The Atom and the Periodic Table
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is the structure of the atom?
Nucleus - protons & neutrons
Orbital - electrons
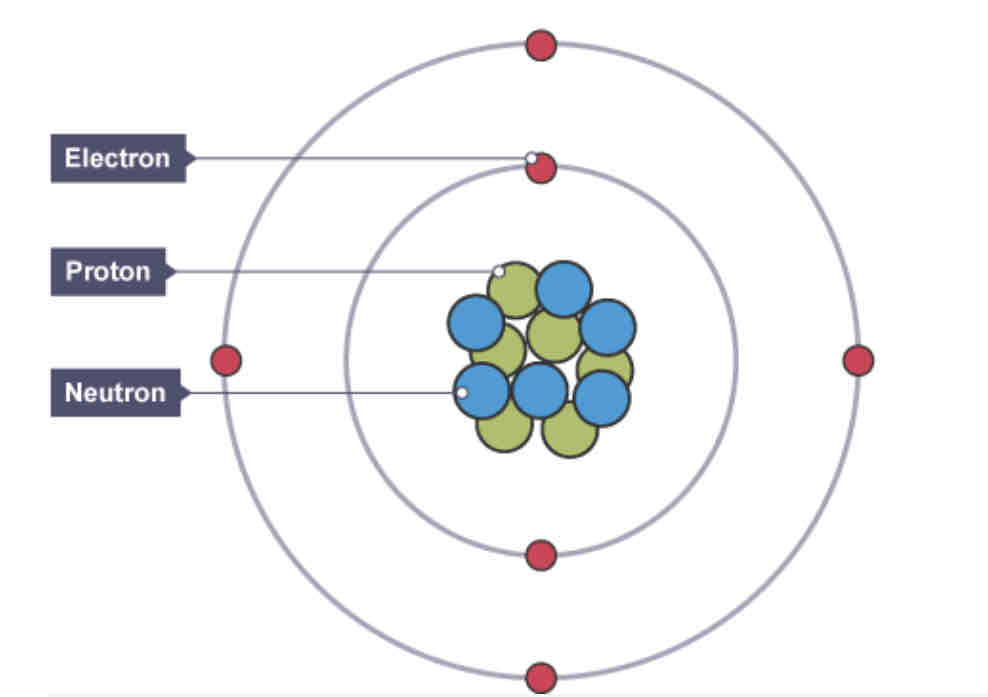
What is an atom
The smallest unit of matter made up of protons, neutrons and electrone
What is the relative mass and charge of a proton?
mass: 1
charge: +1
What is the relative mass and charge of a neutron?
mass: 1
charge: 0
What is the relative mass and charge of a electron?
mass: close to 0/ very small
charge: -1
What is the charge of an atom?
Neutral

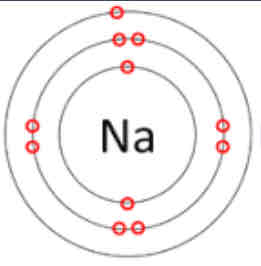
What is the atomic structure of sodium?
2 8 1

What version of the atom is this?
John Doltan’s
What was Dalton theory?
the atom was a solid sphere and different spheres made up different elements
Who created the plum pudding theory?
JJ Thomson
What is the plum pudding theory?
An atom is a solid ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded into the it.
What experiment did Ernest Rutherford do to test the plum pudding theory?
the alpha particle scattering experiment
What is the alpha particle scattering experiment ?
In the experiment positively charged alpha particles were fired at the gold foil most of the alpha particles went through the foil but some of the alpha particles scattered in different directions.
