Immune System
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
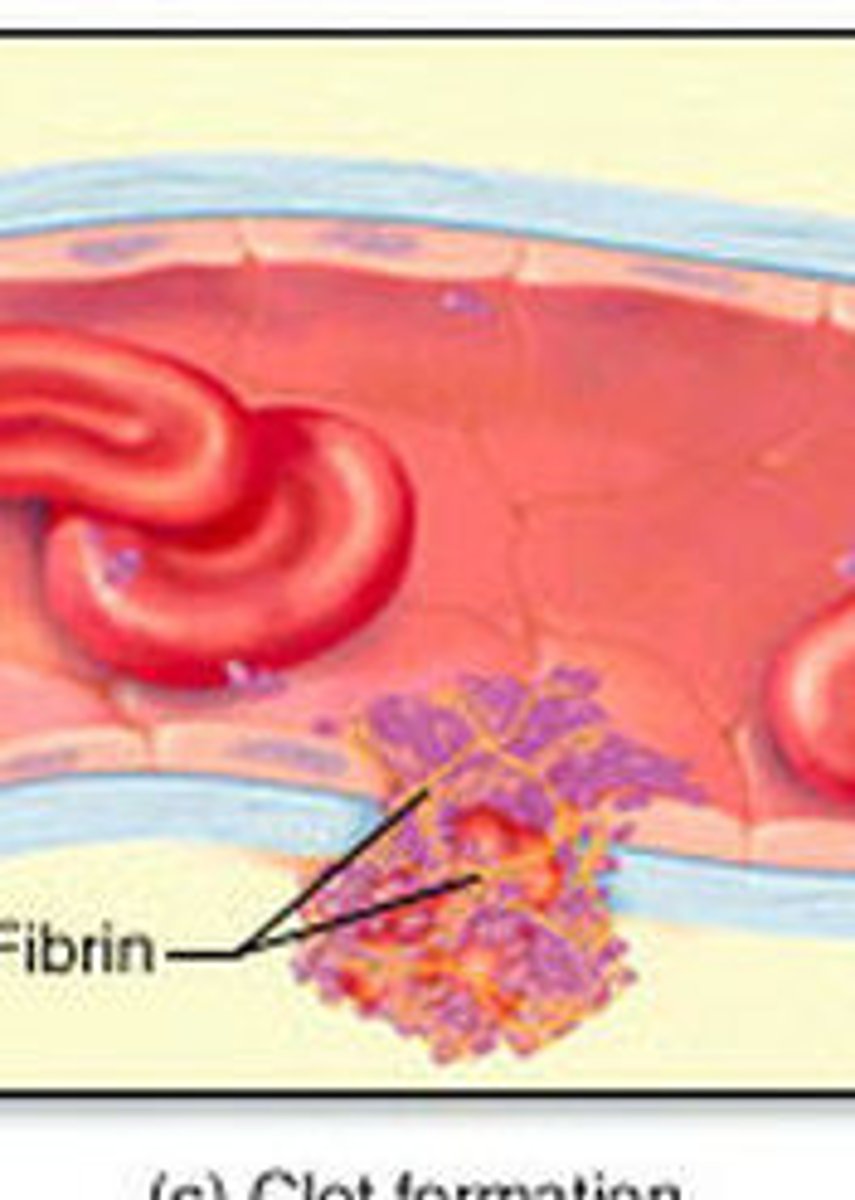
blood clotting
damaged tissue releases clotting factors -> platelets form sticky plug & triggers PROTHROMBIN -> THROMBIN
- thrombin catalyzes FIBRINOGEN -> FIBRIN (fibrous/insoluble; holds clot/thrombus in place)
1st line defense
NONSPECIFIC
- skin (stratified/layered, keratinized/tough, slightly acidic)
- mucus membranes (trap pathogens)
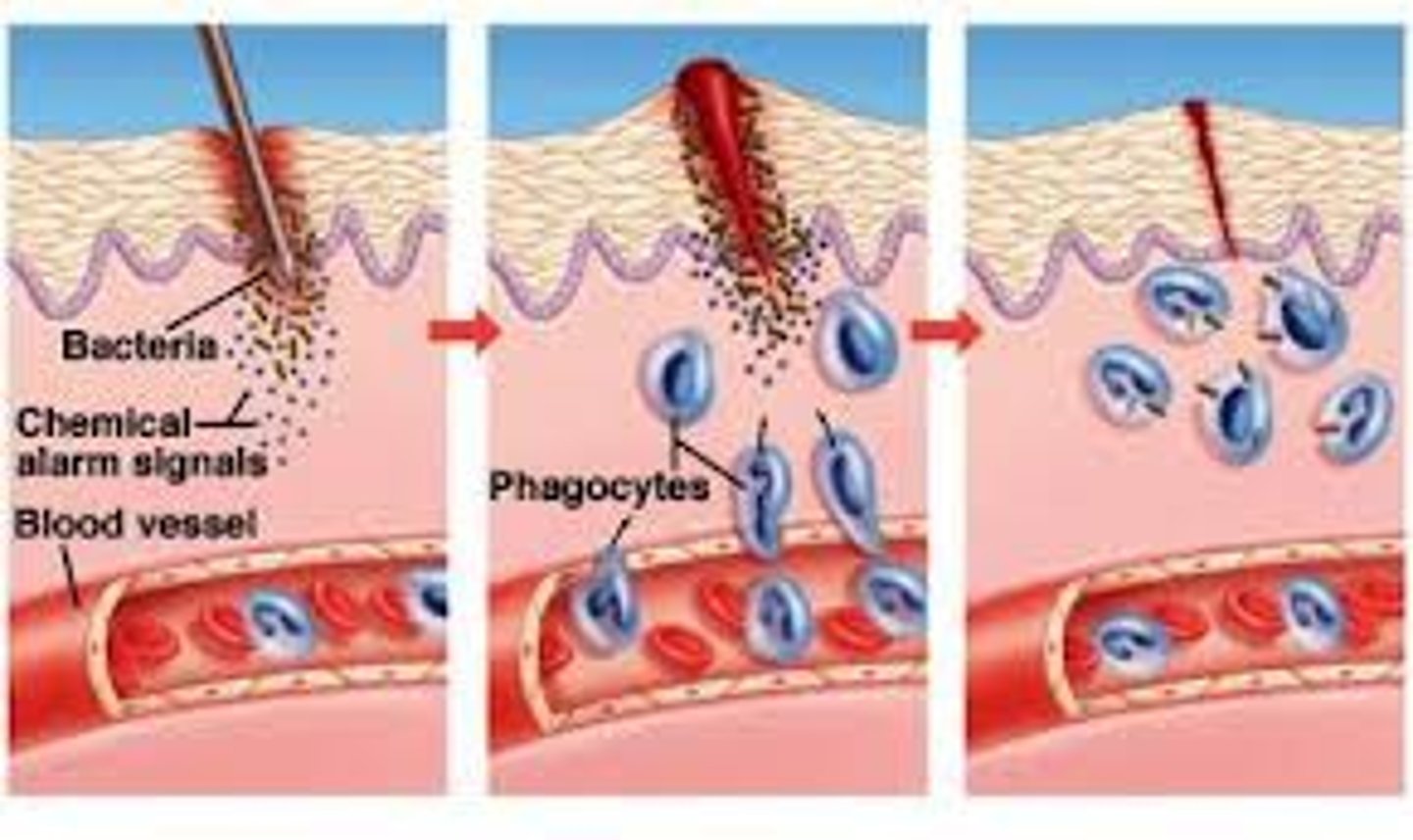
