3RD LE - BIO 11.1
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
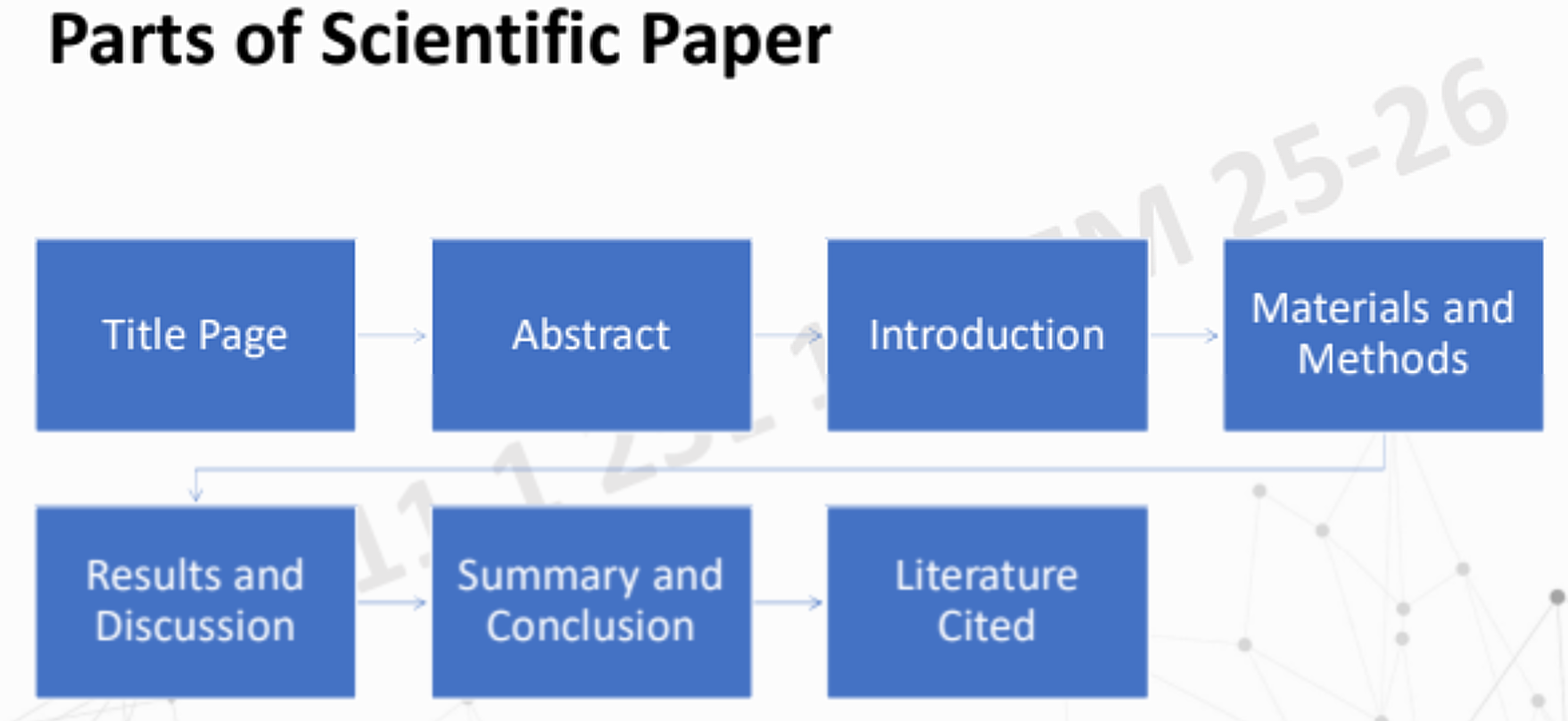
All Parts of Scientific Paper from start to finish.
Title
Attracts the reader
Must broadly explain the paper is about
Informative and concise
Title of the Study: Comparative Analysis on the Protein Profiles of Plant-Based Burger Patties Made from Soybean (Glycine max) and Mung Bean (Vigna Radiata)
Study: You want to determine the protein profile of burger patties made from soybeans and mungbeans
Working Title: Comparing Protein Profiles of Burgers Made from Soybeans and Mungbeans
what would be your title?
