Purchasing Final Study Guide pt. 2
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Food and labor cost.
What are the two highest expenses in a restaurant?
One Stop, Full Line Distributors
These are the companies that carry everything else that you will use in addition to meat. Their selection will be very large and run the spectrum from frozen processed items to fresh-cut, custom fabricated meat. Their prices will usually be very competitive.
Specialty Meat Purveyors and Distributors
This distribution’s selection will probably be more towards fresh and frozen, as well as specialty meat items, but not have as much processed. Their prices may be competitive, or be high due to the specialty nature of their business. They will usually be able to “custom” cut items for you easier than with one stop distributors.
Smaller “Butcher” Shops
Suppliers with much smaller selection, significantly higher prices, less consistency due to smaller batches of meat produced, but higher level of service.
Commodities Brokers
Bulk purchasing of a smaller selection of products at lower prices, usually frozen goods.
Broadline Brokers
These suppliers represent many manufacturers and can offer some aspects of different distributors.
1.) Tenderness and consistency
2.) Juiciness
3.) Flavor
What are the three factors that are evaluated to determine meat quality?
most tender
In general, the parts of the animal that get the least amount of use, are going to be the ______, and vice versa.
1.) Fat Trim
2.) Age
3.) Origin
4.) Grading - both for quality and yield
5.) Specific fabrication details. (size, weight, dimension, etc.)
What are examples of specifications that can be made for meat?
1.) Fresh or frozen
2.) Steaks, roasts, ground, chops
3.) Whole primal or fabricated
4.) Higher/lower grades
5.) Canned products
6.) Cooked, partially cooked, or raw
7.) Cured, smoked, brined, pickled
8.) Processed entrees
What are examples of forms of meat that can be purchased?
Half Carcass Cut
A meat cut where it’s literally half the animal, gutted, beheaded, and skinned.
Quarter Carcass Cut
Same as a half carcass cut, but into hind and fore-quarter sections of the animal.
Primal Cuts
Major cuts of the animal….loin, rib, chuck, brisket, round, shank, still requiring much further fabrication.
Sub-Primal Cuts
The primal cuts broken down to small items - generally some type of roast.
Portion Cuts
The sub primal cuts broken down to smaller or even single service sizes of cuts. Typically steaks and smaller roasts.
Custom Cuts
Cuts such as ground, diced, julienned, chopped, or any random cut.
Cryovacing
The process by which meat or any other items are placed into air-tight bags with all the air removed. Extends the shelf life for meat by weeks, making purchasing, storage, and usage much easier, with less waste.
Study this!
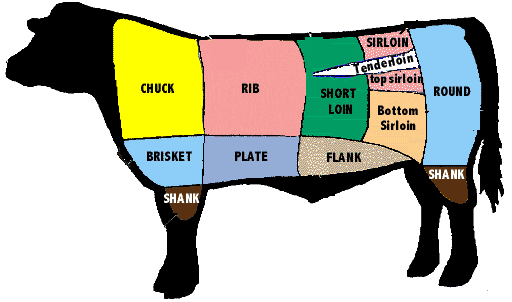
Study this!
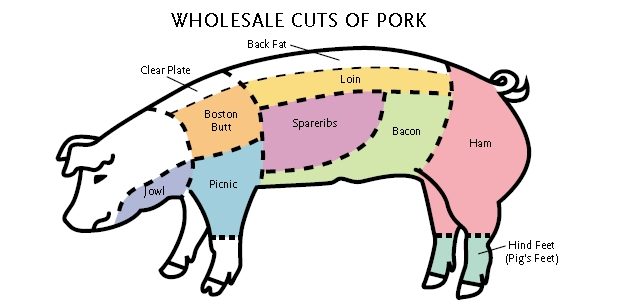
Dry Aging Meat
The type of aging that is the most expensive and takes the longest amount of time. Meat is hung in a clean, temperature and humidity-controlled cooler for a period of two to four weeks. During this time, enzymes within the meat to break down the muscle and tissues, making it tender. Moisture is lost, forming a crust that needs to be trimmed and discarded.
Wet Aging Meat
Occurs when meat and its own juices are vacuum packed in plastic and boxed for distribution. Because the plastic packaging doesn’t allow loss of moisture, the meat may absorb more moisture which results in an increase in juciness and tenderness.
1.) Wholesomeness (ensures the meat is safe for consumption)
2.) Quality (most processers have it done in order to market their product, meat is given a grade)
3.) Yield (determines amount of external fat)
What are the three ways that meat is inspected?
Swiss Cheese
Medium-hard cheese made from cow’s milk. The “eyes” are formed by CO2 gas bubbles during fermentation.
Bleu Cheese
Injected or natural mold to ripen and give flavor. An example is roquefort, typically only from France.
Fresh Cheese
Unripened and eaten quickly. An example is fresh mozzarella.
Hard Cheese
Parmesan like, long aging, and low moisture.
Semi-Soft Cheese
Very high in moisture, example is Havarti.
Sausage
Any meat that is chopped, seasoned and formed into a symmetrical shape.
