formed elements of blood
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what are the formed elements?
erythrocytes: red blood cells. leukocytes: white blood cells. platelets/thrombocytes: cell fragments.
what is the main function of a erythrocyte?
carry oxygen through the capillaries
what shape are the RBCs?
biconcave discs. helps b/c they move smoothly through capillaries and good in gas exchange.
nucleus or no nucleus in a RBC?
no nucleus. ANUCLEATE
do RBC have a lot or a little amount of organelles and why?
small amount because need more space for hemoglobin
what kind of protein is hemoglobin?
iron-containing protein
how many hemoglobin molecules per erythrocyte?
250 million hemoglobin
how many grams of hemoglobin per 100 mL of normal blood?
12-18 g
examples of homeostatic imbalance of RBCs
anemia, sickle cell anemia, polycythemia
what is anemia?
decrease in oxygen-carrying ability of blood.
what is sickle cell anemia (SCA)?
abnormally shaped hemoglobin
what is polycythemia?
excessive or abnormal increase in the number of erythrocytes
what does osmolality mean?
number of solutes per solution
why are leukocytes important to the body?
defense against disease
can leukocytes move? in where? how?
yes they can move in and out of the blood vessels (diapedesis) by ameboid motion.
how many leukocytes per cubic millimeter of blood?
4,000 - 11,000
what are the 3 abnormal types of leukocytes
leukocytosis, leukopenia, leukemia
leukocytosis
leukocytes count above 11,000 per mm³. indicates infection
leukopenia
low leukocyte. commonly caused by certain drugs (corticosteroids or anti cancer agents)
leukemia
bone marrow = cancerous. turns out excess leukocytes
2 types of leukocytes
granulocytes and agranulocytes
GRANULOCYTES: granules or no? nuclei shape? examples of them?
granules in cytoplasm. lobed nuclei. neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
AGRANULOCYTES: granules or no? nuclei shape? examples of them?
lack visible cytoplasmic granules. nuclei are spherical/oval/kidney shaped. lymphocytes, monocytes.
most to least abundant leukocytes
Neutrophils, Lymphocytes, Monocytes, Eosinophils, Basophils
NEUTROPHILS: type of granules? type of nucleus? what does it act as and where?
fine/small amount of granules. multilobed nucleus. acts as phagocytes (consume) at active infection sites
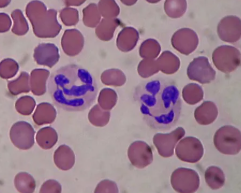
EOSINOPHILS: type of granules? type of nucleus? where?
large brick red granules. bilobed nucleus. found in response to allegories and parasitic worms.
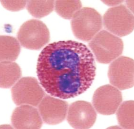
BASOPHILS: type of granules? type of nucleus? what do they do?
histamine-containing granules. S shaped nucleus. initiate inflammation.
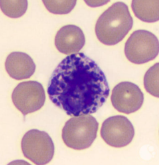
LYMPHOCYTES: size of nucleus? important role in what?
nucleus fills most of the cell. important role in the immune system.
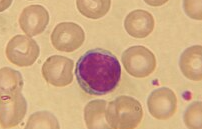
MONOCYTES: size? function as? important role in?
largest of WBC. function as macrophages. important in fighting chronic infection.
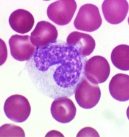
what are platelets from?
derived from ruptures multinucleate cells/MEGAKARYOCYTES
what are platelets needed for?
need for the clotting process
what is the normal platelet count?
300,000/mm³