Topic 5 - A Level Biology Edexcel B
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
State the purpose of aerobic respiration
Produces ATP, which can be hydrolysed to ADP + Pi
To release energy for metabolic reaction/ phosphorylate compounds to make them more reactive.
Name the 4 main stages in aerobic respiration and where they occur.
Glycolysis: cytoplasm
Link reaction: mitochondrial matrix
Krebs cycle: mitochondrial matrix
Oxidative phosphorylation: via electron transfer chain: membrane of cristae
Stages of glycolysis
Glucose is phosphorylated to hexose bisphosphate by 2x ATP.
Hexose bisphosphate splits into 2x triose
phosphate (TP).2x TP is oxidised to 2x pyruvate.
Net gain of 2x reduced NAD, 2x ATP and 2x Pyruvate per glucose.
How does pyruvate from glycolysis enter the mitochondria?
via active transport
What happens during the link reaction?
Pyruvate is completely oxidised to acetate. It produces 1 reduced NAD and releases 1x CO2(decarboxylation).
Acetate combines with coenzyme A (CoA) to form AcetylCoA.
Give a summary equation for the link reaction
pyruvate + NAD + CoA → acetyl CoA + reduced NAD + CO2
What happens in the Krebs Cycle?
series of redox reactions produces:
● ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation.
● Reduced coenzymes.
● CO2 from decarboxylation.
Outline the stages of the Krebs cycle.
Acetyl group (2c) + Oxaloacetate (4c) = Citrate (6C)
Citrate loses CO2 and H2 so produces 5C compound, CO2and reduced NAD
5C compound loses CO2 and H2 so produces Oxaloacetate, CO2, reduced NAD, reduced FAD and ATP.
Oxaloacetate combines with a new molecule of acetyl CoA and the cycle restarts
Hydrogen carriers take H to the electron transport chain.
Definition of decarboxylation and dehydrogenation
decarboxylation= removal of CO2
dehydrogenation= removal of hydrogen
What is the electron transport chain?
a series of carrier proteins attached to the membrane of the cristae in the mitochondria
Name the process that the electron transport chain uses to produce ATP in aerobic respiration
Oxidative phosphorylation via chemiosmosis
What happens in the electron transport chain?
Electrons released from reduced NAD & FAD undergo successive redox reactions.
The energy released is coupled to maintaining proton gradient or released as heat.
Oxygen acts as final electron acceptor
How is a proton concentration gradient established during chemiosmosis?
Some energy released from the electron transport chain is coupled to the active transport of H+ ions (protons) from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space
How does chemiosmosis produce ATP?
H+ ions (protons) move down their concentration gradient from the intermembrane space into the mitochondrial matrix via the channel protein ATP synthase.
ATP synthase catalyses ADP + Pi --> ATP
State the role of oxygen in aerobic respiration.
terminal electron acceptor in electron transfer chain.
combines with H+ to produce water
What is the benefit of an electron transport chain rather than a single reaction?
Energy is released gradually
Less energy is released as heat
What is anaerobic respiration?
Partial breakdown of hexose sugars (glucose) in oxygen-deprived conditions to produce a limited ATP yield.
What happens during anaerobic respiration in animals?
Only glycolysis continues
reduced NAD + pyruvate --> oxidised NAD (for further glycolysis + lactate
Draw a flowchart to show how lactate is produced in anaerobic respiration
pyruvate acts as a hydrogen acceptor
reduced NAD gets oxidised into oxidised NAD
lactate is formed
What happens to the lactate produced in anaerobic respiration?
Transported to the liver via bloodstream.
Oxidised to pyruvate by lactate dehydrogenase
Involves conversion of NAD to reduced NAD
Enters the link reaction in liver cells or is converted to glycogen
How does lactate affect muscle contraction in mammals?
Lactate is acidic so it decreases pH, as a result this causes muscle fatigue
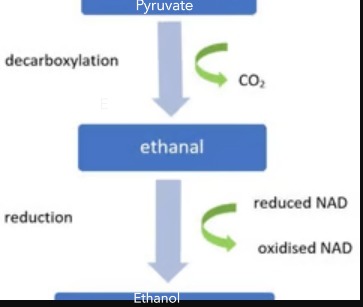
What happens during anaerobic respiration in some microorganisms e.g. yeast and some plant cells?
