AP Psychology - Personality
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
personality
an individual's characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting.

free association
in psychoanalysis, a method of exploring the unconscious in which the person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind, no matter how trivial or embarrassing.

psychoanalysis
Freud's theory of personality and therapeutic technique that attributes thoughts and actions to unconscious motives and conflicts. Freud believed the patient's free associations, resistances, dreams, and transferences—and the therapist's interpretations of them—released previously repressed feelings, allowing the patient to gain self-insight.

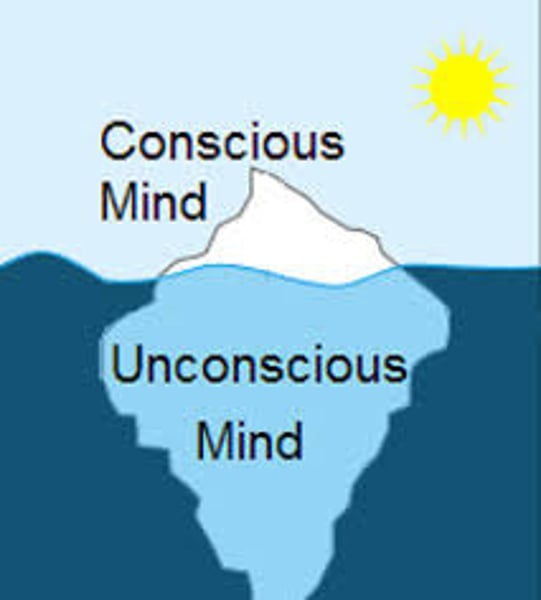
unconscious
according to Freud, a reservoir of mostly unacceptable thoughts, wishes, feelings, and memories. According to contemporary psychologists, information processing of which we are unaware.
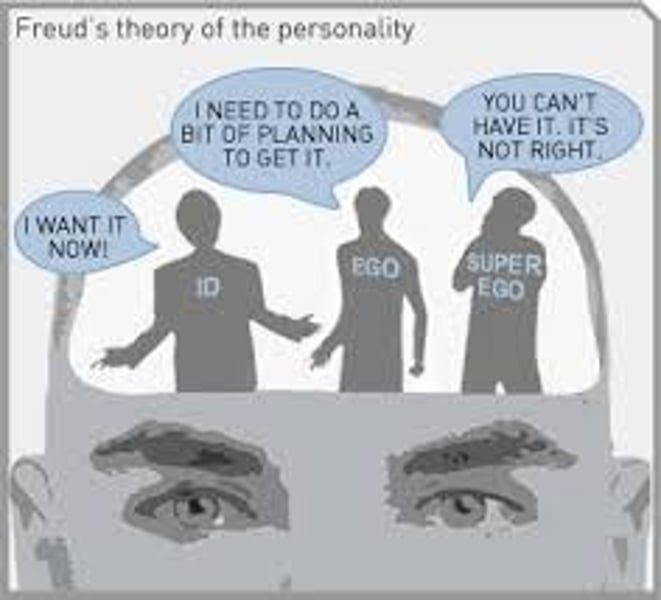
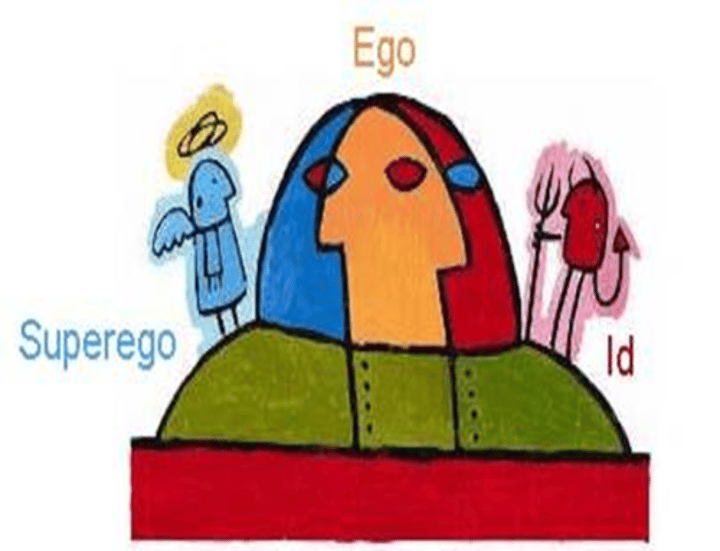
id
