MRI Exam 3 Quiz
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What causes the loud thumping noise during an MRI scan?
Lorentz Force
What is the process of gradually decreasing the current in a superconducting magnet to return it to a non-superconducting state called?
Ramping down
Which of the following components of an MRI magnet functions to deliberately spoil magnetic field homogeneity?
Gradient coil
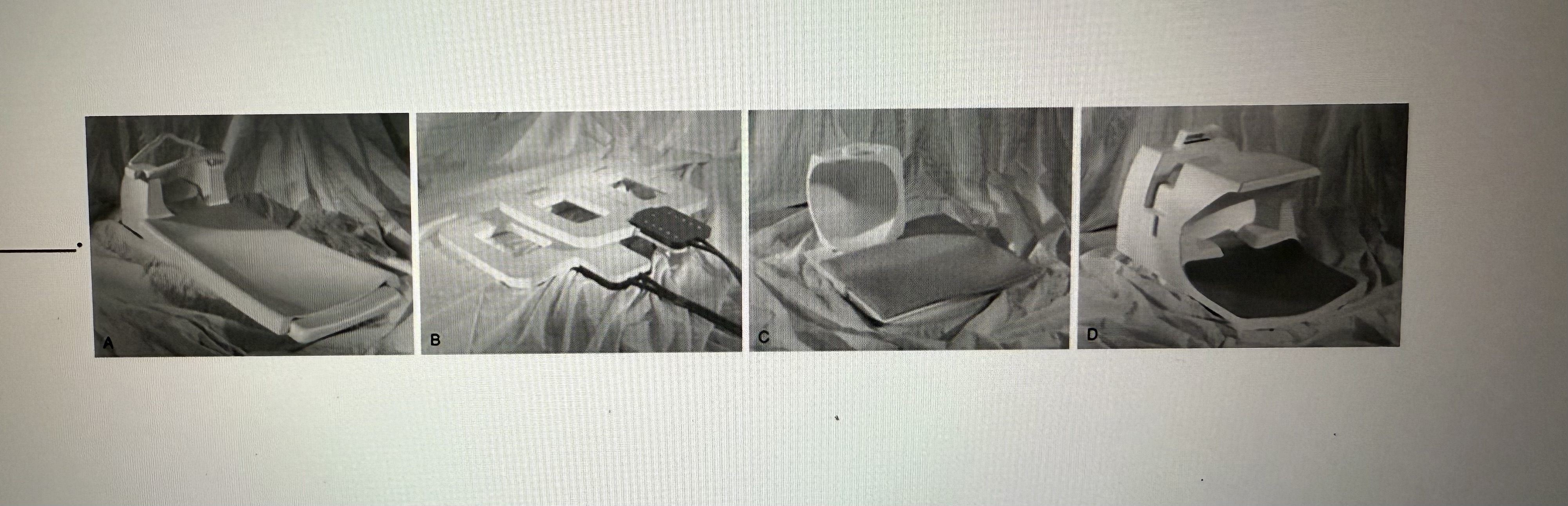
The objects pictured here are _______
RF coils
Which of the following components of an MRI magnet functions to receive the MRI signal?
RF receive coil
What is the only moving part of an MRI machine?
The table
In which zone is the MRI Operating Console Room typically located?
Zone 3
What is the maximum magnetic field strength typically achieved by permanent magnets in whole-body MRI systems?
0.3T
What is the container that houses the superconducting wires and cryogens called?
Cryostat
What is the purpose of shimming a magnet?
Creating a more homogenous magnetic field
What is the most common type of magnet used in MRI systems?
Superconducting electromagnet
Which type of MRI system produces a vertical B0 field and looks like a large C-arm?
Resistive electromagnet
What is the cryogen used primarily to cool MRI magnet coils?
Liquid helium
What material is commonly used in superconducting electromagnets for MRI?
Niobium-titanium alloy
Which of the following components of an MRI magnet functions to help keep the main magnetic field more homogeneous?
Shim coil
Which type of RF receive coil can detect signals from multiple directions?
Quadrature coil
In a permanent magnet MRI system, which axis is vertical?
Z-axis
Which type of MRI system is most often used in clinical settings today?
Superconducting electromagnet
What is the typical weight limit for a patient on an MRI couch?
350 lbs
What is the critical temperature for superconductivity in niobium-titanium alloys used in MRI magnets?
9 Kelvin
What is the term for the loss of superconductivity in the B0 coil that may occur unexpectedly?
Quench
What does the term slew rate refer to?
The maximum rise of a gradient coil
What is a bore diameter of a typical clinical MRI magnet?
60 cm
What units do we use to specify magnetic field homogeneity?
Parts per million (ppm)
What is the primary advantage of a permanent magnet MRI system?
Low fringe magnetic field
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of permanent magnet MRI systems?
High magnetic field homogeneity
An MRI head coil is typically what type of coil?
Birdcage coil
Which of the following is NOT one of the four electrical states of matter mentioned in the document?
Plasma
What are the three major components of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system?
Magnet (Gantry), Operating console, System electronics
Which of the following components of an MRI magnet functions to create a large magnetic field?
B0
Which component is often referred to as the “traffic cop” of the MRI scanner?
Sequencing system (Pulse programmer)
Which of the following components of an MRI magnet functions to change the direction of the net magnetization vector?
RF transmit coil
Which of the following is NOT a subassembly of a superconducting MRI system?
Resistive coils
How many sets of gradient coils are inside an MRI machine?
3
What is the purpose of shim coils in an MRI system?
To make the B0 field homogenous
What is the purpose of the frequency synthesizer in an MRI system?
To generate the fundamental resonance frequency
What is a major disadvantage of a resistive electromagnet MRI system?
High electric power consumption
What is the geometric center of an MR magnet called?
Isocenter