Atomic Theory (On Learning Objectives)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Elements ___ break down further. There are only 7 elements that are found as diatomic molecules. Name them. (Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer)
cannot; H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2
Atoms are the ____ unit of matter. Compounds are composed of two or more ___ elements.
smallest; different
Who proposed the atomic theory?
John Dalton
What are the four things the atomic theory states?
Matter is composed of ___
Atoms of the same element are ___ and have the ___ mass.
Chemical compounds form in ___ number ratios
Atoms in a chemical reaction are ___, they are not ___ nor ___
Matter is composed of atoms
Atoms of the same element are identical and have the same mass
Chemical compounds form in whole number ratios
Atoms are rearranged in a chemical reaction, they are not created nor destroyed
Who discovered the electron and its charge-to-mass ratio using cathode rays?
JJ Thomson
Who discovered the electron’s charge and mass with the oil-drop experiment?
Millikan
What is the absolute charge of the electron and proton? (saying the first four sig figs is enough but try to get all 7)
proton: +1.602177 × 10^-19 C (coulomb)
electron: -1.602177 × 10^-19 C (coulomb)
Who discovered the nucleus in 1911 and claimed that atoms are mostly empty space with a dense, positively charged nucleus? What experiment did he use?
Rutherfold and used the gold-foil experiment
What is 1 amu in kg?
1 amu = 1.661 × 10^-27 kg
What is the mass of a proton, neutron, and electron?
Proton: approx 1.007 amu
Neutron: approx 1.009 amu
Electron: approx 5.5 × 10^-4 amu
Protons control the element’s ___, whereas electrons control the ___
identity; charge
Location and charge of p+, n, and e-?
p+ = nucleus charge +1
n = nucleus, charge 0
e- = electron cloud, charge -1
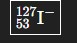
In this photo, the mass number is ____, the number of protons is ___, and the charge is ___
127, 53, -1
How do you find the number of neutrons?
Mass number - Atomic number
How many electrons are in O²-? How about in Mg²+?
O = 8 protons, 10 electrons
Mg = 12 protons, 10 electrons
What is an isotope
They are the same number of protons but with differing numbers of neutrons.
True or False: The atomic mass on the periodic table is considering all known isotopes combined?
True
Cations are ___ charged overall, meaning they ___ electrons. Usually they are ____
Anions are ___ charged overall, meaning they ___ electrons. Usually are ___
positively; lose; metals
negatively; gain; nonmetals
Monoatomic cations are named by adding the word ___ at the end. For instance, Na+ would be called a ___ ___
ion; sodium ion
With some cations, specifically in the transition metals, we use Roman Numerals to specify the charge. The “no-numeral” list consists of 2 groups and 5 elements. What are they? (Use table if needed)
Group 1 and 2, Ag+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Sc3+ Al3+
With monoatomic anions, you add ___ at the end of the element + ____ For instance: Cl- would be a ____ ____
-ide; ion; chloride ion
In compounds, the ___ element takes the name. For instance, NaCl is called ____ ___
sodium chloride
Oxoanions are ____ anions that have one or more ___ atoms and one atom of another element.
polyatomic; oxygen
The most common form of oxoanions in a series change the central element’s name to ___ and adding the word ___. For instance, ClO3^- is the most common form, and it’s called ___ ___
-ate; ion; chlorate ion
Two less oxygens that the most common ionic form has ___ in front, ___ at the end, and the add the word ___. For instance; ClO- is called ____ ____
hypo; ite; ion; hypochlorite ion
One less oxygen than the most common ionic form has ___ at the end and add the word ___. For instance, ClO2^- is called a ____ ____
ite; ion; chlorite ion
One more oxygen than the most common ionic form has ___ in the beginning, ___ at the end, and adds the word ___. For instance, ClO4^- is called a ____ ____
per; ate; ion; perchlorate ion
Mass number is equal to ___ + ___ for an isotope, whereas atomic mass is the ___ ___ on the periodic table.
protons, neutrons, weighted average