2nd line defense
NONSPECIFIC; inflammatory response (more bloodflow to that area so more PHAGOCYTES can "leak" out of capillaries & engulf pathogens)
3rd line defense
SPECIFIC response to each antigen (unique shape, specific antibody produced)
- involved in autoimmune disease
- includes humoral (B cell) & cell-mediated (T cell) responses
- Helper T activates BOTH of these pathways SIMULTANEOUSLY after antigen is presented
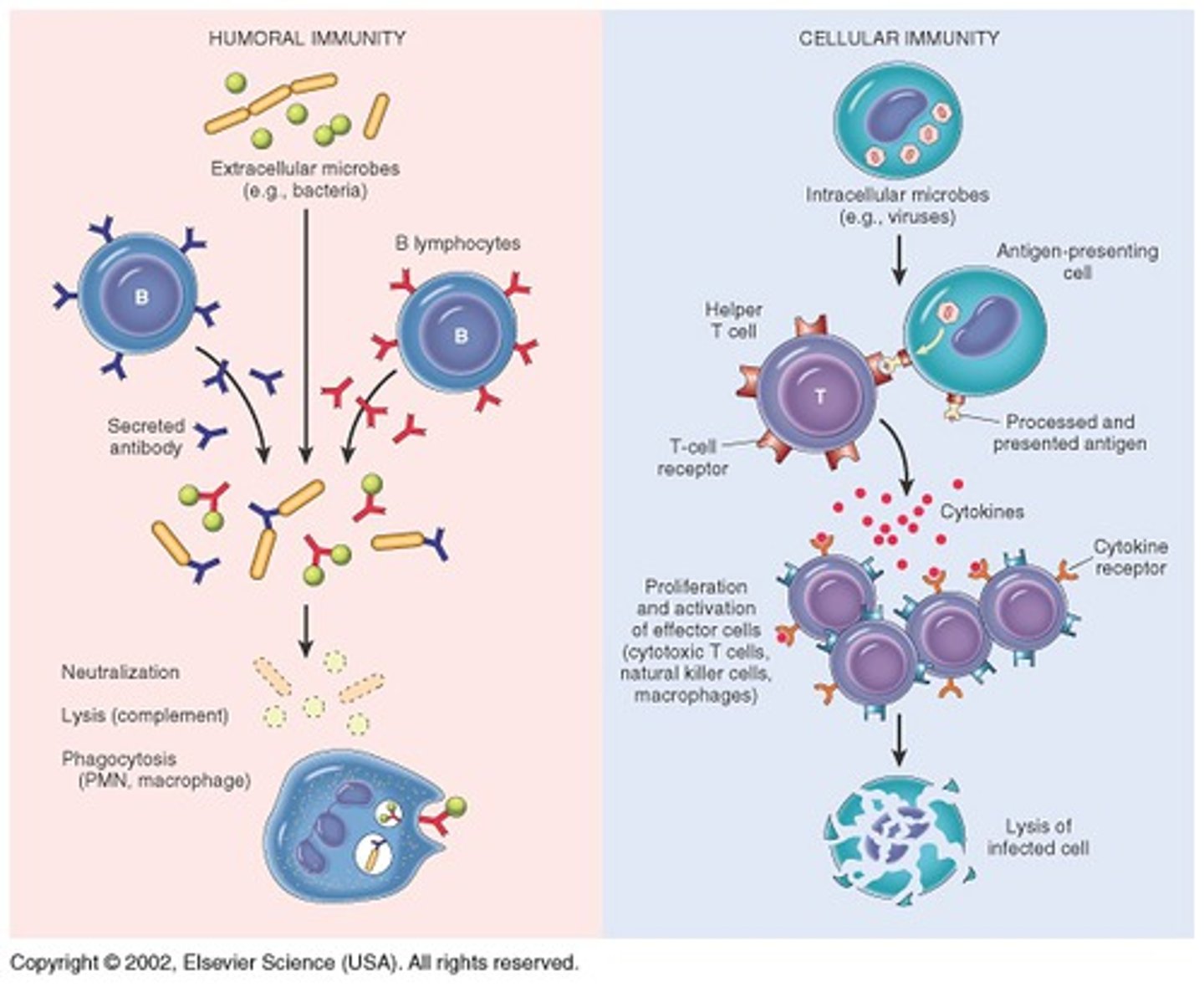
humoral response