Only glycolysis continues.
Pyruvate is decarboxylated to form ethanal
Ethanal is reduced to ethanol using reduced NAD to produce oxidised NAD for further glycolysis
Draw a flowchart to show how ethanol is produced during anaerobic respiration.
What is the advantage of producing ethanol/lactate during anaerobic respiration?
Converts reduced NAD back into NAD so glycolysis can continue
What is the disadvantage of producing ethanol during anaerobic respiration?
Dissolves cell membranes so cells die when the concentration is above 12%
Compare ATP yields per molecule of hexose sugar from aerobic and anaerobic respiration
Aerobic : 38 in ideal conditions
Anaerobic : 2 from glycolysis
Explain the principle behind using a respirometer
Pressure changes in the boiling tube due to CO2 production (anaerobic experiments) or O2 consumption (aerobic experiments) cause a drop of coloured liquid to move.
What is the purpose of sodium hydroxide solution in a respirometer set up to measure the rate of aerobic respiration?
-Absorbs CO2 so that there is a net.
-Decrease in pressure as O2 is consumed.
How could a student calculate the rate of respiration using a respirometer?
-Volume of O2 produced or CO2 consumed / time x mass of sample
-Volume = distance moved by coloured drop x (0.5 x capillary tube diameter)^2 x pi
What is an absorption spectrum?
Graph that shows the percentage of each wavelength of light that a pigment absorbs.
What is an action spectrum?
graph that shows the overall rate of photosynthesis at each wavelength of light
strongly corresponds to absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a (most abundant pigment)
Suggest how changing wavelength of light affects rate of photosynthesis
-Highest rate in violet range = 450
-Chlorophyll reflect green light so rate slows 490 - 570
-Rate increases in orange range 590 - 620
-Slowest rate above 650
Name the 2 main groups of photosynthetic pigment.
● Chlorophyll (made of chlorophyll a & chlorophyll b)
● Carotenoids (carotene & xanthophylls)
Where are photosynthetic pigments found?
thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts
Explain the role of chlorophyll A.
Primary photosynthetic pigment.
Mainly absorbs wavelengths in violet-blue (430 nm) & orange-red (662 nm) parts of spectrum.
Emits electrons after absorbing photons of light.
Explain the role of chlorophyll B.
Accessory pigment with absorption peaks 453 nm & 642 nm.
Explain the role of carotenoids
Act as antioxidants to prevent damage to other pigments via non-photochemical quenching of excess photons.
Mainly absorb wavelengths in the blue-green part of the spectrum.
Why do many plants have a variety of photosynthetic pigments?
To widen the range of wavelengths of light they can absorb to ensure maximum rate of photosynthesis. Particularly important for plants in shaded conditions.
State the purpose and principle of paper chromatography.
Molecules in a mixture are separated based on their relative attraction to the mobile phase (running solvent) vs the stationary phase (chromatography paper).
Outline a method for extracting photosynthetic pigments.
Use a pestle and mortar to grind a leaf with an extraction solvent e.g. propanone
Outline how paper chromatography can be used to separate photosynthetic pigments.
Use a capillary tube to spot pigment extract onto pencil "start line" (origin) 1 cm above bottom of paper.
Place chromatography paper in solvent. (origin should be above solvent level).
Allow solvent to run until it almost touches the other end of the paper. Pigments move different distances.
What are Rf values? How can they be calculated?
● Ratios that allow comparison of how far molecules have moved in chromatograms.
● Rf value = distance between origin and centre of pigment spot / distance between origin and solvent front.
Describe the structure of chloroplast
● Usually disc-shaped.
● Double membrane (envelope).
● Thylakoids: flattened discs stack to form grana.
● lamellae: tubular extensions attach thylakoids in adjacent grana.
● Stroma: fluid-filled matrix.
Where do light-dependent & light-independent reactions occur in plants?
