Molecular Biology
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Which nitrogenous bases are pyrimidines? (“CUT the Py”)
(Cytosine, Uracil, Thymine are PYrimidines)
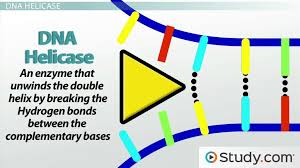
What is the role of helicase during DNA replication?
Helicase is the enzyme that unwinds and separates the two strands of the DNA double helix at the replication fork.
What is the role of DNA ligase in DNA replication?
DNA ligase is an enzyme that joins two DNA fragments by forming a phosphodiester bond between their sugar-phosphate backbones.
What does primase do during DNA replication?
Primase is an enzyme that synthesizes a short RNA primer at the start of DNA replication.
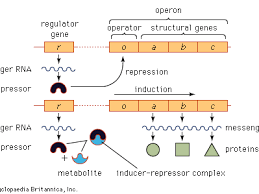
What is an operon? (“OPERON = OPERATOR + genes turned ON or OFF”)
An operon is a cluster of functionally related genes that are controlled together by a single promoter and regulated as a unit—mostly in prokaryotes.
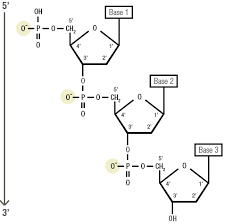
Is DNA negatively or positively charged and why?
DNA is negatively charged due to its phosphate backbone.
🔋 Each phosphate group (PO₄³⁻) in the sugar-phosphate backbone carries a negative charge, giving the entire molecule a net negative charge.
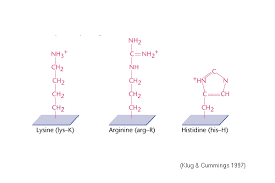
Which amino acids are positively charged at physiological pH?
“HAL is basically positive”
Histidine
Arginine
Lysine
🔹 These amino acids have basic side chains that carry a positive charge
What are base recognition sites in molecular biology?
“Restriction enzymes Recognize Regular Repeat Regions”
Base recognition sites are specific DNA sequences recognized by proteins or enzymes (e.g., restriction enzymes, transcription factors).
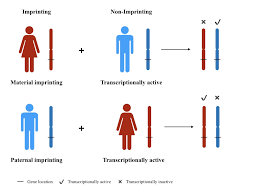
What is an imprinted gene?
“Imprinted genes: One parent’s voice, the other is silent.”
An imprinted gene is a gene whose expression depends on the parent it was inherited from due to epigenetic marks (like DNA methylation).
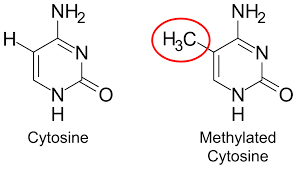
What is DNA methylation and what role does it play? (“Methylation = Mute button for genes”)
DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification where a methyl group (-CH₃) is added to the 5-carbon of cytosine bases in DNA, usually in CpG islands.
Regulates gene expression by silencing genes when methylated
What are the differences between X-linked and Y-linked genes?
“X = eXtra common in males; Y = Y chromosome, Father to Son only.”
What is epigenetics?
💡 “Epi = Above; genetics = genes — Control above the genes.”
Epigenetics refers to heritable changes in gene expression that do not involve changes to the underlying DNA sequence.
Examples of epigenetic processes (“M H N I X”)
(Methylation, Histones, Non-coding RNAs, Imprinting, X-inactivation)
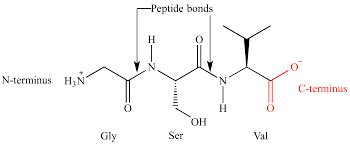
What is the C-terminus of a protein?
The C-terminus (carboxyl-terminus) is the end of a protein or polypeptide chain that has a free carboxyl group (-COOH).
How do protein chains grow during protein synthesis?
Protein chains grow by adding amino acids to the C-terminus (carboxyl end) of the polypeptide.
The ribosome catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between the amino group (N-terminus) of the incoming amino acid and the carboxyl group (C-terminus) of the growing chain.
This means the chain elongates from the N-terminus toward the C-terminus.
How do RNA viruses replicate their genetic material? ("Reverse it to replicate it!")
Some RNA viruses, especially retroviruses, use an enzyme called reverse transcriptase to convert their RNA genome into DNA.
