GEO 1303 Lecture Exam 2
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Weathering
Erosion
Physical weathering
Reduces solid rock to small fragments without altering the chemical composition of rocks and minerals (Ex- gravel, sand, salt, clay sized particles)
Chemical weathering
substances derived from solution by inorganic or biochemical processes (Ex- clay minerals and ions, compounds and solution)
Regolith formation on Moon
Regolith formation on Mars
Regolith formation on Earth
Soil degradation
Earthquakes Causes
Movement along faults
Volcanic eruptions
Landsides
Explosions
Seismic waves
They cause the most of the damage and shaking people feel
during an earthquake
Body waves travel through Earth. P wave fastest a first wave, S-wave shears material and second wave
Surface waves trave; along or just below the surface
Measuring earthquakes
Intensity ( qualitative)- measures the kind of damage
Magnitude (quantitative)- measures the amount of engergy that is released
Destruction from earthquakes
Ground shaking
Liquefaction (water-saturated clays becomes fluid during ground shaking)- ground is no longer stable and buildings fall
Fire-natural gas and water lines break
Tsunami- seafloor earthquakes generate deadly waves
Ground failure-landslides and rockslides
Human death
Earth’s interior
Volcanism in the solar system
Jupiter moon Io is the most volcanically active body in the solar system
Mars Volcano Olympus Mons is the tallest in the solar system
Venus has volcanoes and flood basalt
Mercury has widespread flood basalts
the dark parts of the moon are flood basalts
Features of Volcanoes
Parts of Volcanoes
Vent- where magma and other volcanic products erupt onto the surface
Crater- hole at the hop of the volcano
Caldera- circular depression formed from the collapse of rock above an empty magma chamber (example-Crater Lake)
Fissures- linear cracks along the side of the volcano that magma can also erupt from
Volcanic gases
Mostly water vapor
Also contains CO2, SO2, HS, N2
Very small amounts of C), Hydrogen, and chlorine
Flood basalts
involve HUGE volumes of magma and represent the largest basalt eruptions on Earth. (example-Columbia Plateau)
Volcanic hazards
Basaltic
Lava Flow
Volcanic ash
Lava/fire fountain
Lahar
Pyroclastic flow
Locations of volcanoes
Most are found at plate boundaries (60% are at the ring of fire)
Divergent plates are mostly mafic sheild volcanoes with pillow basalts
Convergent plates and subduction caused the ring of fire. They form intermediate or felsic volcanoes
Intraplate (hot spots) form mafic shields (Hawaii)
Depositional environments
A geographic setting where sediment
is accumulating. Determines the nature of the sediment that accumulates
Depositional environments resulting rock types
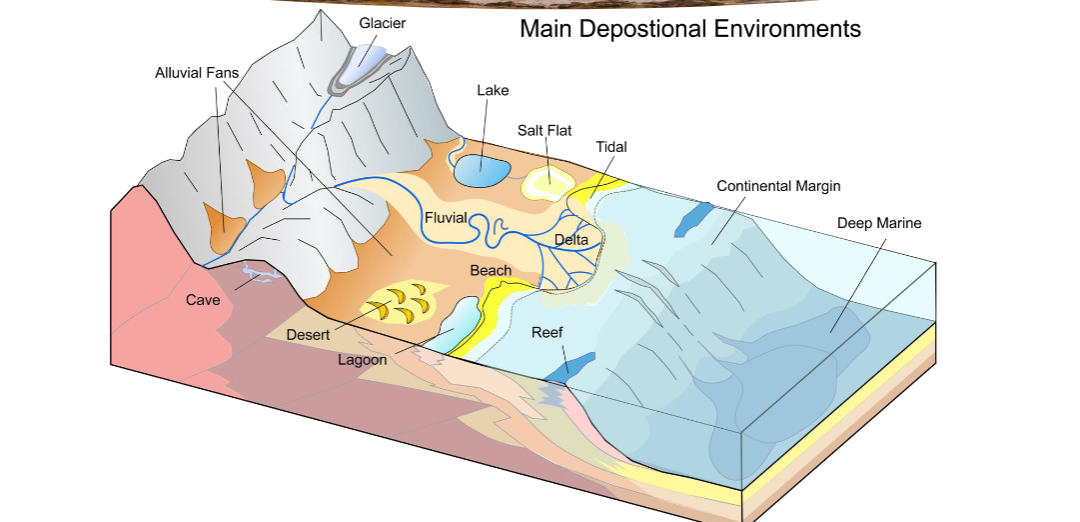
Detrital sediments Formation
Conglomerate-forms in water
Breccia- forms with little water
Detrital sediments classification
Conglomerate- well rounded pebble sized clast. Mix of sand slit or clay
Breccia- angular pebble sized clasts with sand silt or clay
Sandstone-sand sized grains, layers
Shale- very fine grained clay particles that breaks in chips
Detrital sediments types
Gravel, Boulder, Cobble, Pebble, sand, mud, slilt, and clay
Chemical sedimentary rocks classification
Evaporites- rock salt and rock gypsum, Chemcial sediments formed by precipitation of a mineral during the evaporation of water. Forms in dired up lakebed
Carbonate- limstone and dolostone, primarily containing the carbonate ion such, forms when magnesiu replaces some calcium in limstone. Forms in calm saltwater
Coal- composed of altered land plant remains
Chert- flint and jasper, forms in deep marine, microcrystalline quartz
Sedimentary facies
Sediment or sedimentary rocks that are recognizably
different from adjacent sediment or sedimentary rocks
and are deposited in a different depositional
environment. Sea levels either increase or decrease to create these
Bedding types
Cross bedding- perserves layers deposited at an angle. Sand dunes and shallow marines.
Graded bedding- largest heavist particles settel first and then smaller particles on top
Parallel bedding-This type of bedding typically forms in environments with relatively low energy, allowing sediments to settle uniformly and create distinct layers that run parallel to each other.
Sedimentary structures
Currnet ripple marks- asymmetric ripple marks
Wave formed ripple marks- symmetrical shappe ripple marks
Mud cracks-when mud dries out and leaves cracks
Fossils- remains and traces of ancient life
Petroleum Gas
Made from microoganism,Oil gets trapped in sandstone
Sedimentary rock resources
Sand and gravel
Clay
Coal
Limestone
Phosphates
Gold, uranium, and other
metals
Salt
Gypsum (used in drywall)
Banded iron formations
Petroleum (oil and
natural gas)
Metamorphism
transformation (change) of rocks without melting, usually beneath Earth's surface. Caused by heat, pressure, or fluids
Contact-high temp low pressure
Dynamic- when rocks are crushed. high pressure low temp
Regional-msot common, found at convergent plates. High temp and pressure.
Meteorite impact- ultrahigh temp, ultrahigh pressure
Metamorphic grade
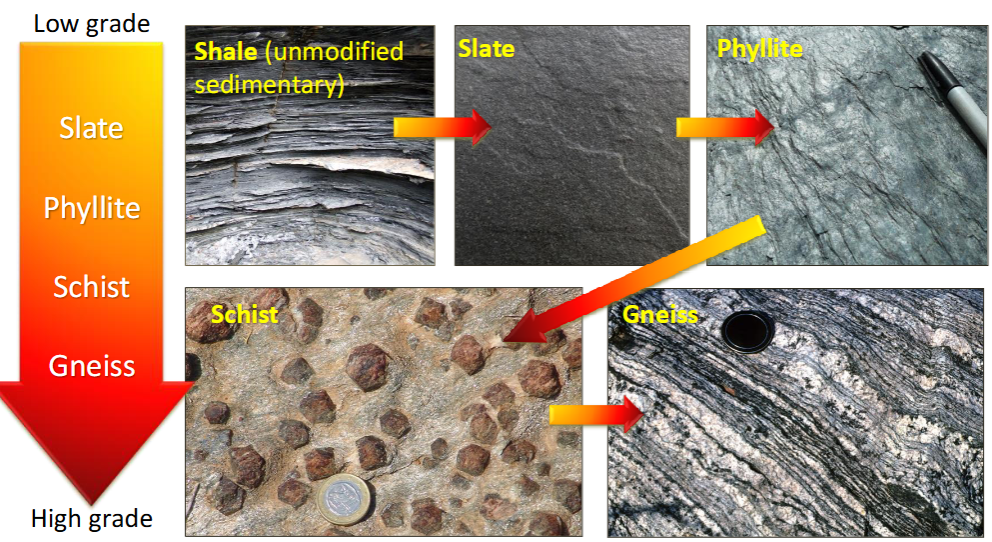
Index minerals
the degree of metamorphic change a rock
has undergone, usually listed as low(small change), intermediate (medium change), or high (large amount of change)
Classification of metamorphic rocks
Foliated textures are produced
by the preferred orientation of
platy minerals, such as
muscovite, because of pressure
Nonfoliated textures do not
have preferred orientation of
minerals (minerals are
randomly oriented)
Metamorphic facies
a group of rocks containing a distinctive mineral assemblage formed under similar conditions of temperature and pressure
Metamorphic mineral and rock resources
Slate Marble Gneiss. Graphite, Talc, Garnet, Metallic ores
Shield Volcano
Looks like Captain America’s shield sitting on the ground
Gentle slopes
Basalt
Non explosive and poses little danger to humans
Begins with a lava/fire foundation. Scoria forms a cinder/scoria cones in a few months
low viscosity (more fluid)

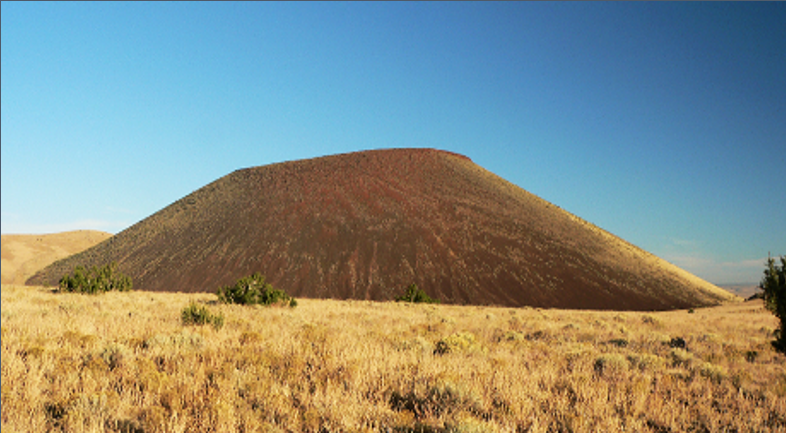
Cinder/ Scoria Conde Volcano
Steep-sloped rarely exceeding 300m high
Mafic compositions
Found with shield volcanoes
Scoria and other pyroclastic materials

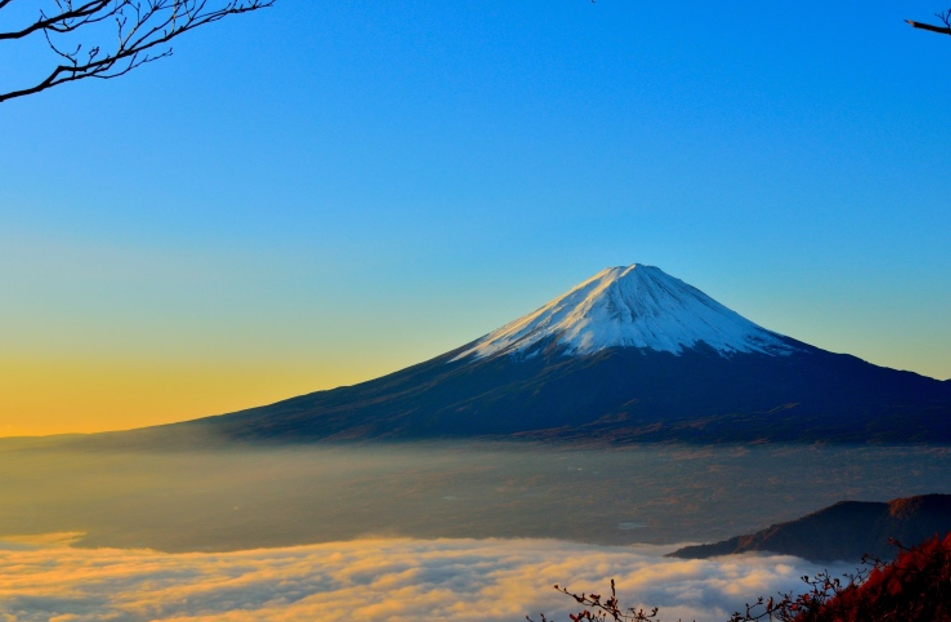
Composite Volcano
Composed of layers of lava flow, pyroclasitc debris and volcanic mud flows
Explosive and most dangerous to humans
Volcanoes rimming the pacific ocean are mostly these types
most have intermediate compositions
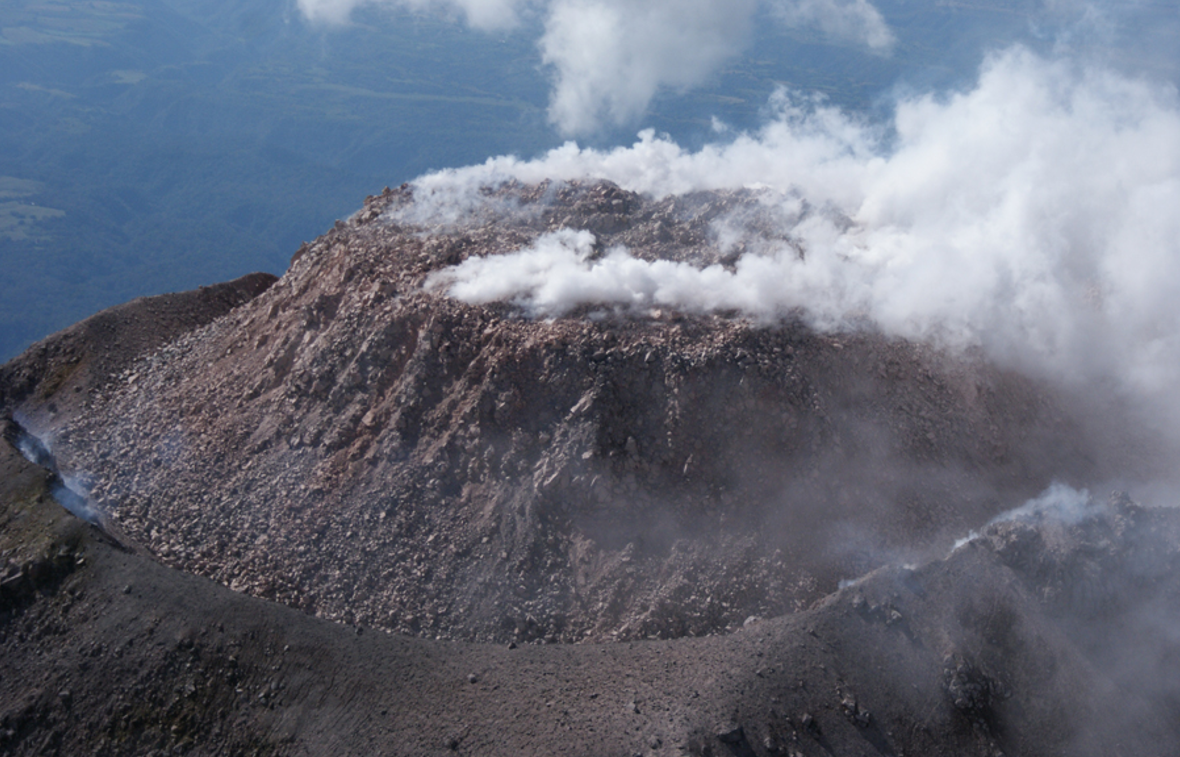
Tephra is pyroclasitc material that ejected during eruption
Eruption columm is tephra and gas that rises upwards into the atmoshphere
Pyroclastic flow forms when eruption column collapses as a dense, swirling cloud of hot gases, volcanic rock and ash
Lahar is rain and snowmelt mixing with lose ash and rock

Lava Domes
Viscous and usually felsic or intermediate lavas are forced up through the conduits of some volcanoes
these erupt explosively

Elastic Rebound theory
Rocks deform
Rocks rupture when pressure builds in rocks on either side of a fault to a level l which exceeds the rocks strength
Rocks rebound and returns to original shape when pressure is released
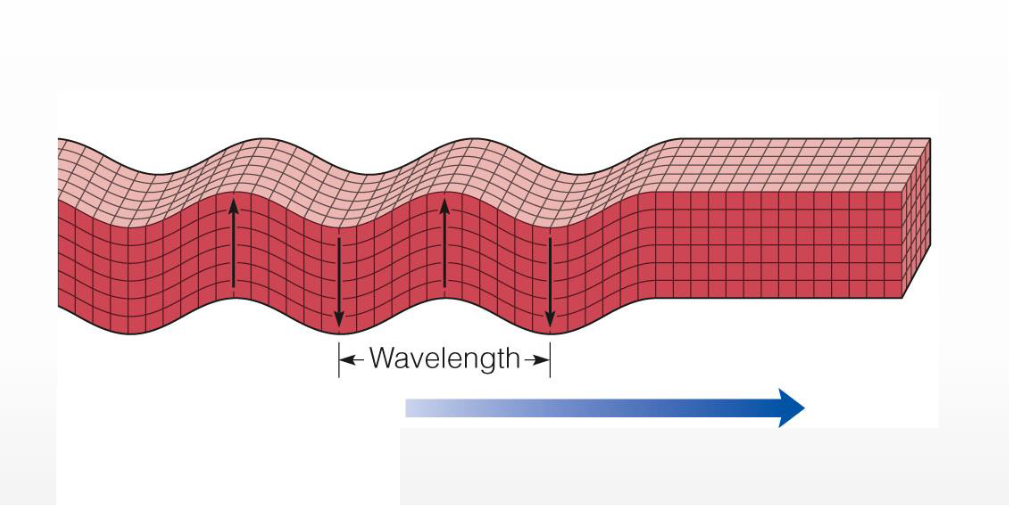
Name that Feature
S-wave, can only travel through solids
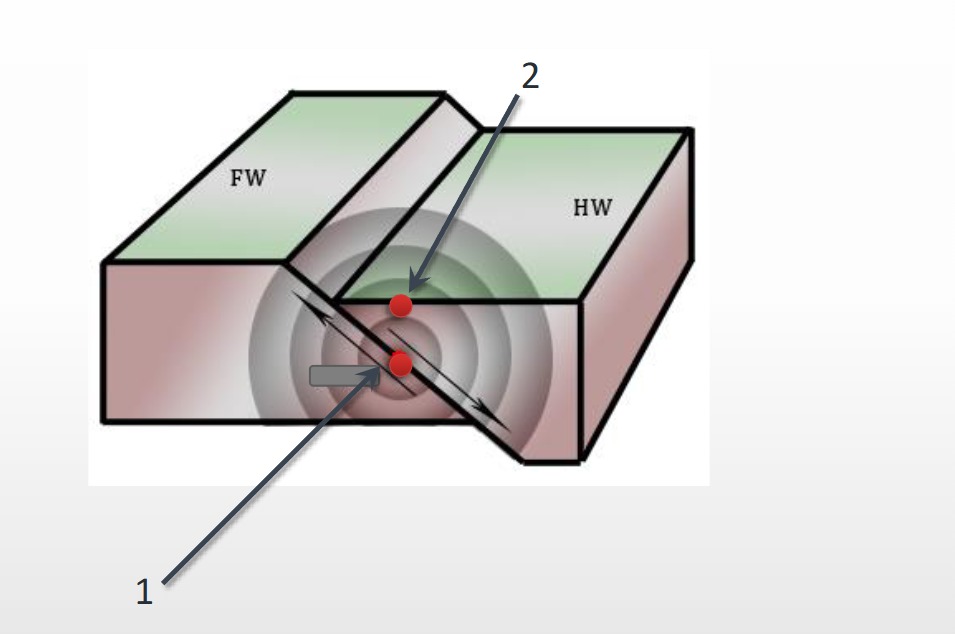
Name that feature
1- Focus/hypocenter
2- Epicenter
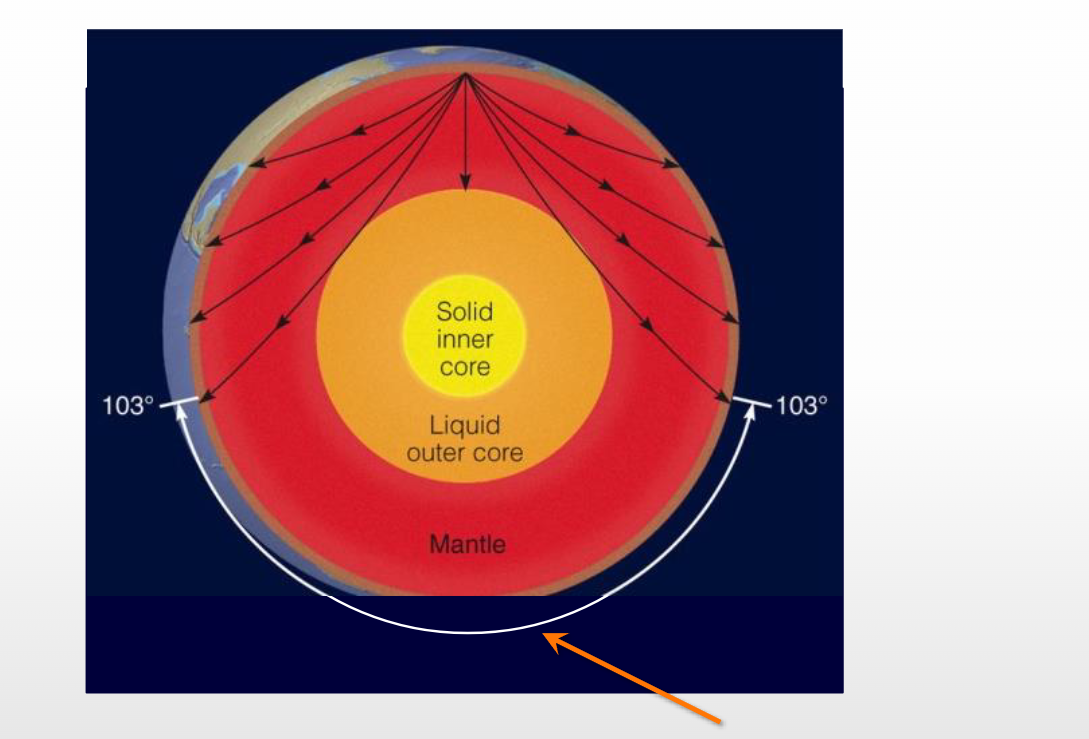
Name that Feature
S-wave shadow zone- blocks where s waves can go because it is liquid
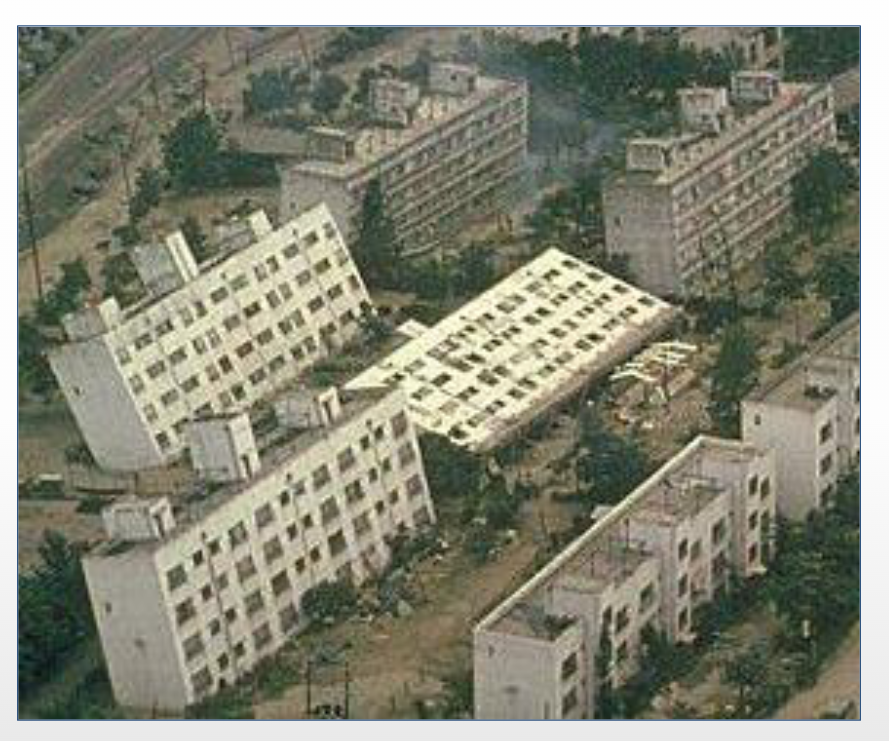

Name that feature
The ground becoming no longer stable because of liquefaction
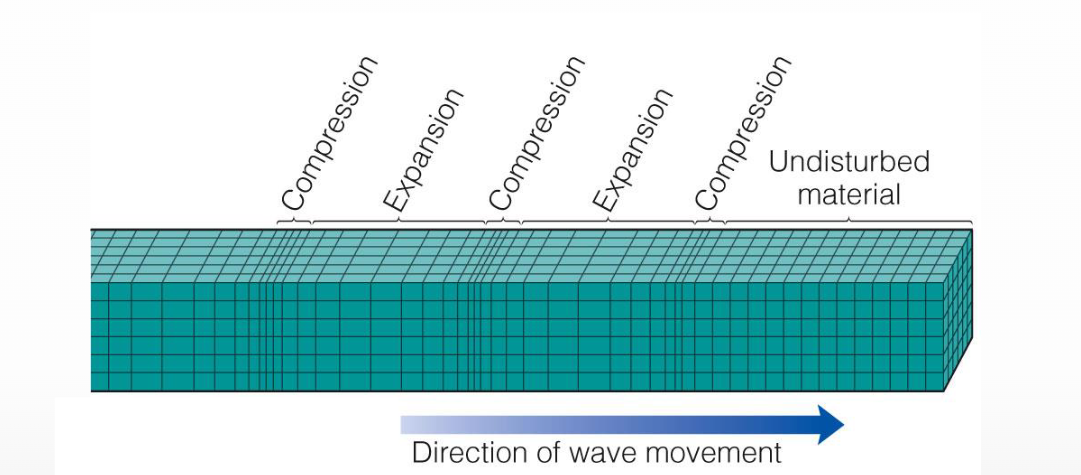
Name that feature
P-wave, travels through solids and liquids, fastest wave
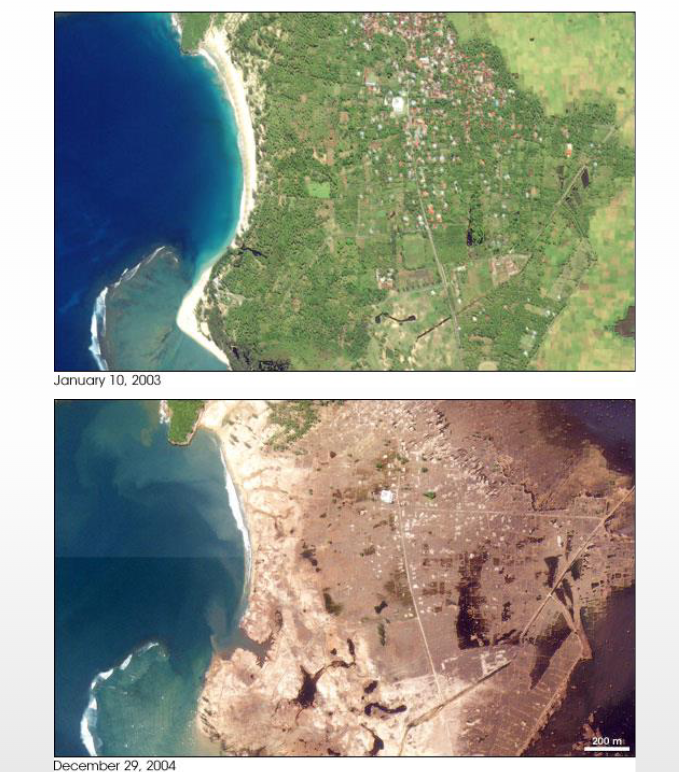

Name that feature
Effects of a tsunami
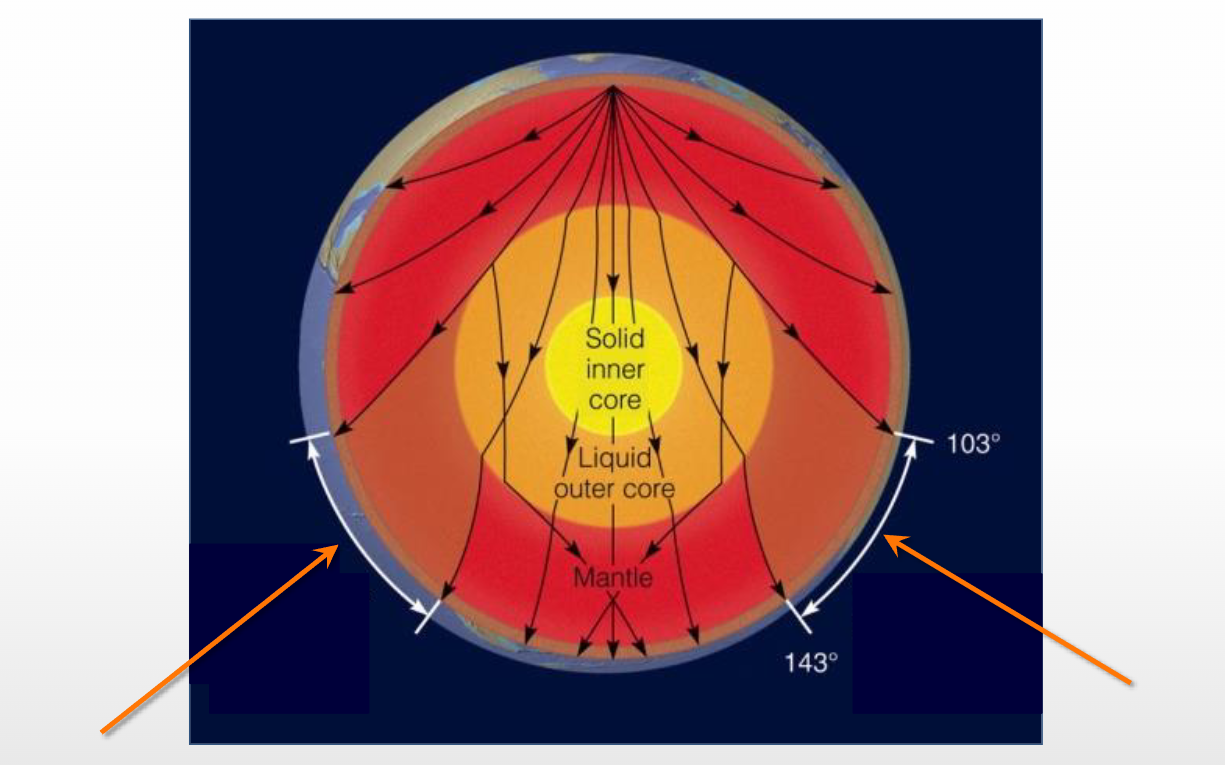
Name that feature
P-wave shadow zone- the core diffracted the p-wave some little make it to the surface in this area
What happened in Pompeii in the year 79?
Vesuvius covered the city in pyroclastic flow
Which is NOT a type of physical weathering
Hydrolysis
Which is the term for the spot on the surface directly above where the earthquake occurs?
Epicenter
Which of the following is involved in regolith formation on mars?
Meteorite impact
water
wind
Which of the below volcano types would you expect to form fro the highest viscosity magma?
Composite
Which of the following is the most common and destructive earthquake hazard?
Ground shaking
Which mineral on Bowne’s reaction series is most resistant to weathering?
Quartz
Volcanoes found at subduction zones are mostly _____; volcanoes found at hot spots are _____.
Composite, shield