ARC 1013 - Briar Jones/MSST - Test 3
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Renaissance Characteristics
math, rational properties, universal order
not aspire to heavens, grounded to Earth/human reason
circle & square; pure geometric form
15th C
Humanism
philosophical system based upon the capacity of humankind for rational, objective through, and action; stresses human reason and is centered in human nature, interests, and ideals, as distinct from religious philosophies based on God
Renaissance
the activity, spirit, or time of humanistic revival of classical art, lit, and learning originating in Italy in the 14th C-17th C
Renaissance Architecture
the various adaptations of Italian Renaissance architecture that occurred throughout Europe until the advent of Mannerism and the Baroque in the 16th & 17th Cs, characteristized by the use of Italian forms and motifs in more or less traditional buildings
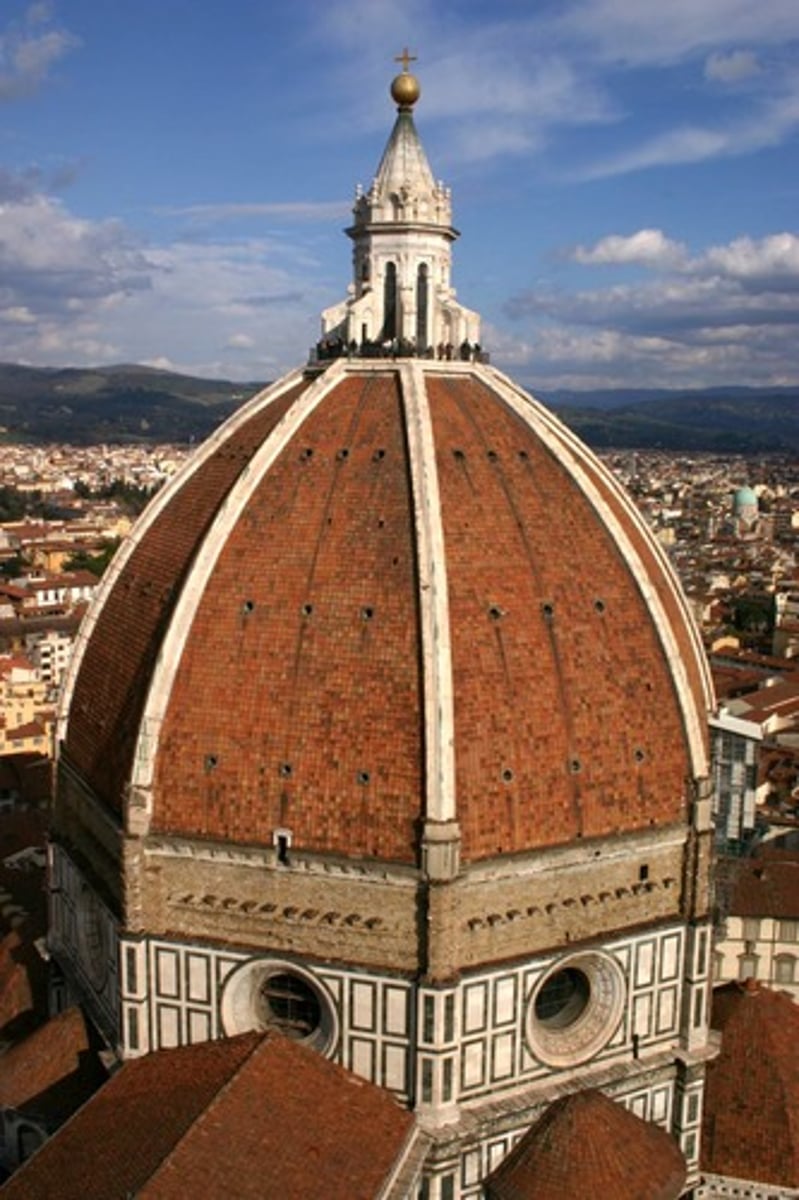
Cathedral in Florence
dome is witness to human achievement
dome is double shell
built by Brunelleschi

Brunelleschi
architect, painter, sculptor, goldsmith. Father of the Renaissance
Early Renaissance
a style of Italian Renaissance art and architecture developed in the 15th C, characterized by the development of linear perspective, chiaroscuro, and in buildings, by the free and inventive use of classical detail
Piazza
where the "community" came together to get water and socialize
Duomo
Dome of Cathedral in Florence (1418-36)
largest dome built since Romans
no centering, self supported
employed ribs and double shell

Church of San Lorenzo
Brunelleschi
Medici hired Brun to redo it

Church of San Spirito
Brunelleschi
proportions and style fully realized
Pazzi Chapel
Brunelleschi

Vitruvius
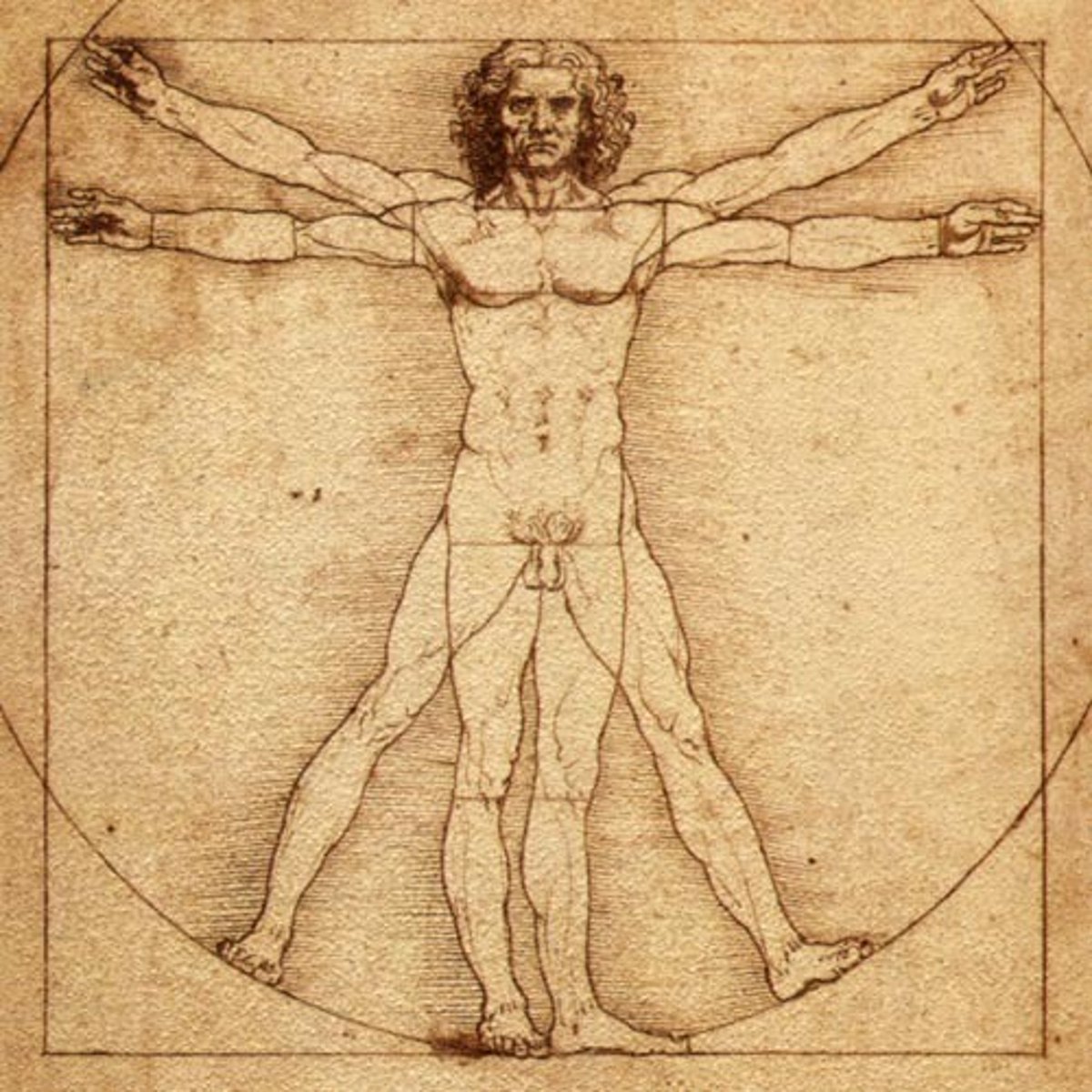
Church of Saint Andrea
Alberti
wrote his own 10 books arch modeled after Vitruvius
promoted arch as an intellectual activity

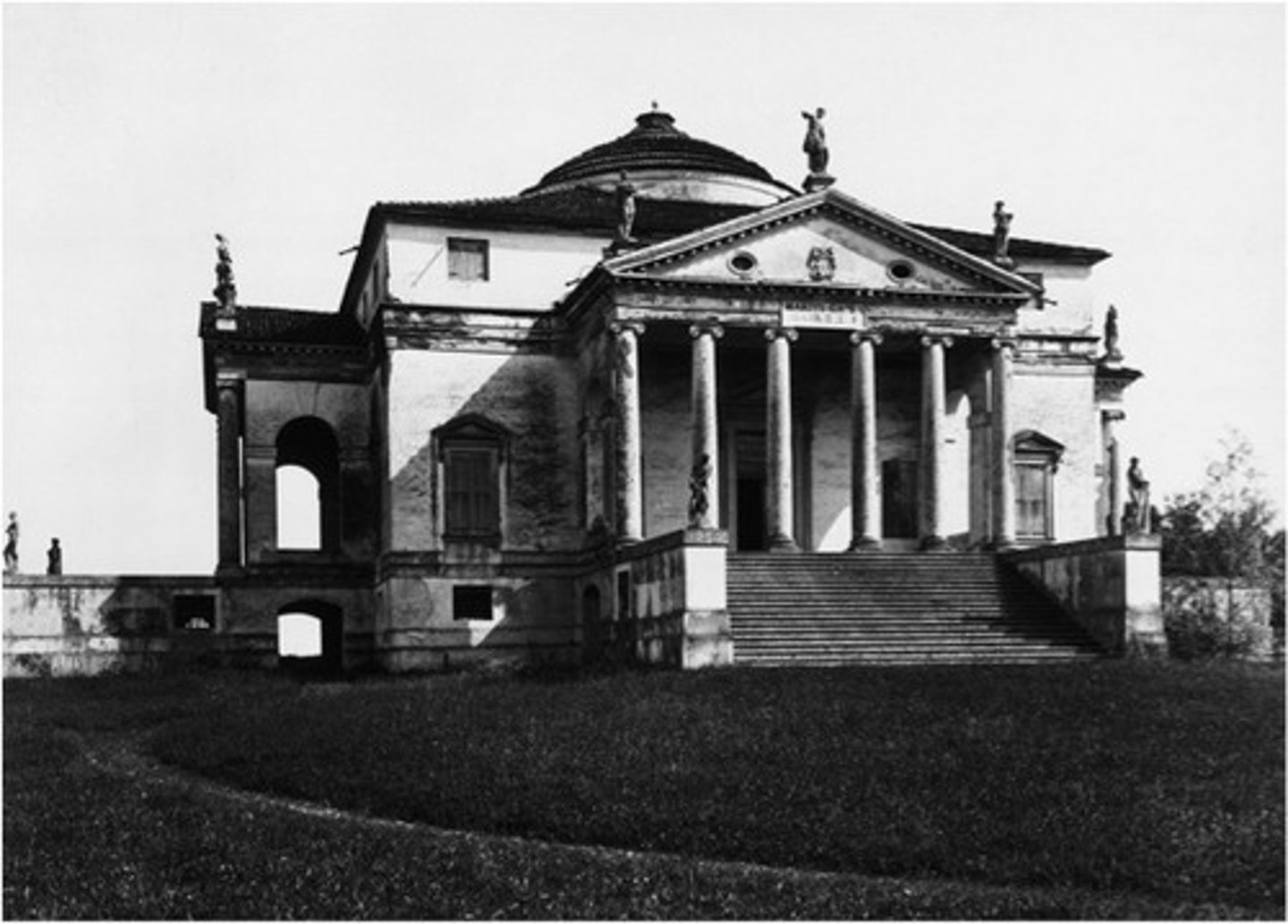
Villa Rotando
1500 Vicenza, Italy
Palladio
supreme example of theoretically inspired design (completely symmetrical, elements all governed by proportional relationship, turned house into temple)

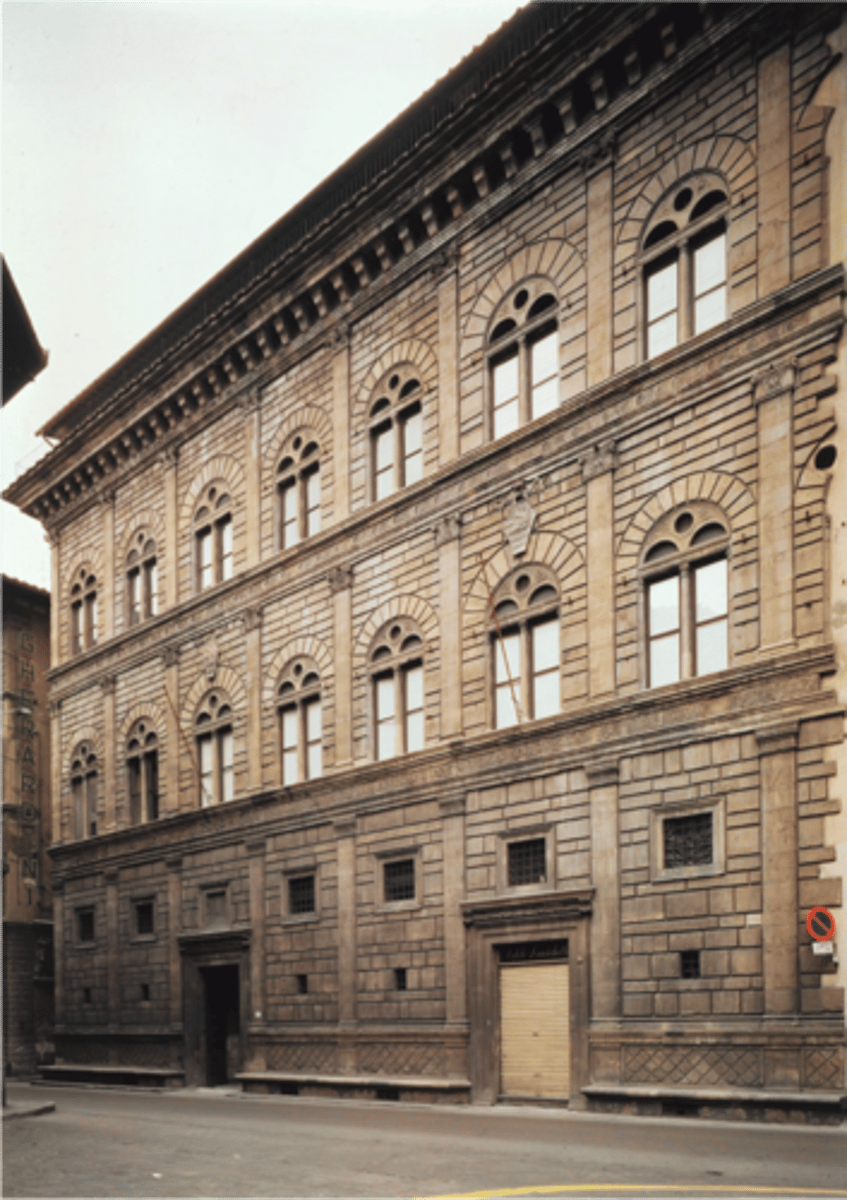
Palazzo
city house

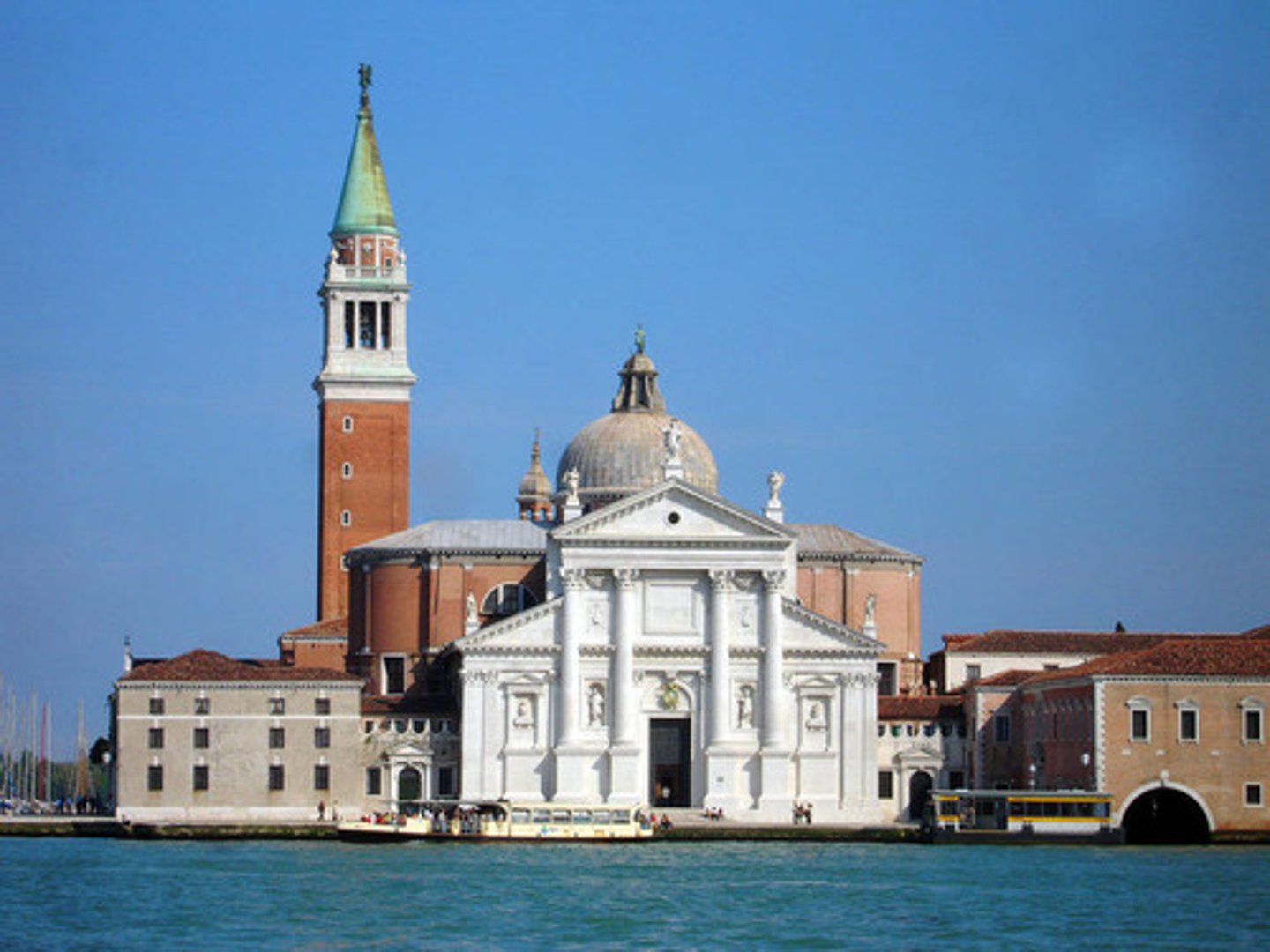
San Giorgio Maggiore
Venice, Italy
scaled to present a face to the town of Venice

High Renaissance
a style of Italian renaissance art and architecture developed the late 15th C, characterized by an emphasis on draftsmanship, the illusion of sculptural volume in the paintings, and in building, by the imitative use of orders and compositional arrangements in the classical style, with great attention to the formulation of compositional rules after the precepts of Vitruvius and the presidents of existing ruins
Tempietto of San Pietro
Bramante
perfection of circular geometry
believed St. Peter martyred here
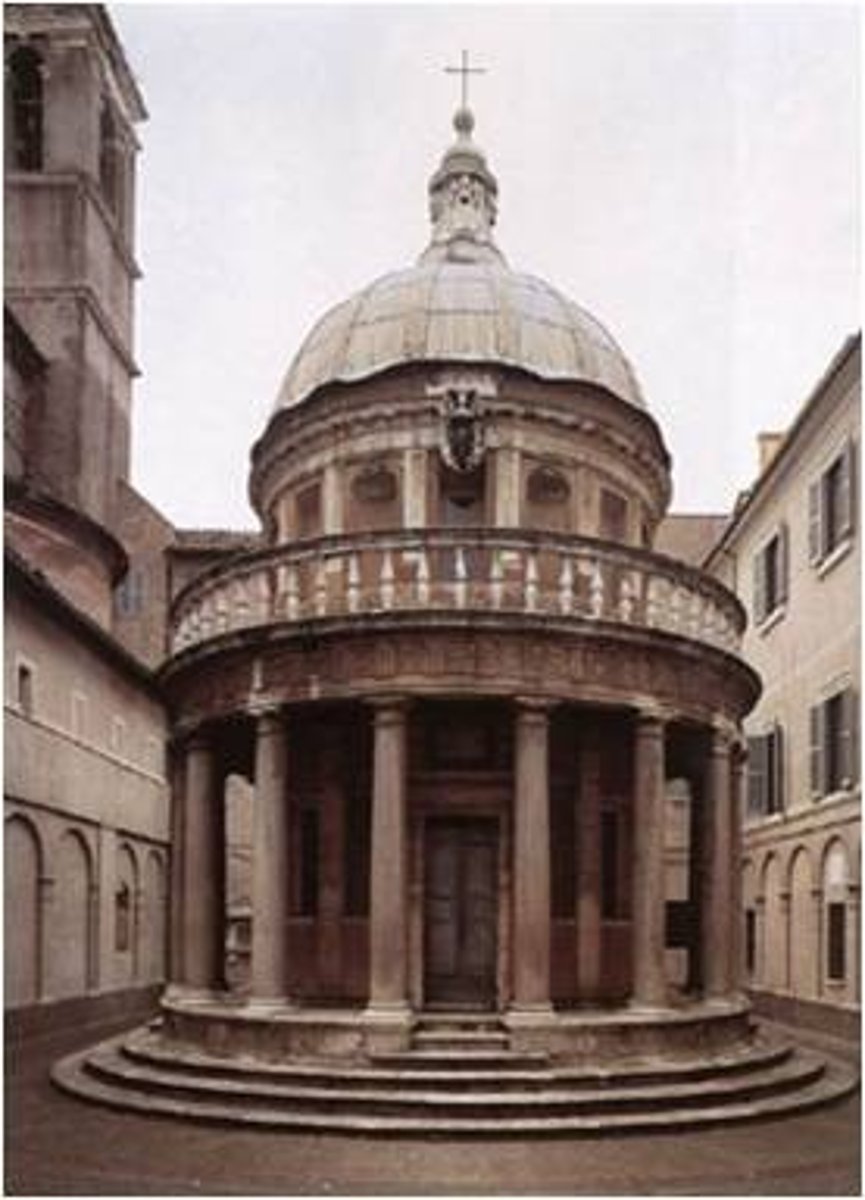

Donte Bramante
1444-1514
close to da Vinci
early work in Milan
moved to Rome after French sack of Milan (1499)
Pope Julius II
1503
humanist ideals introduced into Papal Court (Rome Queen City - consolidate temporal power; return glory from Roman antiquity)
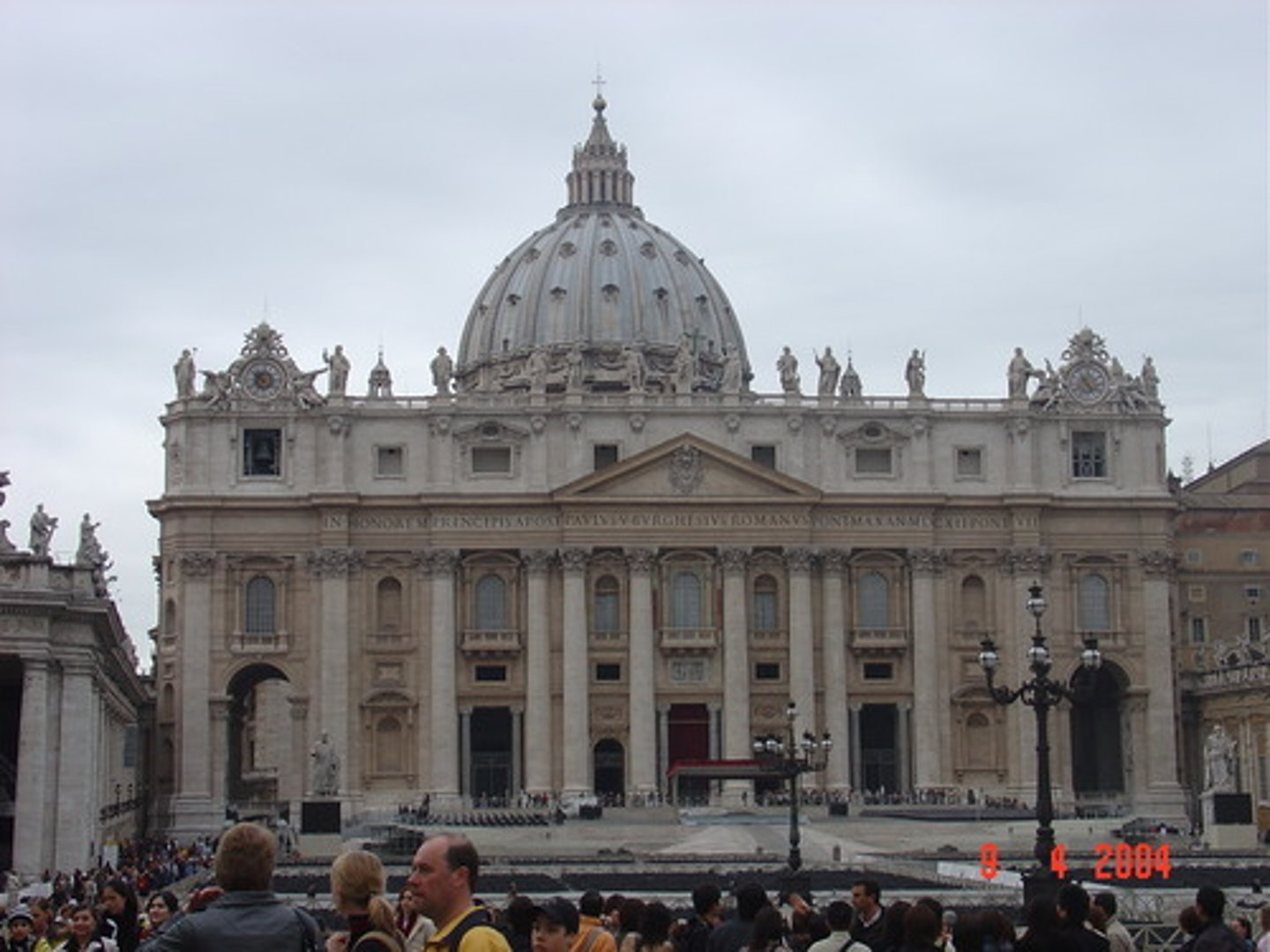
St. Peter's
1505-1612
Michelangelo changed it
a magnificent new church over the crypt of St. Peter
dome becomes icon, often repeated
tomb of Pope Julius II wouldn't fit in old basilica
Bramante's scheme was on a scale grander than any Roman structure (dome compared to Pantheon)