Title of the Study: Antihypertensive Effects of Compound X Isolated from Plant A (insert scientific name)
Study: You want to investigate if a new plant compound (Compound X) from a native plant (Plant A) can lower blood pressure (Hypertension)
Working Title: Compound X from Plant A and its blood-pressure lowering activity
What would be your title?
Introduction
Background Information
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
Important terms that need to be defined
Introduction
Background Information
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
Important relationships on the factors that are under study
Introduction
Background Information
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
e.g. Background about burger patties (how they are made), soybeans (botanical, economic significance
Introduction
The Problem
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
What the issue the paper is trying to address
Introduction
The Problem
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
e.g. ethical consumption of meat products, rise of lifestyle diseases, expensive meat ingredients
Introduction
Significance of the Study
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
Where will the data from this study be used/who will benefit from this research?
Introduction
Significance of the Study
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
e.g. people who are looking for cheaper protein options
General Objective
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
(e.g. The ____________ objective was to compare the protein profiles of burger patties made from soybean and mungbean)
Specifically
Specific Objectives
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
e.g. ____________, the study aimed to: (your method must answer this objective)
Hypothesis of the Study
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
Educated guess based on available literature
e.g. It is hypothesized that burger patties made from soybeans would give better protein profiles compared to mungbeans due to higher amounts of essential amino acids.
Date and Place of the Study
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
Where and when you conducted your study
e.g. The study was conducted at the Institute of Biological Sciences, UPLB from January 2025 – December 2025.
reagents/chemicals; equipment; food ingredients
Matterials and Methods
Materials (e.g. ___________, _________, __________) that were used the experiment.
F
note: you don’t need to list down the glasswares, beakers, or common materials in the lab. Only the relevant ones
T or F
For materials and methods, you need to list down the glassware, beakers, or common materials in the lab.
rationale
Materials and Methods
Detailed methods on how the experiments were performed (if modifications were made, indicate them)
Appropriate methods should be chosen depending on the (specific) objectives of your study
You may provide a __________ as to why you chose that method (e.g. Bradford assay was used to quantify the total proteins present in the burger patties.)
positive; negative
If method required the use of controls, indicate the ________ and ________ controls
E.g. Quantification of protein concentration was done using Bradford assay using bovine serum albumin as the positive control and water as the negative control.
Abstract
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
Gives an impression what the paper is all about
Capture the essence of the paper
Abstract
Which chapter and specific part of the scientific paper?
Usually composed of 250 words
Contains keywords – important words that are related to your study


















Vascular; root; shoot
__________ plants (i.e. those with conducting tissues like xylem and phloem) have two major organ systems: the _____ and _______ systems.
vegetative (nonreproductive); reproductive
The shoot system is found above the ground and consists of the ______________ parts of the plant such as the leaves, buds and the stems, and the _______________ parts which include flowers, fruits and seeds.
root
The __________ system consists of the subterranean parts which anchor the plant to the soil and allows for absorption of water, as well as inorganic and organic nutrients.
transpiration
Essential plant processes such as ____________ involve the use of vascular tissues. This refers to the loss of water through the stomata in the form of water vapor.
absorption at the roots
capillary action in the xylem vessels
evaporation at the aerial parts.
Transpiration involves three basic steps:
_____________________
_____________________
_____________________
pulling; negative; cohesive
Water loss by transpiration creates a _________ force that produces a ___________ hydrostatic pressure. The __________ property observed in most liquids allows water to be pulled from the soil through the xylem as water molecules are evaporating at the leaf surface, simultaneously.
Transpiration; underside
______________ occurs mostly on the __________ of the leaf surface where stomata are found abundantly but it may also take place through cuticles and lenticels.
thermoregulation
Transpiration plays an important role in ______________.
Rapid evaporation of water from the aerial parts of the plant through transpiration lowers their temperature and thus allows them to survive in extreme heat conditions.