a reservoir of unconscious psychic energy that, according to Freud, strives to satisfy basic sexual and aggressive drives. It operates on the pleasure principle, demanding immediate gratification.
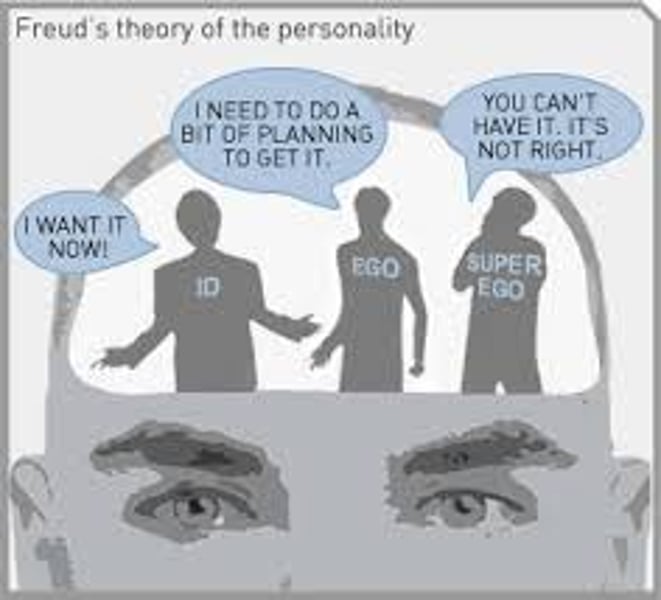
ego
the largely conscious, "executive" part of personality that, according to Freud, mediates among the demands of the id, superego, and reality. It operates on the reality principle, satisfying the id's desires in ways that will realistically bring pleasure rather than pain.
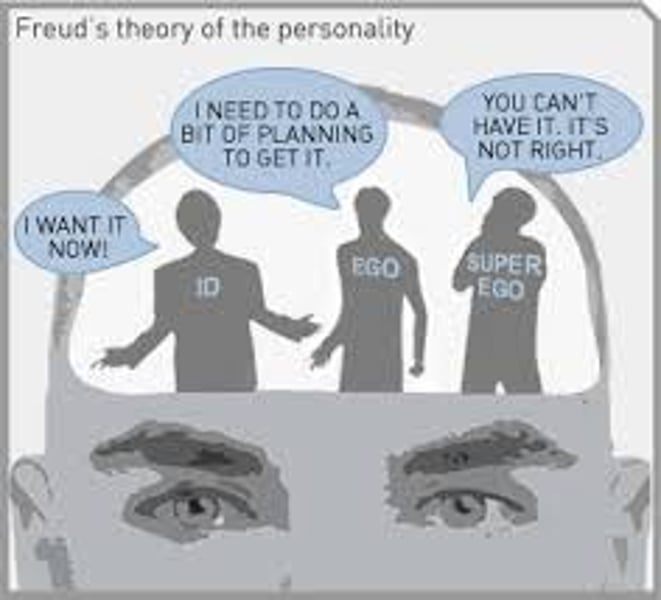
superego
the part of personality that, according to Freud, represents internalized ideals and provides standards for judgment (the conscience) and for future aspirations.
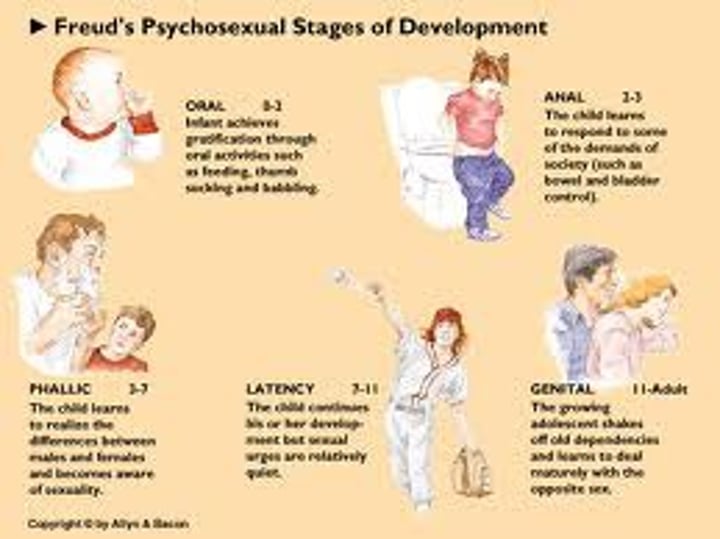
psychosexual stages
the childhood stages of development (oral, anal, phallic, latency, genital) during which, according to Freud, the id's pleasure-seeking energies focus on distinct erogenous zones.
Oedipus complex
according to Freud, a boy's sexual desires toward his mother and feelings of jealousy and hatred for the rival father.

