Anatomy chapter 7 Axial Skeleton
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What is composed of in the axial skeleton
composed of bones that run along the central axis of the body
skull
vertebral column
thoracic cage
What are the cranial bones
they are rounded bones that make up the cranium
ethmoid
frontal
occipital
sphenoid
parietal (2)
Temporal (2)
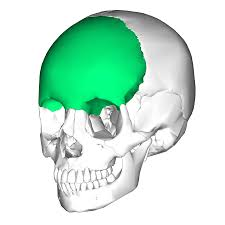
Forms forehead and part of the roof of the cranium
Frontal Bone
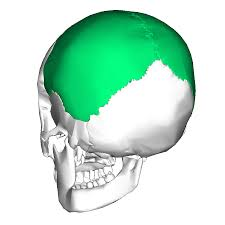
form most of cranial roof and part of its lateral walls
parietal bone
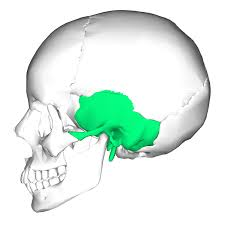
Form lateral walls and part of floor of cranial cavity
temporal bone
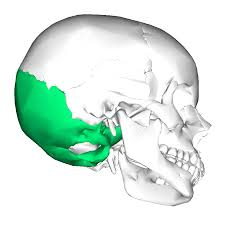
forms rear and base of the skull
Occipital bone
what does anterior mean
front of
What does posterior mean
back of
what does medial mean
towards the midline
what does lateral mean
away from the midline
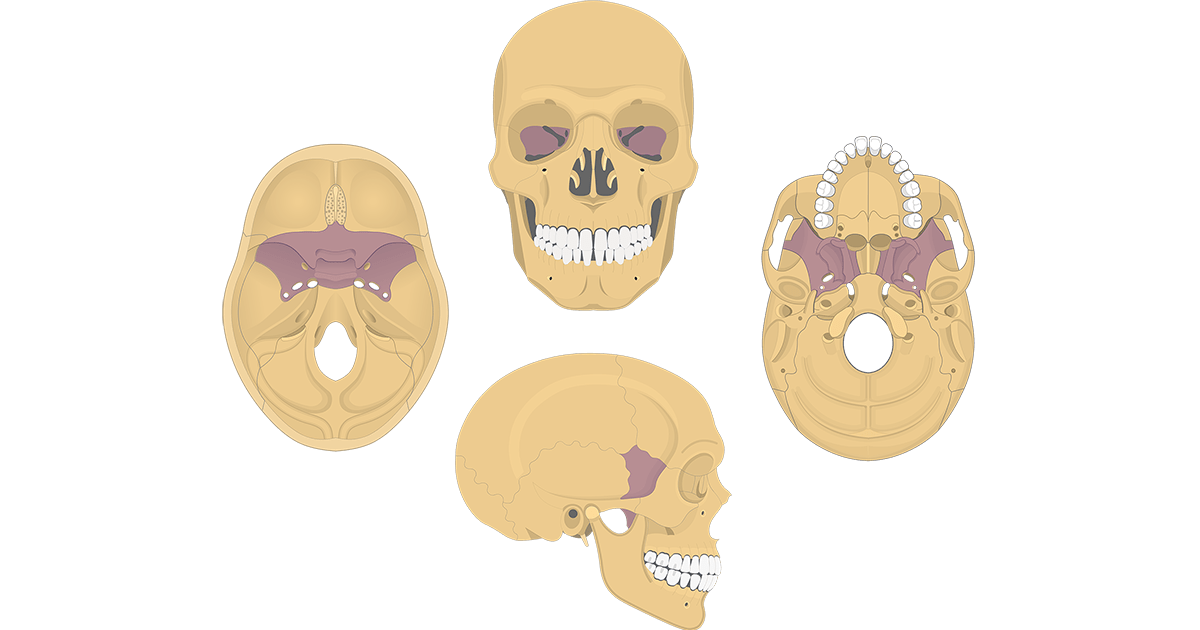
keystone bone of the skull
Sphenoid bone
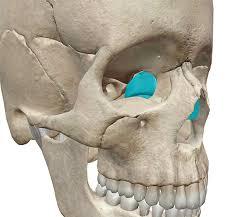
located between eyes, contributes to medal wall of orbit, walls and roof of nasal cavity and nasal septum
Ethmoid bone
encloses, protects and supports the brain
cranial cavity
eyes
orbital cavity
oral cavity
mouth
Nasal Cavity
nose
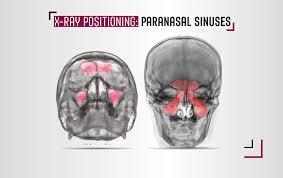
paranasal sinuses
What do the facial bones do
provide shape to each individual’s face
form part of the orbit and nasal cavity
support the teeth
attachment of muscles involved in facial expression and chewing
What bones are apart of the facial bones
lacrimal (2)
Nasal (2)
Inferior nasal conchae (2)
Palatine (2)
Vomer
Mandible
Zygomatic (2)
Maxilla (2)
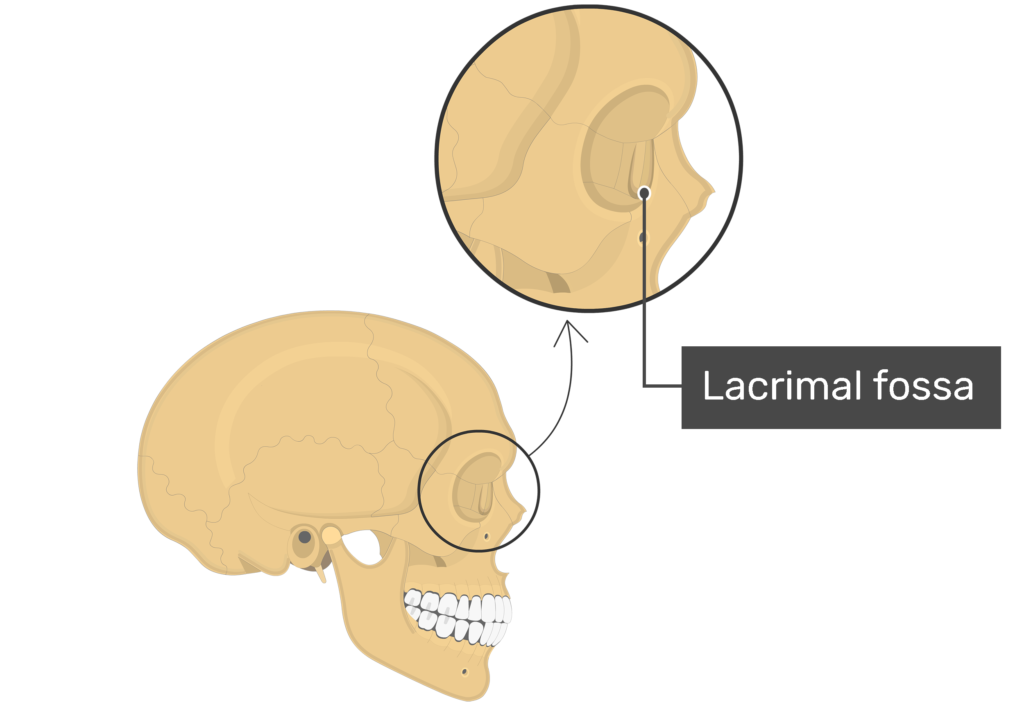
What type of bone is this
lacrimal bone