Transpiration
The process takes place throughout the day, peaking at noon, the hottest part of the day.
number, size, position and the movement of
Transpiration rates are affected by internal and external factors.
Internal factors include plant parameters such as _________, _________, _________, and ____________ stomates, the thickness of the boundary layer of still and humid air on the surface of the leaf and the thickness of the cuticle layer.
air temperature; humidity; wind speed
Transpiration rates are affected by internal and external factors.
External factors such as ____________, relative ________, __________, and radiation intensity strongly influence the rate of evaporation, as well.
photosynthesi; CO2
Furthermore, transpiration supports ______________ as it would allow _____ to enter the open stomata, allowing gas exchange between the atmosphere and the leaf.
Organs
__________ are body structures composed of various types of tissues that constitute a distinct structural and functional unit.
organ system
An __________ is a group of organs with related functions that performs major activities for the body.
coelom (body cavity); skeleton of jointed bones; accessory organs; integument
The general body plan of vertebrates is characterized by the presence of a digestive tract or tube suspended in the ____________ surrounded by an internal ________________, _______________-, and ____________.
dorsal; skull and vertebrae; ventral; rib cage; muscles
Vertebrates possess both a ___________ (back) body cavity formed within the _________________, as well as, a ____________ (belly) body cavity enclosed by ___________ and lower abdominal __________.
thoracic cavity; peritoneal (abdominal) cavity
The ventral body cavity is divided by the diaphragm into two parts: the ________________, which contains the heart and lungs, and the ________________, which holds most of the organs such as stomach, intestines, liver, and kidneys.
pericardial cavity; pleural cavities
The space around the heart is called the _______________ and the space around the lungs corresponds to the ________________.
Periplaneta americana L.; Insecta; Blattodea; Blattidae
The domestic cockroach, __________________ belongs to Phylum Arthropoda, Class ___________, Order ____________and Family ____________.
chitin
Being an invertebrate, the cockroach lacks an internal skeleton or endoskeleton. This however is compensated by the presence of a waxy exoskeleton made of __________.
The exoskeleton provides protection against mechanical injury and prevents excessive loss of water.
head, thorax, and abdomen.
Two pairs of wings are found on the dorsal side while the three pairs of legs are located on the ventral side. The cockroach has three body regions: _______________
SYSTEMS |
Circulatory |
FUNCTIONS |
Distributes materials, respiratory gases, and chemical compounds throughout the body |
SYSTEMS |
Circulatory |
COMPONENTS |
Heart, blood vessels, blood |
SYSTEMS |
Digestive |
FUNCTIONS |
Procures and processes nutrients from ingested food |
SYSTEMS |
Digestive |
COMPONENTS |
Mouth, esophagus, stomach, Intestines, liver, pancreas, anus |
SYSTEMS |
Endocrine |
FUNCTIONS |
Coordinates and integrates the activities of the body |
SYSTEMS |
Endocrine |
COMPONENTS |
Pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal and other hormone-secreting glands |
SYSTEMS |
Integumentary |
FUNCTIONS |
Covers and protects the body against injury, infection, and dehydration |
SYSTEMS |
Integumentary |
COMPONENTS |
Skin and its derivatives such as hair, nails, scales, feathers, and sweat glands |
SYSTEMS |
Lymphatic and Immune |
FUNCTIONS |
Vessels transport extracellular fluid and fat to circulatory system; lymph nodes and lymphatic organs provide defenses to microbial infection and cancer |
SYSTEMS |
Lymphatic and Immune |
COMPONENTS |
Lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, bone marrow, thymus, tonsils, spleen |
SYSTEMS |
Muscular |
FUNCTIONS |
Facilitates locomotion and other body movement |
SYSTEMS |
Muscular |
COMPONENTS |
Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle |
SYSTEMS |
Nervous |
FUNCTIONS |
Receives stimuli, integrates information, and directs the responses to stimuli |
SYSTEMS |
Nervous |
COMPONENTS |
Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory organs |
SYSTEMS |
Reproductive |
FUNCTIONS |
Carries out reproduction |
SYSTEMS |
Reproductive |
COMPONENTS |
Testes, ovaries, and associated reproductive structures |
SYSTEMS |
Respiratory |
FUNCTIONS |
Captures oxygen and exchanges gases |
SYSTEMS |
Respiratory |
COMPONENTS |
Lungs, trachea, gills, and other air passageways |
SYSTEMS |
Skeletal |
FUNCTIONS |
Protects the body and provides support for locomotion and movement |
SYSTEMS |
Skeletal |
COMPONENTS |
Bones, tendons, cartilage, and ligaments |
SYSTEMS |
Urinary or Excretory |
FUNCTIONS |
Removes metabolic wastes from the bloodstream and regulates osmotic balance |
SYSTEMS |
Urinary or Excretory |
COMPONENTS |
Kidney, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra |
Rhinella marina L.; Amphibia; Anura; Bufonidae
A vertebrate model often used in the laboratory is the marine toad, ____________ which belongs to Phylum Chordata, Class __________, Order __________, and Family ____________.