- APC presents antigen to Helper T
- Helper T activates SPECIFIC B cells; differentiate into plasma cells & memory B cells
- plasma cells make antibodies
- attack toxins, viruses, bacteria OUTSIDE of cells
cell-mediated response
- APC presents antigen to Helper T
- Helper T activates Killer T cells (SPECIFIC to the antigen) & triggers them to clone themselves (some differentiate into memory T cells)
- attack viruses/bacteria IN cells (tell infected cell to die- lysis/apoptosis)
B-cells
originate AND mature in bone marrow
T-cells
originate in bone marrow; mature in thymus
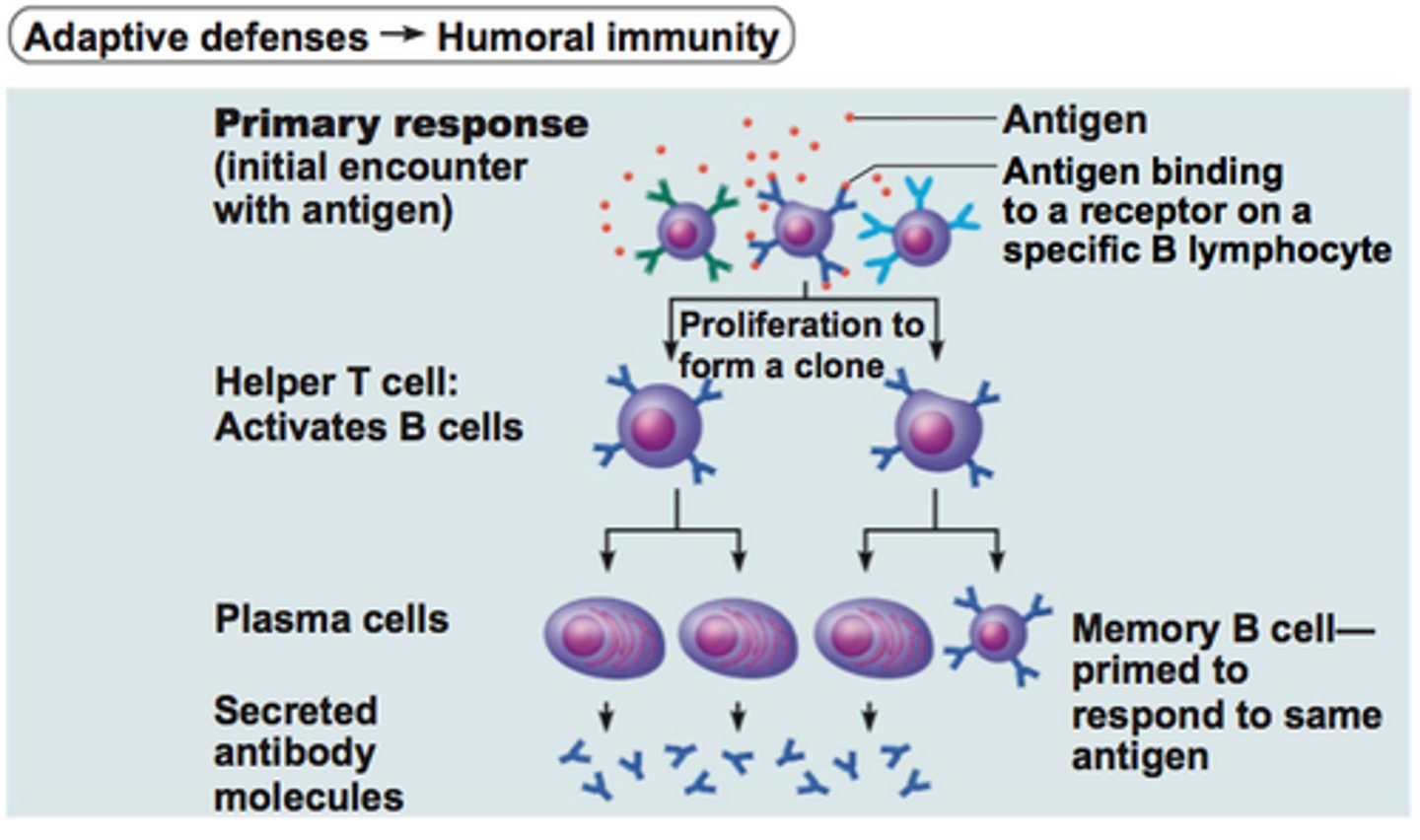
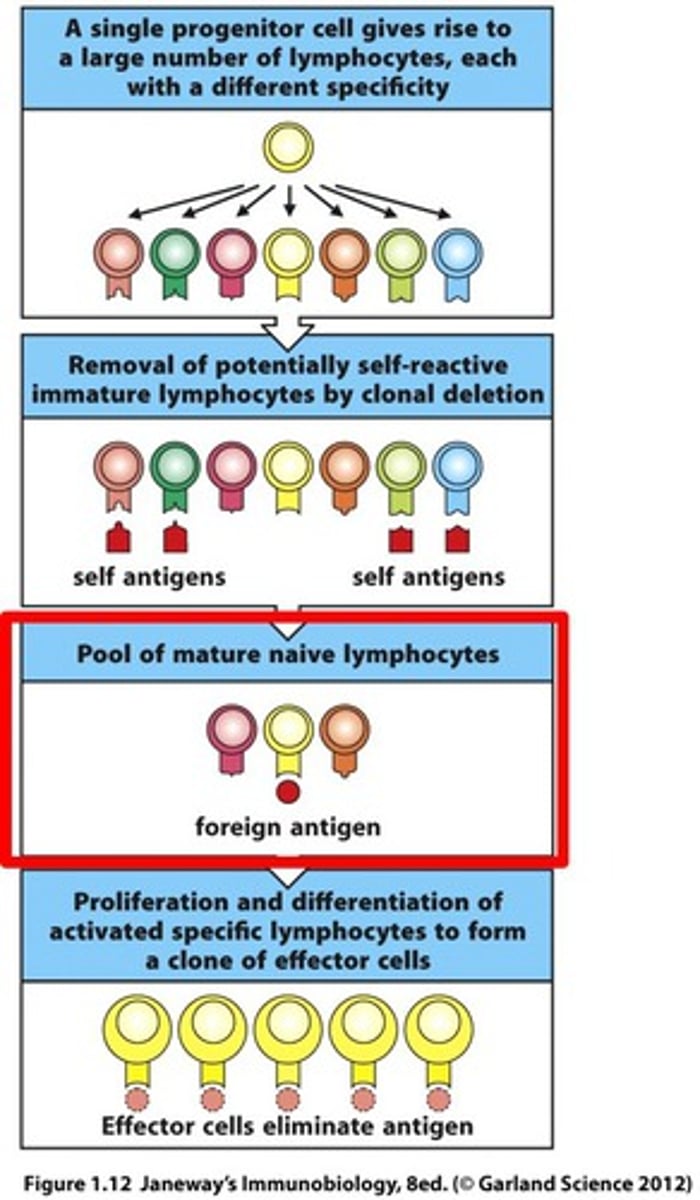
clonal selection
when presented w/ antigen, Helper T releases cytokines that activate specific B or T cell (that corresponds to the antigen) to clone itself/divide millions of times
- some clones differentiate into long-lived memory cells
APC
antigen presenting cell - often macrophage, can be B-Cells