identification
the process by which, according to Freud, children incorporate their parents' values into their developing superegos.

fixation
(1) the inability to see a problem from a new perspective, by employing a different mental set. (2) according to Freud, a lingering focus of pleasure-seeking energies at an earlier psychosexual stage, in which conflicts were unresolved.

defense mechanisms
in psychoanalytic theory, the ego's protective methods of reducing anxiety by unconsciously distorting reality.

repression
basic defense mechanism that banishes anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories from consciousness

regression
allows us to retreat to an earlier, more infantile stage of development

reaction formation
the ego unconsciously makes unacceptable impulses look like their opposites

projection
disguises threatening impulses by attributing them to others

rationalization
occurs when we unconsciously generate self-justifying explanations to hide from ourselves the real reasons for our actions

displacement
diverts sexual or aggressive impulses toward an object or person that is psychologically more acceptable than the one that aroused the feelings

sublimation
the transformation of unacceptable impulses into socially valued motivations

denial
protects the person from real events that are painful to accept, either by rejecting a fact or its seriousness

collective unconscious
a common reservoir of images derived from our species' universal experiences

projective test
a personality test, such as the Rorschach or TAT, that provides ambiguous stimuli designed to trigger projection of one's inner dynamics

Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
a projective test in which people express their inner feelings and interests through the stories they make up about ambiguous scenes

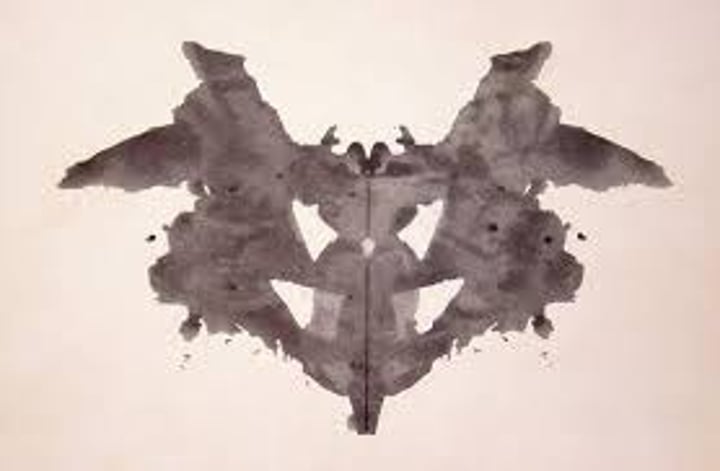
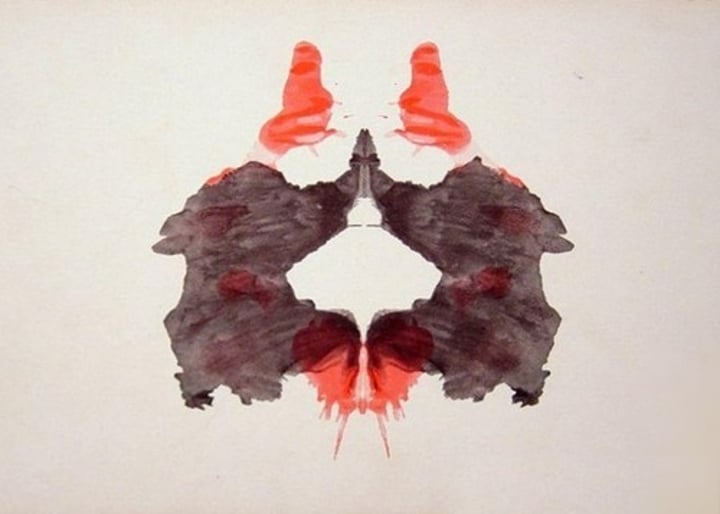
Rorschach inkblot test
the most widely used projective test, a set of 10 inkblots, designed by Hermann Rorschach; seeks to identify people's inner feelings by analyzing their interpretations of the blots.