What does the lacrimal bone do
form part of medial wall of the orbits
Lacrima means “tear”
When an excess of tears are formed they drain into the lacrimal groove, to the nasal cavity
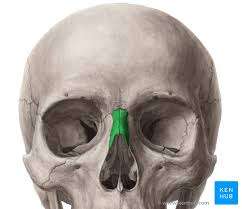
What type of bone is this
Nasal bone
What does the nasal bone do
it is the most anterior portion of the facial area
forms the bridge of the nose, tip is cartilage
most often fractured when hit in the nose
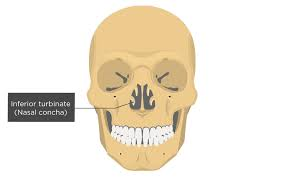
What is this bone
inferior nasal conchae
What does the inferior nasal conchae do
located inside the nasal cavity
creates turbulence in inhaled air, helps warm the air
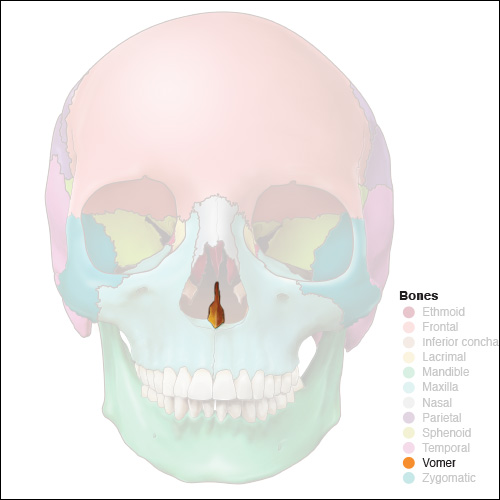
what type of bone is this
vomer
What does the vomer do
it articulates with the maxilla and the ethmoid bone
forms the nasal septum with the ethmoid bone
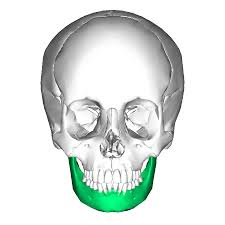
what is this bone
mandible
What does the mandible do
forms the entire lower jaw
supports teeth and muscles for mastication (chewing)
What forms a joint called the temporomandibular joint
which allows us to move our jaw when we talk and chew
temporal bone and the mandible
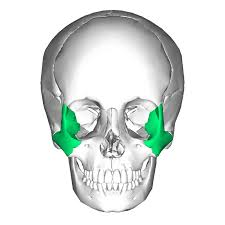
What type of bone is this
zygomatic bone (2)
What does the zygomatic bone do
cheekbones
found between the maxilla and temporal bones
helps give structure to face
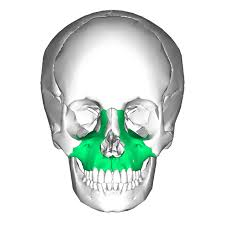
What bone is this
maxilla
what does the maxilla do
keystone of the facial bones
form upper jaw, inferior orbit area, and support teeth
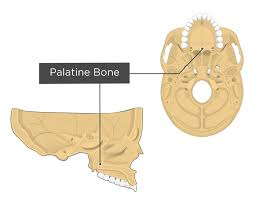
what type of bone is this
palatine bone
what does the palatine bone do
small with a distinct L shape
part of hard plate, nasal cavity, and orbit
works with maxilla to separate oral from nasal cavity