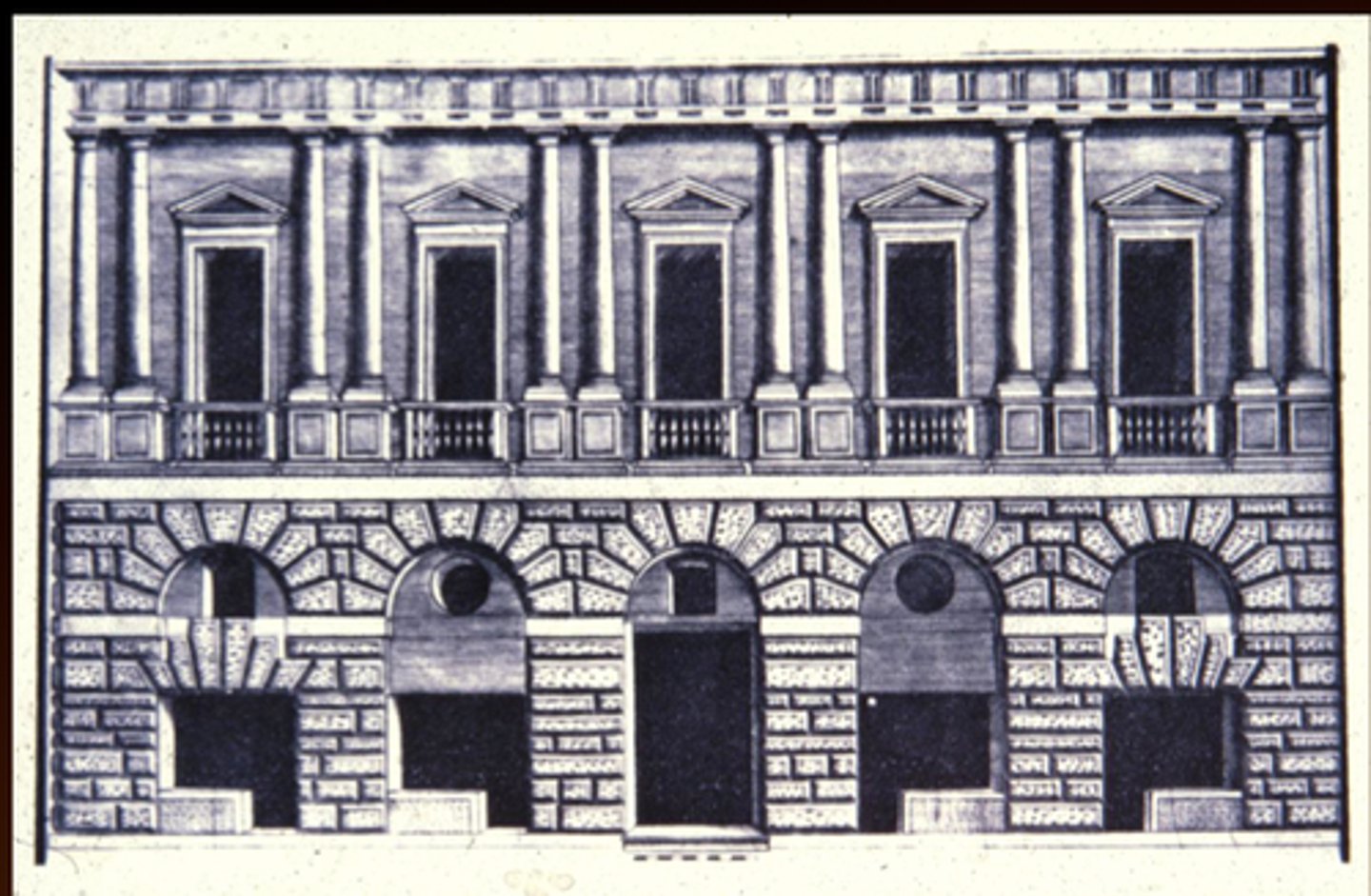
Palazzo Caprini
Rome, 1512; Bramante
Manerism
A traditional style in European architecture in the late 16th C, particularly in Italy, characterized by unconventional use of classical elements
Michelangelo
1475-1564
rebelled against Renaissance decorum; adjusted proportions, details to suit his purpose
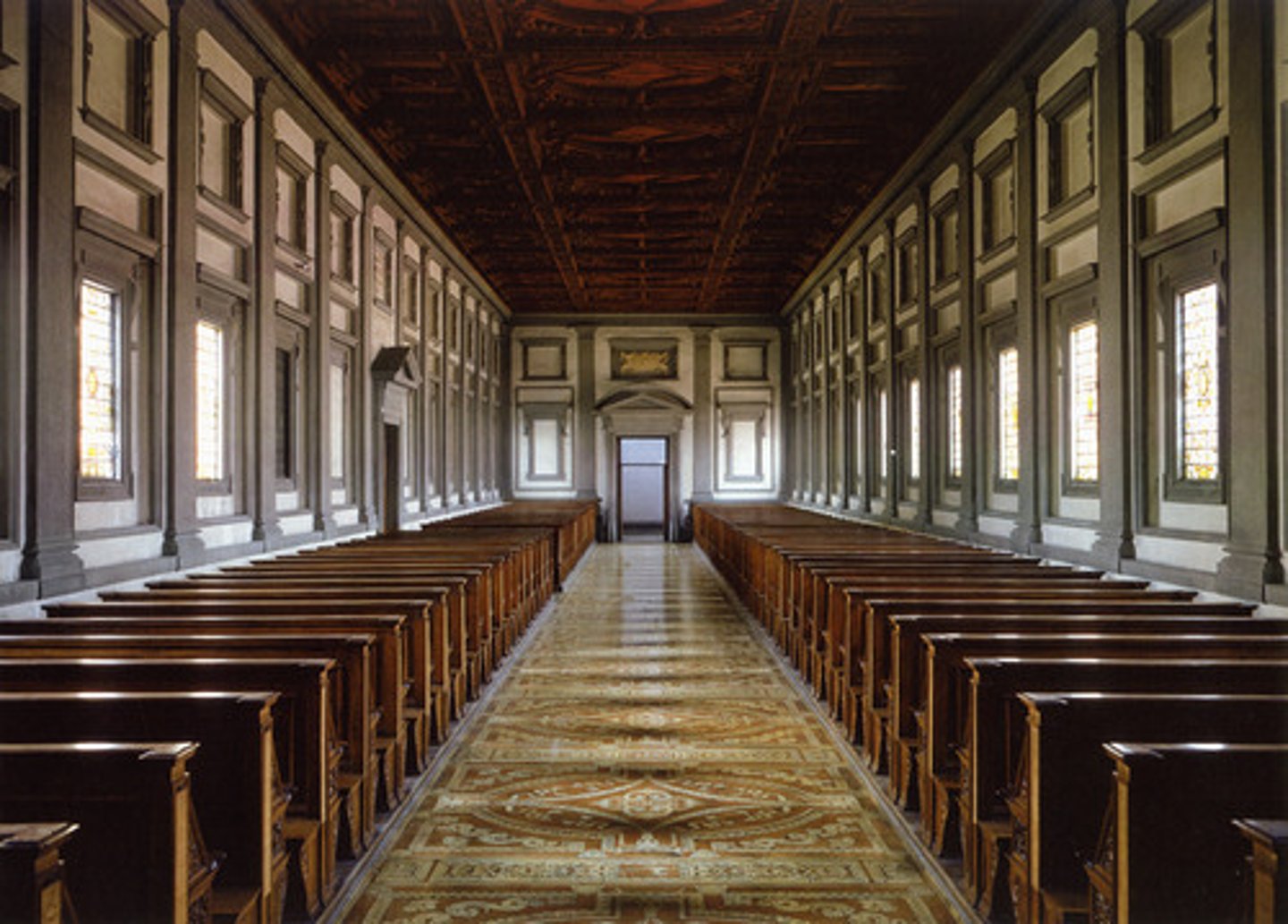
Laurentian Library
1524; Michelangelo
compete challenge to Renaissance rules of order, proportion, and use of historic elements
Michelangelo manipulated architecture into sculpture

Campidoglio, Capitoline Hill
1536; Michelangelo
organization deviates from purity of Renaissance geometry (subtle tension of angled plan & overall plaza)
Ideas begin to become "Mannerism"

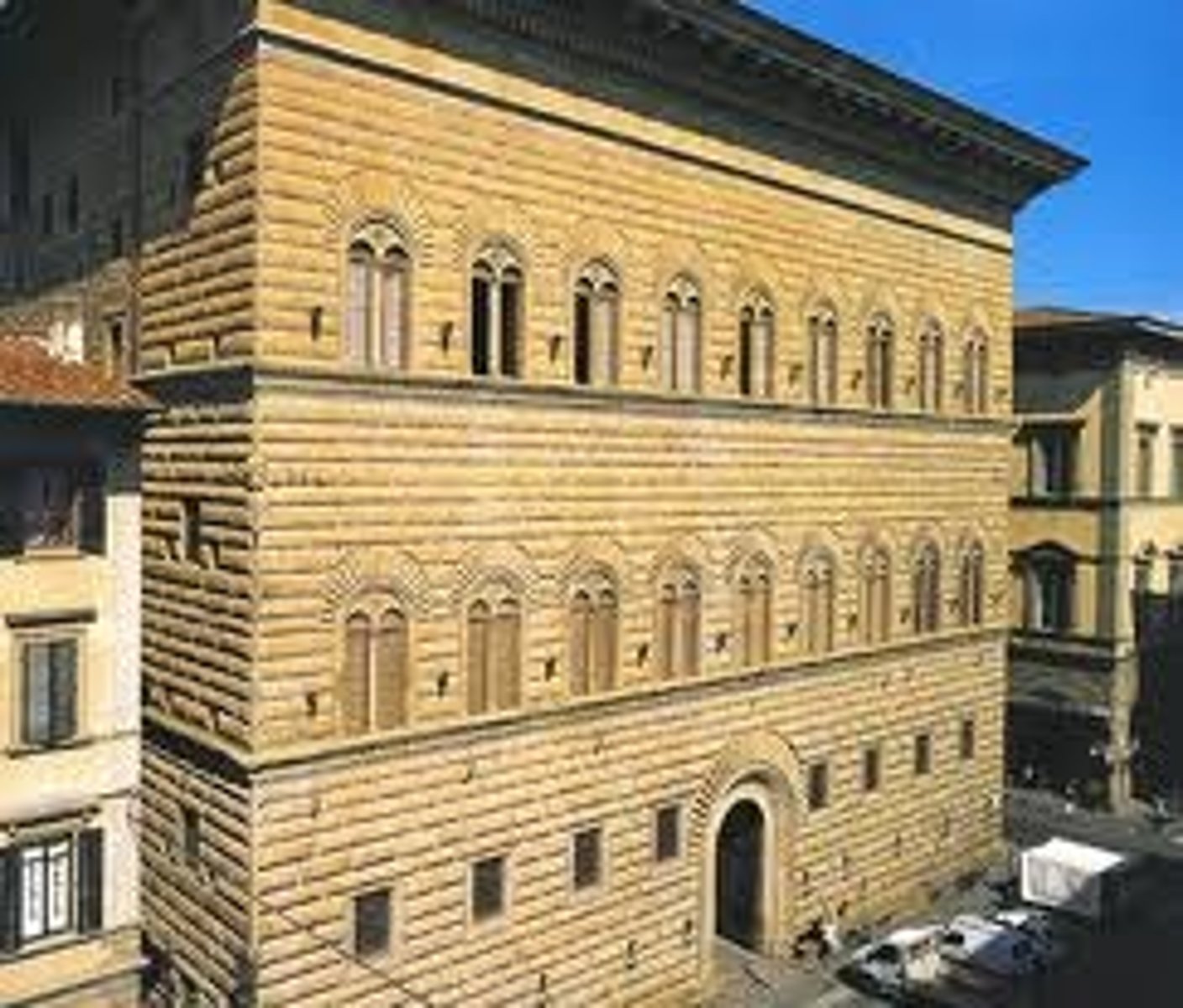
Palazzo Strozzi
began 1489; Florence, Italy

Palazzo Farnese
1559; Barozzi da Vignola
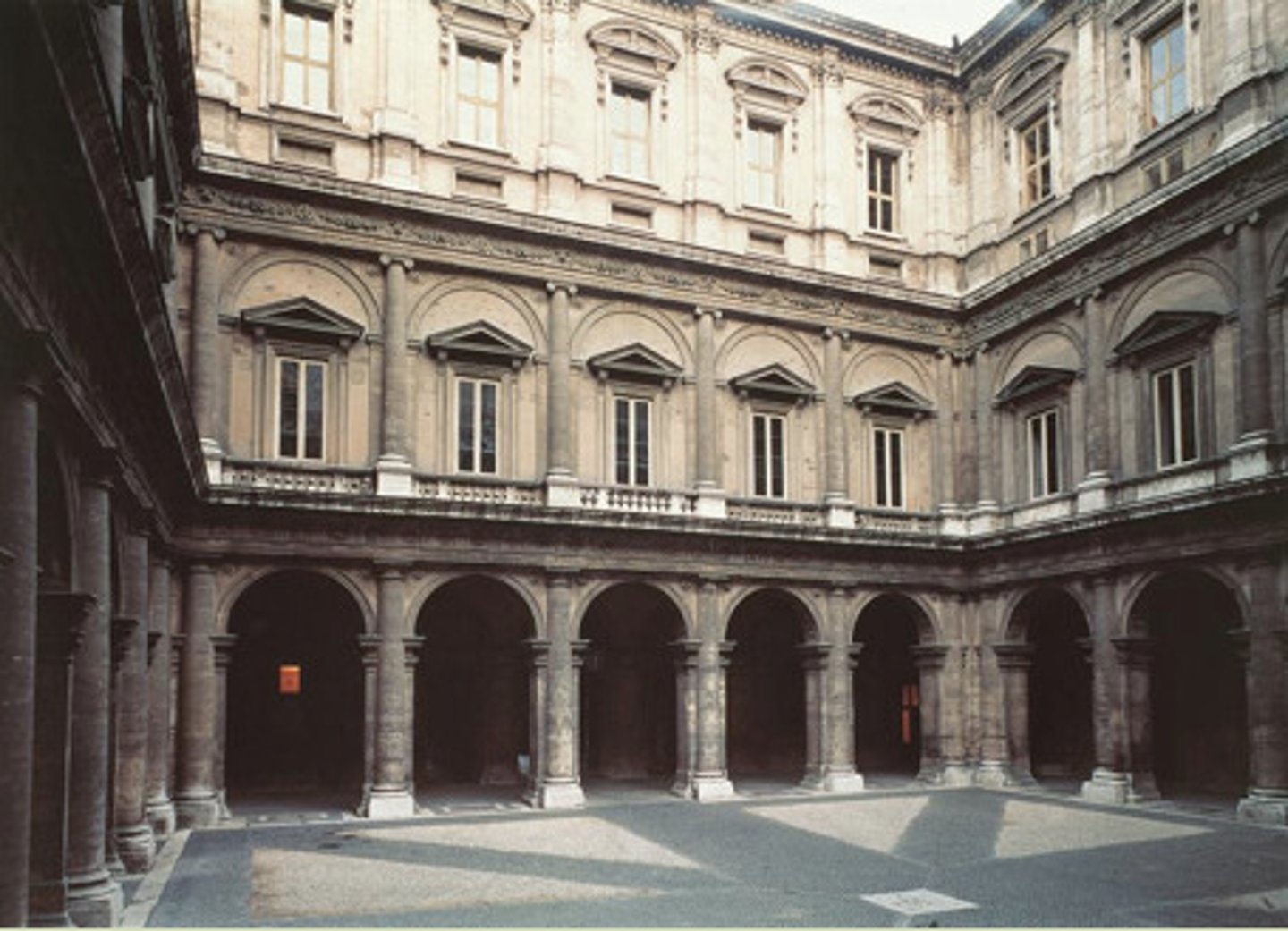

Inigo Jones
1572-1652
Englishman
Queen's House
1616, Greenwich; Jones
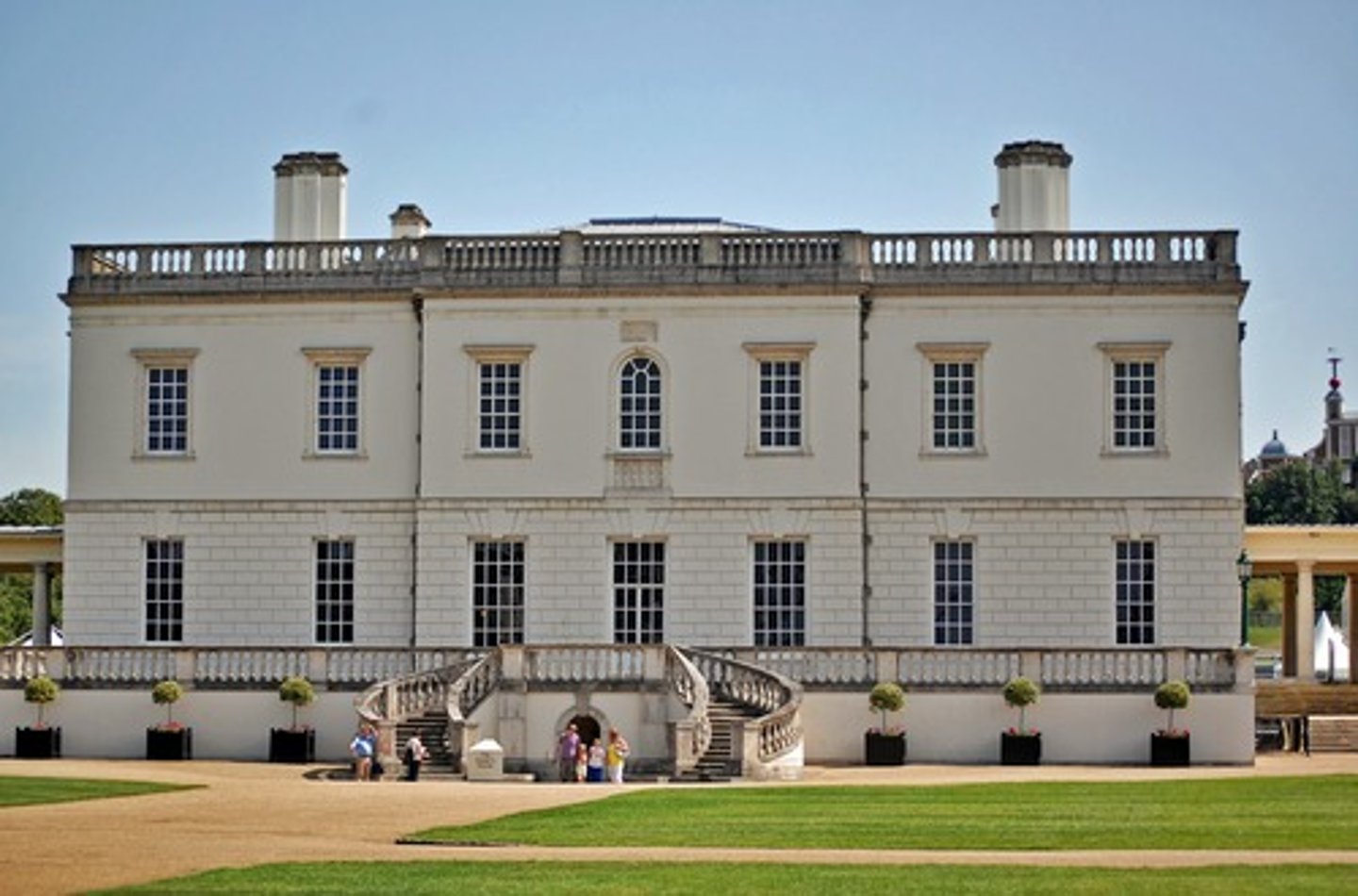

