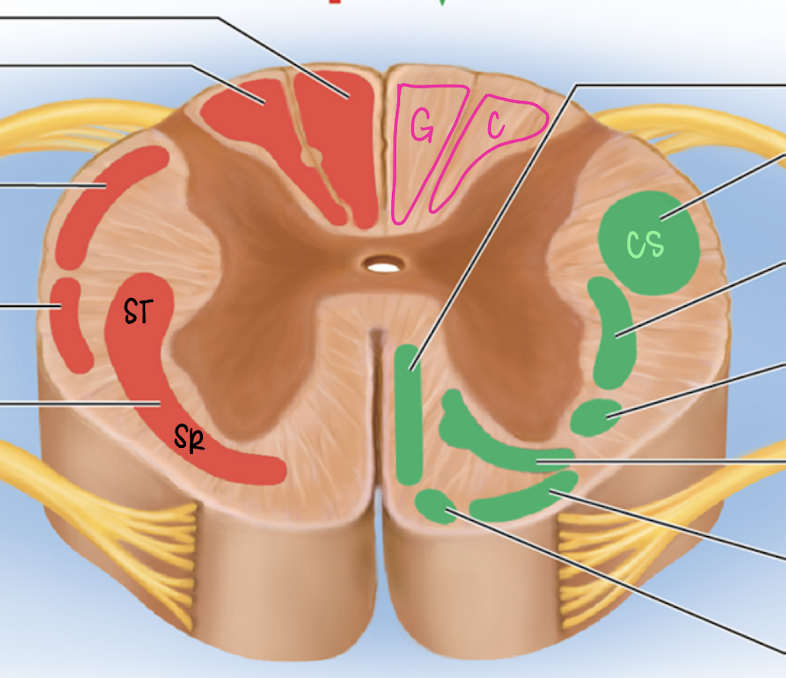
spinothalamic tract
ascending spinal tract
lateral and ventral columns
pain and temperature signals to brain
decussates in spinal cord
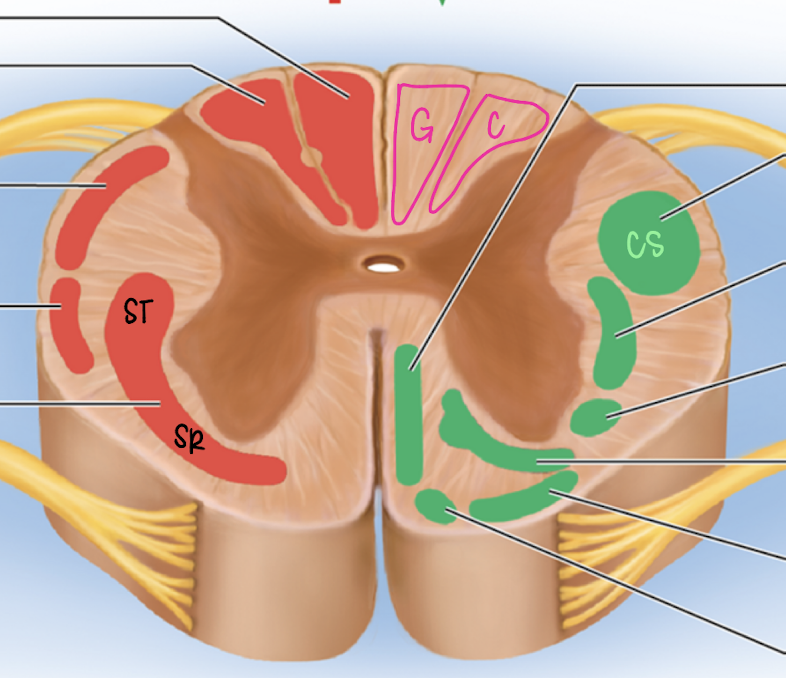
corticospinal tract
descending spinal tract
anterior and lateral columns
carry info from motor cortex of brain to cord
lateral corticospinal
descending
lateral dorsal column
voluntary limb movement
90% cross at medulla (brainstem)
anterior corticospinal
descending
ventral dorsal column (medial)
voluntary truck control
crosses at spinal cord
decussating
crossing over of motor tracts, left brain control right side of body
Upper motor neuron
myelinated by ogliodendrocytes in the CNS
travel in spinal cord (corticospinal tracts)
descends to level of cord where it can synapse with LMN
TRIGGER MUSCLE CONTRACTION
lower motor neuron
myelinated by schwann cells in the PNS
communicates with muscle cells that begin to release Ca to trigger muscle contraction
multipolar neuron
neuron with many processes that leave cell body (motor neuron)
cell body lives in the ventral horn and axon leaves through ventral root
unipolar neuron (pseudo)
neuron with one process leaving the cell body that splits into a peripheral and central process
cell body lives in dorsal root ganglion
peripheral process carries sensory info to cell body from receptors
central process sends info to the dorsal horn
dorsal root
connected by rootlets to dorsal root ganglion
ventral root
ventral, no root ganglion, rootlets connect to spinal cord
root
either motor OR sensory, not both
rootlets
connect root to the spinal cord
dorsal root ganglion
where cell body of sensory (afferent) neurons live
mixed spinal nerve
ventral root joins dorsal root (motor AND sensory)
Intervertebral foramen
formed by pedicle and vertebral notches
allow spinal nerves to leave canal
where mixed spinal nerves (joined ventral and dorsal roots) exit and SPLIT after IVF into dorsal and ventral ramus
dorsal ramus
sends motor and sensory fibers to muscle and skin of back
ventral ramus
contains nerves that go everywhere else in the body
cervical spinal nerves
8 total
thoracic spinal nerve
12 total
lumbar spinal nerve
5 total
sacral spinal nerve
4 total
lumbar & thoracic spinal nerves
spinal nerves leave below/inferior to corresponding vertebrae
cervical spinal nerves
8 cervical spinal nerves, but inly 7 cervical vertebrae
exits above corresponding vertebrae
C3 SN would exit between C2 and C3
plexus
jumble of ventral rami
4 somatic plexus
cervical plexus
ventral rami C1 though C4
gives rise to the phrenic peripheral nerve
innervates the diaphragm
brachial plexus
ventral rami C5 through T1
gives rise to median peripheral nerve
provides motor and sensory to upper limb structures
lumbar plexus
ventral rami L1 through L5
gives rise to femoral peripheral nerve
innervates quads (motor) and skin of thigh (sensory)
sacral plexus
Ventral rami S1 through S4
gives rise to sciatic peripheral nerve
innervates all other muscles of the lower limbs
spinal nerve fascicle
collection of nerve fibers
composed of motor (efferent) and sensory (afferent) neurons
make up spinal nerves (mixed)
neurons within are myelinated and unmyelinated
endoneurium
outside CT sheath around a neuron
perineurium
outside CT sheath around a fascicle
epineurium
outside CT sheath around an entire nerve
relfex arc
NO BRAIN INVOLVED
stimulation of receptor in muscle
peripheral process of sensory neuron sends an afferent signal up a nerve fiber, to the cell body in the DRG, and into the central process that innervates the dorsal horn
Synapse on cell body of multipolar motor neuron (LMN)
Efferent response is sent down a motor nerve fiber
LMN stimulates an effector