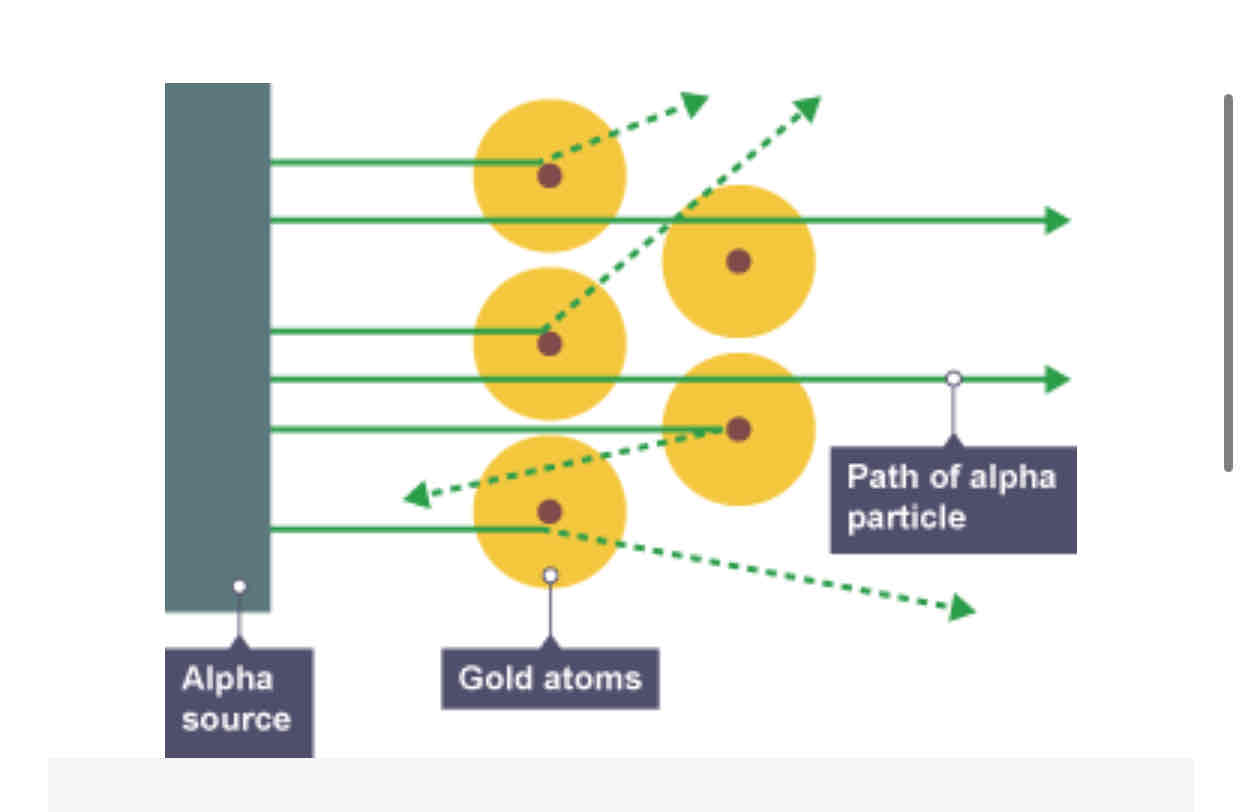
What did the alpha scattering experiment lead to ?
Rutherford suggest a new model for the atom called the nuclear model
an atom has a concentrated mass at the centre, the nucleus
the nucleus is positively charged
What did Bohr find out about the atom model?
Bohr found out that the atom has orbitals that the electrons go around
what is the atomic number?
the number of protons
What is the mass number?
mass of protons and neutrons
What is an ion?
a charged particle that has either gained or lost an electron
What is an isotope?
atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons
they have the same atomic number
different mass number
What did Mendeleev’s periodic table look like
arranged the elements in order of increasing relative atomic mass
he noted that the chemical properties of the elements and their compound showed a periodic trend
putting those with similar properties below each other into groups
he left gaps for yet to be discovered elements
he switched the order of a few elements to keep the groups consistent
What does the modern periodic table look like?
After the discovery of protons, scientists realised that the atomic number of an element is the same as the number of protons in its nucleus.
the elements are arranged according to their atomic number - not their relative atomic mass