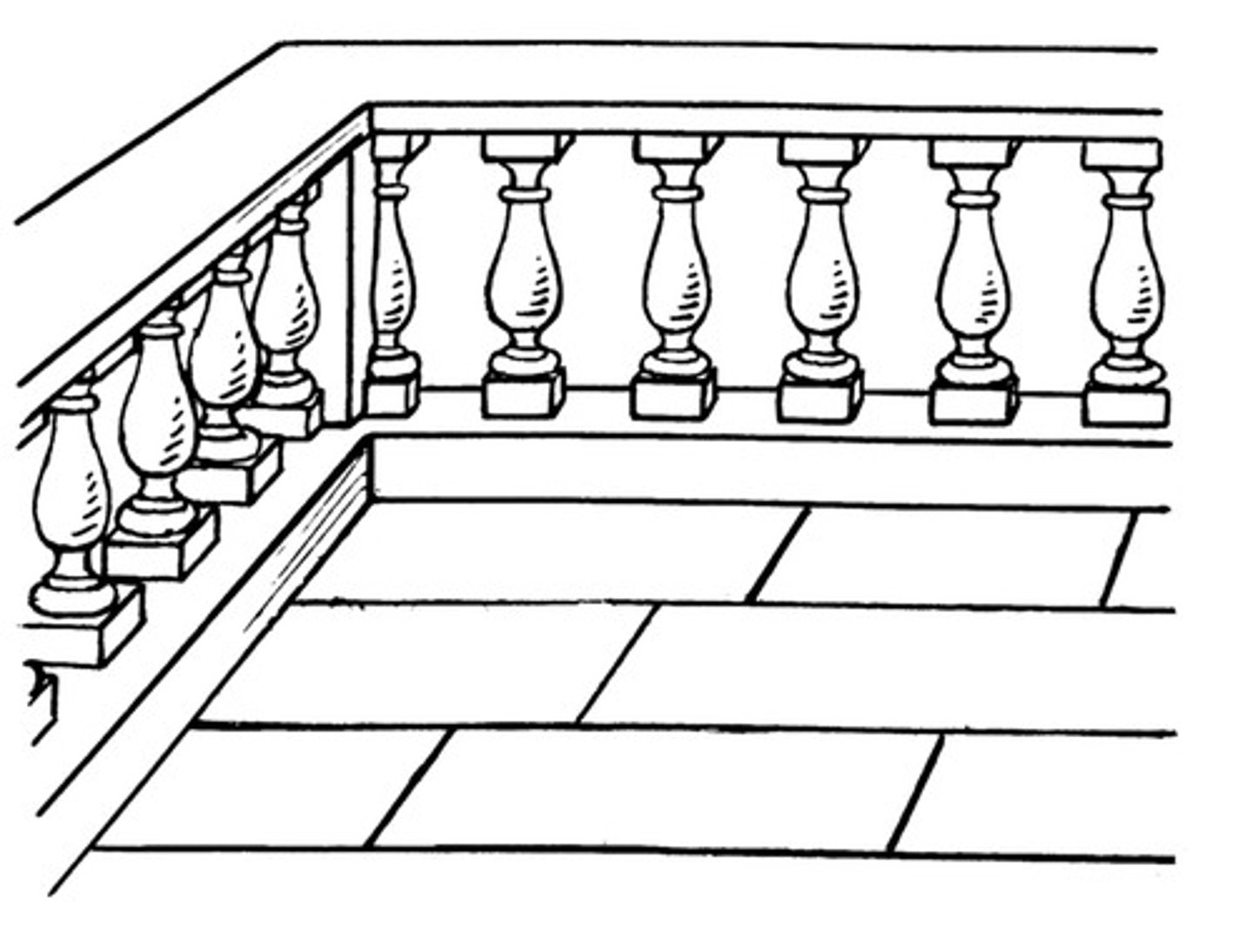
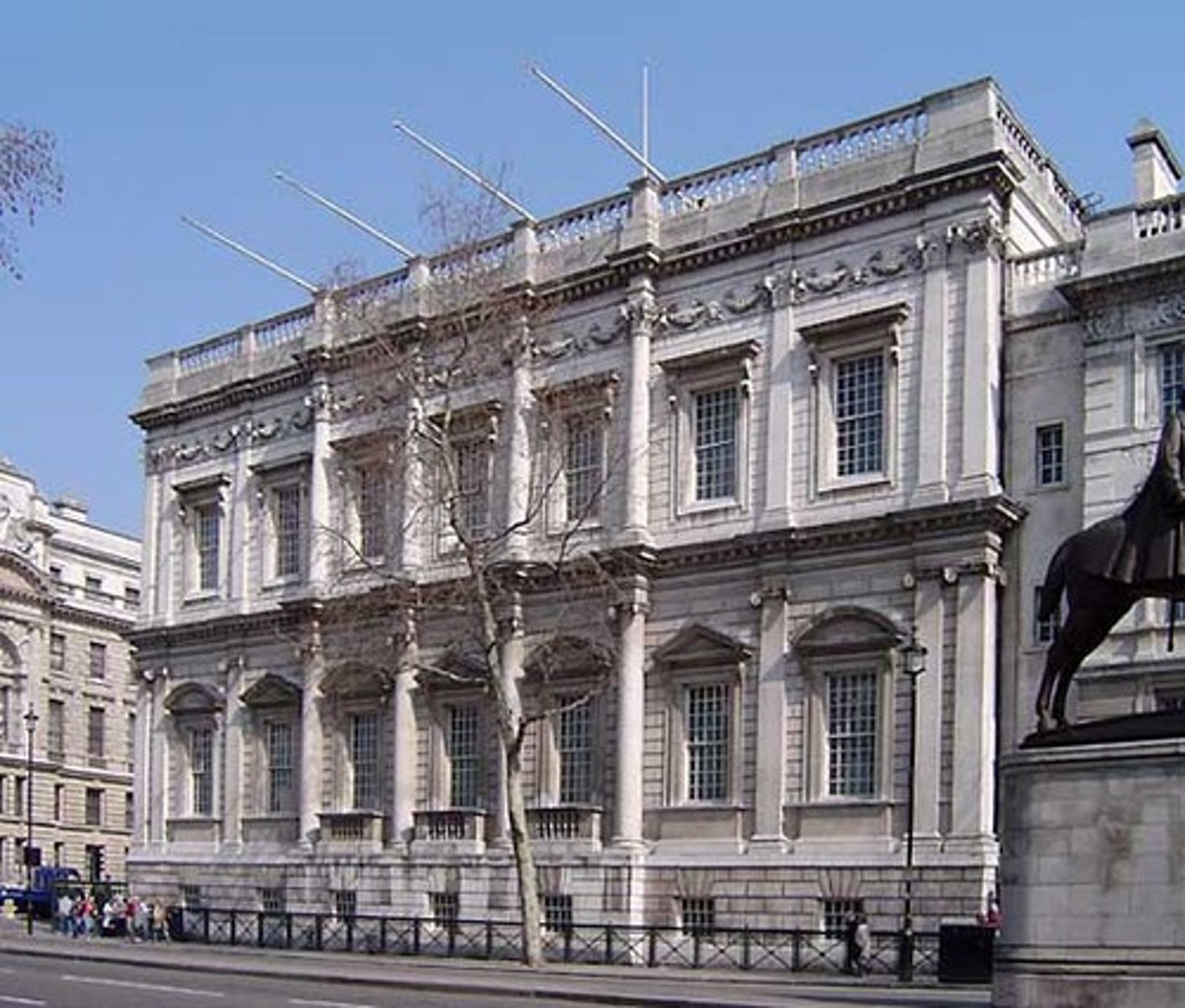
Balustrade
a railing supported by balusters
Banqueting Hall
1619-22, Whitehall, London; Jones

Renaissance v. Baroque (17th C)
R:
engage intellect
pure forms
emphasis individual in isolation
arch for wealthy
individual isolated buildings
B:
engage the emotions
illusionary effects
emphasize on as part of social classes
arch for all social classes
buildings designed to fit context
Baroque Architecture
A style of architecture originating in Italy in the early 17th C and variously prevalent in Europe and the New World for a century and a half characterized by free and sculptural use of classical order and ornament, dynamic opposition and interpretation of spaces, and the dramatic combined effects of architecture, sculpting, painting, and the decorative arts
Bernini & Borromini
Baroque in Rome
reaffirmation of catholic church after reformation
building to awe
counter reformation
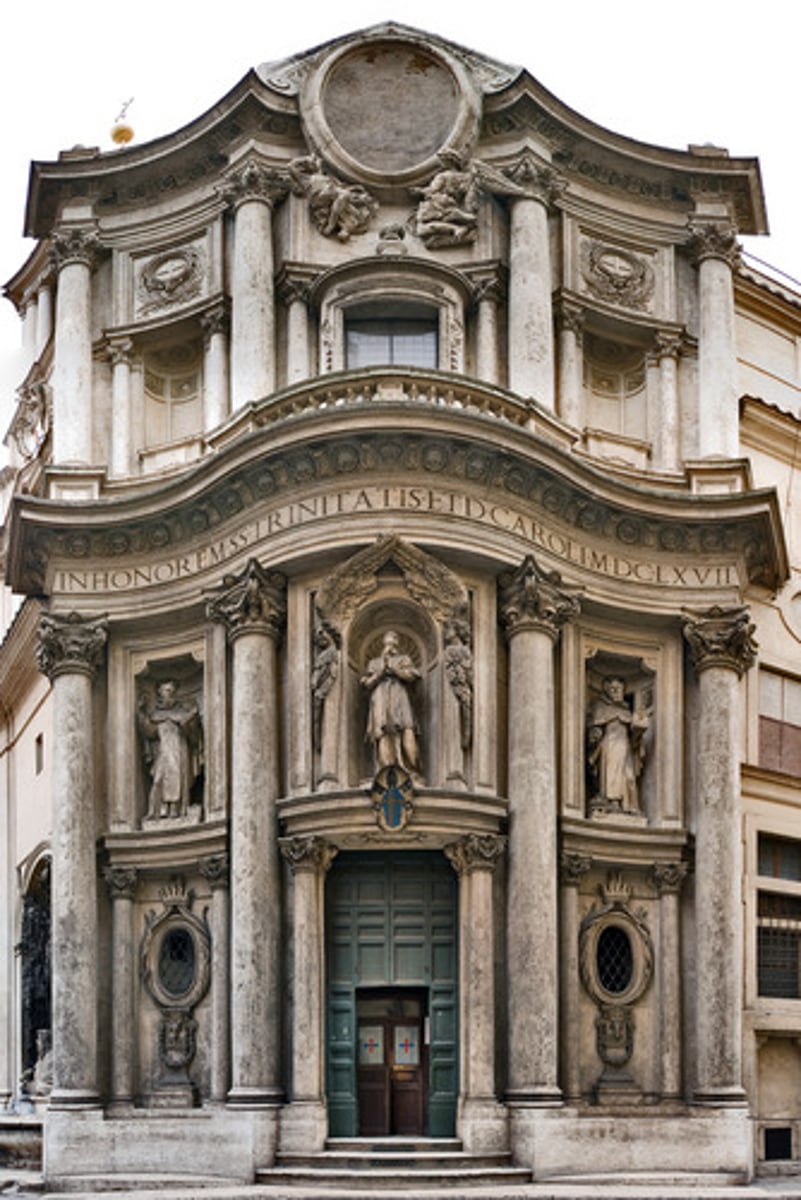
S. Carlo alle Quattro Fontane
Rome, 1634; Borromini

Colonnade at St. Peter
Rome, Bernini
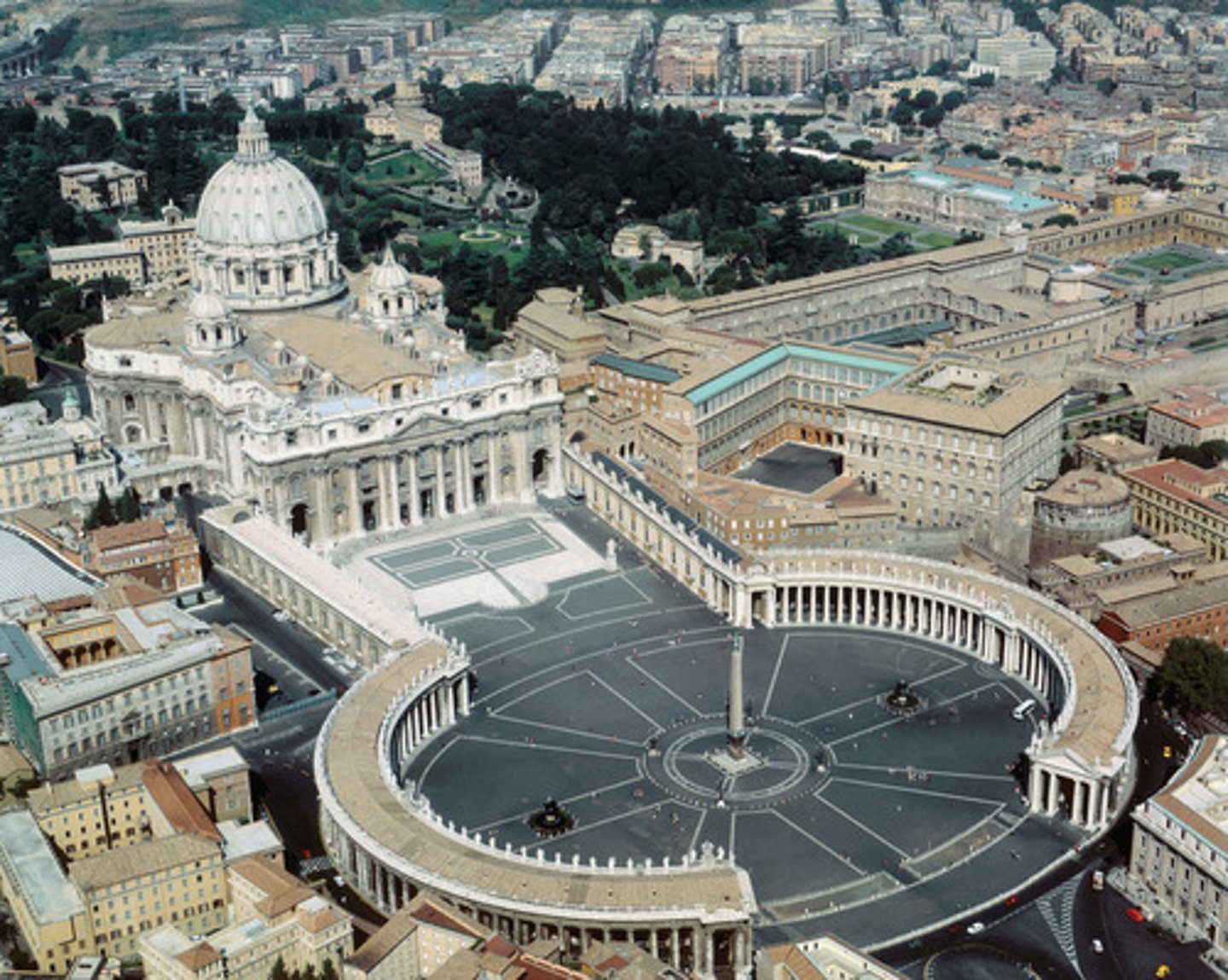

Piazza Navdna
Rome, 1644; Bernini & Borromini
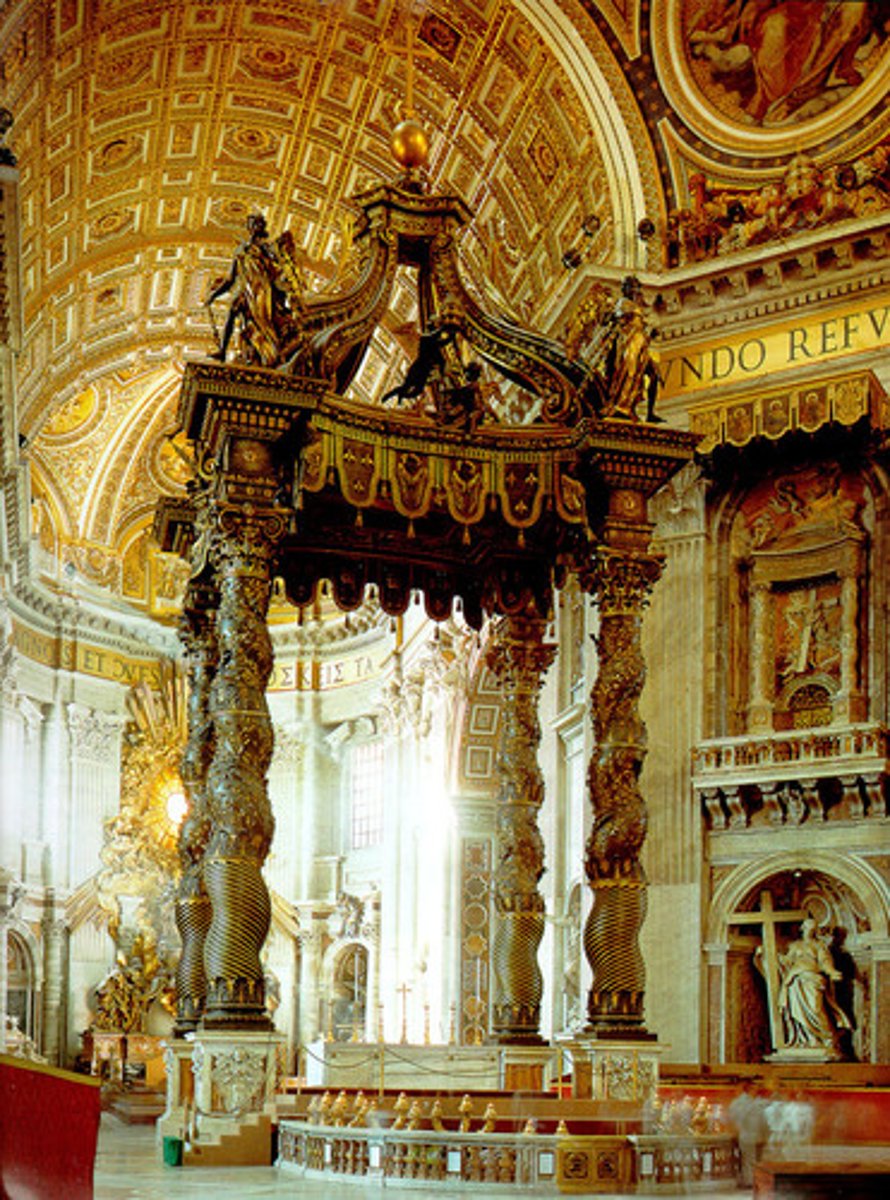
Baldacchino
St. Peter's, Bernini

London - FIre of 1666
after rebuilding city of London, early building code
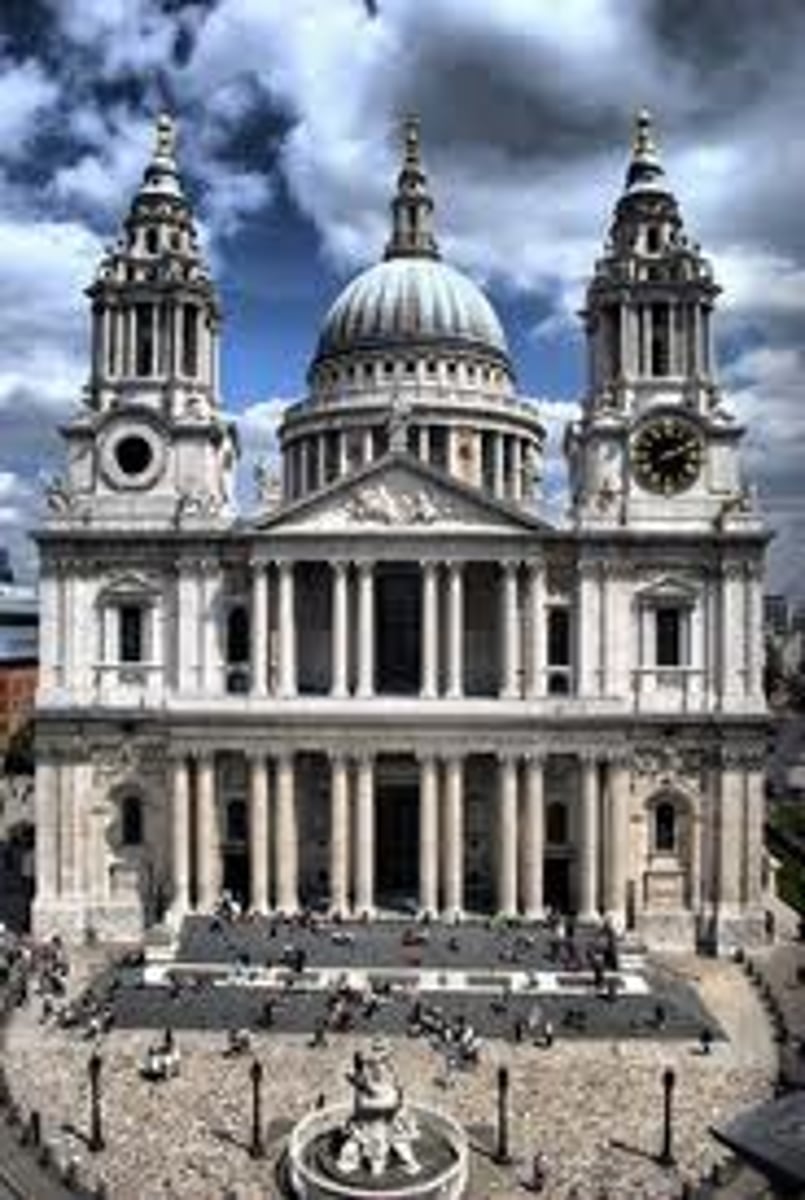
Sir Christopher Wren redesigned St. Paul' s & 50+ others
St. Paul's
London, 1675-1709; Sir Wren

St. Clemente Dane
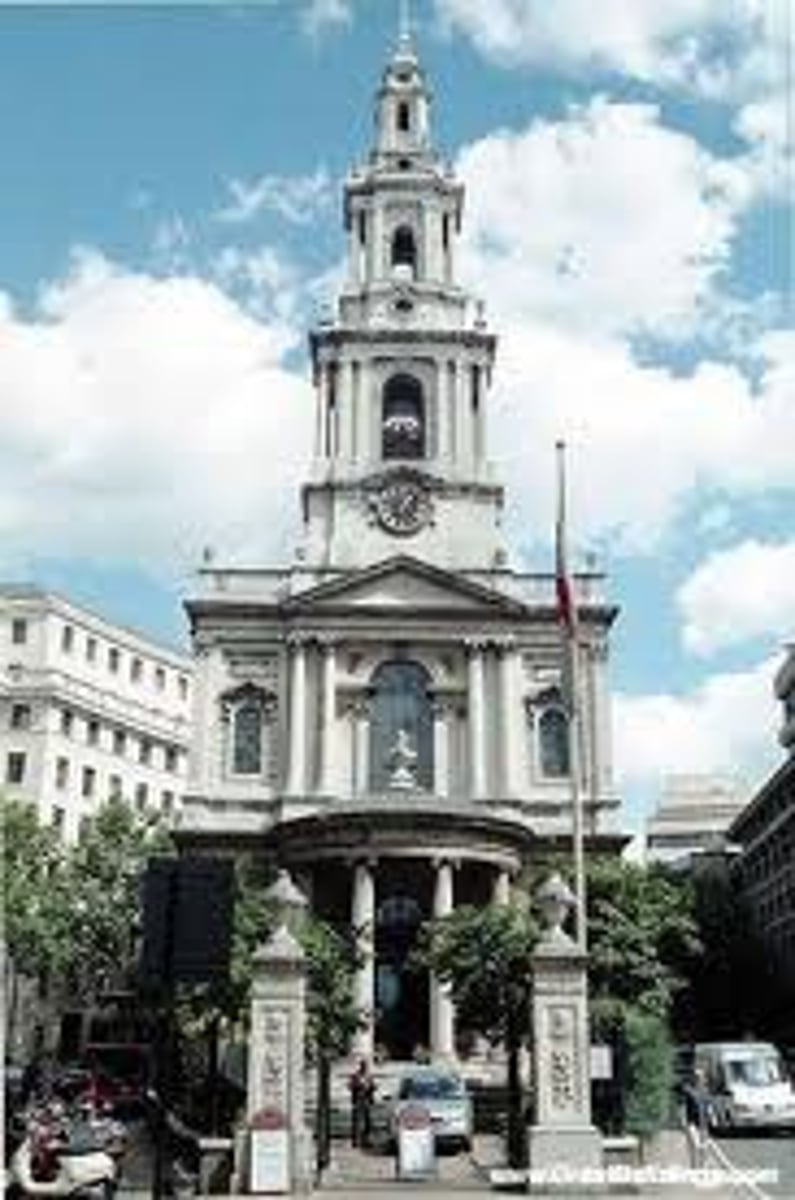

St. Mary-Le-Bow

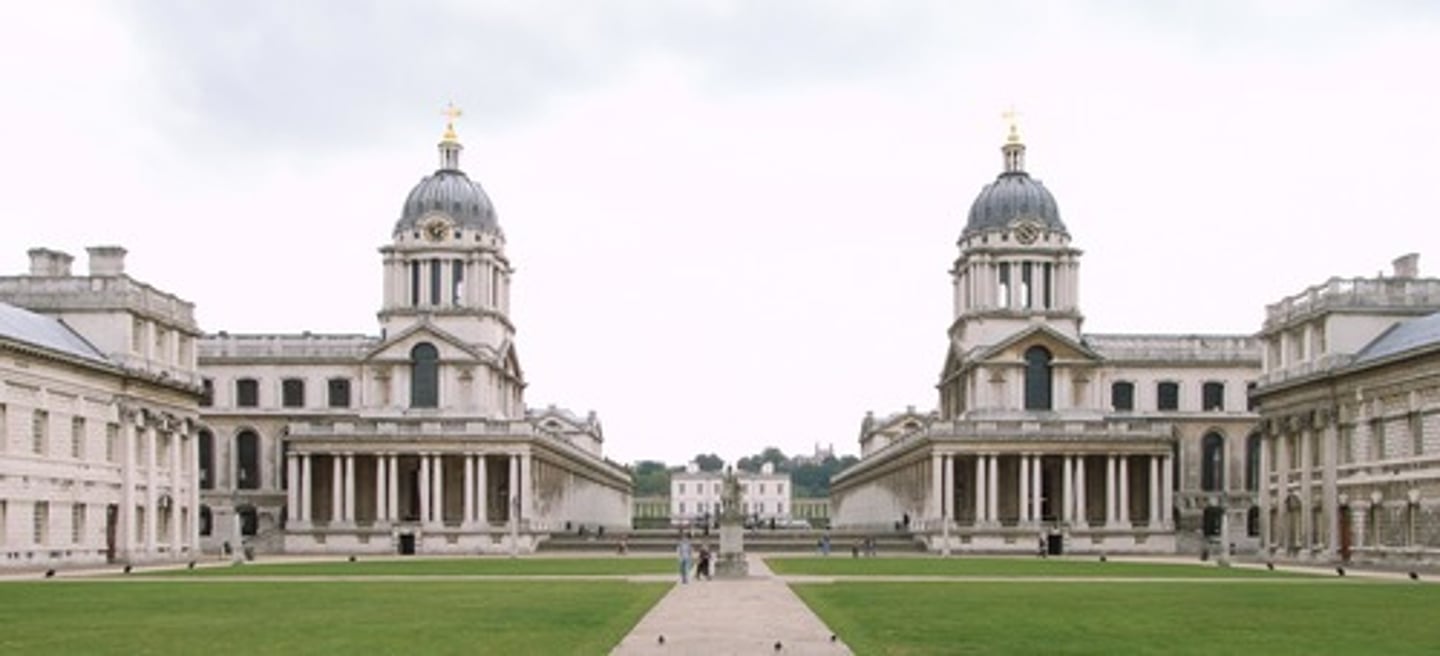
Royal Hospital in Grenwich
1696-1702

Christ Church & St. Mary Woolnoth
London
Versailles
outside Paris, begun 1661
baroque (inside and landscape)
Louis XIV's hunting lodge
gardens included almost 1400 fountains; water from Siete River