bumpy skin due to the presence of numerous wart-like irregularities.
The marine toad, Rhinella marina L. can be easily recognized from the true frogs (Rana sp.) by their?
parotoid glands
The marine toad, Rhinella marina L. also possess two huge ____________ situated behind each eye, which function as venom glands capable of producing toxic milky secretions when squeezed
Dissection; vivisection
___________ involves the display or removal of pads of any dead animal, in contrast to ___________, which is an operation done on a living animal.
humane treatment
maximum utilization of the dissected animal
preparedness for the procedure
There are some important rules to bear in mind for dissection to be an acceptable procedure in studying animal biology. These include:
____________________
____________________
____________________
gizzard; Malpighian tubules
Posterior to the crop is a small, hard, conical structure, the _________. It has teeth-like structures that are used in grinding food.
This is followed by the mesenteron, marked anteriorly by finger-like gastric caeca and posteriorly by hair-like ______________.
These tubules serve as the excretory organs of the cockroach.
ostia (sing. ostium)
In front of each dilatations except in the last, a pair of opening, the _________________ is present. They are guarded by valves to prevent backflow of blood into the heart.
pericardium
In the marien toad, locate the heart contained within a membranous sac called the _____________.
brachial plexus
In the marine toad, there are ten pairs of spinal nerves that pass out from openings of the vertebrae.
The first three nerves have interconnecting branches that form the _____________ which innervates the forelimbs and shoulder muscles.
sciatic plexus
The seventh, eighth, and ninth nerves have many interconnections, forming the _____________ which passes into each hindlimb.
Epithelial tissue
Tissue that covers the outside of the animal body and its internal organs.
Connective tissue
Tissue made up of scattered cells held in an extracellular matrix and holds organs and tissues together and in place.
Muscle tissue
Tissue that functions in different types of movement.
Nervous tissue
Tissue that functions in the receipt, processing, and transmission of information.