What is the most inferior (towards the bottom) of the facial bones *
Mandible *
the two bones that form the nasal septum *
vomer and the ethmoid bone *
the most posterior (in back of) bone of the cranial area *
Occipital bone *
The keystone bone of the cranial are *
Sphenoid bone *

what bone is this
mastoid process
what does the mastoid process do
bulge on inferior surface of the temporal bone (larger in males, smaller in females)
anchoring site for muscles that move the neck
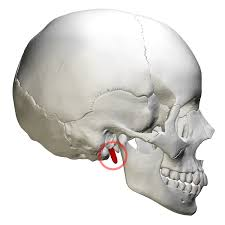
what bone is this
styloid process
what does the styloid process do
thin, pointed bone, located on the temporal bone
site for attachment of many hyoid and tongue muscles
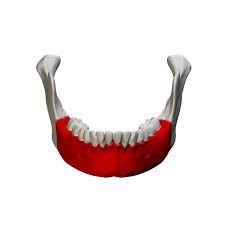
what type of bone is this
the body of mandible
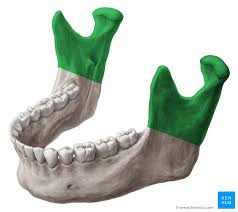
what type of bone is this
ramus
what does the sutures of the skull do
immovable fibrous joints that can form the boundaries between the cranial bones
allow the cranium to grow and expand during childhood
dense regular connective tissue seals cranial bones firmly together as a suture

what type of suture is this
saggital suture
line that separates left and right parietal bones
saggital suture
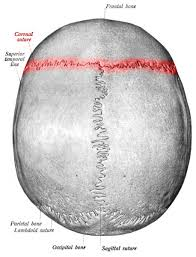
what type of suture is this
coronal suture
line that separates frontal and parietal bones
coronal suture

what type of suture is this
lambdoidal suture
line that separates parietal and occipital bones
lambdoidal suture
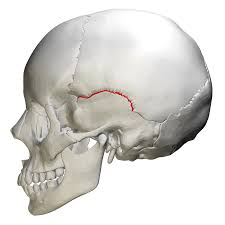
what type of suture is this
squamous suture
line that separates parietal and temporal bones
squamous suture
what is the vertebral column composed of
composed of 26 bones (24 vertebrae, fused bones of sacrum and coccyx)
