5.2 pathogens
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
primary pathogens
make healthy people ill
opportunistic pathogens e.g., Pseudomonas aeruginosa in burns, Staphylococcus epidermidis on vascular catheters).
exploit breaks in barriers or lowered immunity
Some bacteria switch roles depending on location
for instance, E. coli is beneficial in the colon but pathogenic in the urinary tract.
virulence factors
factors than envoke disease
virulence factor examples
surface receptors that bind to host cells]
surface coats that inhibit immune responses like phagocytosis and toxins
virulence factors allow bacteria
to colonise invade and replicate withing an immune competent host
bacterial toxins manipulate the funcitons of host cell functions
resulting in the hijacking of vital processes in order to favour microbial infection
this interference with host cellular processes often involves
toxins secreted across their outer membrane through different secretion systems or by direct injection into the host cell
bactieral toxins have 2 classifications
exotoxins
endotoxins
exotoxins
able to damage the host through either causing cellular damage/ destruction or by disrupting cellular metabolism
exotoxins are highly potent
and can cause major damage to the host
Major GI relevant exotoxin diseases
botulism,
diphtheria,
Dysentery
and Cholera.
endotoxins are a type of LPS.
Soluble endotoxin are released when the bacteria are destroyed, and also released physiologically as outer membrane vesicles.
exotoxin explained
exotoxins are proteins
produced inside pathogenic gram positive bacteria, part of their grown and metabolism
rereleases into the surrounding medium following lysis
endotoxin explained
endotoxins are lipid proportions of lipopolysaccharides LPSs