- engulfs/partially digests antigen & displays part of it on cell membrane along w/ MHC molecule
- Helper T recognizes the antigen & activates immune response
antibodies
immunoglobulins (Ig's); Y-shaped, 4 polypeptide chains - tips of the Y = antigen binding sites
SPECIFIC ANTIBODIES FOR SPECIFIC ANTIGENS
neutralization: bind to pathogen & prevent it from infecting cells
agglutination: clump pathogens so macrophage can clean up
precipitation: make dissolved pathogens insoluble
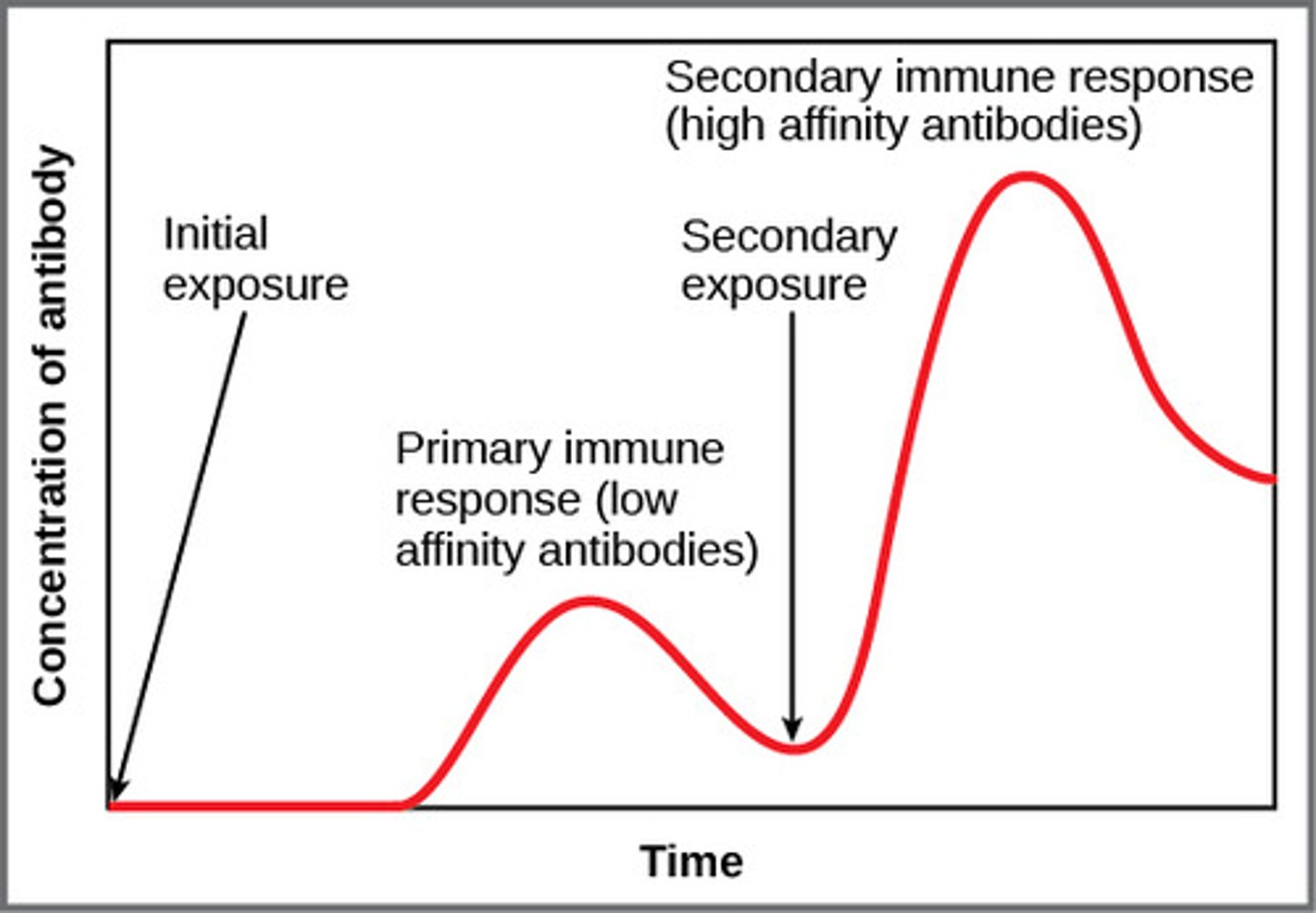
primary VS secondary response