Dissection and Vivisection
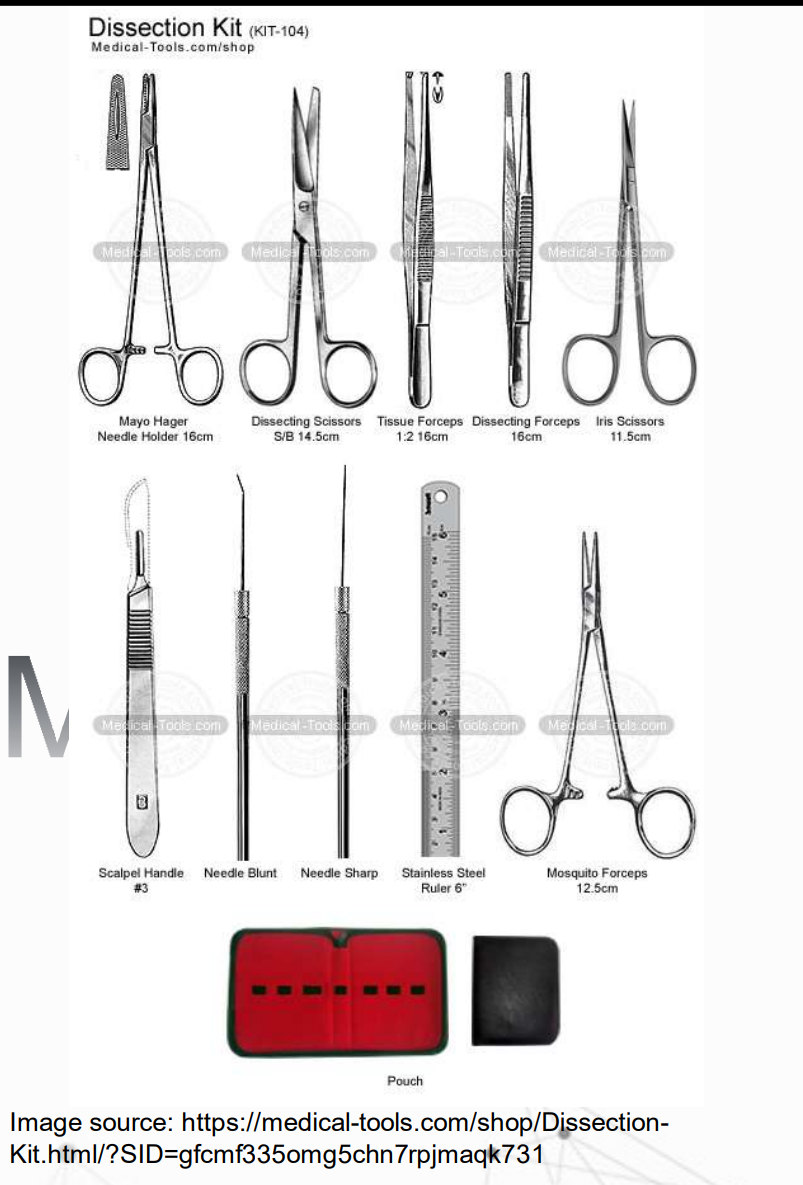
These techniques require basic equipment which include scalpel, forceps, dissecting scissors, flapper, pins, and dissecting pan.
Anterior; posterior
___________ means up/front while ____________ means down/back from a reference point.
Dorsal; ventral
__________ = back while __________ = front
chitin
Insects have an exoskeleton made of ______.