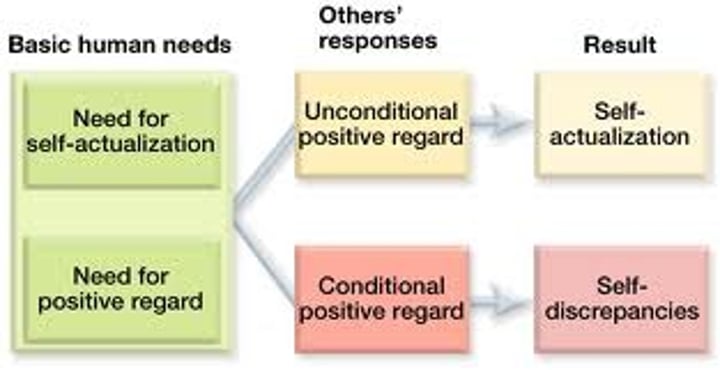
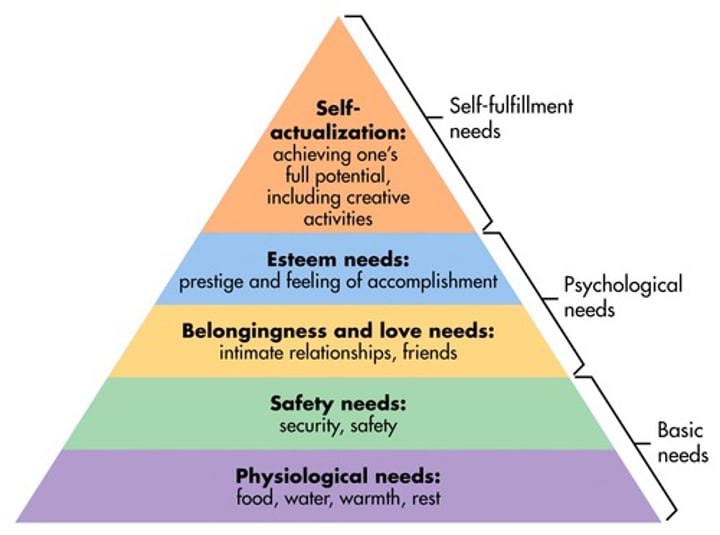
self-actualization
according to Maslow, one of the ultimate psychological needs that arises after basic physical and psychological needs are met and self-esteem is achieved; the motivation to fulfill one's potential.
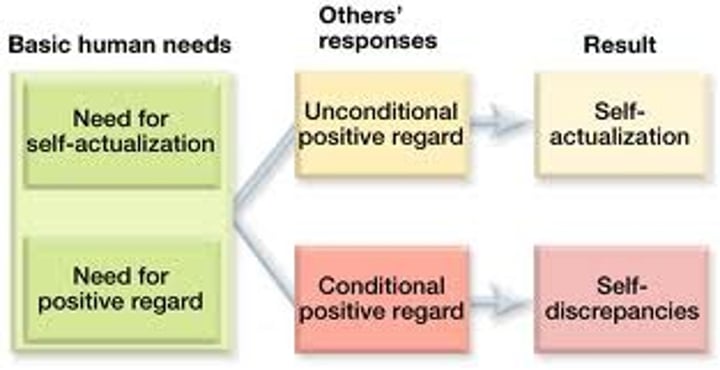
unconditional positive regard
a caring, accepting, nonjudgmental attitude, which Carl Rogers believed would help clients to develop self-awareness and self-acceptance.
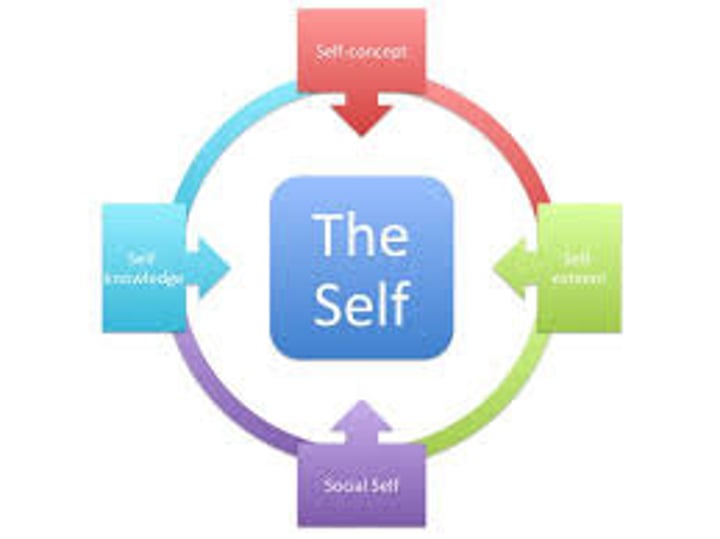
self-concept
all our thoughts and feelings about ourselves, in answer to the question, "Who am I?"
trait
a characteristic pattern of behavior or a disposition to feel and act, as assessed by self-report inventories and peer reports.
personality inventory
a questionnaire (often with true-false or agree-disagree items) on which people respond to items designed to gauge a wide range of feelings and behaviors; used to assess selected personality traits.
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
the most widely researched and clinically used of all personality tests. Originally developed to identify emotional disorders (still considered its most appropriate use), this test is now used for many other screening purposes.