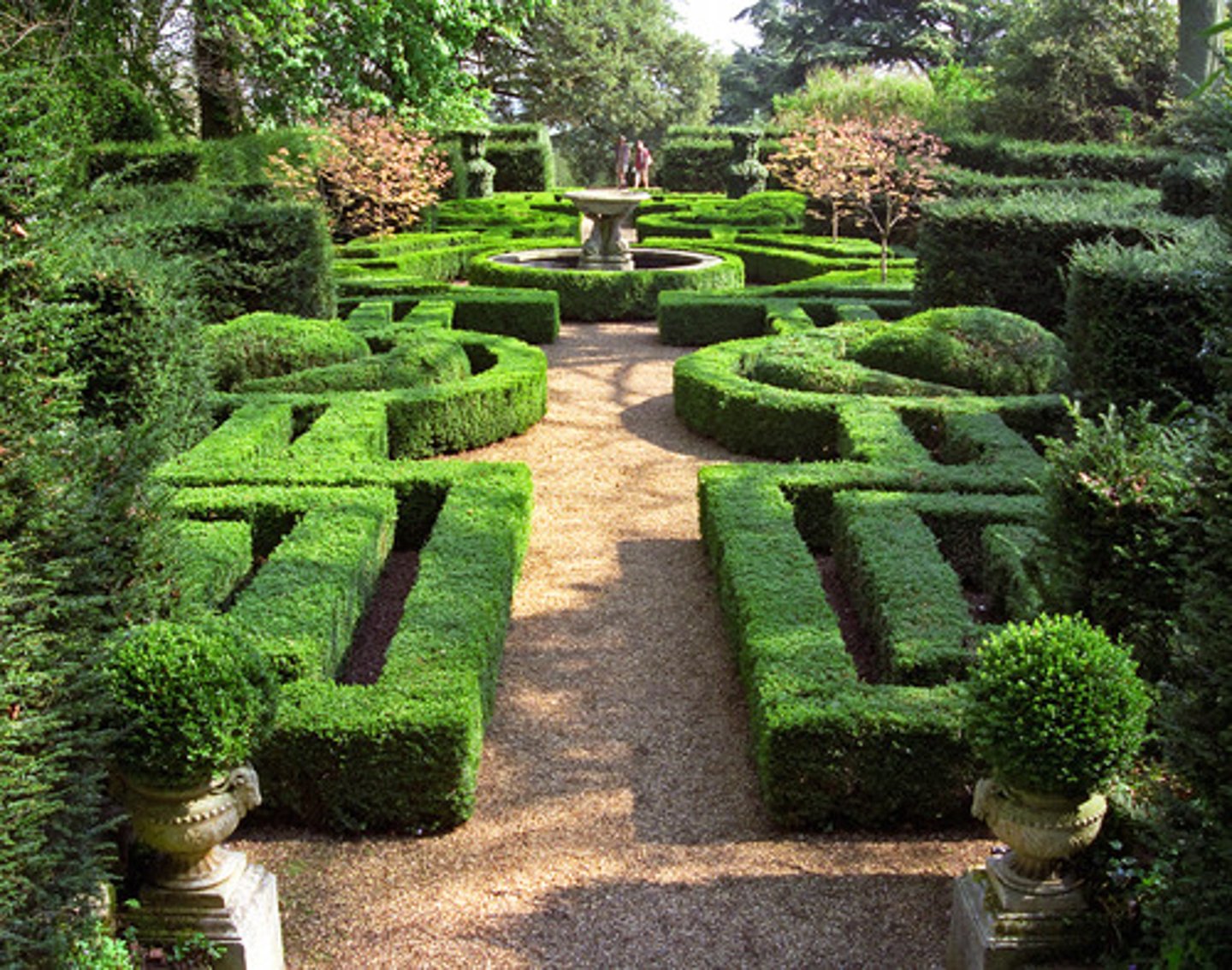
Parterre
geometrically organized gardens

Allee
pathway lined with trees
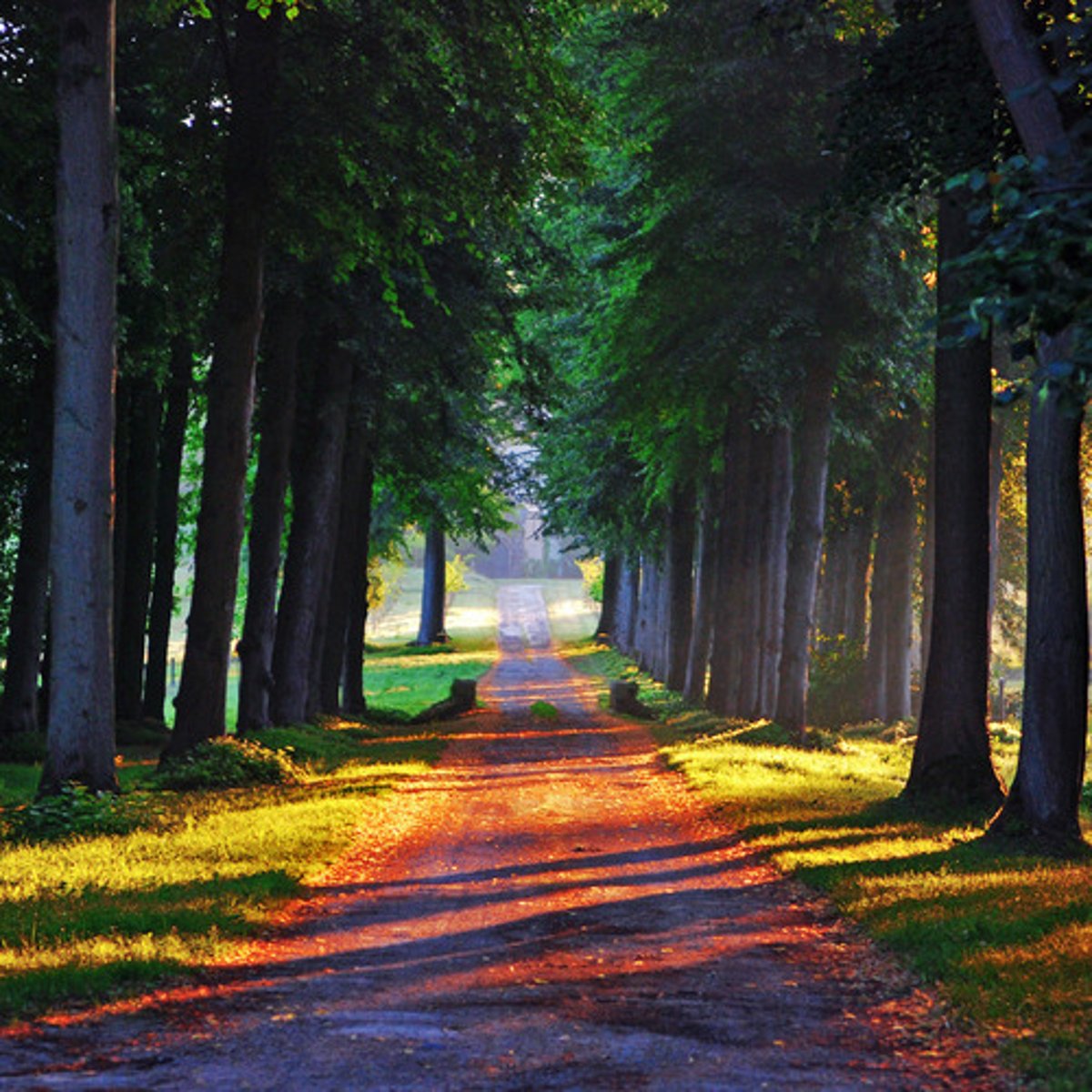

Rococo
a style of decorative art that evolved from baroque; distinguished by fanciful, curved spatial forms
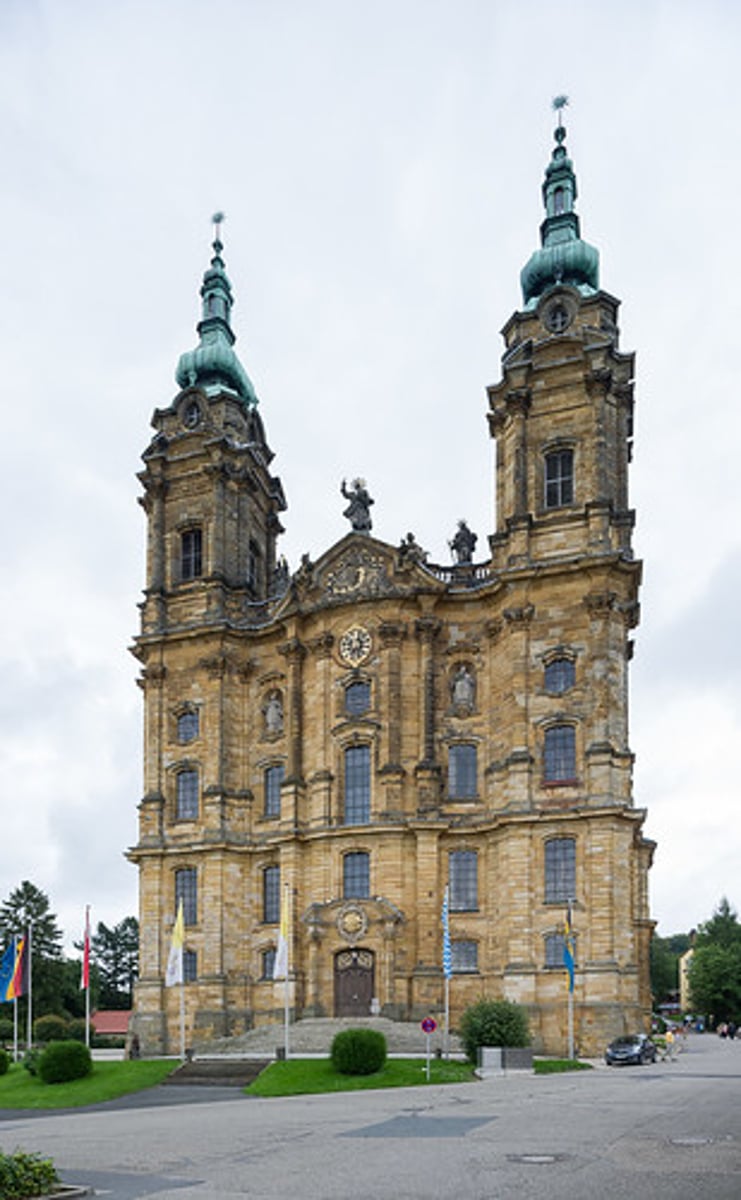
Die Weis
Dominikus Zimmerman
church in rural Bavaria
designed by Zimmerman bros
plain outside
Johann Balthasar Neuman
Vierzehhailgen

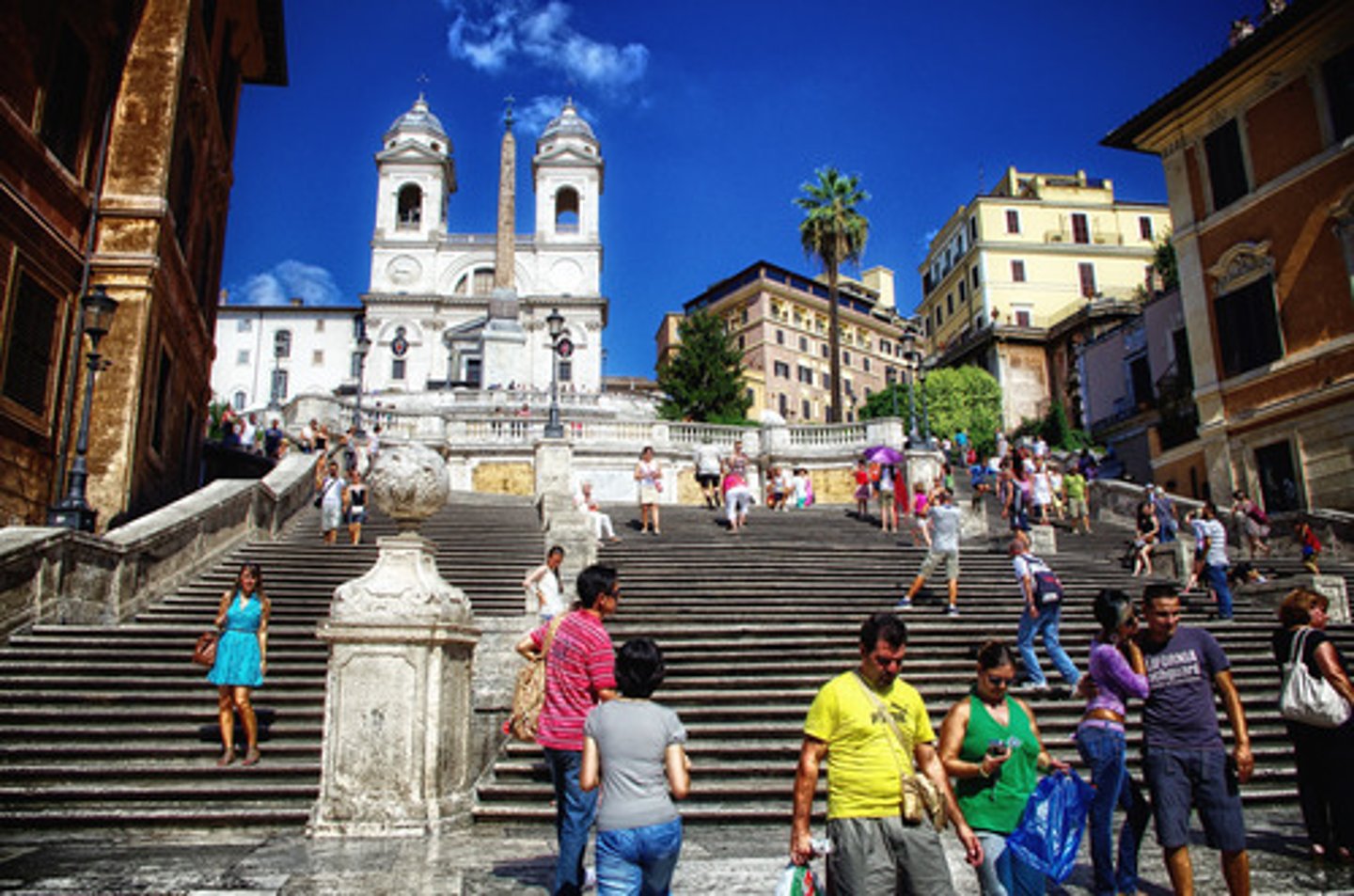
Spanish Steps
Rome, 1723-5

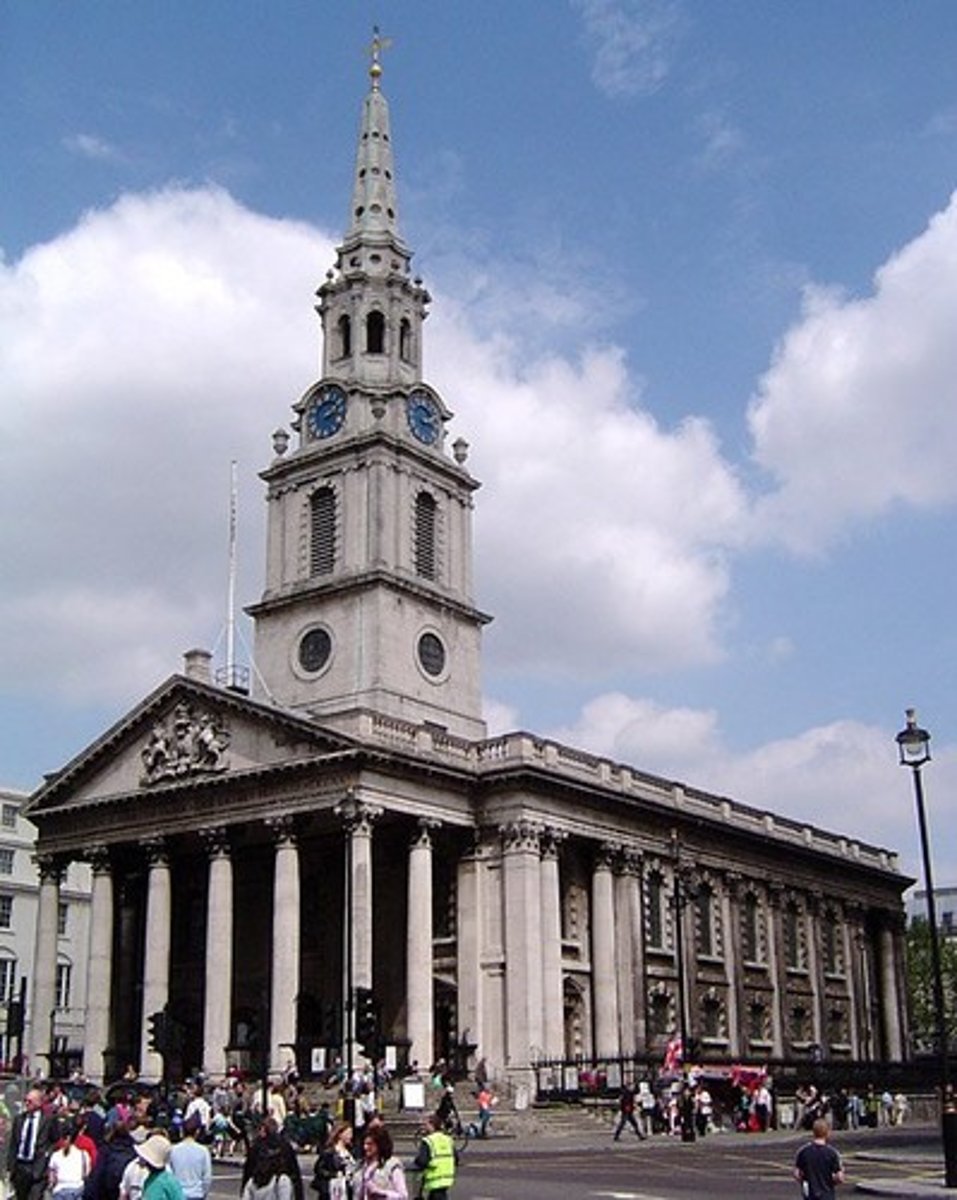
St. Martin-in-the-Field
London, 1722-6
James Gibbs design copied throughout US

Federal style
American version of Georgian after American Revolution
copied from British architect Robert Adams (1728-92)

Benjamin Latrobe
first architect in States
Baltimore Cathedral and U.S. Capital
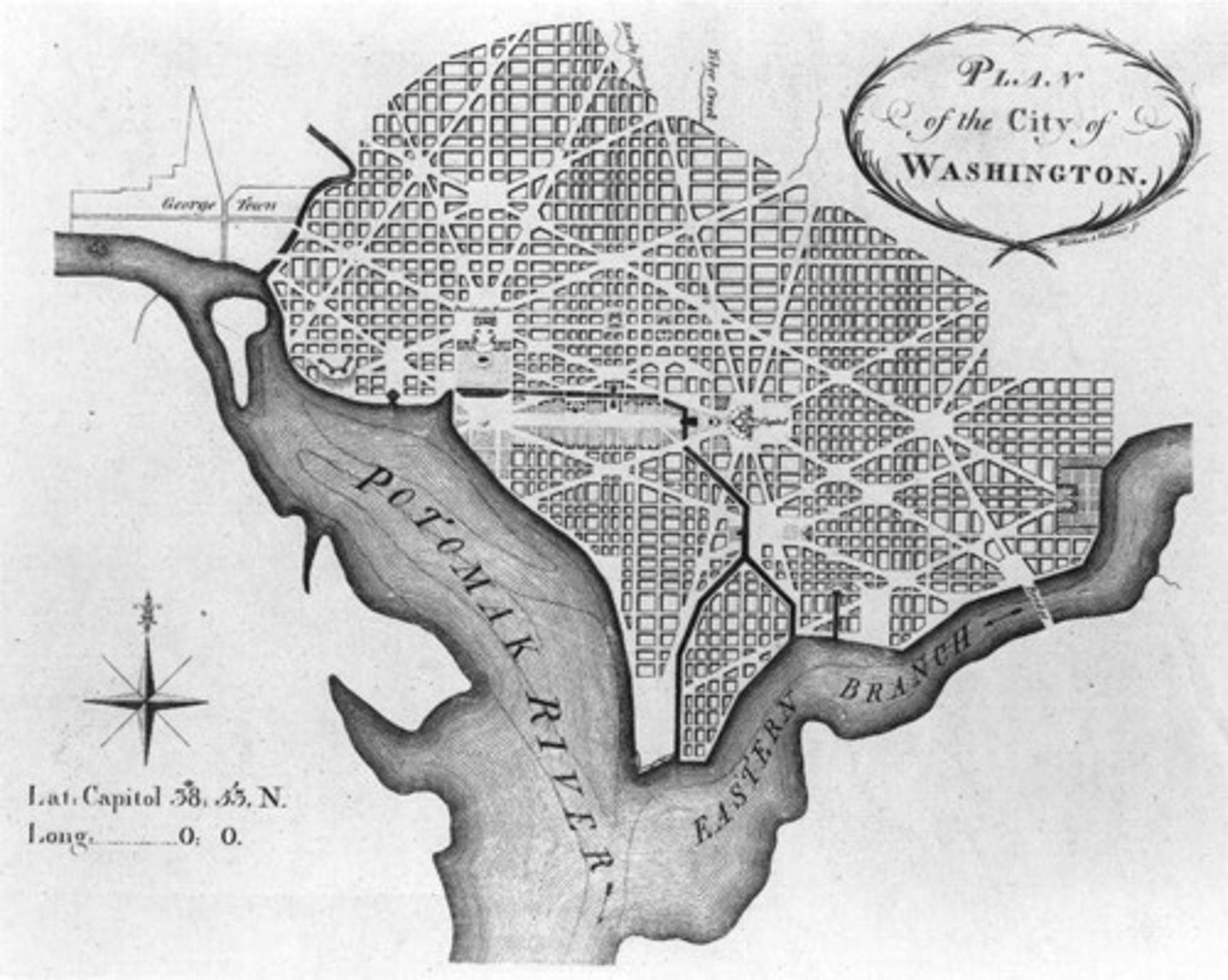
Pierre Charles L'Enfant
plan of D.C.
US & England going thru Greek revival
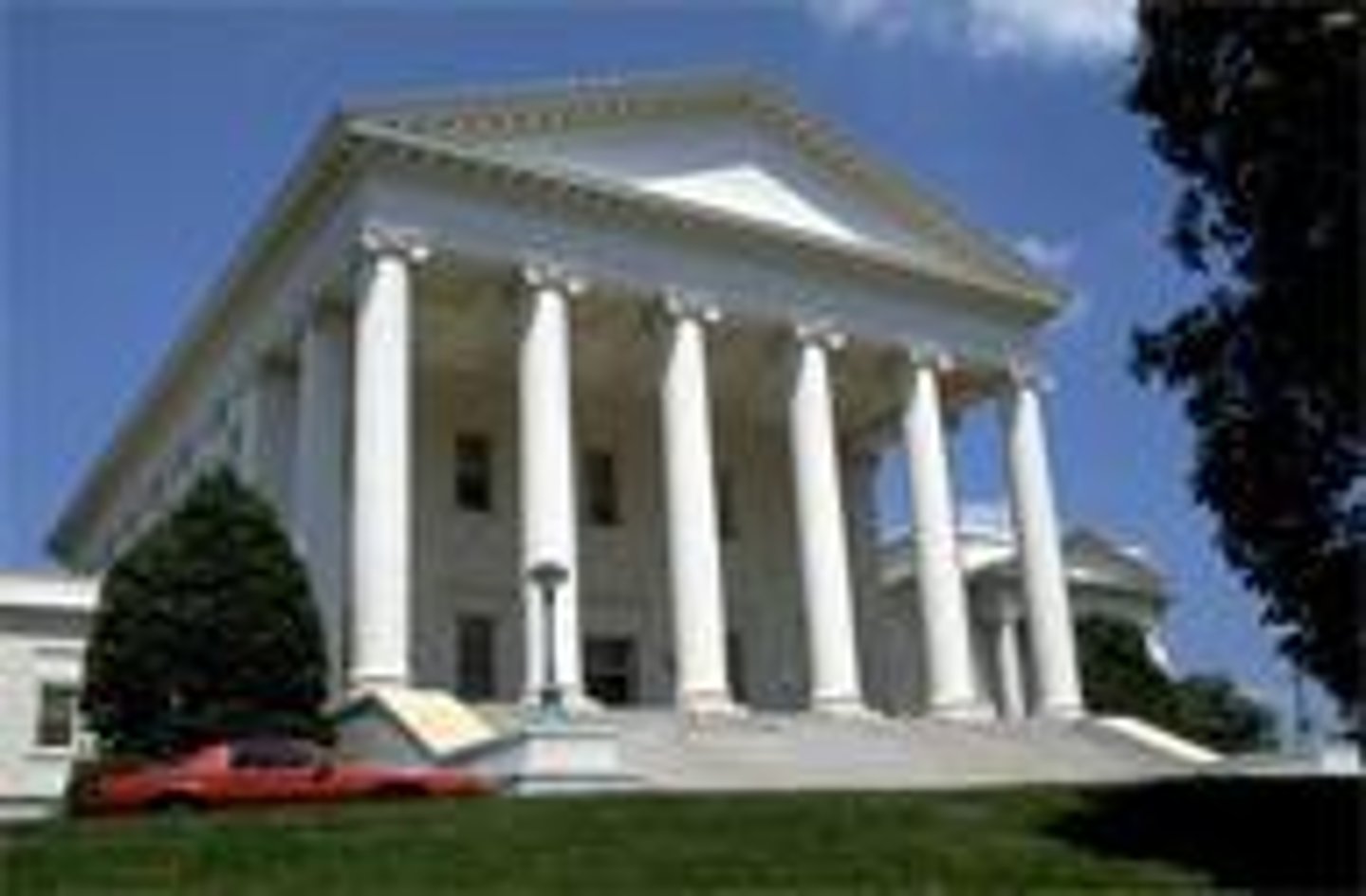
Virginia State Capital
1785-9; Jefferson
based on Maison Carree in Nimes