Chitin
_________ is a polymer (aminopolysaccharide) of N-acetyl-Dglucosamine.
Esophagus
Salivary Gland
Crop
Gizzard
Gastric Caeca
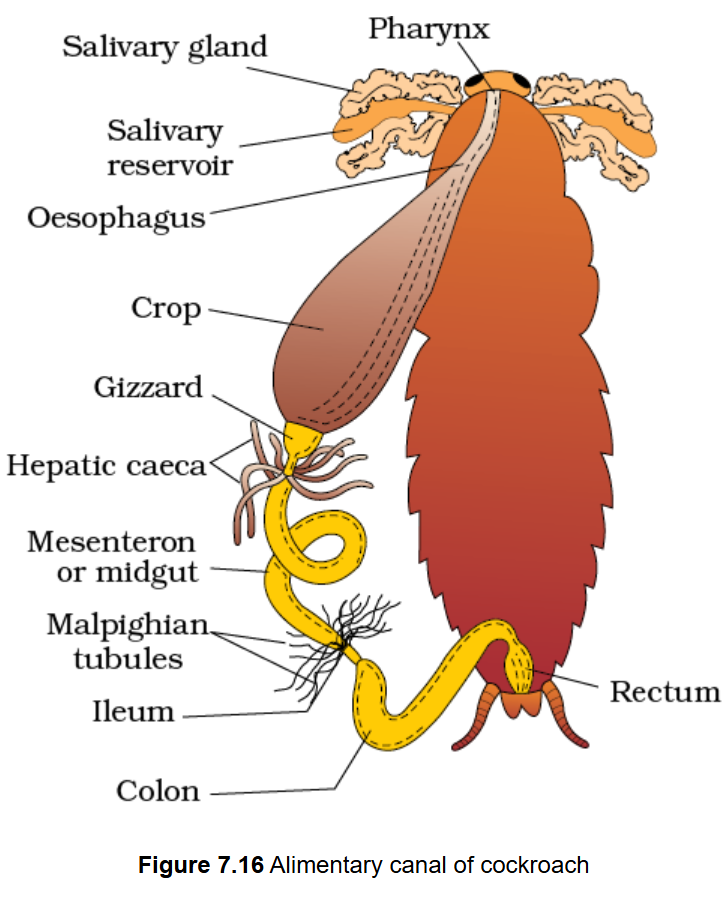
Activity 1. Dissection of Cockroach
Digestive System – immediate visible organ
A. Foregut
__________ - connects the mouth to the crop; transports food down the digestive tract
____________ - produces saliva, begins the enzymatic digestion of food in the mouth
__________ - storage organ for food prior further digestion
____________ - grinds food with its chitinous teeth
_____________ - finger-like projections that produce digestive enzymes and aid in nutrient absorption.
Mesenteron

Activity 1. Dissection of Cockroach
Digestive System – immediate visible organ
B. Midgut
______________ - primary site of digestion and absorption
Ileum
Colon
Rectum
Anus

Activity 1. Dissection of Cockroach
Digestive System – immediate visible organ
C. Hindgut