empirically derived test
a test (such as the MMPI) developed by testing a pool of items and then selecting those that discriminate between groups.
social-cognitive perspective
views behavior as influenced by the interaction between people's traits (including their thinking) and their social context.
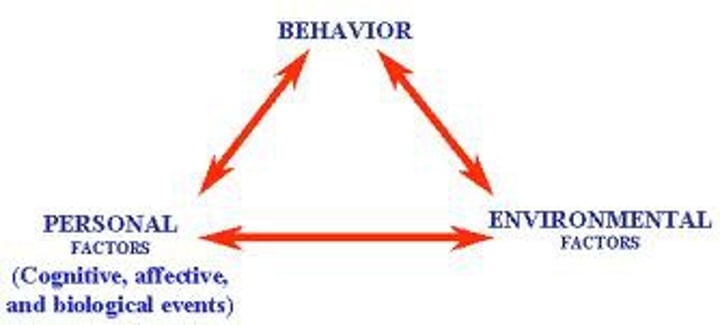
reciprocal determinism
Albert Bandura - the interacting influences of behavior, internal cognition, and environment.
personal control
the extent to which people perceive control over their environment rather than feeling helpless.
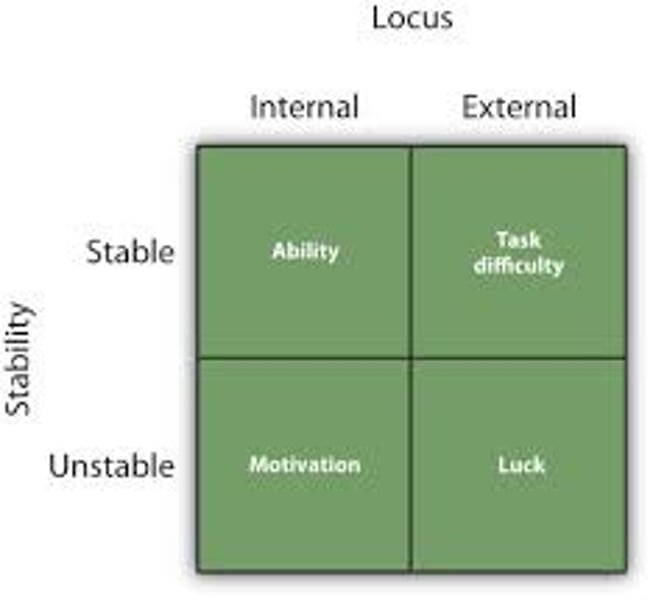
external locus of control
the perception that chance or outside forces beyond your personal control determine your fate.
internal locus of control
the perception that you control your own fate.
positive psychology
the scientific study of optimal human functioning; aims to discover and promote strengths and virtues that enable individuals and communities to thrive.
self
in contemporary psychology, assumed to be the center of personality, the organizer of our thoughts, feelings, and actions.

self-esteem
one's feelings of high or low self-worth.

learned helplessness (review)
A condition that occurs after a period of negative consequences where the person begins to believe they have no control.
Sigmund Freud
developed the psychoanalytic theory of personality development, which argued that personality is formed through conflicts among three fundamental structures of the human mind: the id, ego and the superego
Abraham Maslow
Hierarchy of Needs. Maslow said that humans strive for self-fulfillment, or realization of their full potential, once they have satisfied their more basic needs.
Alfred Adler
founder of Adlerian psychology (individual psychology) He is considered the 1st community psychologist, because his work pioneered attention to community life, prevention, and population health.
"The individual feels at home in life and feels his existence to be worthwhile just so far as he is useful to others and is overcoming feelings of inferiority."

Karen Horney
Feminine Psychology
She challenged Freud's "penis envy" view of women and attempted to balance his masculine bias.

Carl Jung
analytical psychology, also called Jungian psychology, is a school of psychotherapy that emphasizeds the importance of the individual psyche and the personal quest for wholeness.
Collective unconscious - his concept of a shared, inherited reservoir of memory traces from our species' history.

Carl Rogers
central to Rogers' personality theory is the notion of self or self-concept. This is defined as "the organized, consistent set of perceptions and beliefs about oneself." the self is the humanistic term for who we really are as a person.

