Gas Pressure (Part I)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Gas pressure
Caused by the force exerted by gas molecules colliding with the surfaces of objects.
Yes, it is true
Is it true that the normal air pressure is strong enough to crush a metal container when not balanced by equal pressure from inside the container
Atmospheric pressure
Caused by the weight of the column of air molecules in the atmosphere above an object
African elephant
At sea level the atmospheric pressure is roughly the same as that exerted by a full-grown ________________ standing on a doormat
Pressure
Force exerted on a given area
P = F/A
Formula to calculate pressure
Force
Pressure is directly proportional to what?
Area
Pressure is inversely proportional to what?
Increase the force or decrease the area
2 ways to increase the pressure
Decrease the force or increase the area
2 ways to decrease the pressure
pascal (Pa)
The SI unit of pressure
1 Pa = 1 N/m^2
Define pascal
1 kPa = 1000 Pa
I kilo pascal is how many pascals?
1 bar = 100,000 Pa
1 bar is how many pascals
Pounds per square inch (psi)
The unit used in the US to measure a pressure
atmosphere (atm)
Unit used to measure pressure which originally represents the average sea level air pressure at the approximate latitude of Paris (45°)
14.7 psi
The approximate air pressure at sea level in pounds per square inch (psi)
bar
Unit which is commonly used in the discipline of meteorology to measure the pressure.
1 bar = 1000 mbar
1 bar is how many millibars
inches of mercury (in. Hg)
The unit that is used to measure a pressure in the aviation industry and also in some weather reports
1 in. Hg = 3386 Pa
1 inches of mercury is how many pascals?
Barometer
A device used to measure atmospheric pressure.
A glass tube that is closed at one end, filled with nonvolatile liquid such as mercury, and then inverted and immersed in a container of that liquid
Evangelista Torricelli
The inventor of the barometer
torr
The unit used to measure a pressure, which is named after the inventor of the barometer
1 torr = 1/760 atm
1 torr is how many atm?
1 torr
1 millimeters of mercury is approximately how many torr?
outside, inside, liquid surface
The atmosphere exerts pressure on the liquid _______ the tube, the column of liquid exerts pressure ______ the tube, and the pressure at the ______________ is the same inside and outside the tube.
proportional
The height of the liquid inside the tube is therefore ____________ to the pressure exerted by the atmosphere.
13.6
Mercury is about ____ times denser than water
102,325 Pa
1 atm at sea level is how many pascals?
760 mm of Hg or 29.92 in. of Hg
1 atm is how much Mercury?
Hydrostatic pressure
The pressure exerted by a fluid due to gravity
p
Symbol that represents hydrostatic pressure
h
Symbol that represents the height of the fluid
ρ
Symbol that represents the density of the fluid.
g
Symbol that represents the acceleration due to the gravity
p = hρg
Formula to calculate the Hydrostatic pressure
Manometer
A device similar to a barometer that can be used to measure the pressure of a gas trapped in a container
Closed-end manometer
A U-shaped tube with one closed arm, one arm that connects to the gas to be measured, and a nonvolatile liquid (usually mercury) in between
Open-end manometer
Same as the close-end manometer but one of its arms is open to the atmosphere.
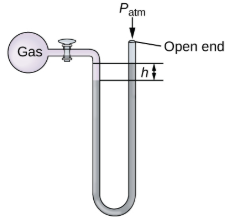
Pgas = Patm - hρg
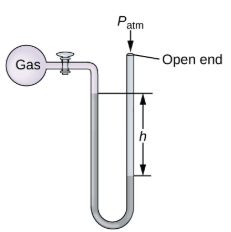
Pgas = Patm + hρg
Sphygmomanometer
A device used to measure the blood pressure.
Consists of an inflatable cuff to restrict the blood flow.
It is basically a manometer
Sphygmos
The Greek word for pulse
1881
Year when sphygmomanometer was invented
Manual sphygmomanometer
The sphygmomanometer type that is used by by the medical professionals
Mercury sphygmomanometer
The sphygmomanometer type that is used when the most accuracy is required
Upper-arm
The area around where the cuff is placed around and inflated until the blood is completely blocked
arteries
As the heart beats, blood forced through the ________ causes a rise in pressure
Systolic pressure
The peak pressure in the cardiac cycle.
The rise in pressure at which the blood flow begins.