This DNA is then integrated into the host cell’s genome
The host machinery is used to transcribe and translate viral proteins
RNA → DNA → mRNA → Protein
What is the function of a ribosome in cells?
Ribosomes are the protein factories of the cell. They translate messenger RNA (mRNA) into polypeptide chains, which fold into functional proteins.
What does high sequence identity between distinct genes suggest?
It suggests an evolutionary relationship through shared ancestry.
Why do multiple genes share similar sequences?
Gene duplication creates extra copies of genes, leading to sequence similarity across multiple loci.
What is a locus in genetics? (location)
A locus is the fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located.
Loci = multiple gene positions
What is an open reading frame (ORF)? (“Start to Stop, No Stops in Between”)
An open reading frame is a stretch of DNA or RNA that begins with a start codon (usually AUG) and ends with a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA), without any intervening stop codons.
What base replaces thymine in RNA?
“U in RNA, T in DNA”
U for Uracil in RNA
T for Thymine in DNA
What is transcription in molecular biology and how does it begin?
Transcription is the process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template and it begins with RNA polymerase II binding to the gene promoter region.
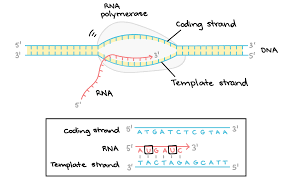
What does RNA polymerase do?
It reads the DNA strand in 3’ to 5’ direction to generate a 5’ to 3’ pre-mRNA molecule. The pre-mRNA transcript undergoes 5’ capping, the addition of a 3’ polytail, and excision of noncoding regions (introns) to be converted into mature mRNA.
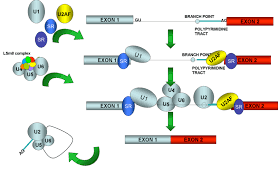
What does the spliceosome do during RNA processing?
The spliceosome removes introns from pre-mRNA by locating specific sequences within introns called 5’ splice donors and 3’ acceptor sites
Where are splice donor and acceptor sites located?
Splice donor sites are located at the 5’ end of the intron next to the exon, and splice acceptor sites are found at the 3’ end of the intron adjacent to the exon.
Where does processing of pre-mRNA happen?
Processing (which includes splicing) of the pre-mRNA transcript into mature mRNA occurs in the nucleus.
What Is Heterochromatin? (Hetero = hidden)
Tightly packed chromatin
composed of deacetylated histones (due to histone deacetylase activity) and transcriptionally repressed
What is euchromatin? (Euchromatin = expressed)
relaxed chromatin
highly acetylated (due to histone acetylase activity) and transcriptionally active
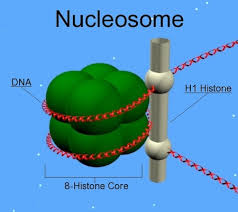
What is chromatin?
DNA wrapped around histone proteins
What are histones?
Histones are positively charged proteins that serve as the architectural backbone of chromatin, helping to package and regulate DNA inside the nucleus.
What do migration patterns in Northern blotting reveal about RNA species?
Small RNA travels farther → bands lower on membrane
Large RNA stays near top → bands higher
Intensity: RNA abundance (stronger = more RNA)
What does it mean when we say the genetic code is “degenerate”?
Degeneracy means multiple codons can encode the same amino acid
What is wobble pairing and why is it important in translation?
Mnemonic: “Wobble lets one tRNA do triple duty”
Flexibility at the third codon base = fewer tRNAs needed
How are amino acids in a protein encoded by mRNA?
"3 letters = 1 word (codon), 1 word = 1 amino acid."
Think of codons like 3-letter words, and each word tells the ribosome which amino acid to add.
What regions in mRNA are not translated into protein?
Stop codon
untranslated regions
What are telomeres and what is their function?
Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences (TTAGGG in humans) found at the ends of chromosomes.
Act as "caps" to prevent chromosome ends from fusing or degrading.
Why do telomeres shorten during cell division?
Each cell division leaves a small section of single-stranded DNA unreplicated, causing progressive telomere shortening.
Why don’t telomeres encode gene products, and what if they did?
Telomeres are made of non-coding, repetitive DNA
Each cell division would delete part of a gene, causing frameshift mutations, truncated proteins, or gene loss.
This would rapidly lead to nonfunctional or harmful proteins and premature cell death or malfunction