what are the functions of the vertebral column
•Vertical support for the body
•Support weight of the head
•Help maintain upright body position
•Transfer axial skeletal weight to the appendicular skeleton of the lower limbs
•House and protect the delicate spinal cord
•Provide a passageway for spinal nerves connecting to the spinal cord
what are the curvature types
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
sacral

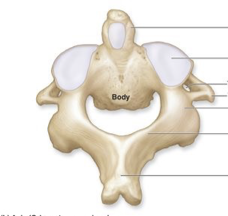
what is the top pointing to
spinous process
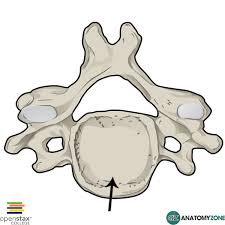
what type is this
body
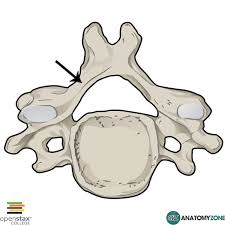
what type is this
vertebral foramen
what is this
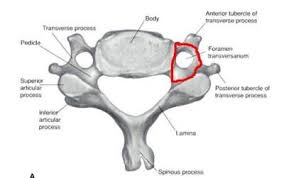
transverse process
what is this
lamina
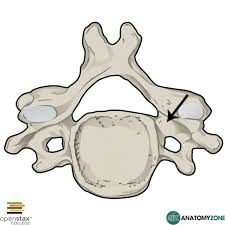
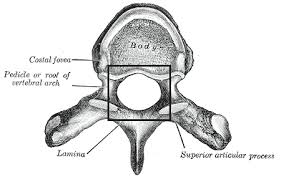
what is the arrow pointing at
pedicle
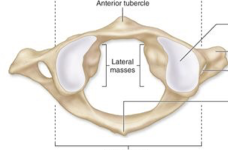
cervical vertebrae (C1)
atlas
Cervical vertebrae (C2)
axis
originate on the thoracic vertebrae, insert on sternum
ribs
attached directly through cartilage to sternum
true ribs
attached indirectly through cartilage to sternum
false ribs
what is the thoracic ribs characterized by
rib facets
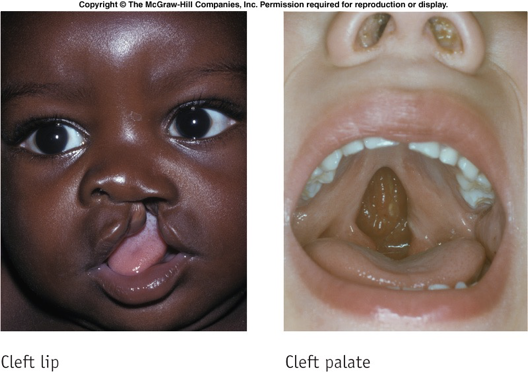
cleft lip on the left and cleft palate on the right
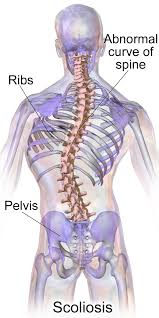
what type of spinal curvature abnormality is this
scoliosis
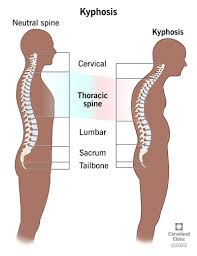
what type of spinal curvature abnormality is this
kyphosis
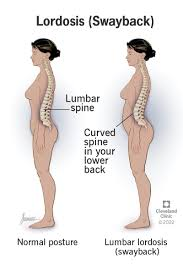
what type of spinal curvature abnormality is this
lordosis
what happens in herniated discs
Disc is slipping into vertebra foramen
- If happens, where soinal cord is located, spinal cord is being pressures, and spine pain can get worse