Hermann Rorschach
developer of the Rorschach Inkblot Personality Test (Rorschach Test), which involves the assessment by a psychiatrist or psychologist of a subject's responses when asked what he or she sees in a series of inkblots.
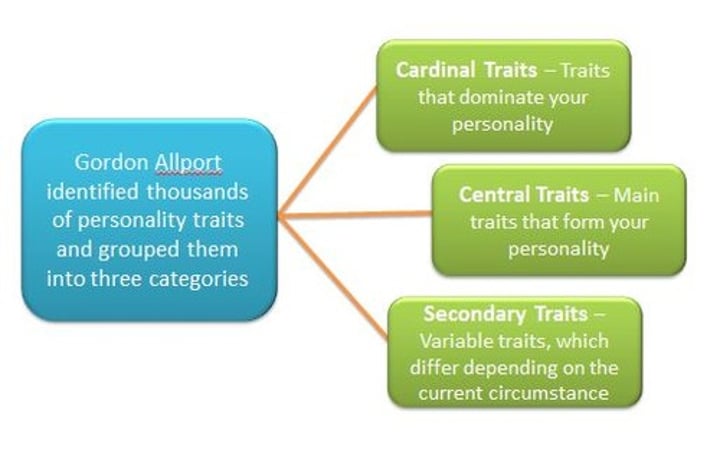
Gordon Allport
often referred to as one of the founders of personality psychology. Today, remembered for his Trait Theory of Personality.
Hans Eysenck
Trait theorist whose theory has two axis: stable/unstable, extrovert/introvert
Eysenck's personality theory focused on temperaments, which he believed were largely controlled by genetic influences.

narcissism
excessive self-love and self-absorption; usually at the expense of another
Trait Theory
A theory of personality that focuses on identifying, describing, and measuring individual differences in behavioral predispositions (NOT Explaining)
Neo-Freudians
Literally "New Freudians"; refers to theorists who broke with Freud but whose theories retain a psychodynamic aspect, especially a focus on motivation as the source of energy for the personality. Ex: Horney, Jung Adler
oral stage
Freud's first stage of personality development, from birth to about age 2, during which the instincts of infants are focused on the mouth as the primary pleasure center.
anal stage
(18-36 months) pleasure focuses on bowel and bladder elimination; coping with demands for control
phallic stage
Freud's third stage of personality development, from about age 4 through age 7, during which children obtain gratification primarily from the genitals.
latent stage
Freud's stage of psychosexual development occuring from about age 6 to puberty during which little happens in psychosexual terms
genital stage
Freud's last stage of personality development, from the onset of puberty through adulthood, during which the sexual conflicts of childhood resurface (at puberty) and are often resolved during adolescence).
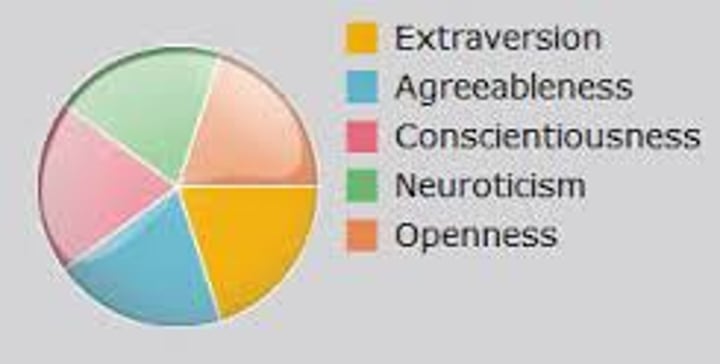
Big Five Personality Traits
openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism
factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (called factors) on a test; used to identify different dimensions of performance that underlie a person's total score.
Intellectualization
An attempt to avoid expressing actual emotions associated with a stressful situation by using the intellectual processes of logic, reasoning, and analysis
belongingness and love needs
Maslow's middle stage; need to love and be loved, to belong and be accepted; need to avoid loneliness and separation
Inferiority Complex (Adler)
individuals sense of incompleteness, imperfection, and inferiority both physically and socially
Birth Order Theory
A person's rank within their family can have an effect on their personality and intelligence
self-concept
all our thoughts and feelings about ourselves, in answer to the question, "Who am I?"
social self
concept of self as reflected in social interactions with others
inner self
awareness of the self's private thoughts and imaginings
Body-Self
physical traits and abilities
Persona
an individual's characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting
Archetypes (Jung)
emotionally charged images and thought forms that have universal meaning