Light-dependent: in the thylakoids of chloroplasts
Light-independent: stroma of chloroplasts
Name the processes in the light-dependent reaction
photoionisation
electron transfer chain
chemiosmosis
non-cyclic only:
reduction of NADP
photolysis of water
Explain the role of light in photoionisation.
Chlorophyll molecules absorb energy from photons of light. This 'excites' 2 electrons (raises them to a higher energy level), causing them to be released from the chlorophyll.
Describe non-cyclic photophosphorylation
Uses Photosystems Ⅰ & Ⅱ. Excited electrons enter ETC to produce ATP. NADP acts as final electron acceptor & is reduced. Water is photolysed to release electrons to replace those lost from PS Ⅱ. Purpose is to produce ATP & reduced NADP for Calvin cycle to produce biological compounds.
Describe cyclic photophosphorylation
Uses only Photosystem Ⅰ. Excited electrons enter
ETC to produce ATP then return directly to
photosystem (so no reduction of NADP & no water
needed to replace lost electrons).
Purpose is to produce additional ATP to meet surplus
energy demands of cell.
State the purpose of cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation
cyclic: produces additional ATP to meet surplus energy demands of the cell.
non-cyclic: Produces ATP and reduced NADP for the calvin cycle to produce biological compounds.
What happens in the photolysis of water?
Light energy splits molecules of water
2H2O → 4H+ + 4e- + O2
What happens to the products of the photolysis of water?
H+ ions: moved out of thylakoid space via ATP synthase & are used to reduce the coenzyme NADP
e-: replaces the electrons lost from chlorophyll
O2: used for respiration or diffuses out of the leaf as a waste gas
How and where is reduced NADP produced in the light-dependent reaction?
NADP + 2H+ + 2e- --> reduced NADP
catalysed by dehydrogenase enzymes.
Stroma of chloroplasts
Where do the H+ ions and electrons used to reduce NADP come from?
H+ ions: photolysis of water
Electrons: NADP acts as the final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain
Name 3 main stages in the calvin cycle
carbon fixation
reduction
regeneration
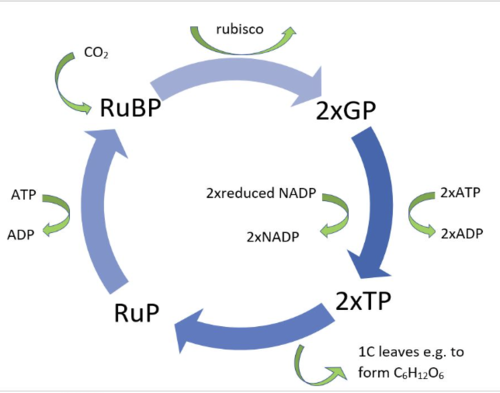
What happens during carbon fixation
CO2 and RuBP catalysed by RUBISCO form an unstable 6C compound that breaks down into 2xGP.
What happens during reduction (in the calvin cycle)
2x GP is reduced to 2x GALP by 2x reduced NADP and 2x ATP
Which Forms 2x NADP & 2x ADP
How does the light-independent reaction result in the production of useful organic substances
GALP can produce glucose (gluconeogenesis)
So can be converted to sucrose or starch
Amino acids
What happens during regeneration (in the calvin cycle)?
After 1C leaves the cycle, the 5C compound RuP forms.
RuBP is regenerated from RuP using 1x ATP
Forms 1x ADP
Outline the sequence of events in the light-independent reaction (Calvin cycle).
State the roles of ATP & (reduced) NADP in the light-independent reaction.
ATP: reduction of GP to TP & provides phosphate group to convert RuP to RuBP
reduced NADP: coenzymes transport electrons needed for reduction of GP to TP
State the number of carbon atoms in RuBP, GP & GALP
RuBP: 5
GP: 3
GALP: 3
Define "limiting factor"
Factor that determines maximum rate of a reaction, even if other factors change to become more favourable.
Name 4 environmental factors that can limit the rate of photosynthesis.
Light intensity (light-independent)
CO2 levels (light-independent)
Temperature (enzyme-controlled)
Mineral levels