Pancetta
An Italian-style bacon that is cured with salt, peppercorns and cloves. Not smoked and packed in a roll, like a sausage!
Irish Bacon
Smoke-cured bacon takes on the appearance of a boneless pork loin roast. Obtained from the “eye” part of a piece of pork loin.
Canadian Bacon
Similar to Irish, also obtained from the pork loin. Contains less fat and calories than American'-style and is referred to as “back bacon” because the meat for the bacon comes from the back of the pig.
American-Style Bacon
Comes from the stomach of the pig, cured in salt and then smoked. Virginia bacon is the most common type.
Slab Bacon
A large, single piece of bacon with the rind left on. Receives additional flavor when it’s smoked over roasted corncobs.
Peppered Bacon
The bacon receives a spicy coating of coarsely ground black pepper.
Apple Wood-Smoked Bacon
Smoke from burning pieces of apple wood is the key to curing this bacon and infusing it with smoke.
Wet-Cured Ham
This type of ham is what is available in stores. Created by submerging that ham in a salty brine solution or injecting the brine into the ham.
Dry-Cured Ham
Ham that is rubbed all over with salt and then left to cure.
Country Ham
The hogs used to make this ham are usually raised on corn and then fed an expensive diet that can include acorns, peaches and peanuts which affects the flavor of the ham.
Spiral-Cut Ham
Fully cooked, wet-cured, smoked hams that have been ingeniously sliced using a special spiral slicing machine that cuts the ham in a continuous motion from top to bottom.
Prosciutto Ham
Generally, these salty hams have been dry-cured and aged but not smoked or cooked.
Iberico Ham
Spain originated, from the wild, dark Iberico pig, which is allowed to forage for wild acorns and herbs.
Tasso Ham
Cajun speciality that is cured, heavily spicy and smoked. Used as seasoning in gumbo, jambalaya, and other regional specialities.
1.) It is safe to use?
2.) Is it good to use?
3.) Is it worth it to use?
What are the three questions to ask when wanting to use leftovers?
Green Meat
Refers to meat that has developed a greenish tint due to one of several factors such as a natural change in pigment due to heat or processing.
Linen
Dishware
Kitchen Equipment
Cleaning Supplies
Staffing
Glassware
To-Go Supplies
POS Systems
Security Cameras
Examples of nonfood expense items?
Advertisement
Pest Control
Cleaning Service
Maintenance (HVAC, plumbing, repair)
Laundry Service
Waste Removal
Landscaping
Security
Examples of services that may need to be purchased in a restaurant?
Grains and Rice
Flour and Baking Mixes
Pasta and Noodles
Legumes and Pulses
Sugar and Sweeteners
Spices and Seasonings
Dried Fruits and Nuts
Powdered and Dehydrated Products
Cereals and Breakfast Items
Snack Foods and Crackers
Examples of types of dry goods?
Milk, bacteria cultures, and rennet (a complex set of enzymes produced in the stomach of mammals. Primary component is chymosin)
What are the three primary ingredients of cheese making?
12-ounce bottle
12-ounce can
Keg (15.5 gallons or 13.2 gallons)
½ Keg (7.75 gallons)
¼ Keg (3.88 gallons)
What are standard sizes for beer?
750-ml bottle
1-liter bottle
1.75-liter bottle
What are standard sizes for spirits?
¼ bottle - 175 ml
½ bottle - 375 ml
1 bottle - 750 ml
2 bottles - 1.2 liters
4 bottles - 3 liters
What are the standard sizes for wine?
Tariffs can significantly impact your business by increasing costs, disrupting supply chains, and altering pricing strategies, necessitating proactive planning and adaptation.
How do tariffs affect a business?
1.) Correct Item/Quantity
2.) Packaging Integrity
3.) Product Quality and Freshness
4.) Temperature Control
5.) Signs of Contamination
What five things should you check when receiving a product?
Ribeye
Sirloin
Tenderloin
Brisket
Chuck Roast
Flank
Short Ribs
Skirt Steak
T-Bone
Porterhouse
Examples of beef cuts?
1.) Prime
2.) Choice
3.) Select
4.) Standard
What is the quality grading for Beef?
1 - 5, the lowest meaning the leanest.
How is beef graded based on yield?
1.) Overall Taste
2.) Appearance
3.) Yield/Shrinkage
4.) EP Cost
5.) Brand Name/Customer Appeal
What are the factors that can be considered when deciding if speciality meat is usable?
1.) Cost
2.) Quality
3.) Staffing
4.) Integrity
What factors go into deciding whether to make or buy a product?
1.) Milk Preparation/Collection
2.) Curdling
3.) Cutting and cooking
4.) Draining
What is the process of making cheese?
Usually the shoulder or the butt of the pig.
Where does pulled pork come from?
The belly.
Where does bacon come from?
The leg.
Where does ham come from?
The loin.
Where do the ribs come from?
Tough
Is the shoulder of beef tough or tender?
Tough
Is the round of beef tough or tender?
Tough
Is the brisket of beef tough or tender?
Tender
Is the rib of beef tough or tender?
Tough
Is the shank of beef tough or tender?