AP Psych, Unit 8 - MESH & Positive Psychology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Motivation
a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior
Instinct Theory
the idea that organisms are motivated due to an unlearned and fixed pattern that is found throughout a species
Instinct
a complex behavior that is rigidly patterned throughout a species and is unlearned
Drive-Reduction Theory
the idea that a physiological need creates an arousal state (a drive) that motivates an organism to satisfy the need
Homeostasis
a steady internal state
Incentive Theory
sometimes we are motivated by a positive or negative environmental stimuli
Incentive
a positive or negative environmental stimulus that motivates behavior
Arousal Theory
theory that our need to maintain an optimal level of arousal motivates behaviors that meet to physiological need
Sensation-seeking Theory
the theory that people will seek out novel experiences
4 traits of a Sensation Seeker
Experience Seeking - a desire for novel sensory or mental experiences
Thrill / Adventure Seeking - an attraction to risky or fear-inspiring activities
Disinhibition - a loss of self-control
Boredom Susceptibility - the inability to tolerate monotony or repetition
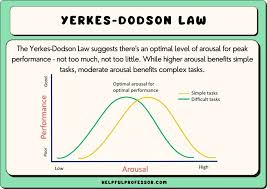
Yerkes-Dodson Law
performance increases with arousal only up to a point, beyond which performance decreases
Self-determination Theory of Motivation
the theory that we feel motivated to satisfy our needs for competence, autonomy, and relatedness
Intrinsic Motivation
the desire to perform a behavior effectively for its own sake
Extrinsic Motivation
the desire to perform a behavior to receive promised rewards or avoid threatened punishment
The role of the Hypothalamus plays in hunger and satiety
controls pituitary gland (hormones)
Lateral Hypothalamus
hunger center —> makes us hungry
lesion = wouldn’t feel hunger
Ventromedial Hypothalamus
satiety center —> makes us feel full
lesion = never feel full
Ghrelin
a hunger arousing hormone secreted by an empty stomuch
tummy grumbling
Leptin
protein hormone secreted by fat cells
increase = causes the brain to increase metabolism & decrease in appetite
Anorexia Nervosa
a person, maintains a starvation diet despite being significantly underweight
has an inaccurate self perception
sometimes paired with excessive exercise
Bulimia Nervosa
an eating disorder in which a persons binge eating is followed by inappropriate weight-loss promoting behavior
ex: vomiting, fasting, excessive exercise
Eating Disorders: Nature v. Nurture
nature:
heredity
nurture:
family
weight obsessed culture
distorted images
Emotion
Three Components of Emotion
bodily (physiological) arousal
expressive behaviors
conscious experience / feelings
James-Lange Theory
the idea that we first have a physiological response then we observe that response, after our actual emotion
idea: laugh until you feel happy / fake it till you make it
Canon-Bard Theory
the idea that our physiological arousal and our emotional experiences occur simultaneously (they don’t cause each other)
this theory would argue that you don’t need either physiological arousal or emotional experiences
Schachter-Singer Two-factor Theory
the idea that emotion have 2 ingredients (1) physical arousal and (2) a cognitive label a emotion requires as conscious interpretation of the physical arousal
Spillover-effect
arousal from emotions can “spill” from one event to another
arousal fuels emotion, cognition channels it
connected to Schachter-Singer Two-factor Theory
Polygraph Exams
Ways we communicate nonverbally
handshake
eye contact
facial expressions
vocal tones
Men v Women - Nonverbal Comunication
men
tend to describe simpler emotional reactions
less likely to describe themselves as empathetic
women
out perform men in emotional detection
greater emotional literacy
more likely to express empathy
Facial Feedback Theory
the tendency of facial muscle starts to trigger corresponding feelings
best supports the James-Lange Theory
Behavior Feedback Effect
the tendency of behavior to influence our own and others thoughts, feelings, and actions
Health Psychology
a subfield of psychology that explores the impact of physiological, behavioral, and cultural factors on health and wellness
Stress
the process by which we perceive and respond to certain events (called stressors), that we appraise as threatening or challenging
Approach-approach
when 2 attractive but imcompatible goals pulls us to choose
Avoidance-avoidance
a conflict between 2 undesirable alternatives
Approach-avoidance
a conflict while we feel simultaneously attracted and repelled
Tend-and-befriend Response
under stress (especially women) may nurture themselves and others (tend) and bond with and seek support from others (befriend)
GAS (general adaptation syndrome)
phase 1:
alarm reaction
mobilize resources
increases SNS activity
stress hormone release (adrenaline)
phase 2:
cope with stressor
bodys resistance to stress only lasts so long)
phase 3:
reserves depleted (adrenaline)
Problem-focused Coping
attempting to alleviate stress directly - by changing the stressor or the way we interact with that stressor
Emotion-focused Coping
attempting to alleviate stress by avoiding or ignoring a stressor and attending to emotional needs related to our stress reaction
Learned Helplessness
the hopelessness and passive resignation humans and other animals learn when unable to avoid repeated aversive events
Internal v External Locus of Control
Internal = you make things happen
External = things happen to you
Positive Psychology
the scientific study of human flourishing, with the goals of promoting strengths and virtues that foster well-being, resilience, and positive emotions, and that help individuals and communities to thrive
Subjective Well-being
self-perceived happiness or satisfaction with life, used along with measures of objective well-being to evaluate people’s quality of life
Relative Deprivation
our tendency to form judgements relatively to a neutral level defined by our prior experience
the perception that one is worse off relative to those we compare oursleves from
Broaden-and-Build Theory
proposes that positive emotions broaden our awareness, which overtime helps us build novel, and meaningful skills and resilience that improves well-being
6 categories of virtues connected to characters strengths
wisdom
justice
courage
temperance
humanity
transcendence
Posttraumatic Growth
positive psychological changes following a struggle with extremely challenging circumstances and life crises