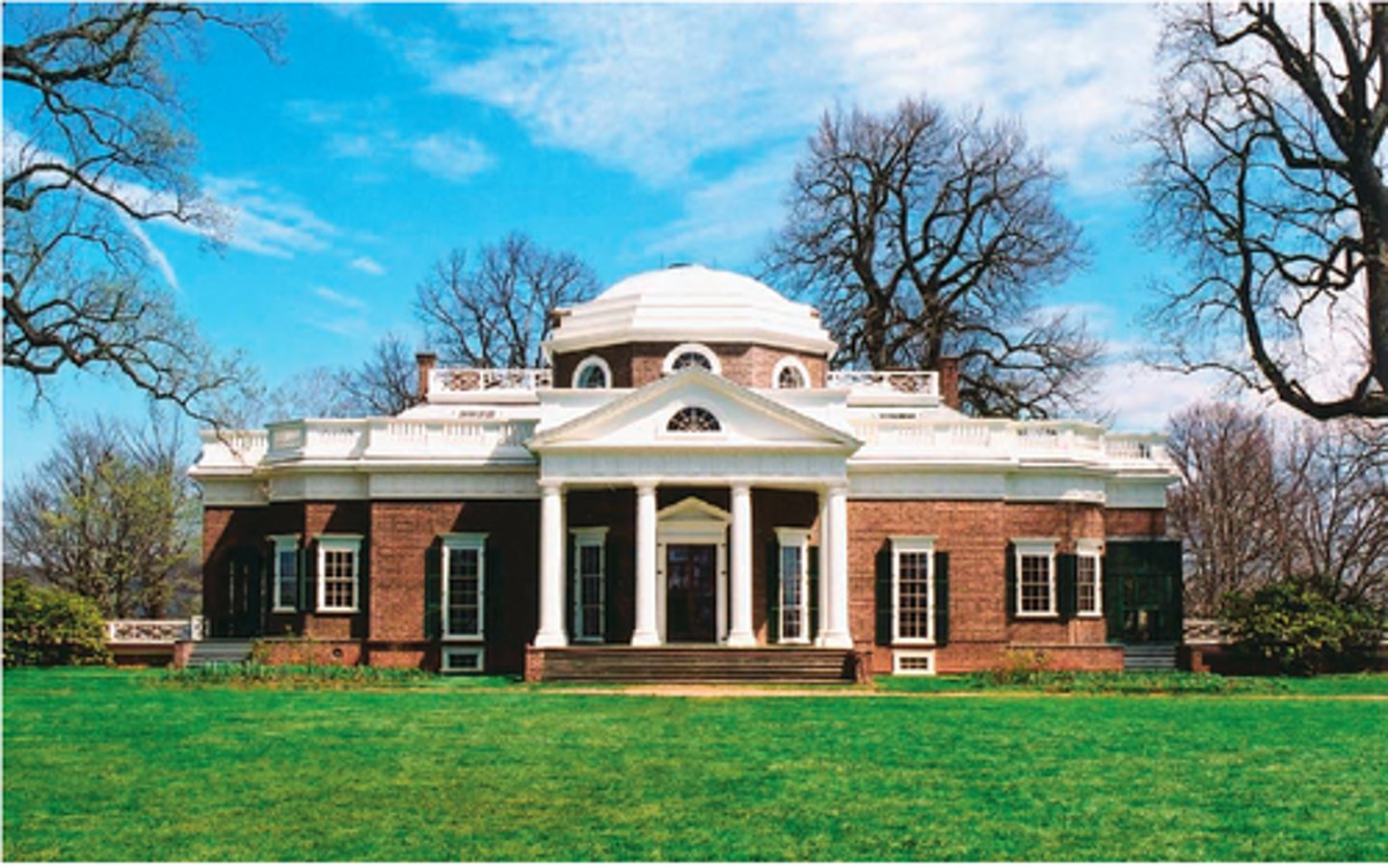
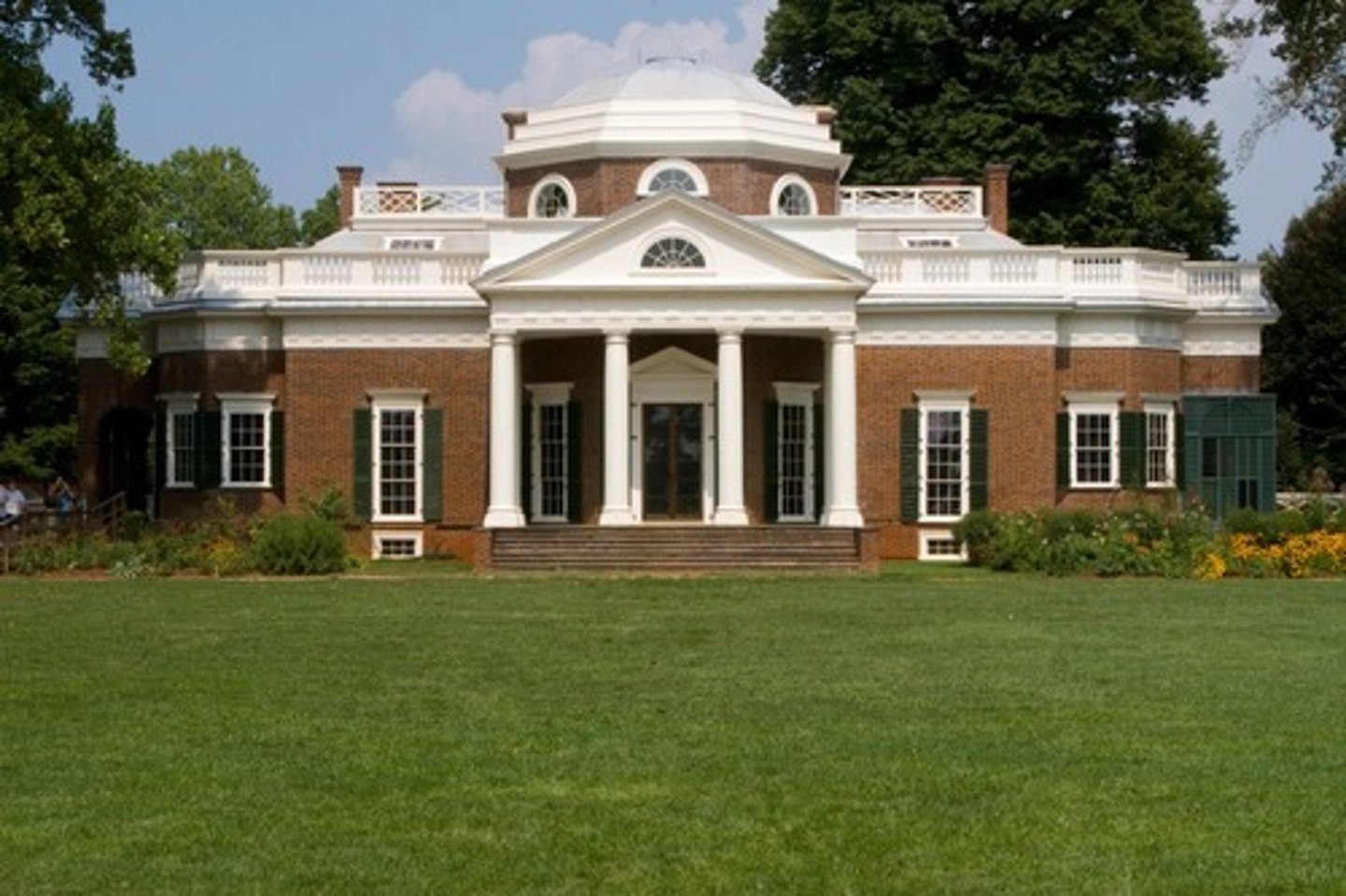
Monticello
1770; Jefferson
finished during presidency

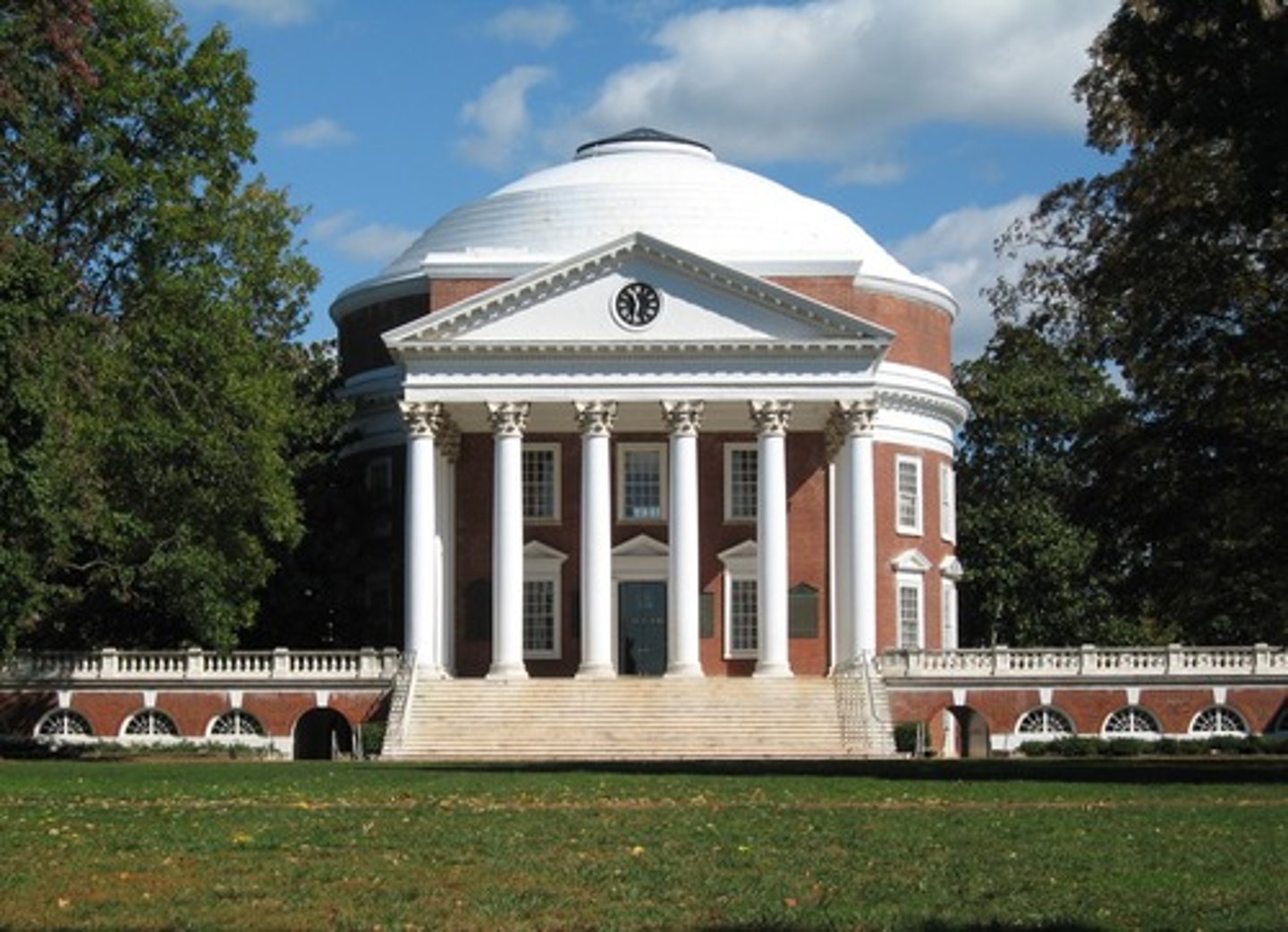
UVA
1817-26; Jefferson

Ecole des Beaux-Arts
first arch school
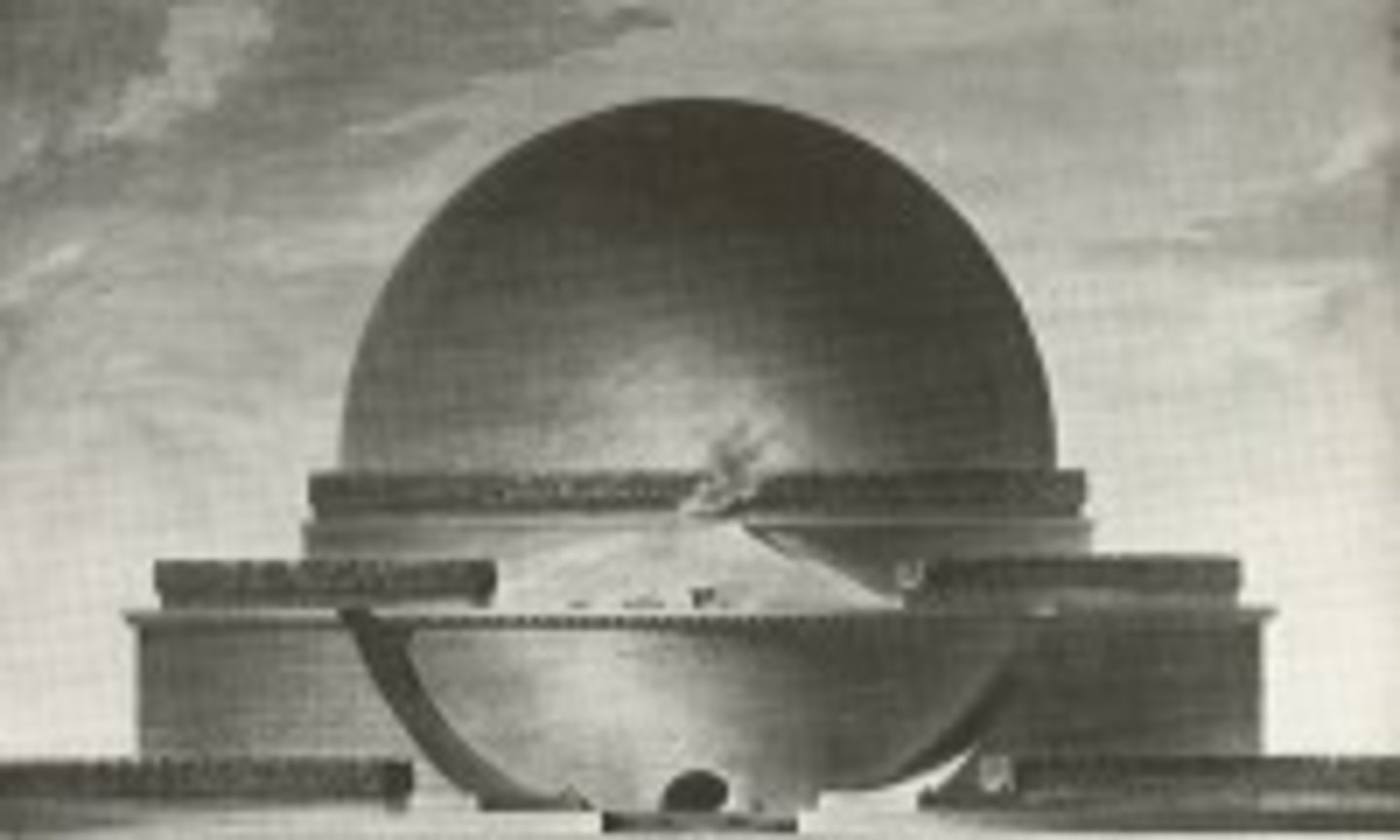
Etienne-Louis Boullee
1728-99
Monument to Newton

Charles-Nicholas Ledoux
1736-1806
Viollet-le-Dec
1814-79
leading proponent of Gothic revival in France
Carpenter Gothic
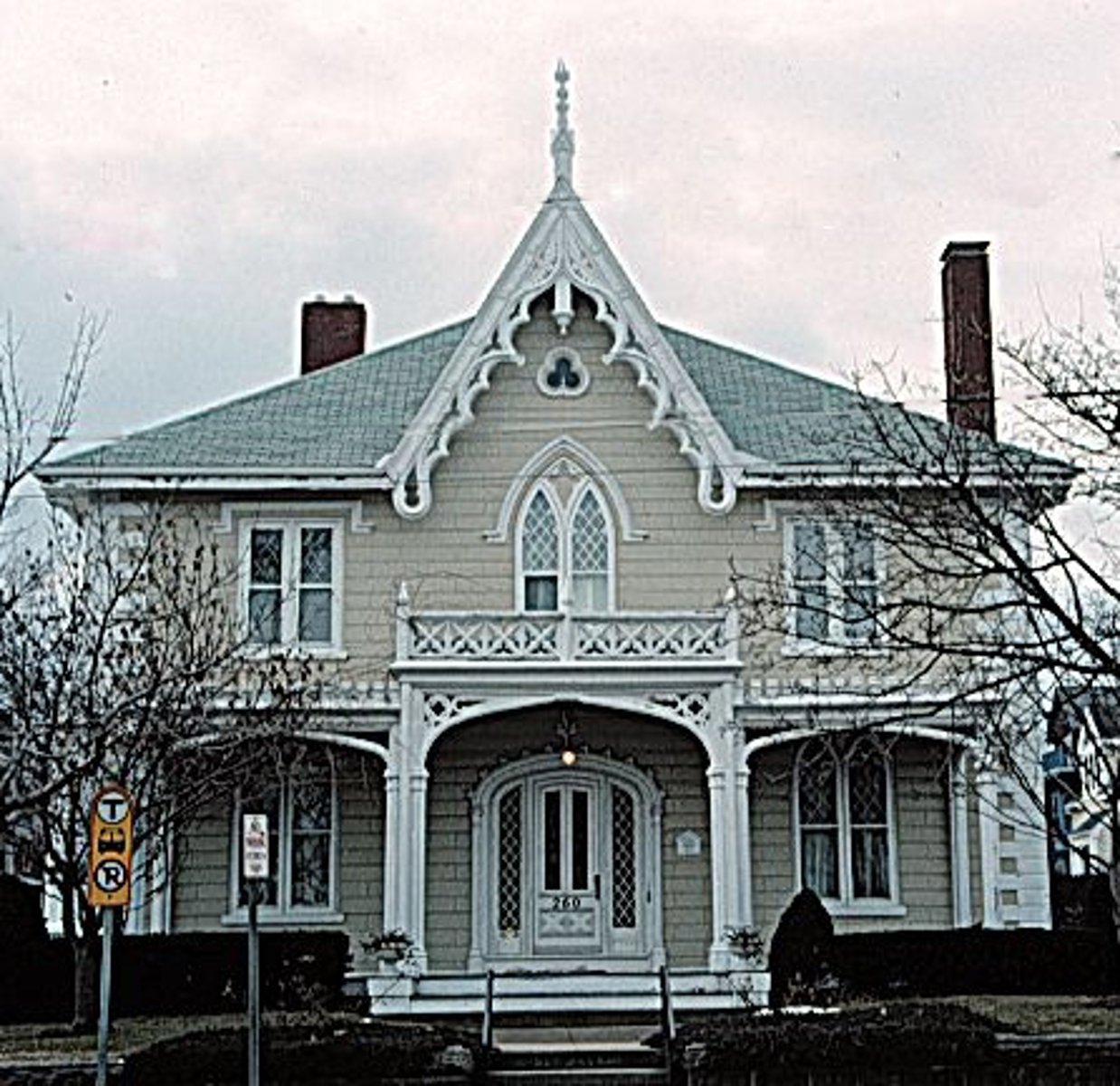

Richardson Romanesque
Henry Hobson Richardson
Trinity Church (1872-7) Boston
Nationalism
want to establish identity through arch using historical references
Crystal Palace
London, 1851; Joseph Paxton
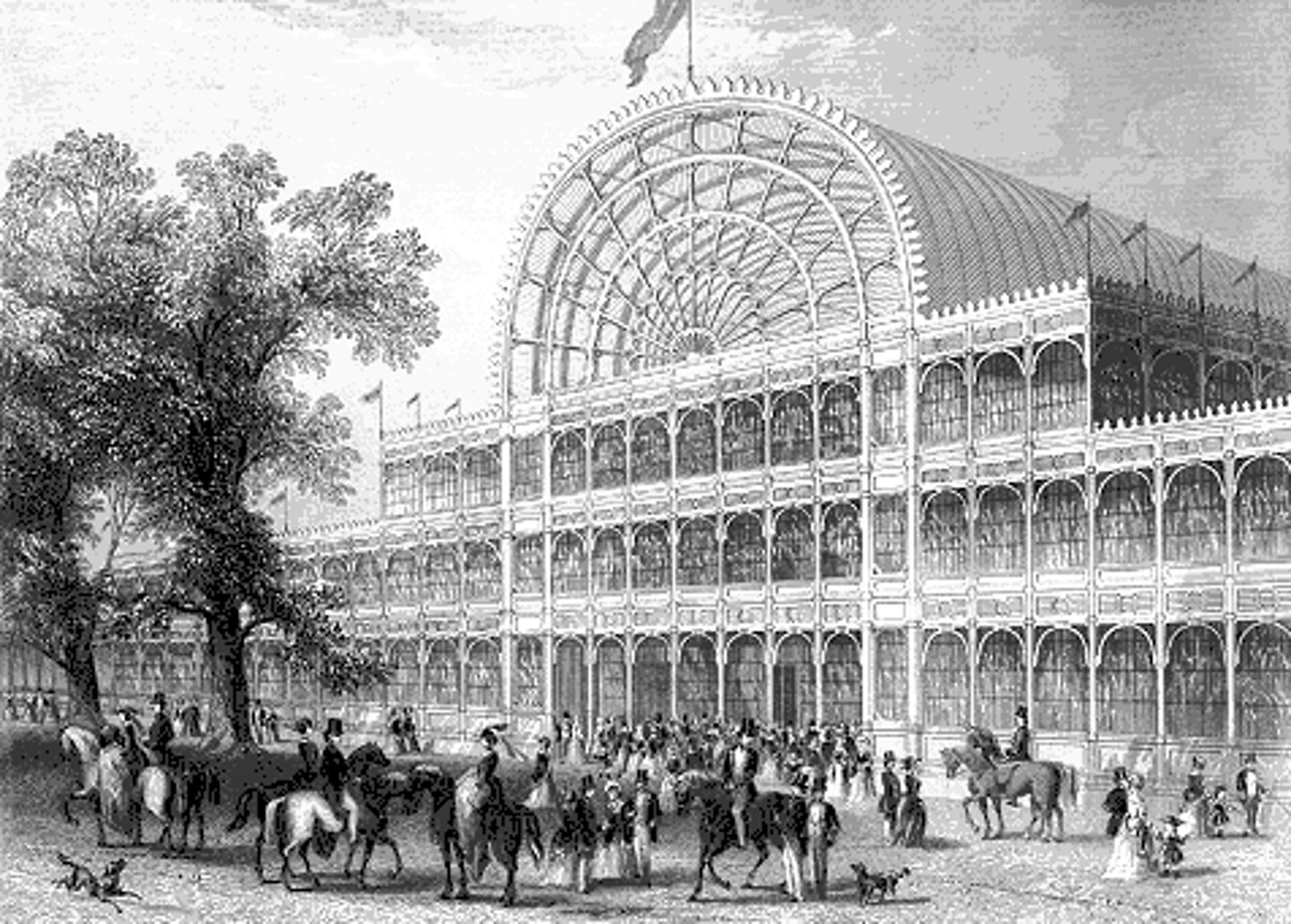

Joesph Paxton
horticulturalist
modular parts that could be disassembled and reassembled
Bibliotheque Ste. Geneieve
1842-50, Paris; Henri Labrouste
symbolic of train station; journey to knowledge
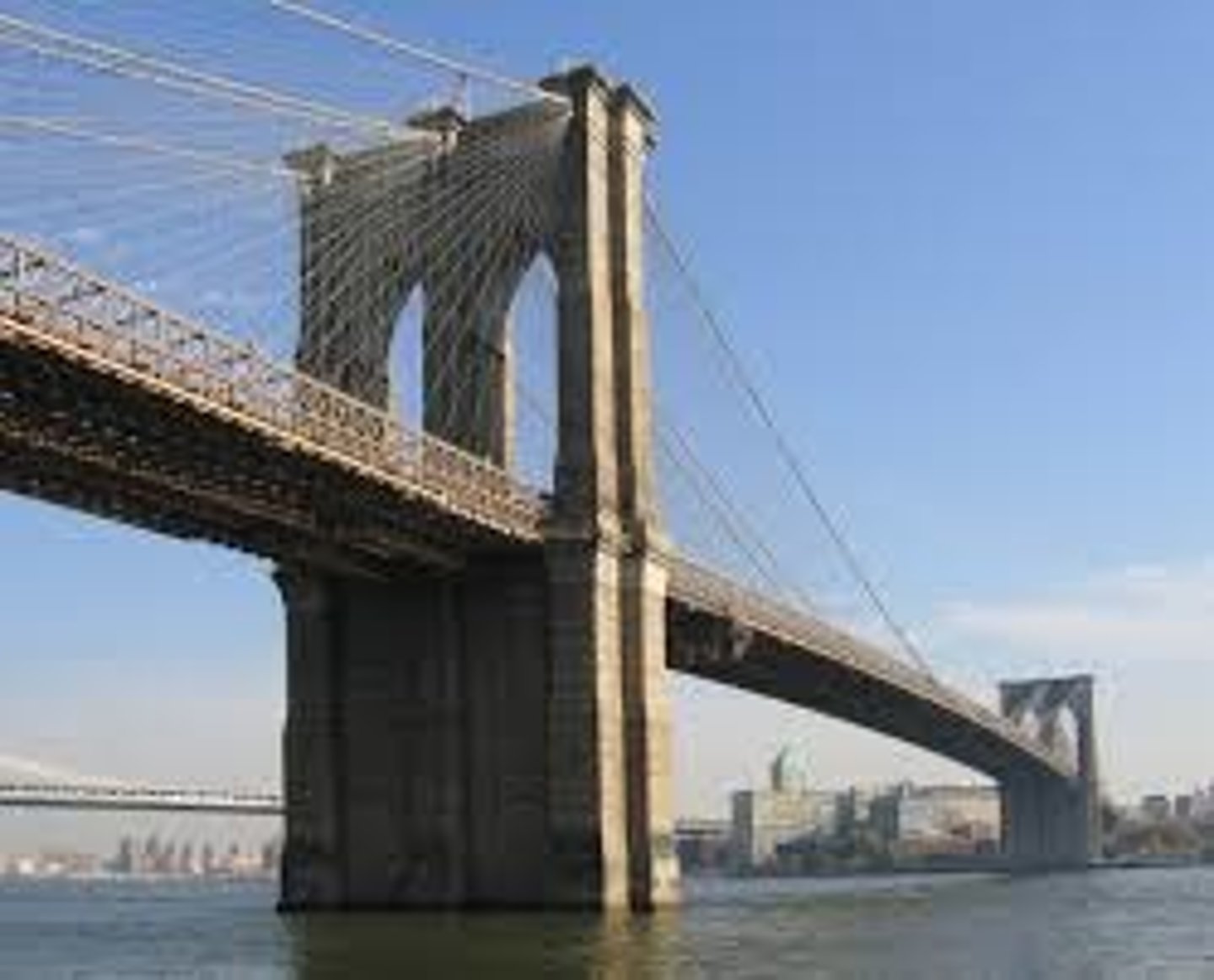
Brooklyn Bridge
1869-83, New York
suspension bridge by tension

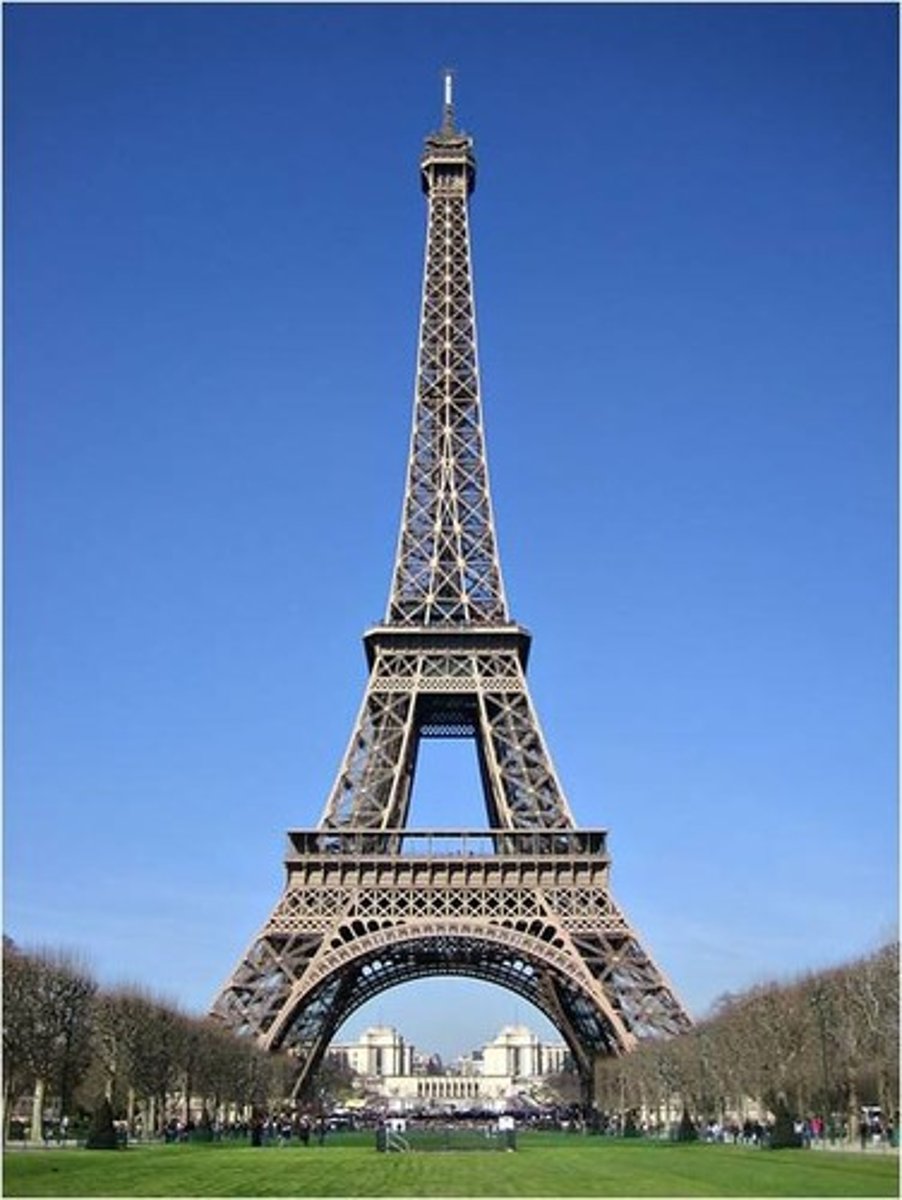
(Gustav) Eiffel Tower
1885, Paris
iron construction

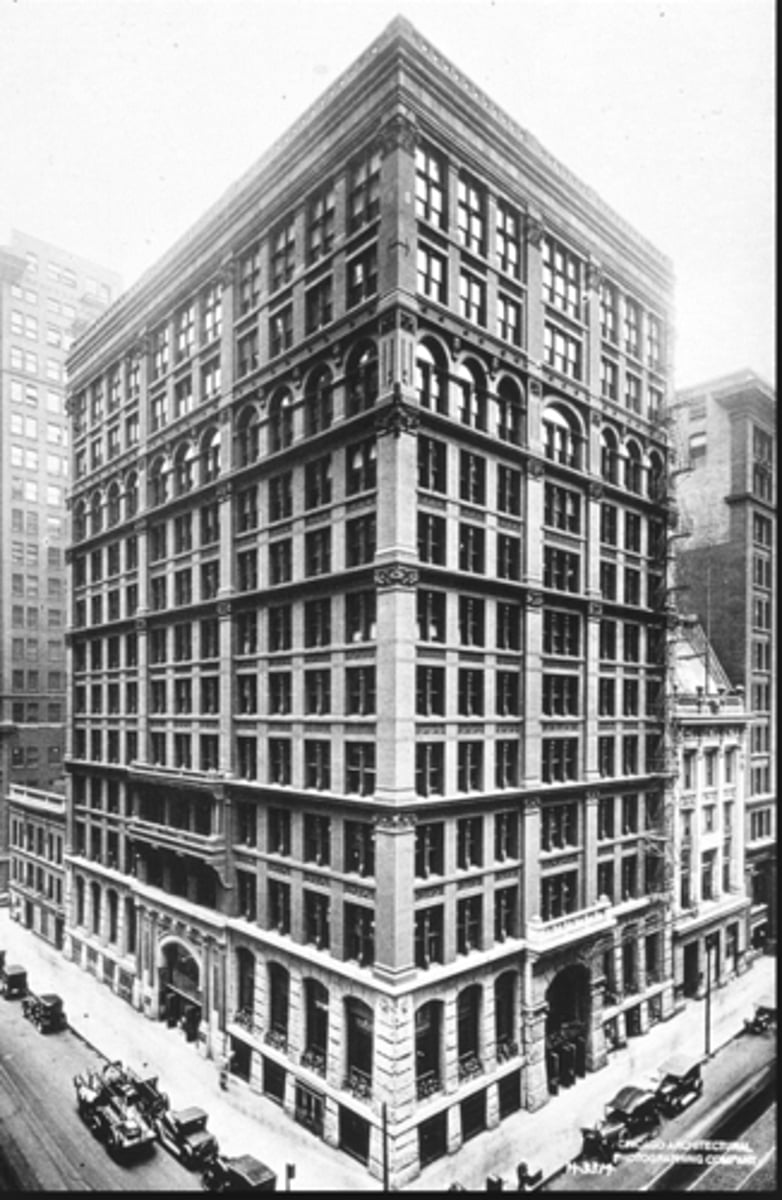
Home Insurance Building
1883
1st skyscraper

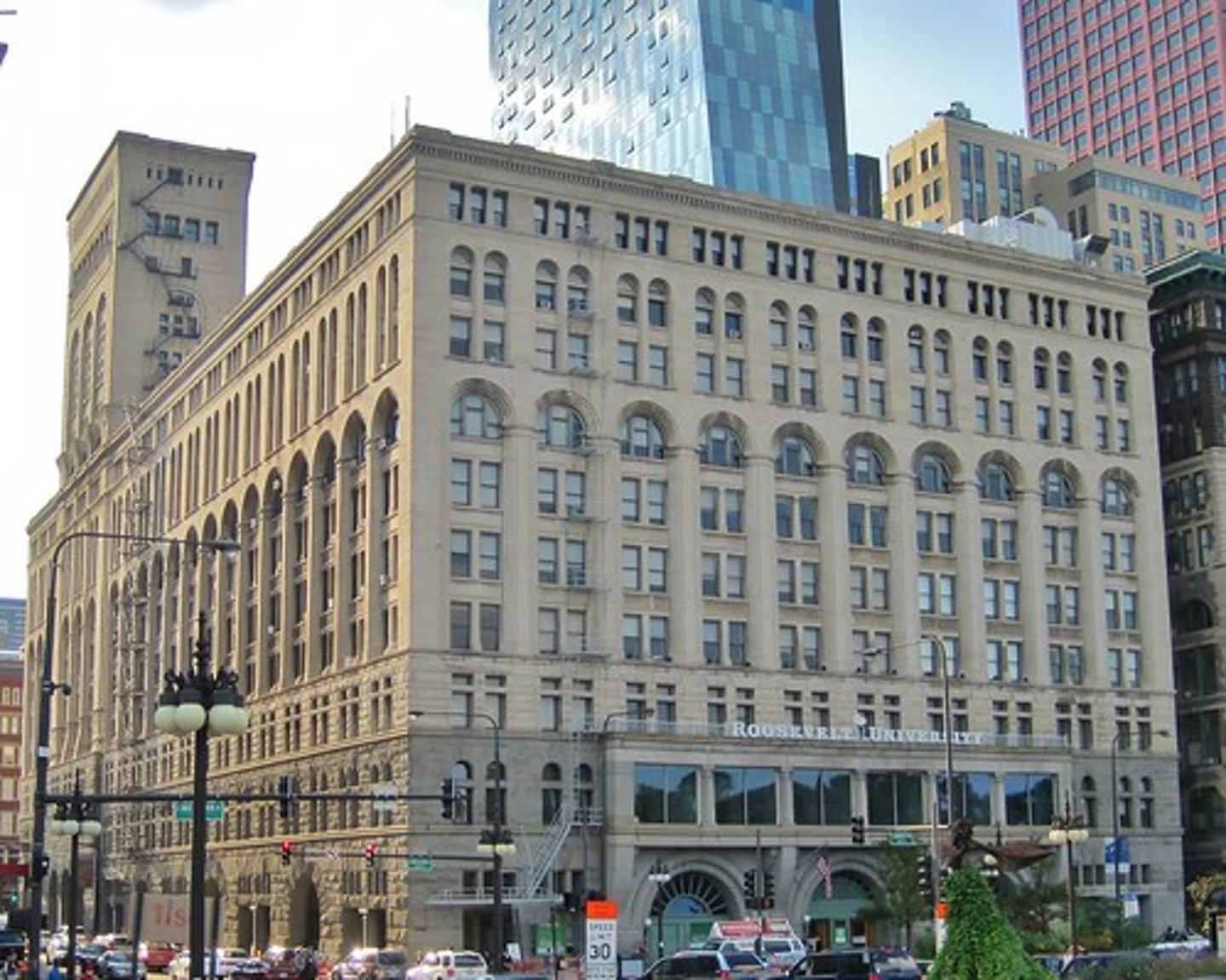
Louis Sullivan
celebrate and express vertically in highrises
3 zones on facade
light curtain wall
Chicago Opera House
Sullivan

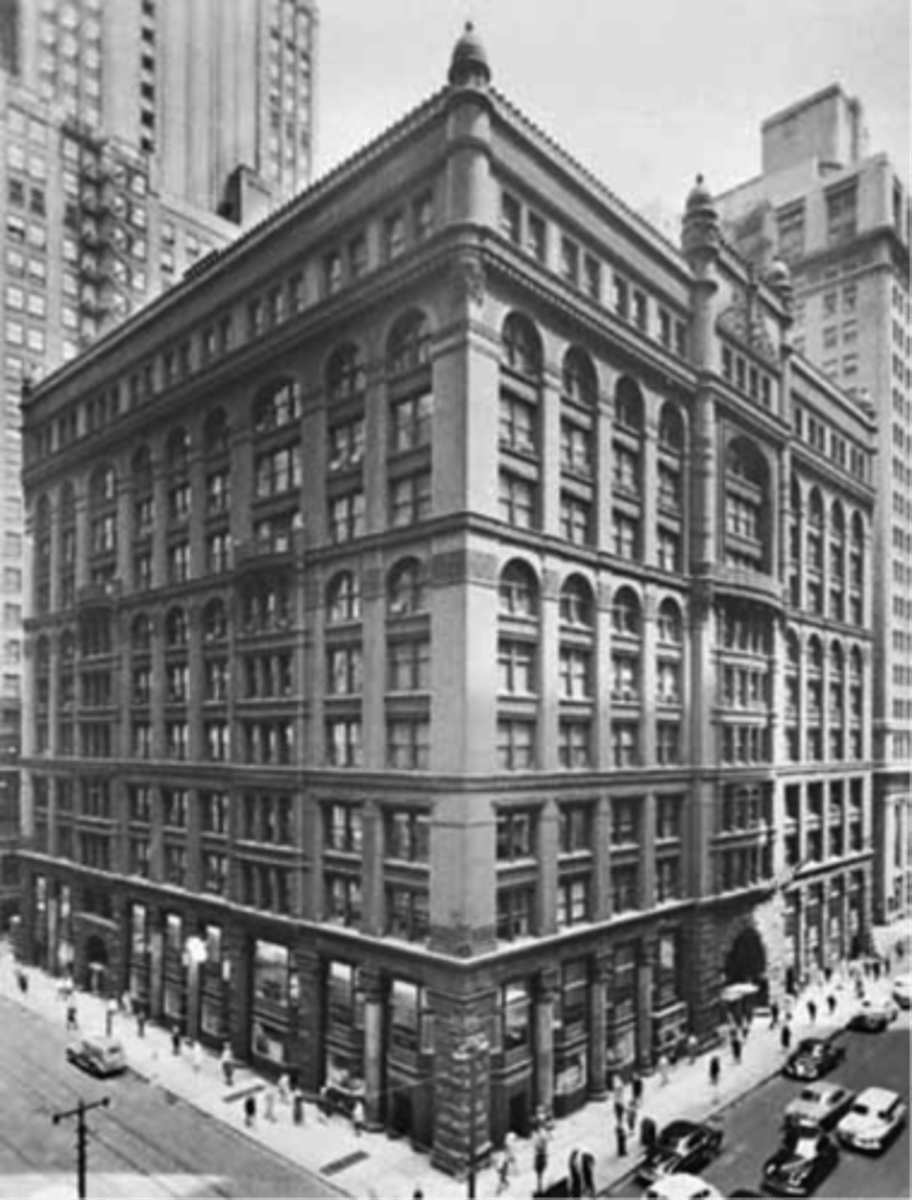
Burnhan & Root
Chicago

Fredrick Law Olmsted
Father of Landscape Arch
designed Central Park
designed grounds of Biltmore
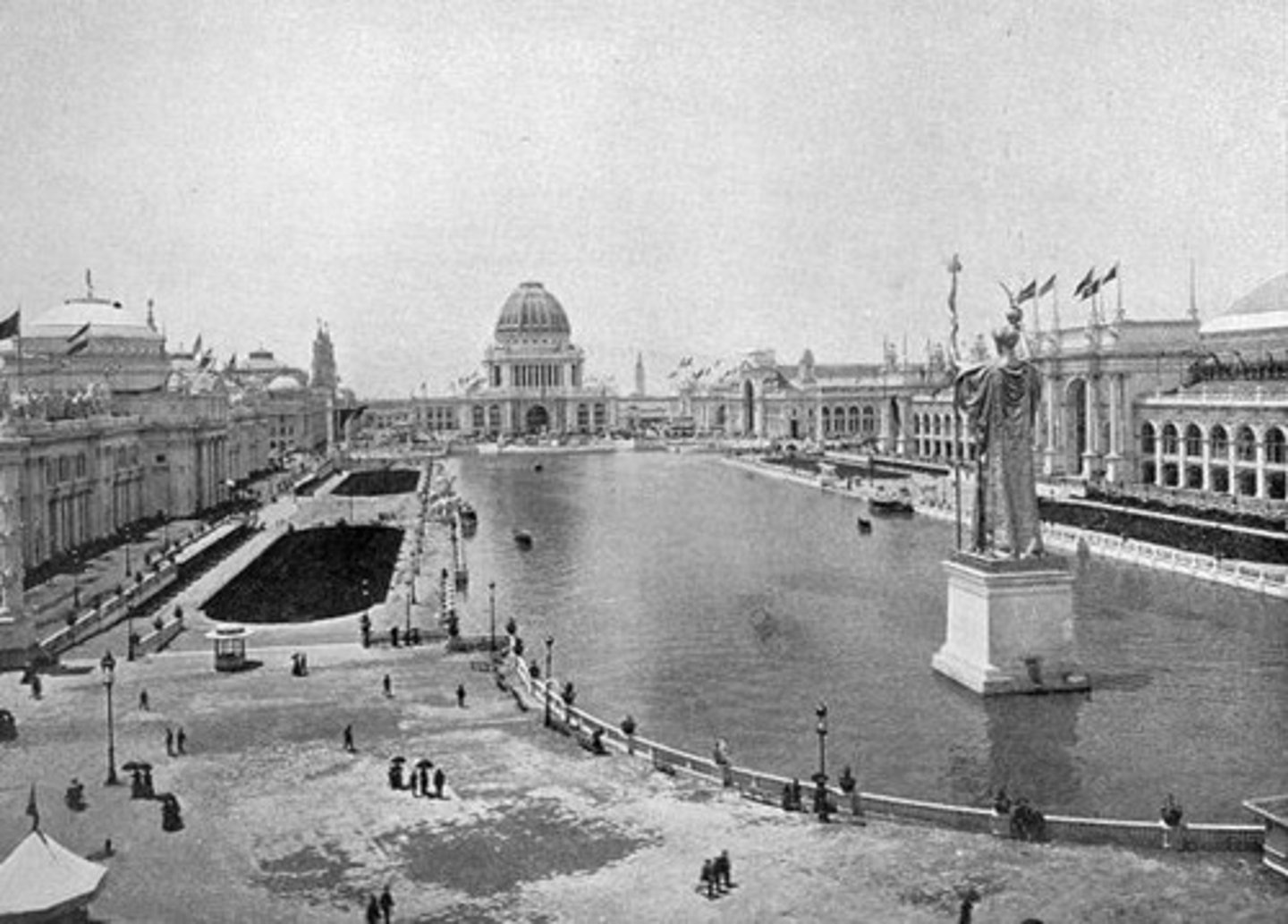
Columbia Exposition of 1893 in Chicago

Frank Lloyd Wright
1869-1959
American/Chicagoan Arch
most significant American arch in 20th C
3 stylistic developments
1. early work - "arts and crafts" derived style
2. "prairie" style - modern horizontal, interwoven spaces
3. mature style - more expressionistic
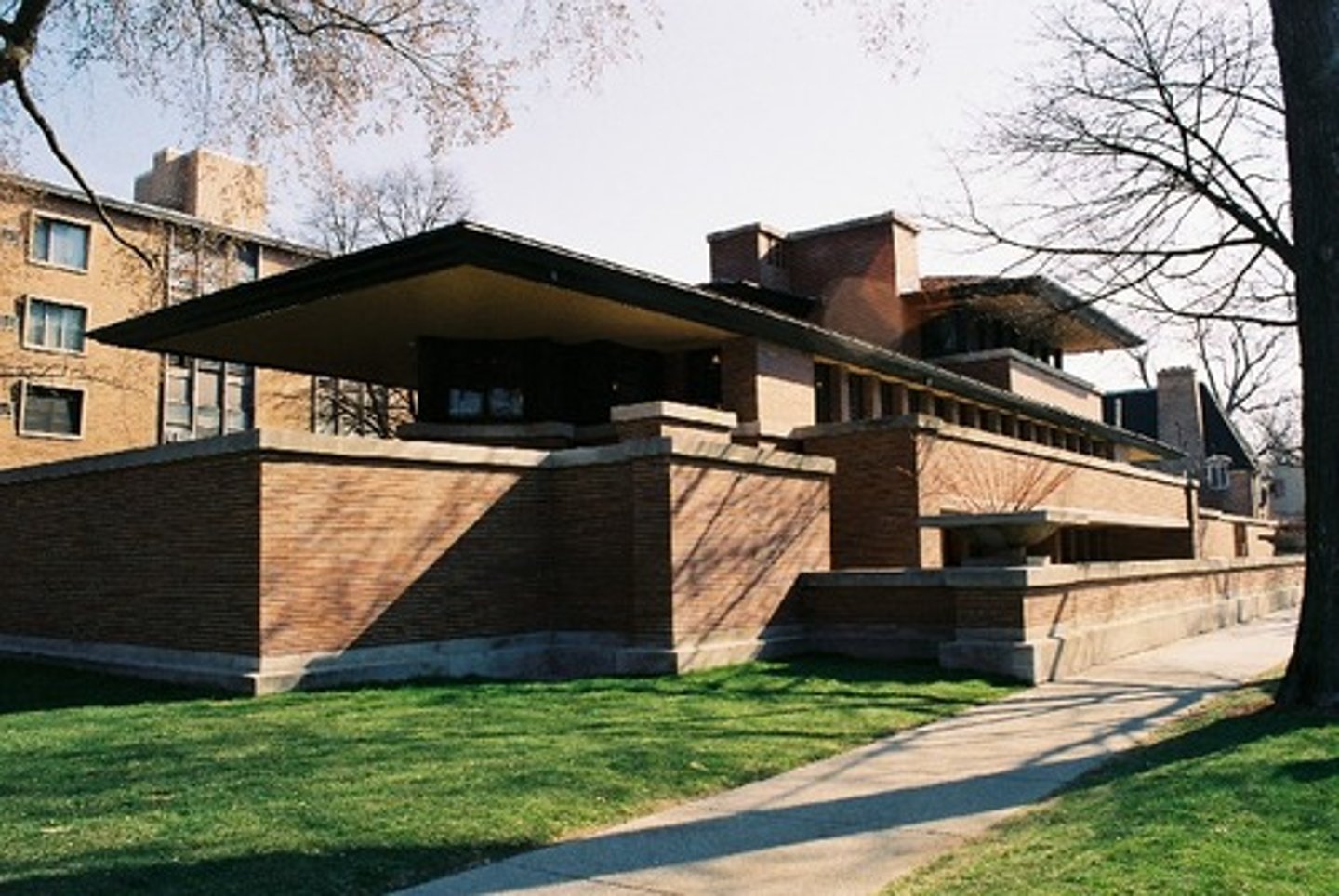
Robie House
1908-9
FLW

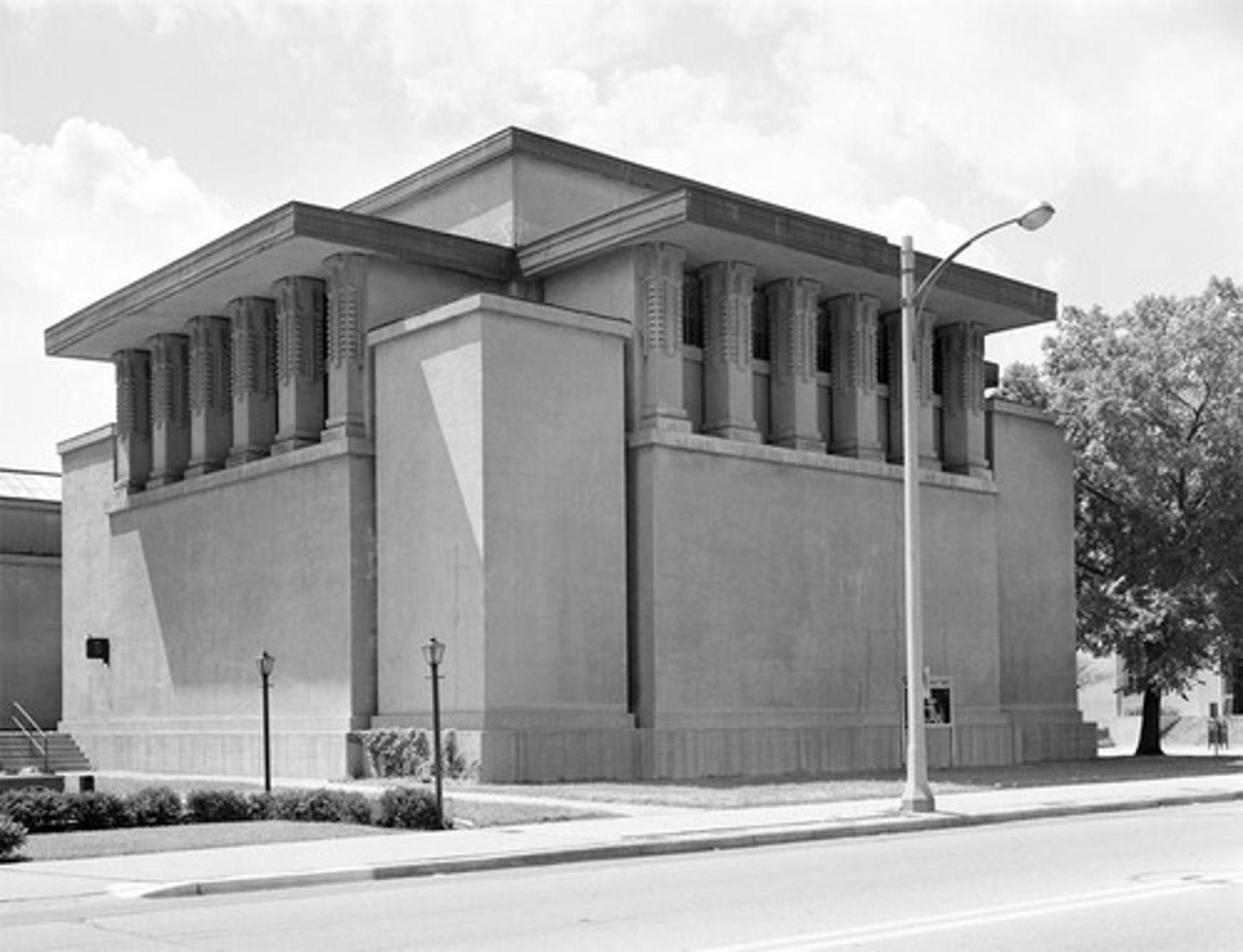
Unity Temple
1909
FLW

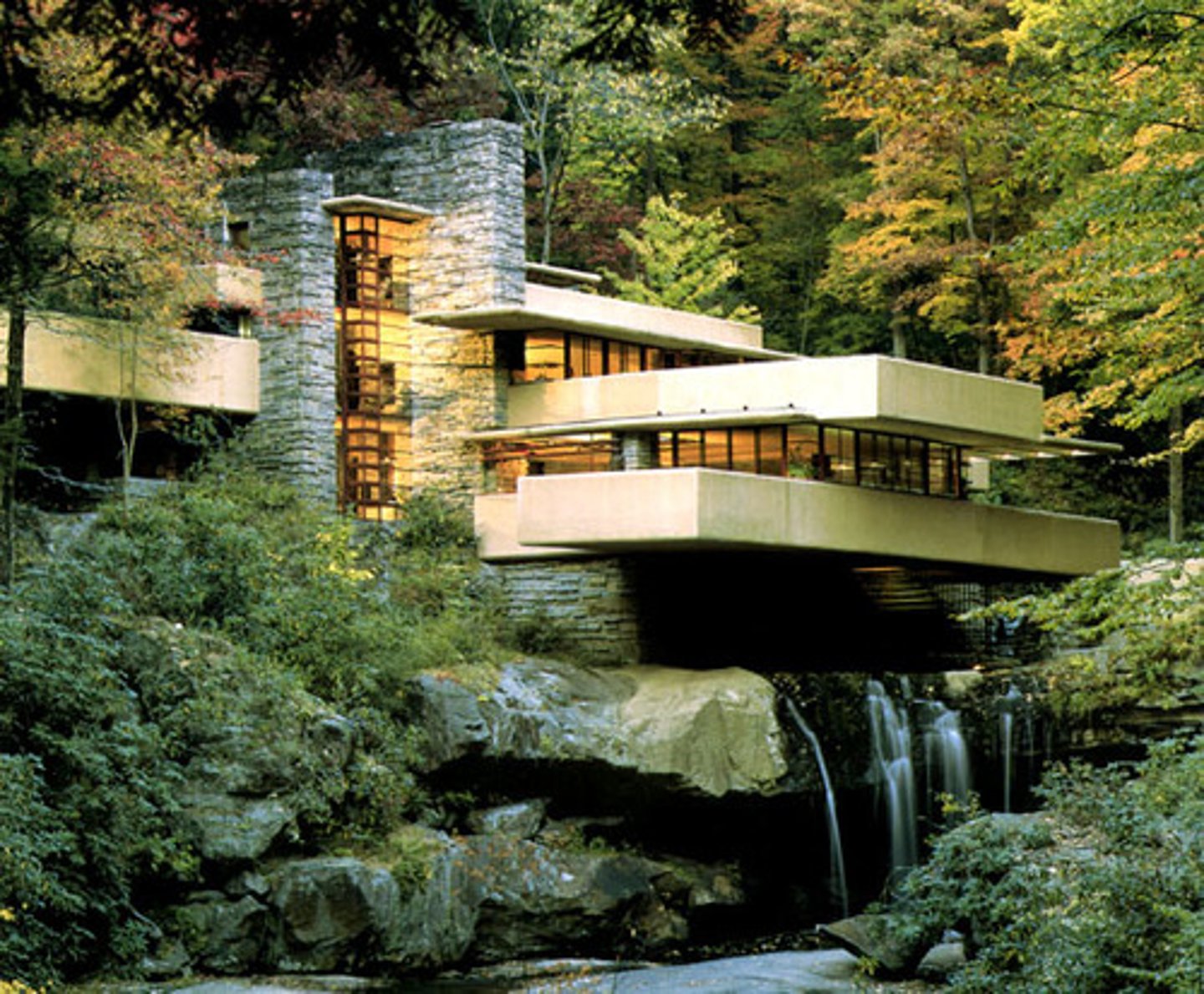
Falling Water
1934-7
FLW

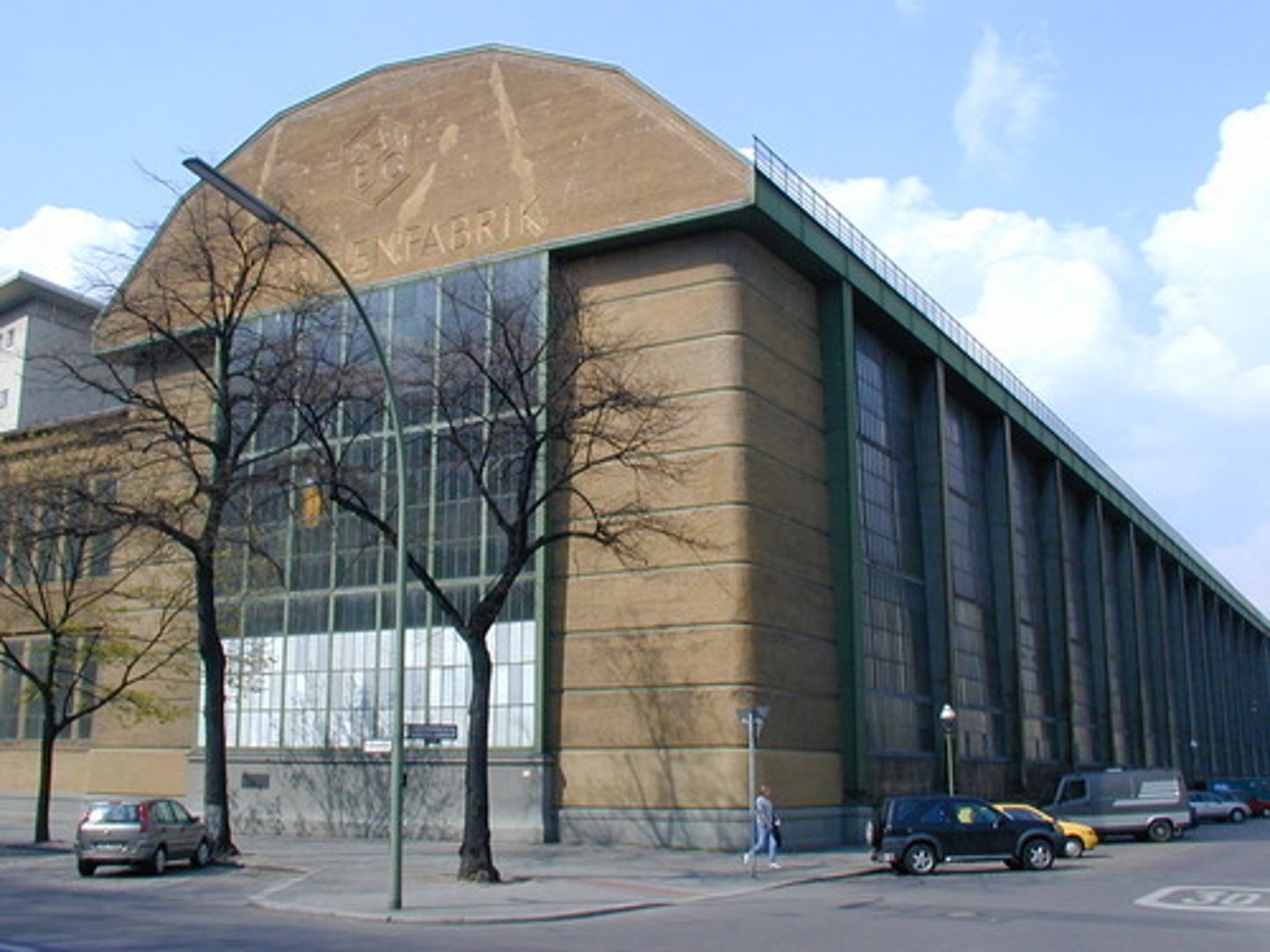
AEG Turbine Factory
Berlin, 1909; Peter Behrens

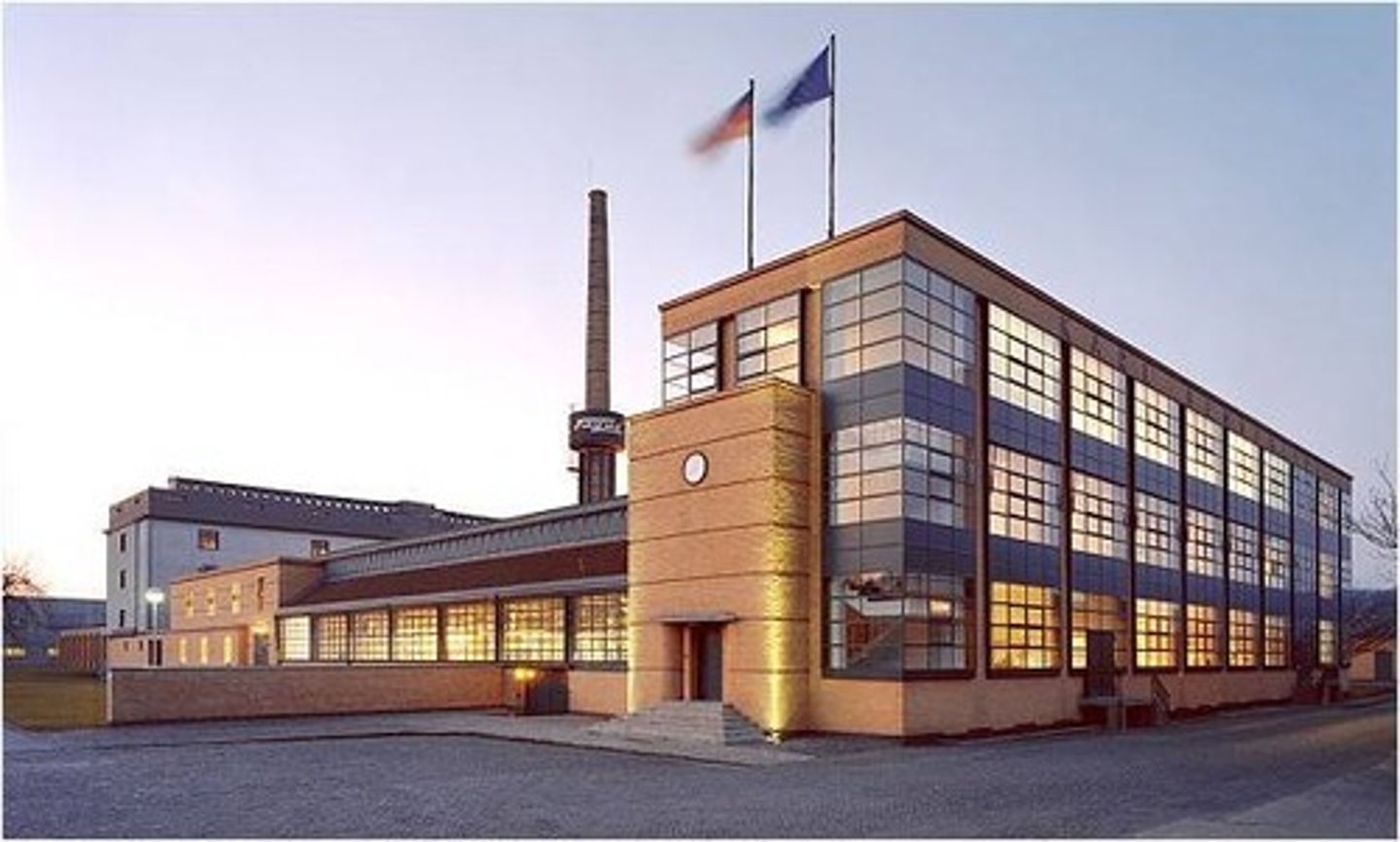
Fagus Factory
Germany, 1911; Walter Gropius

International Style
designing buildings for the world theoretically: an abstract style that can fit anywhere
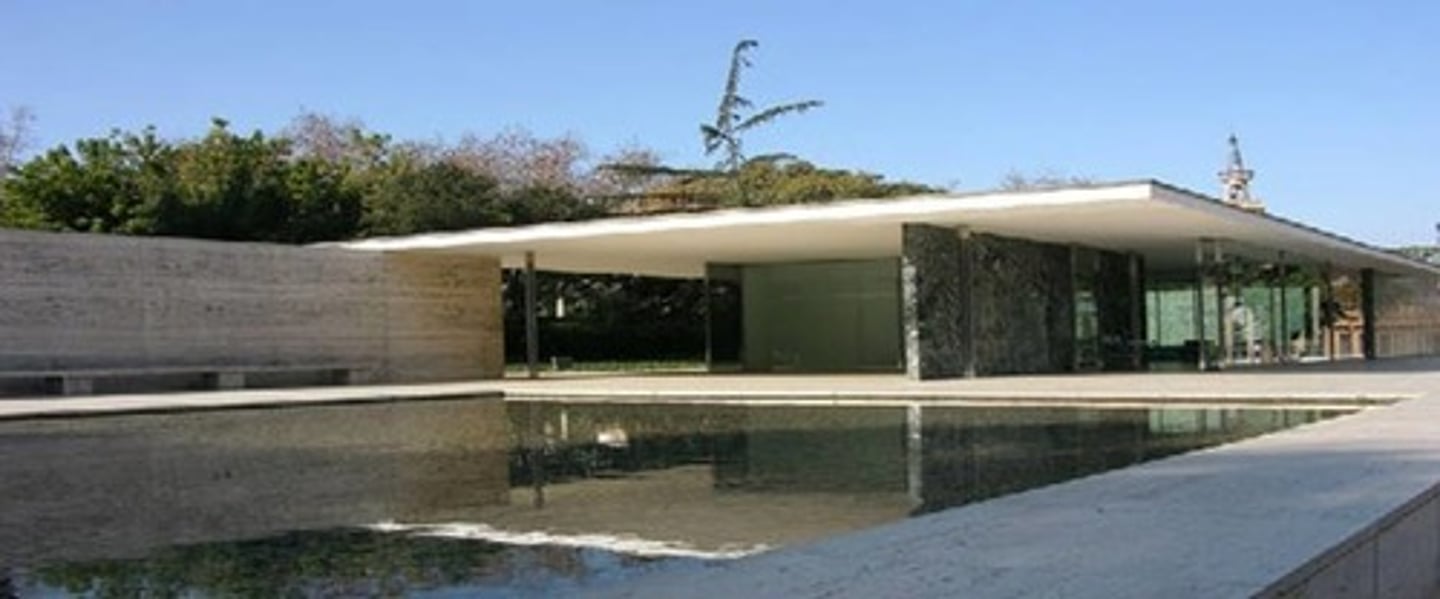
Barcelona Pavilion
Ludwig Mies van der Rowe

Bauhaus
school in Ger. (1919 by Walter Gropius)
huge influence on modern architecture
concept: art, design, & construction are united
promoted "form follows function"
political purpose - housing for masses
about the collective
Piet Mondrian
Dutch painter; 1872-1944
figures in dev. of 20th C abstract art
BANISHED from his work
1. natural objects
2. 3-D pictorial space (perspective)
3. curved lines
4. sensuous qualities of texture & color
Le Corbusier
Charles-Édouard Jeanneret-Gris
French architect 1887-1966
one of the most significant architects of the modern architecture & the 20th C art movement
"Maison Dom-Ino"
complete reduction of a house to element form
idea of the universal house
cities and urban landscape designed the same way
GRID form representing modernity, newness, and efficiency
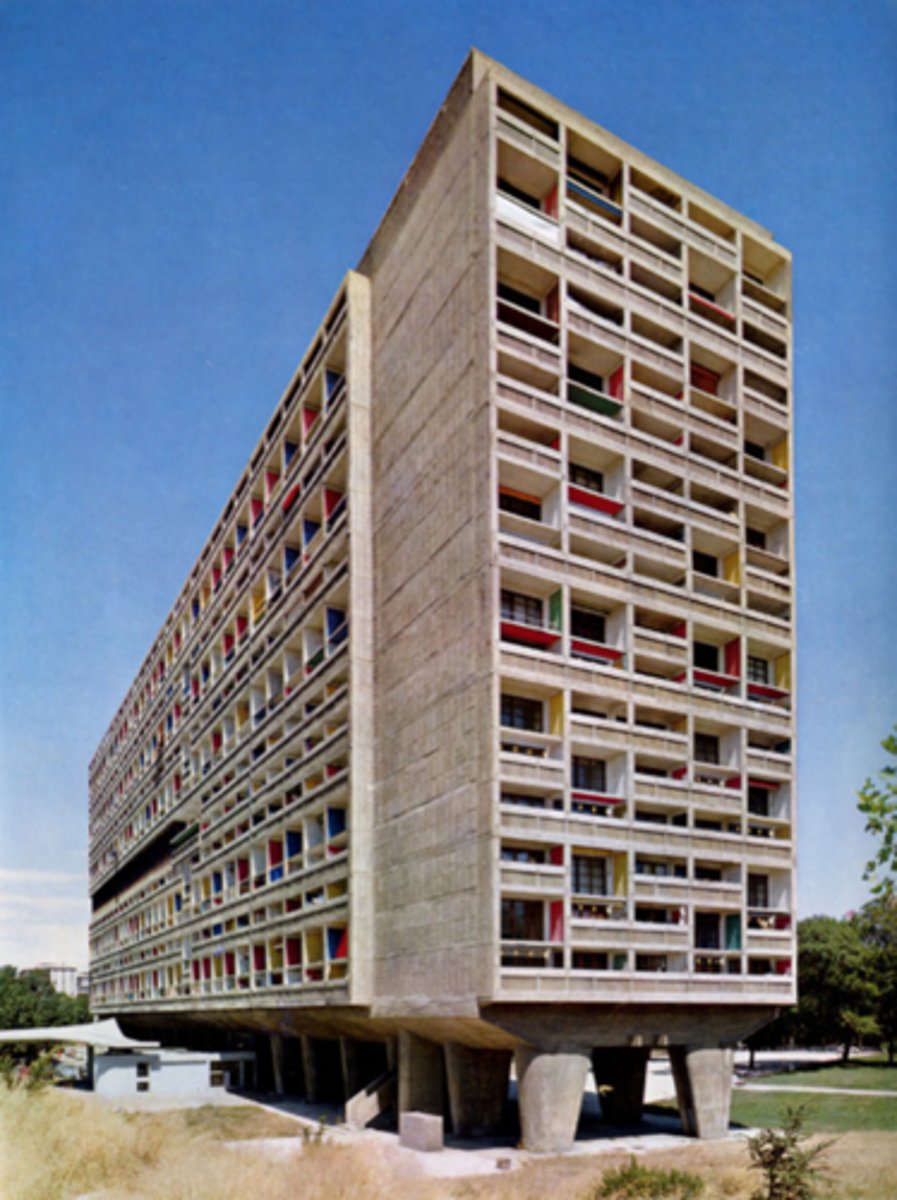
Unite d'habitation
1953-5; Le Corbusier

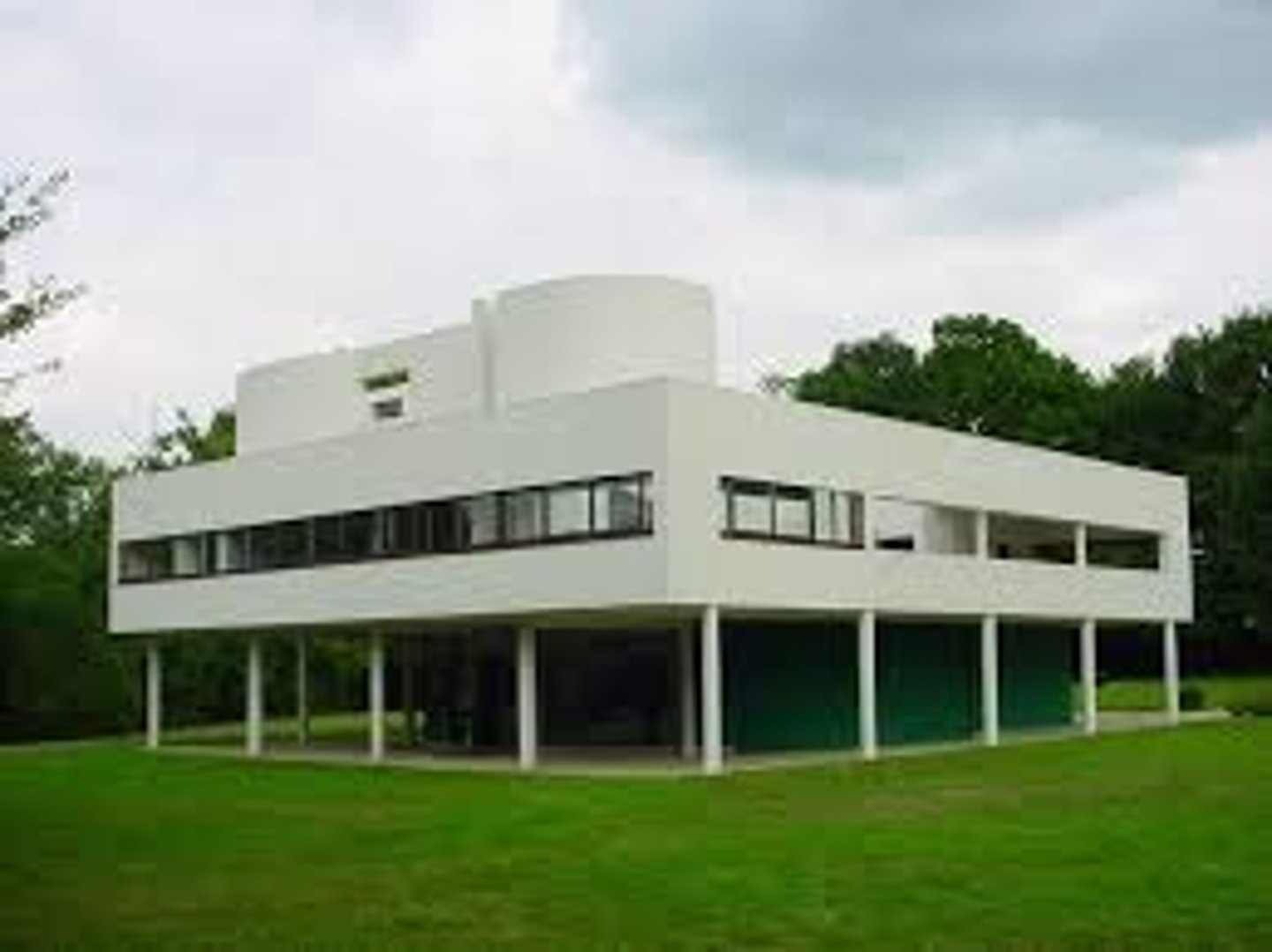
Villa Savoye
1929-31; Le Corbusier

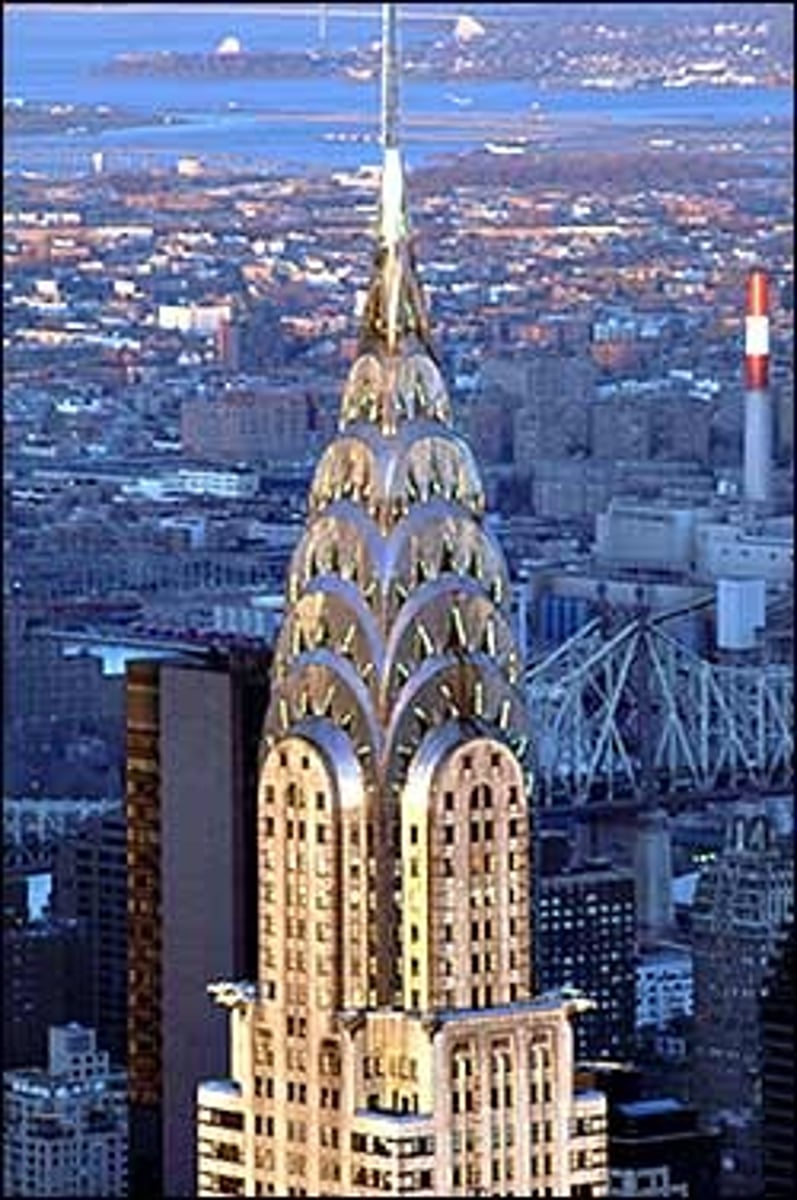
Chrysler Building
1930; William Van Alen

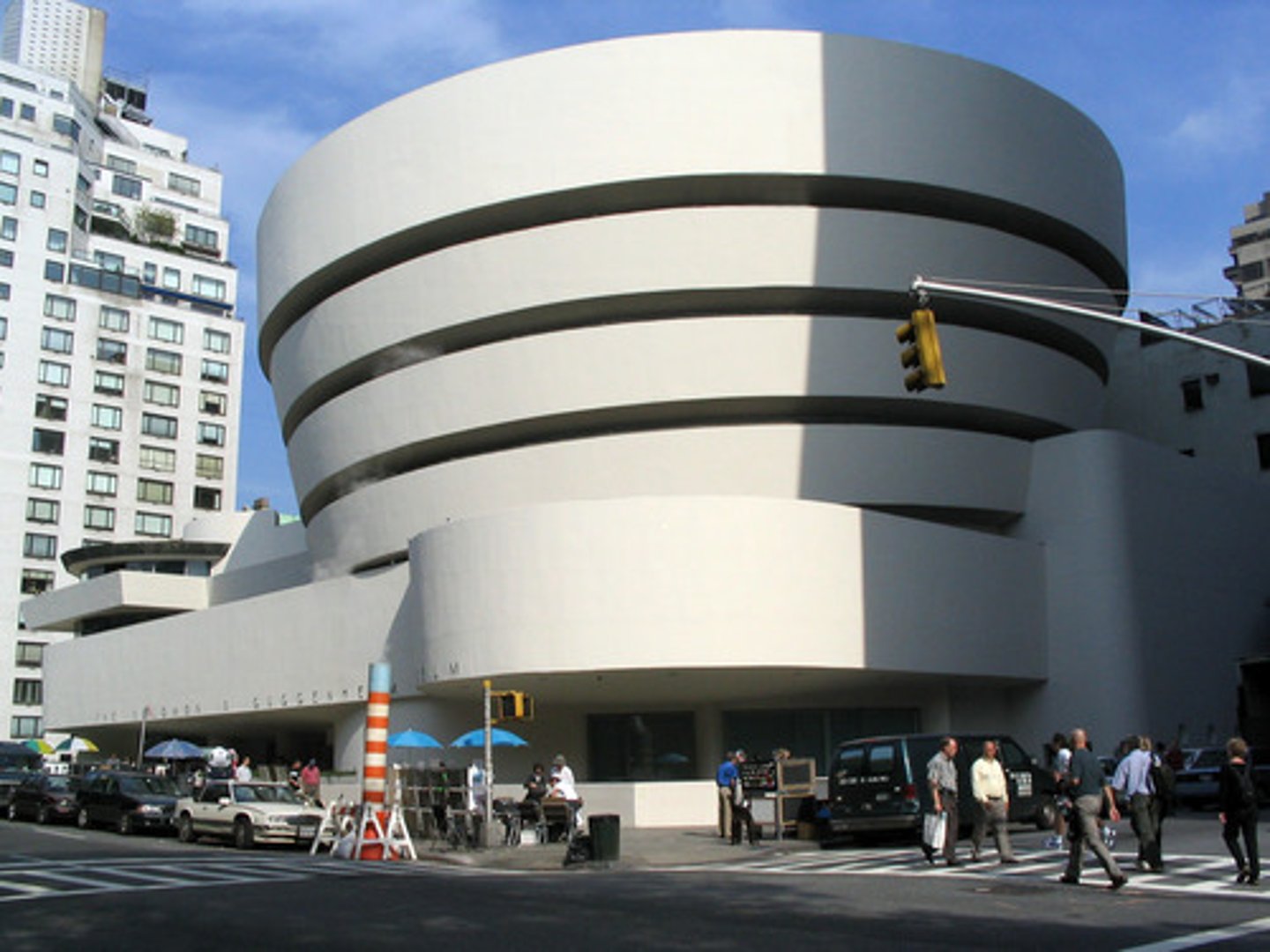
Guggenheim Museum
1943-59; FLW

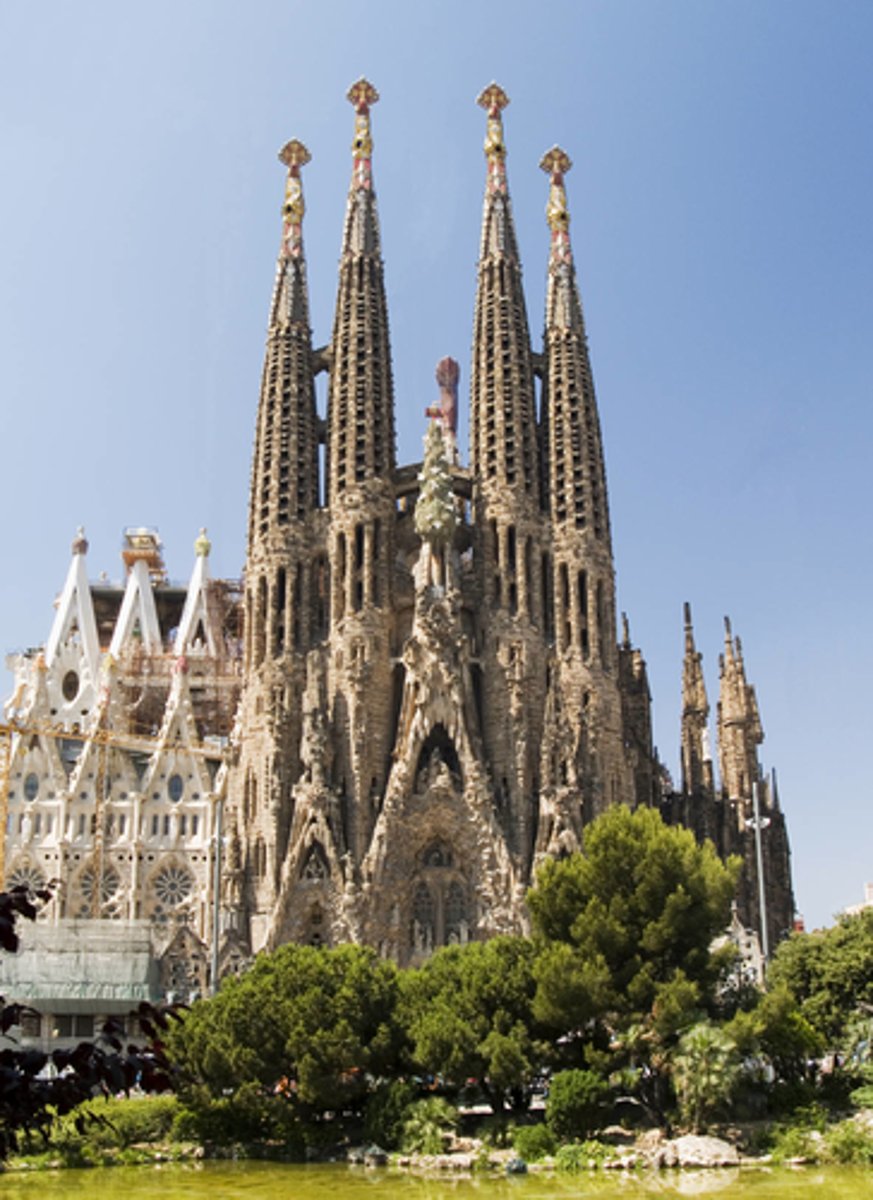
Church of Sagrada Family
Antoni Gaudi

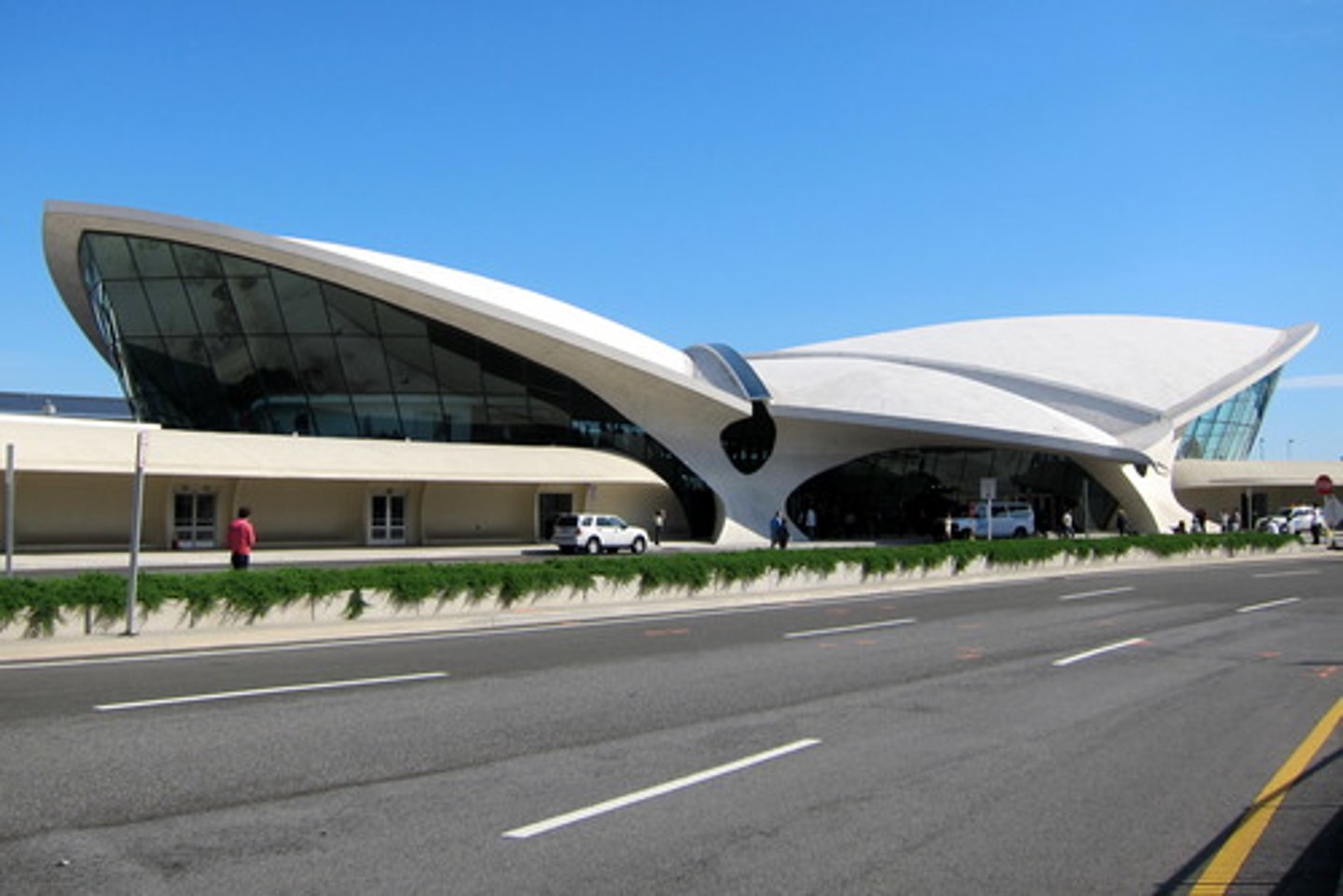
TWA Terminal
NYC; Eero Saarinen

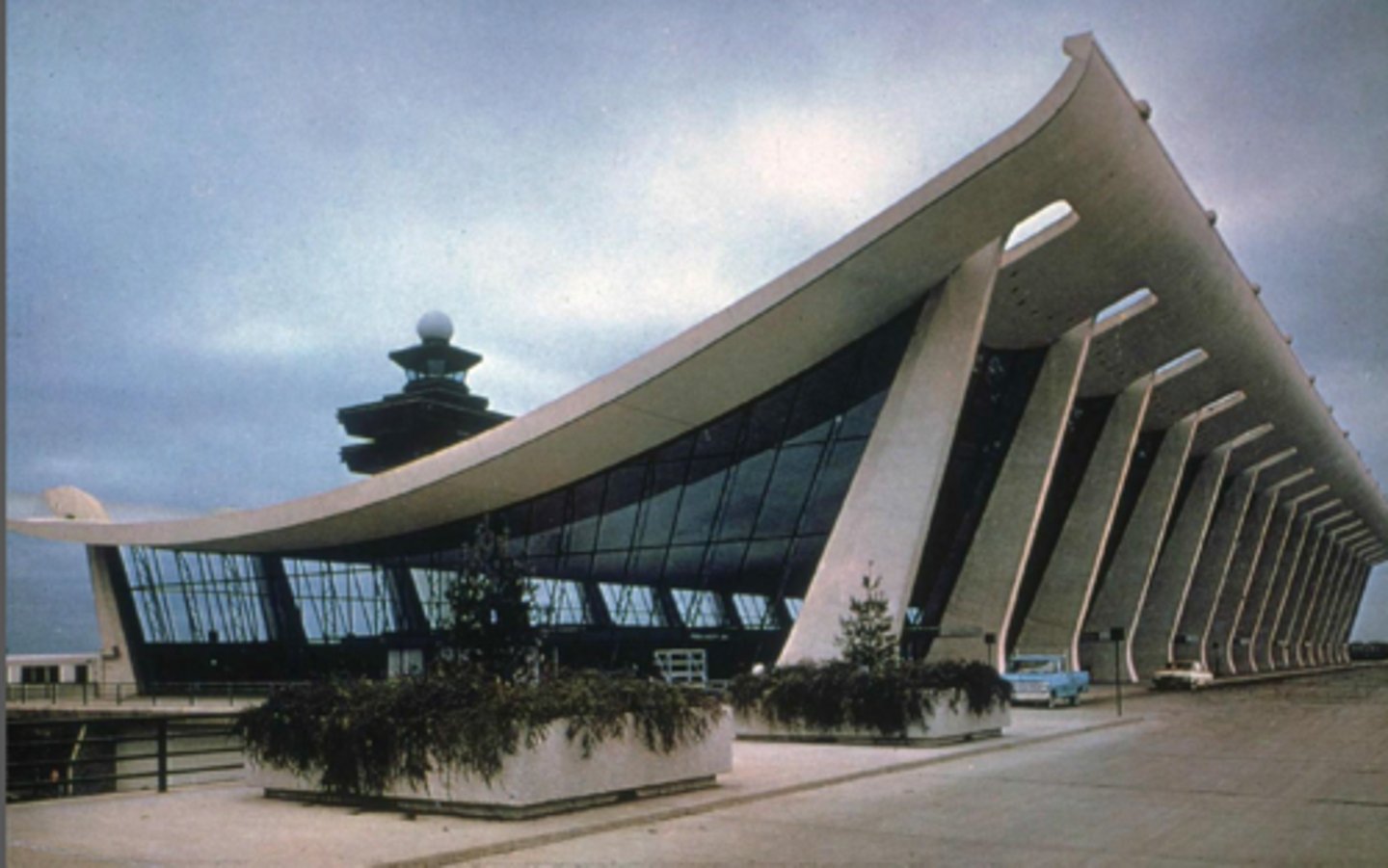
Dulles Airport
D.C.; Eero Saarinen

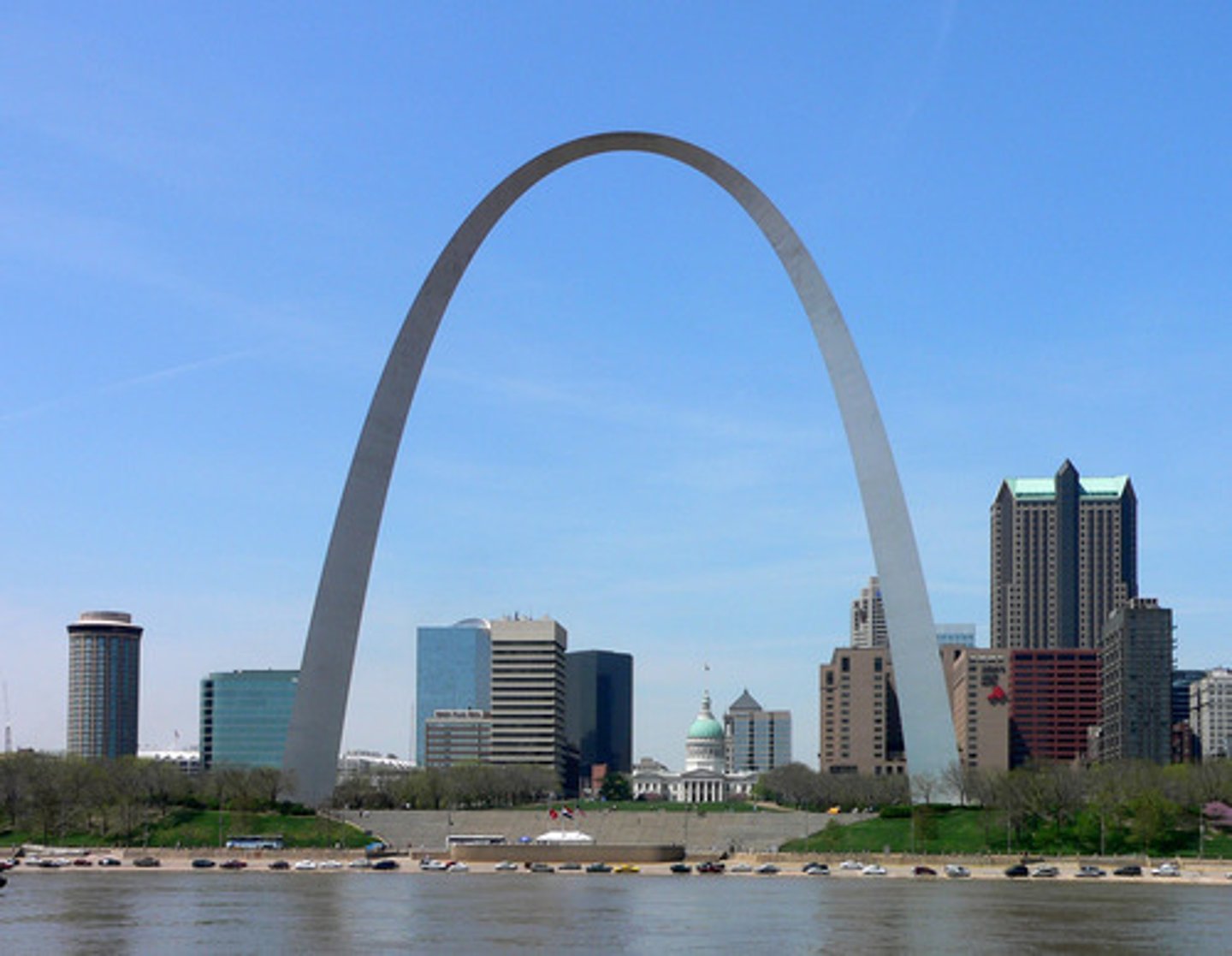
St. Louis Gateway Arch
Eero Saarinen

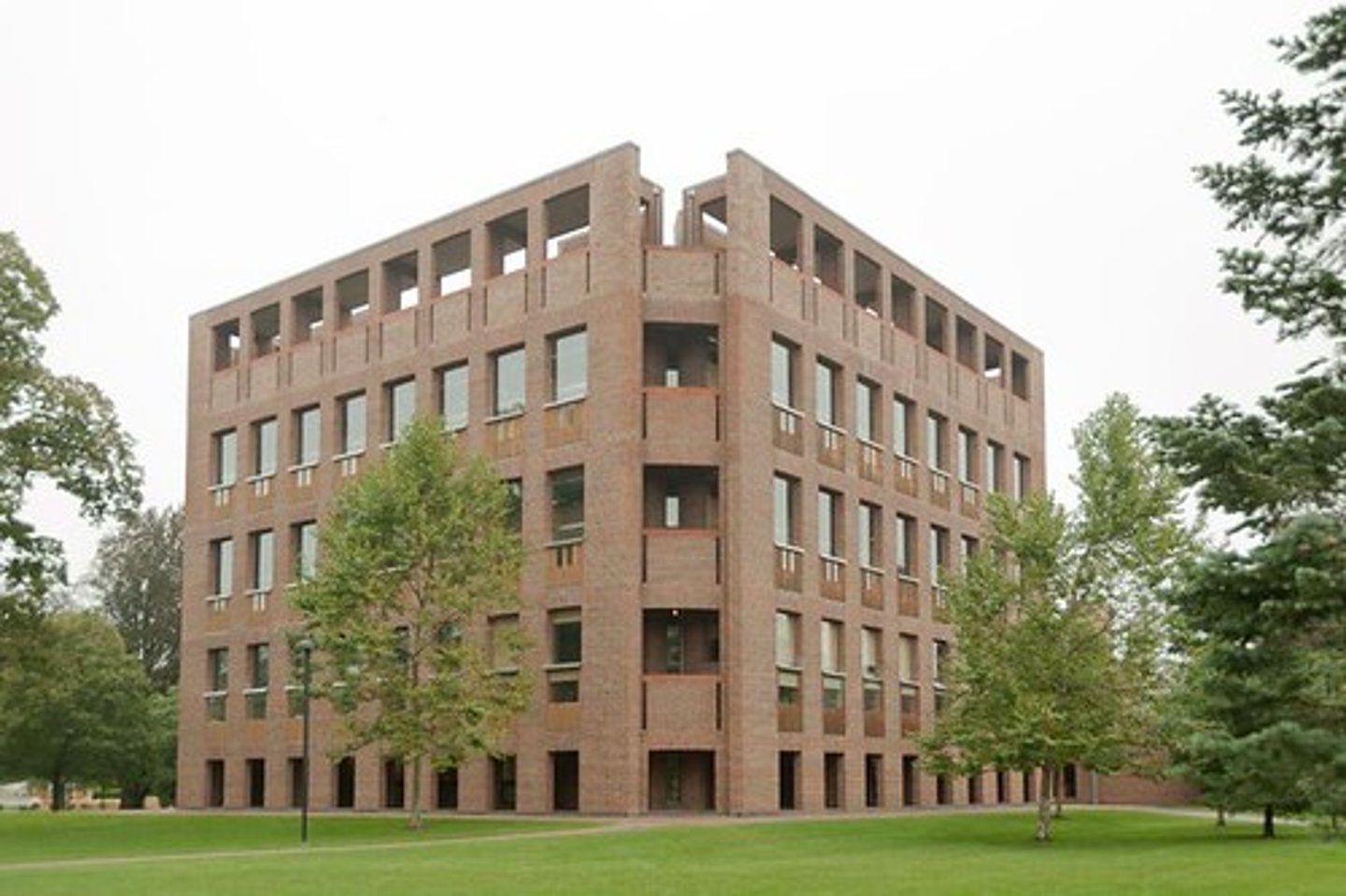
Phillips Exeter Academy Library
1965-72; Louis Kahn

Robert Venturi & Denise Scott Brown
"Less is a Bore"
Vanna Venturi House 1964
Guild House 1960-5
Michael Graves
Swan & Dolphin Hotels; Disney
Portland Building