___________ - water and salts begin to be reabsorbed from the waste.
___________ - further reabsorbs water and packs undigested food.
___________ - waste storage before excretion.
___________ - exit point for waste materials from the digestive tract
Malpighian Tubules

Activity 1. Dissection of Cockroach
Excretory System
- tubular structures (fringed by glandular and ciliated cells) that filter nitrogenous wastes and other solutes from the hemolymph
Malpighian Tubules

Activity 1. Dissection of Cockroach
Excretory System
They lead into the hindgut, where wastes are combined with digestive waste for excretion.

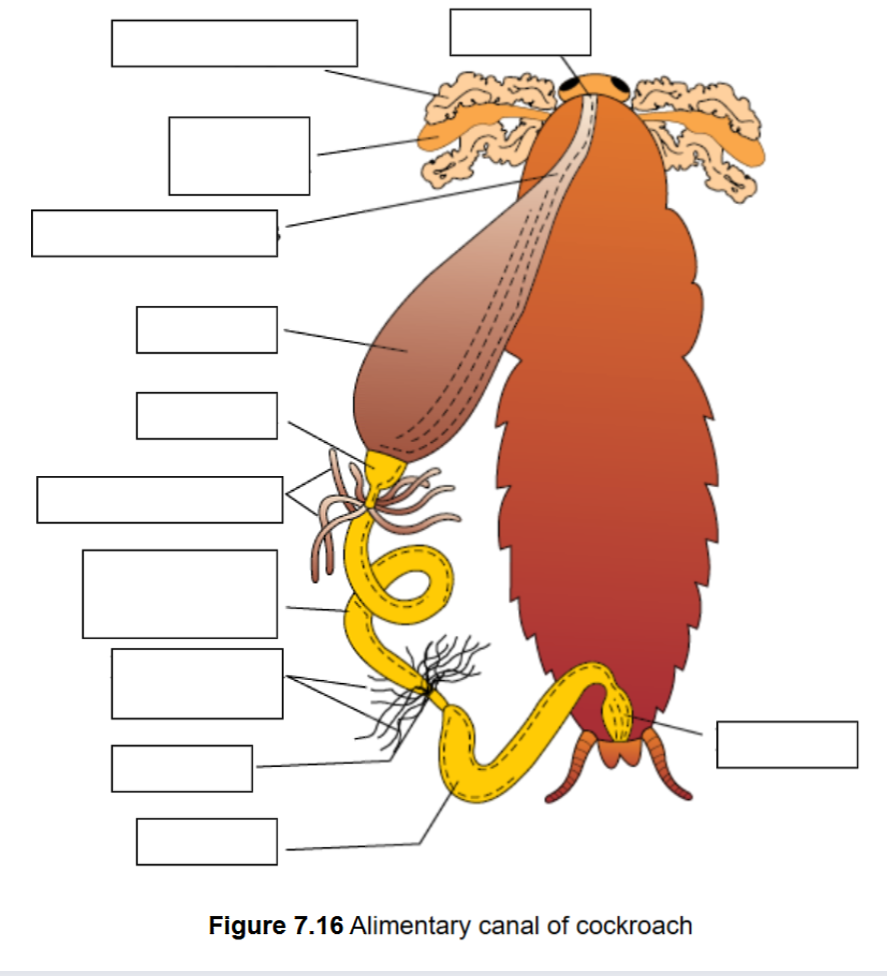
dorsal; open; cavities; closed blood vessels
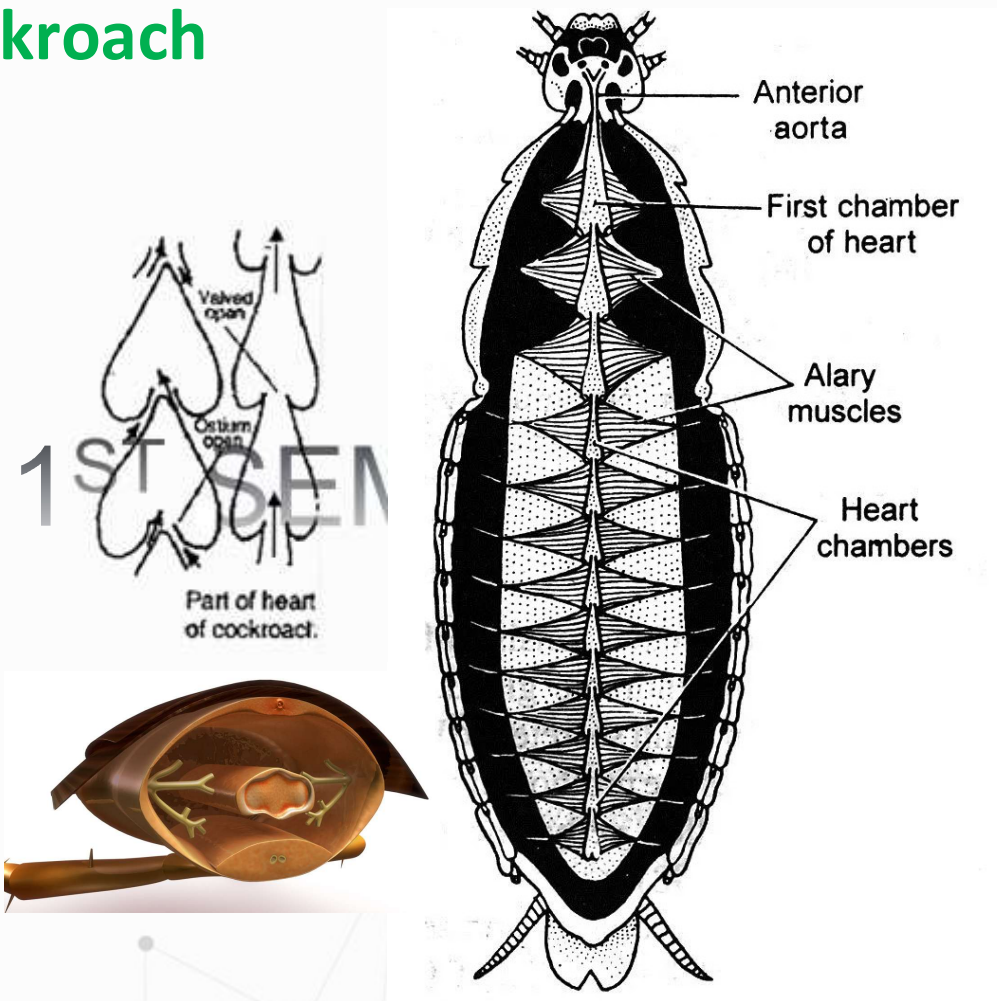
Activity 1. Dissection of Cockroach
Circulatory System – ________ part; ________ circulatory system; blood flows through _________ instead of ________ _________ _________