part of the outer membrane of the cell wall of gram negative bacteria
liberated when bacteria die and the cell wall breaks apart
gram stian process
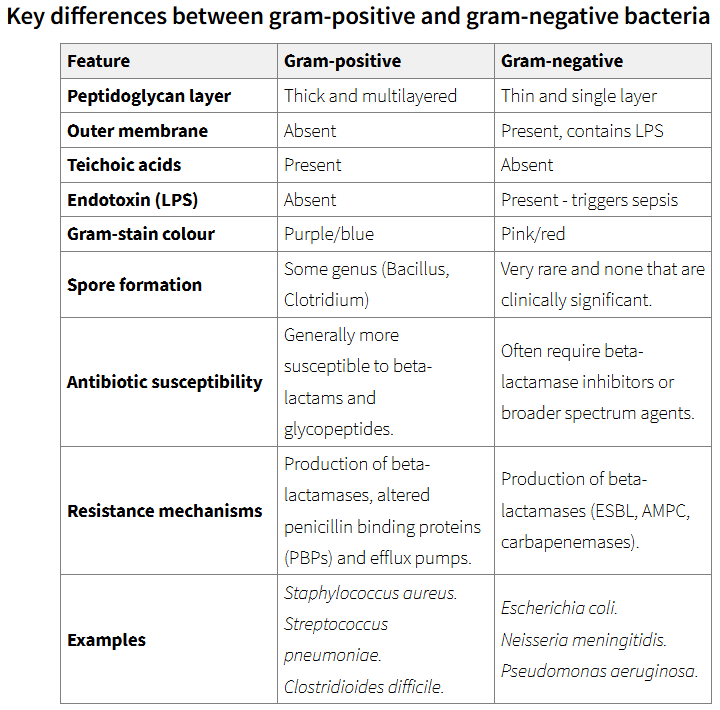
a differential staining technique used to categorise bacteria into gram positive/ gram negative groups based on cell wall structure
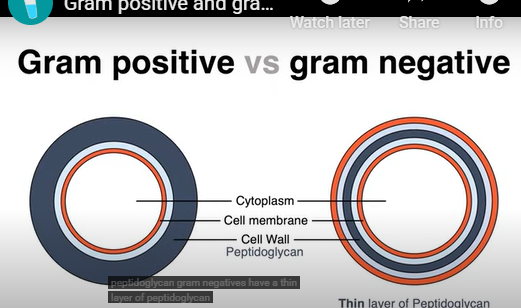
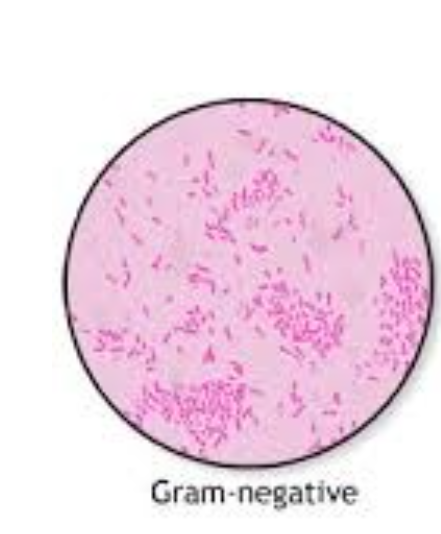
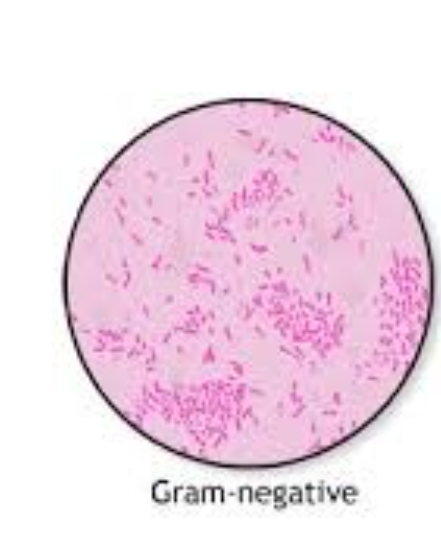
gram negative bacteria
thin wall of peptinoglycan + outer membrane
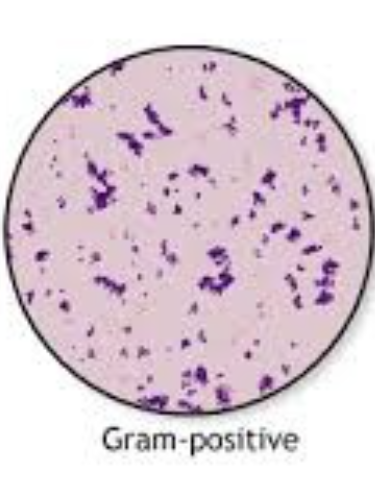
gram positive
thick wall of peptinoglycan
gram staining chemicals required
crystall violet- pass through the cell wall
iodine- interacts with crystal violet ions that trap it-
alcohol- washes out crystal violet-iodine complexes (in gram negatives)
counterstain- taken up by both, recolours gram negative
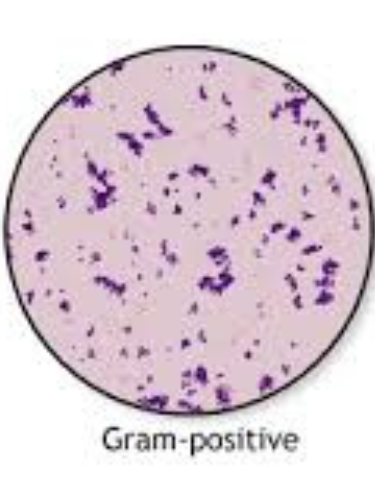
gram positive appear purple
gram negatives appear red/pink
more difficult to treat gram negative bacteira
due to extra outter membrane
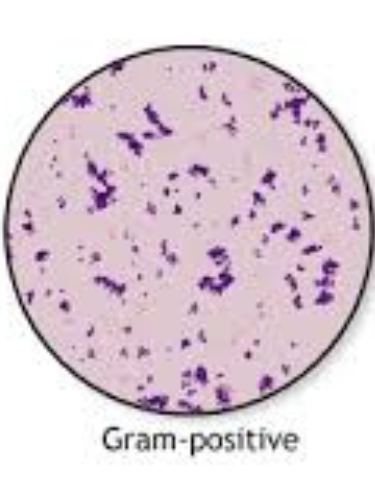
Gram‑positive bacteria (purple)
Thick peptidoglycan retains crystal violet‑iodine complex during alcohol wash.
Usually more susceptible to β‑lactam antibiotics because the wall is exposed.
Examples include Staphylococcus aureus (skin/soft‑tissue infections), Streptococcus pyogenes (pharyngitis), Enterococcus faecalis (UTI).
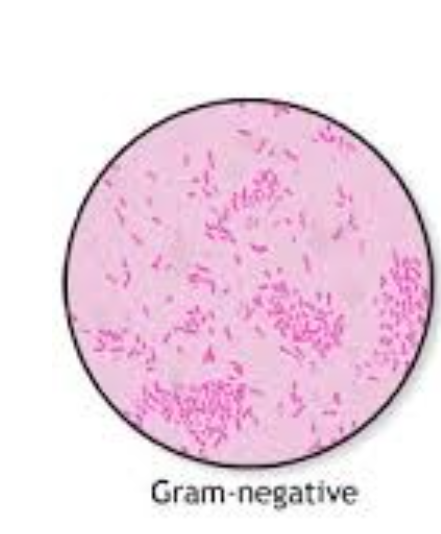
Gram‑negative bacteria (pink/red)
Thin peptidoglycan plus outer membrane. Alcohol easily leaches out the primary stain; cells take up safranin counterstain.
Outer membrane (LPS) restricts large antibiotics, so many Gram‑negatives resist penicillins without β‑lactamase inhibitors.
Representative species: Escherichia coli, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa.