Unit 7: Water Quality
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
What percentage of the global water supply is salt water?
97.5%
What percentage of global water is freshwater?
2.5% but most of it is frozen.
How much freshwater is readily available for use?
Only 0.5%
What is the hydrologic cycle(water cycle)?
the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth.
What drives the hydrologic cycle?
By solar energy, which causes evaporation, and gravity, which influences precipitation and runoff.
Name the major processes of the hydrologic cycle.
The major processes are:
Evaporation
Condensation
Precipitation
Transpiration
What is evaporation in the hydrologic cycle?
The process where water changes from a liquid to a gas (vapor) due to heat energy, primarily from the sun.
How does precipitation occur in the hydrologic cycle?
Occurs when water vapor in the atmosphere cools and condenses into droplets that combine to form clouds. When the droplets grow large enough, they fall to the Earth's surface as rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
How does transpiration contribute to the hydrologic cycle?
The process by which plants release water vapor into the atmosphere from their leaves, contributing to the atmospheric moisture.
Which countries are part of the Lake Winnipeg Watershed?
Canada and the United States.
How many Canadian provinces are included in the Lake Winnipeg Watershed?
Four Canadian provinces.
What is the size of the Lake Winnipeg Watershed?
Approximately 1 million square kilometers.
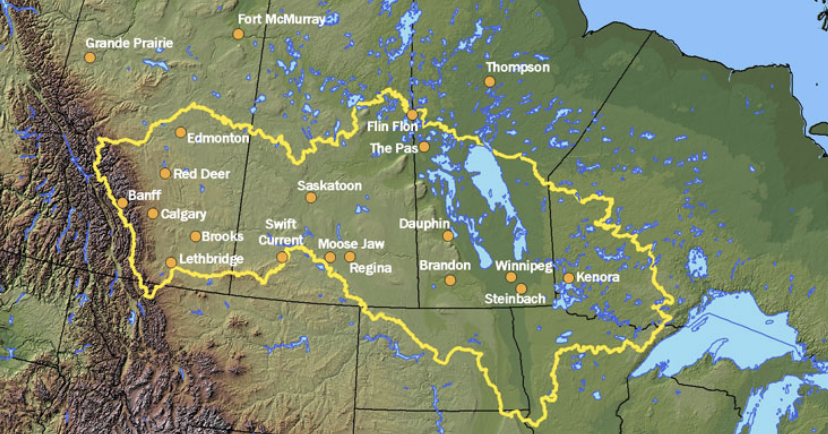
Surface Waters Lake Winnipeg Watershed
How many countries are part of the Amazon Basin Watershed?
Brazil, Peru, Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana.
What is the size of the Amazon Basin Watershed?
It covers approximately 8 million square kilometers.
What are some flood control strategies?
Dams
Diversions, bypasses, and reservoirs
Groundwater replenishment
River defenses (levees, dikes, weirs)
Water barriers
Wetland maintenance
Evacuations
How do wetlands help with flood control?
Absorb excess water, reducing flood impacts.
What are river defenses, and how do they help?
Prevent rivers from overflowing into nearby areas.
What is the role of reservoirs in flood control?
Store excess water during heavy rainfall to prevent flooding.
What percentage of freshwater is used for human residential consumption?
8%
What percentage of freshwater is used for human commercial consumption?
2%
What is the largest use of freshwater?
70%
What percentage of freshwater is used by industry?
20%
Why is there heavy demand for surface and groundwater in agriculture?
It is needed to irrigate crops, especially in arid and semi-arid regions.
How does irrigation benefit arid and semi-arid regions?
Increases crop production in these regions.
What is salinization, and how does it affect agriculture?
Occurs when minerals build up in soil, impairing plant and crop productivity.
How is climate change expected to impact agricultural water use?
Expected to intensify the demand for water in agriculture.
What is the Ogallala Aquifer?
It is one of the largest aquifers in the world.
What happened to the Ogallala Aquifer since the 1950s?
The aquifer has shrunk by 9% since irrigation was introduced.
How much can the water table drop in the Ogallala Aquifer during heavy demand?
The water table can drop 3 meters, or about 1 meter per year.
What is the goal of water management?
To ensure a sustainable supply of high-quality water for today and the future.
What are the main challenges in water management?
Population increase
Linear flow of water
Multiple stakeholders (international, interstate, provincial)
What are some strategies for managing water supply?
Build dams, aqueducts, and channels to alter natural flow
Use seawater
Recycle water through toilet-to-tap and groundwater storage
What is a notable case study related to water management?
California Dry, a CBC National documentary on the Colorado River.
What is the key idea from "California Dry"?
"Everyone is downstream," meaning water use upstream affects downstream communities.
Where does California obtain its water supply?
Columbia River
Columbia River Aqueducts
Delta Region
What are the effects of reduced water flow?
Species are at risk
Drought and climate change lead to water shortages for downstream communities
What is the central issue discussed in "California Dry"?
Is sustainable water use still possible?
What is desalination?
The process of using seawater as a source of freshwater by removing salts and minerals.
What are the challenges of desalination?
High energy demands
Environmental consequences from waste discharge into the ocean
What is habitat banking in desalination?
It is a proposed solution to offset environmental impacts caused by desalination.
What is the toilet-to-tap process?
It reclaims sewage water through primary to tertiary treatment processes and pumps it into the ground to replenish groundwater.
What is a common misperception about Canada's freshwater?
That Canada has an abundance of freshwater.
What percentage of the global freshwater supply does Canada have?
Canada has only 7% of the global freshwater supply.
Where is much of Canada’s freshwater located?
It is geographically located north of major urban developments, like Winnipeg.
How have human activities affected Canada’s freshwater?
They have increased pollution in both surface and groundwater supplies.
What is required to meet increasing water demand in Canada?
Huge infrastructure expansion and significant financial investment.
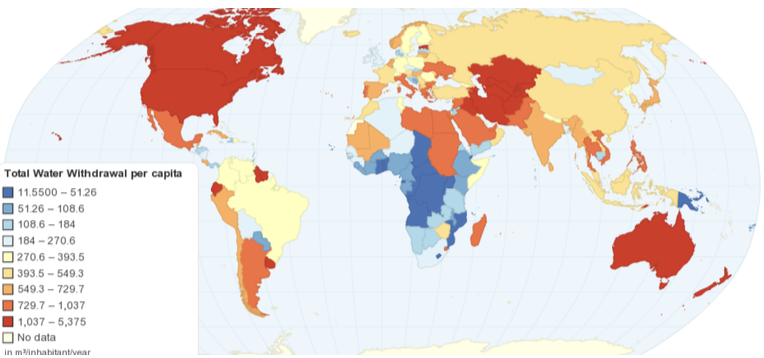
Global Water Consumption
Canada’s rate of water withdrawals increased by?
Almost 90% between 1972 and 19661
What is Global Residential Consumption distribution percentage?
Showers and baths: 35%
Toilet flushing: 30%
Laundry: 20%
Kitchen and drinking: 10%
Cleaning: 5%:
What is the goal of the demand management approach for water?
To increase the efficient use of the existing water supply instead of finding new sources.
What are the 3 R’s of water conservation?
Reduce consumption (e.g., take 2-4 minute showers)
Repair leaking pipes and faucets (accounts for ~30% water loss)
Retrofit with efficient technologies (e.g., dual-flush toilets)
How are celebrities involved in water management?
Celebrities use their profiles to promote the importance of water conservation.
How does Matt Damon support water conservation?
Co-founded Water.org for clean water access.
Launched Buy a Lady a Drink Campaign to highlight the water crisis.
Advocates globally for water sustainability.
How does Penelope Cruz support water conservation?
Advocates for sustainable water use through global campaigns.
Partners with organizations like L’Oréal Paris to promote water conservation efforts.
Raises awareness about water sustainability using her platform.
What is high heat capacity in water?
Water holds a lot of heat and resists temperature changes.
How does water moderate climate?
Water helps keep temperature stable, influencing climate
Why does ice float on ater
Ice is less dense than water
What happens when water freezes?
Water expands and become lesss dense when it freezes
Why is water called a universal solvent?
Water dissolves many substances, making it essential for life
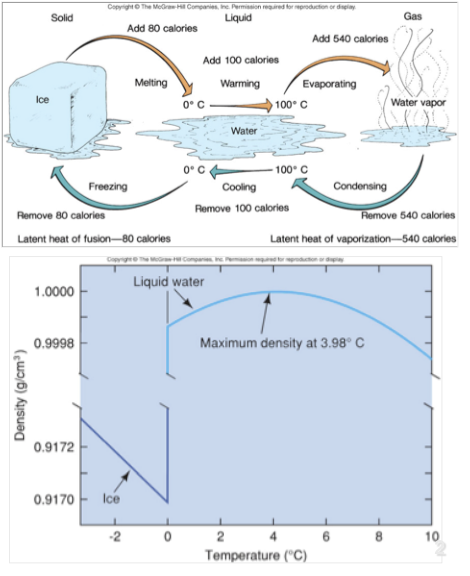
Properties of Water
What percentage of water is freshwater?
Only about 3% of water is freshwater, and it’s unevenly distributed.
Where is most freshwater found?
Most freshwater is frozen or located in the northern regions, leaving about 0.5% in groundwater, soil moisture, water vapor, lakes, and rivers.
What is the hydrologic cycle?
The hydrologic cycle is the continuous cycling and purification of water through evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and transpiration.
What is evaporation?
Evaporation is the process where water turns into vapor and rises into the atmosphere.
What is condensation?
Condensation is when water vapor cools and forms liquid droplets.
What is precipitation?
Precipitation is when water falls from the atmosphere as rain, snow, or other forms.
What is transpiration?
Transpiration is the release of water vapor from plants into the atmosphere.
How is the hydrologic cycle similar to a pot of water boiling dry?
Like a pot of water boiling dry, the water in the hydrologic cycle moves from liquid to vapor and returns as precipitation.
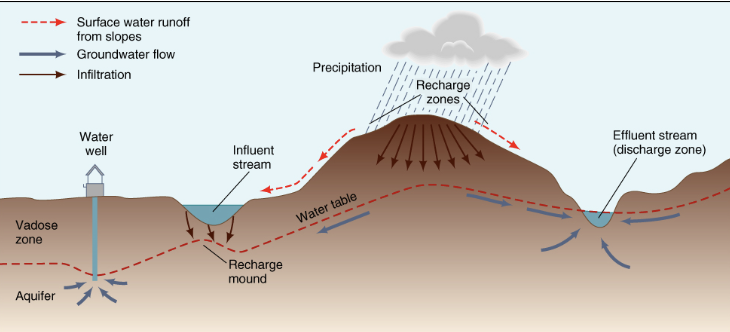
Groundwater Dynamics
What is infiltration in groundwater dynamics?
Infiltration is the process of water percolating into the ground.
What factors affect infiltration?
Infiltration depends on the ground's saturation and permeability, which is influenced by pore spaces and clay content.
What are the main features of groundwater?
Water table
Saturated zone
Unsaturated zone.
What is the water table in groundwater?
The boundary between the saturated and unsaturated zones.
What is the saturated zone in groundwater?
The area where all the pore spaces are filled with water.
What is the unsaturated zone in groundwater?
The unsaturated zone is the area above the water table where the pore spaces contain both air and water.
What is water quality?
Refers to the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of water necessary to sustain desired water uses
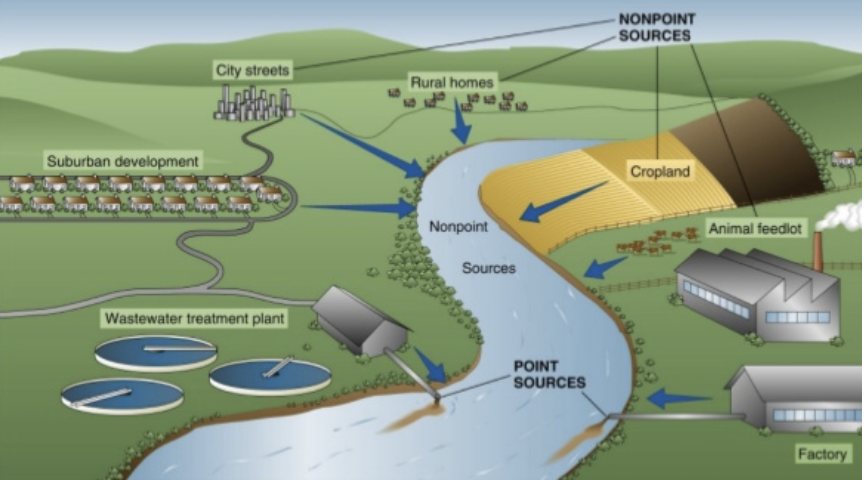
Source of Pollution
What is point source pollution?
Pollution comes from a concentrated discharge, like sewage effluent, often out of a pipe
What is non-point source pollution?
It is a diffuse, spread over a large area within a watershed, and much harder to control
What are the 5 types of pollution?
Sediment Pollution
Eutrophication(Nutrient Pollution)
Decomposition and oxygen sag
Pathogens and Water Quality
Cyanobacterial Dominance
What is sediment pollution?
Occurs when soil particles enter a water body, often due to erosion along shorelines
What happens to sediment pollution in water bodies?
Sediments eventually settle out and accumulate on the bottom of a body water
What are the problems caused by sediment pollution
Problems include turbidity(reducing light penetration and photosynthesis), siltation(destroying fish habitats), and adherence of pollutants like fertilizers and pesticides
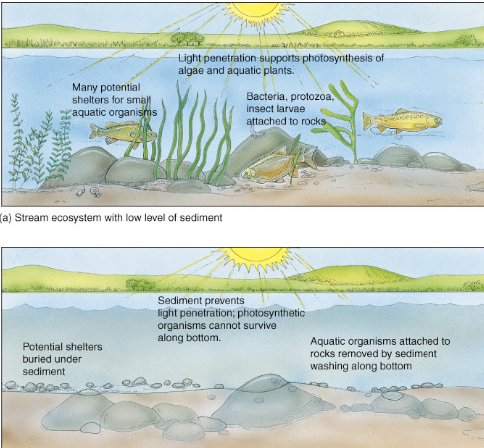
Sediment Pollution
What is eutrophication(nutrient pollution)
The release of nitrogen and phosphorus that “fertilizes” water, encouraging plant growth
What is cultural eutrophication?
Occurs when humans accelerate a natural process a natural process that normally takes thousand of years
How do nitrogen and phosphorus affect plant growth?
Nitrogen and phosphorus stimulate plant photosynthesis, removing natural limitations on plant population growth.
What is the impact of eutrophication on ecosystem?
Leads to large mats of plants that reduce the overall health of the ecosystem.
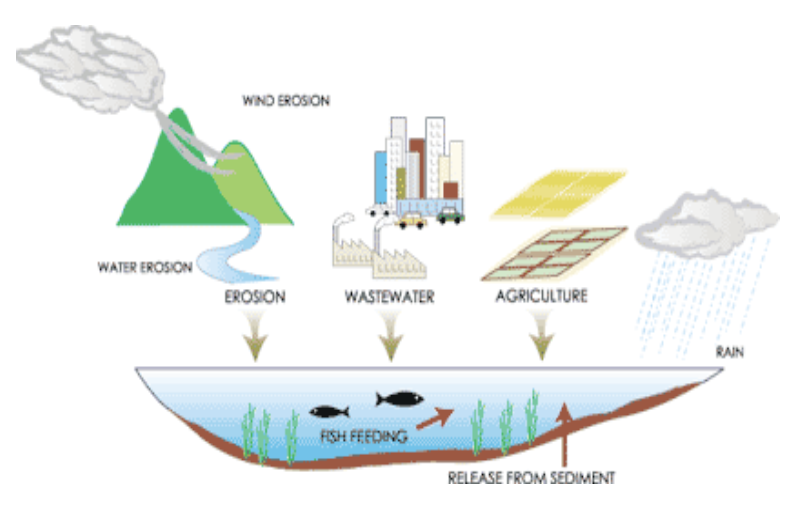
Eutrophication(Nutrient Pollution)

What is oligotrophic water?
Oligotrophic water has low nutrients, clear water, and healthy submerged plants (SAV) because light can easily reach them.

What happens when there are nutrient inputs into water?
When nutrients are added, phytoplankton grow fast, making the water cloudy and blocking light for submerged plants (SAV).
What is eutrophic water?
Eutrophic water has too many nutrients, causing lots of phytoplankton, dead algae, low oxygen, and suffocating fish and shellfish.
What happens during decomposition in water?
Organic matter uses up dissolved oxygen (DO) in the water.
What are natural sources of organic carbon (Org-C)?
Include waste from aquatic organisms, leaf litter, fallen trees, and animals that drown.
What are human sources of organic carbon (Org-C)?
Include manure, sewage from agriculture and urban areas, and industrial discharges of organic waste.
How does eutrophication affect organic matter?
It generates more organic matter due to excessive plant growth.
What is Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)?
BOD measures the amount of oxygen used by bacteria to break down organic matter in water.
How is BOD used to measure decomposition?
Used to determine the rate of decomposition by assessing how much oxygen is consumed by bacteria over time.
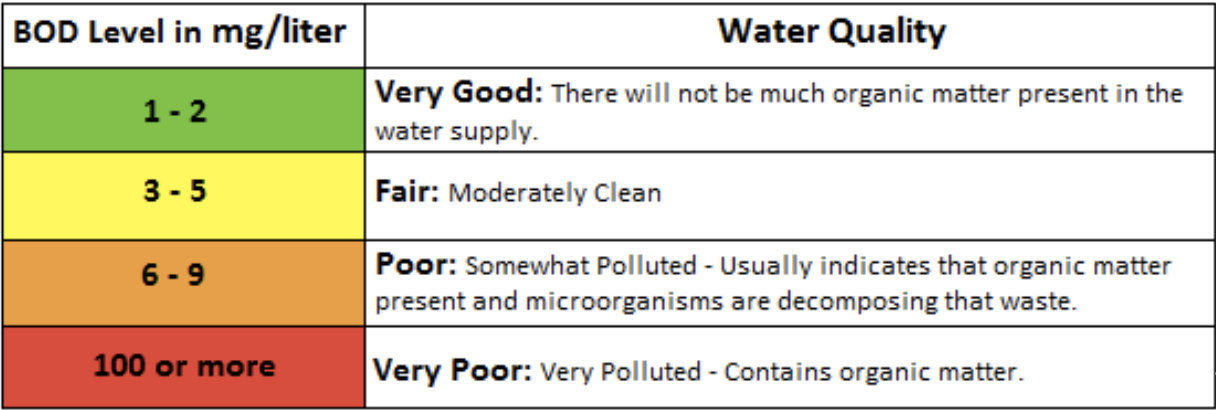
Water Quality Scale