PRIMARY: 1st exposure to antigen; peak in 5-10 days; memory cells produced but not used (takes time to produce B/T cells that will respond to the antigen)
SECONDARY: 2nd exposure, peak in 3-5 days; memory cells activated = much faster & stronger response (quickly divide into B/T cells)
vaccination pros/cons
PROS: avoid & eradicate fatal diseases (smallpox), herd immunity, avoid epi/pandemics
CONS: allergy/death (RARE), minor side effects (pain at injection site)
AIDS
acquired immune deficiency syndrome, caused by HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)
transmission: bodily fluids
attack method: infiltrates & kills Helper T cells, basically destroying the immune system -> death from other pathogens
social issues: stigma (homophobia, etc)
zoonotic diseases
diseases that can spread from animals to humans
active/passive immunity
Active: body produces its own antibodies against an infection
Passive: antibodies from outside source (ex. breast milk, monoclonal)
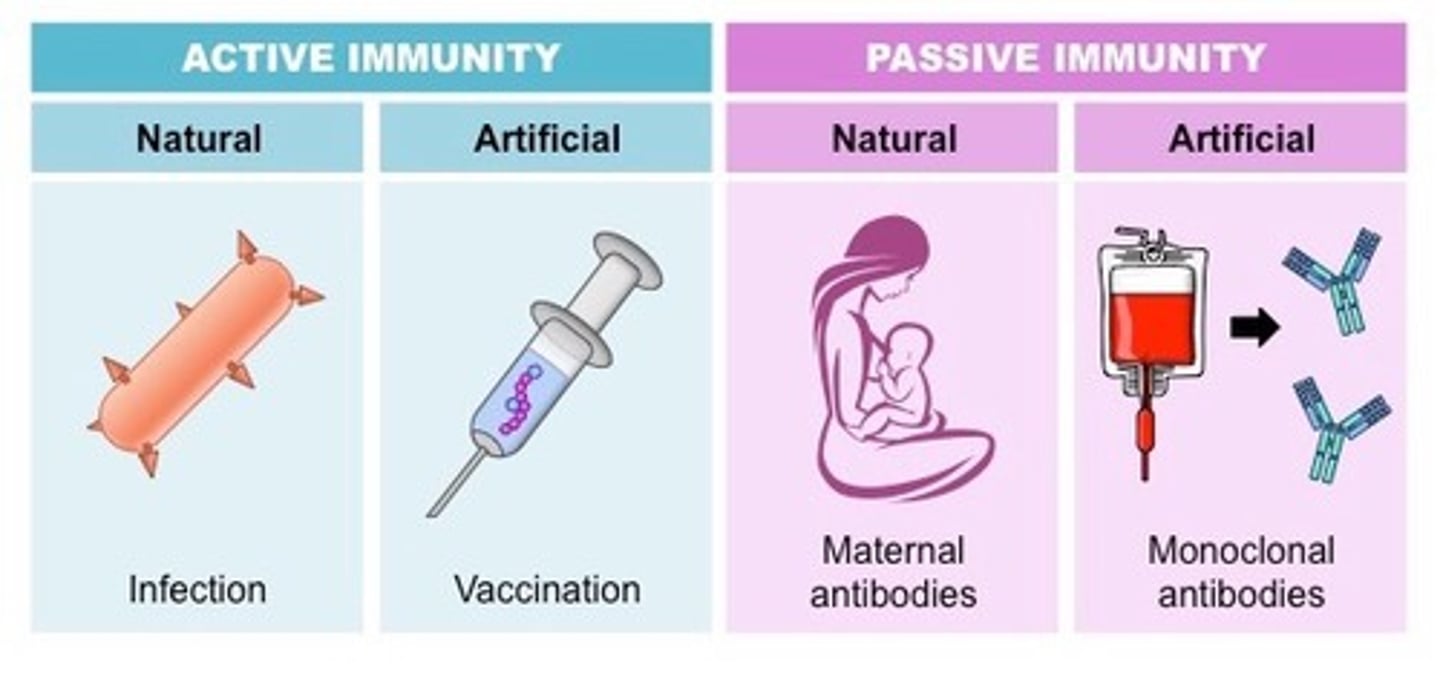
natural/artificial immunity
Natural: from naturally acquired disease/source
Artificial: from vaccination/manmade source
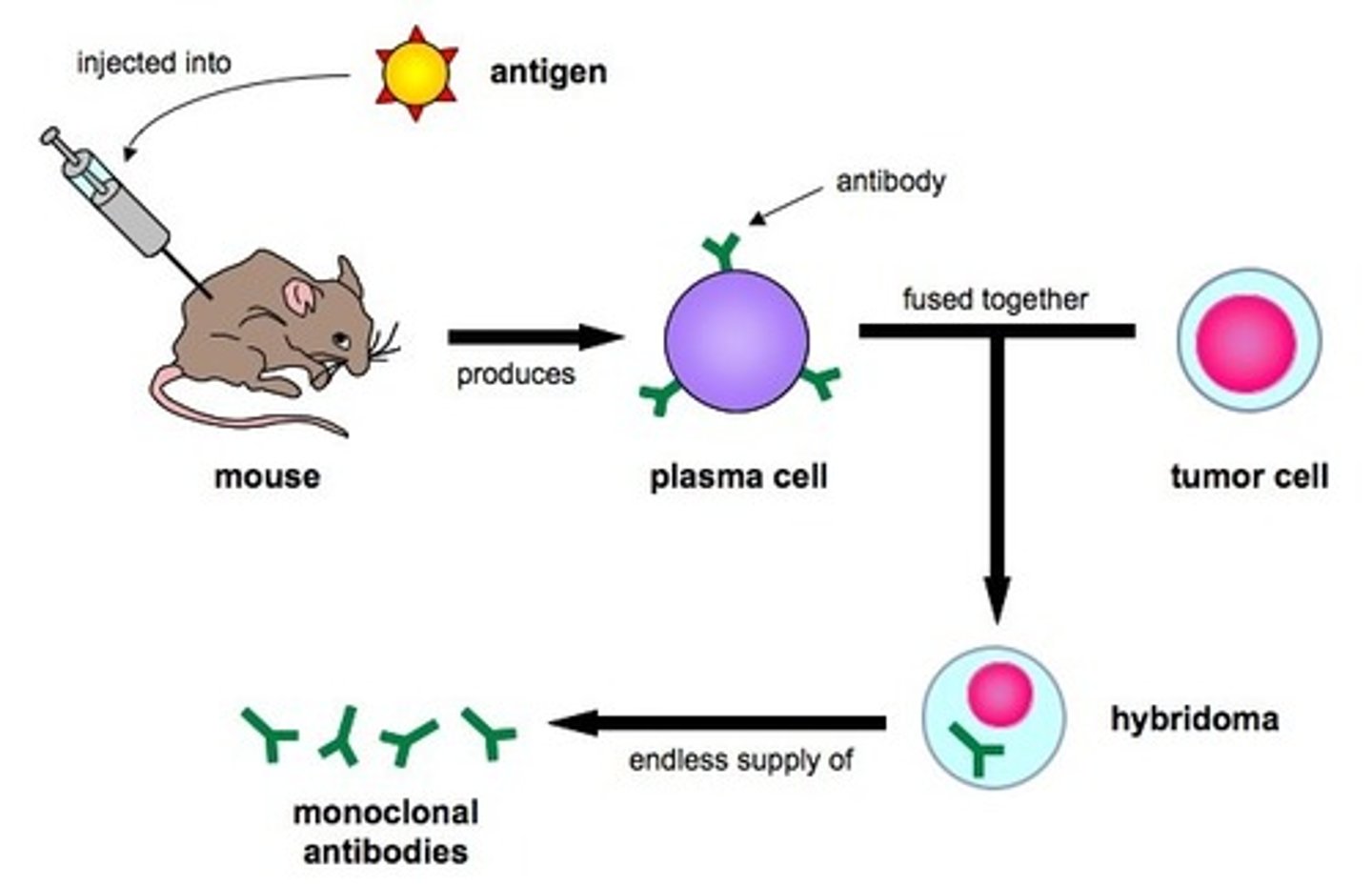
monoclonal antibody production
- inject rat w/ antigen, collect matching B-cell & combine w/ tumor cell -> hybridoma
- hybridoma divides rapidly & mass produces desired antibodies
diagnosis: pregnancy tests (HCG)
treatment: cancer (targeted chemo)
pathogen
any organism that causes disease
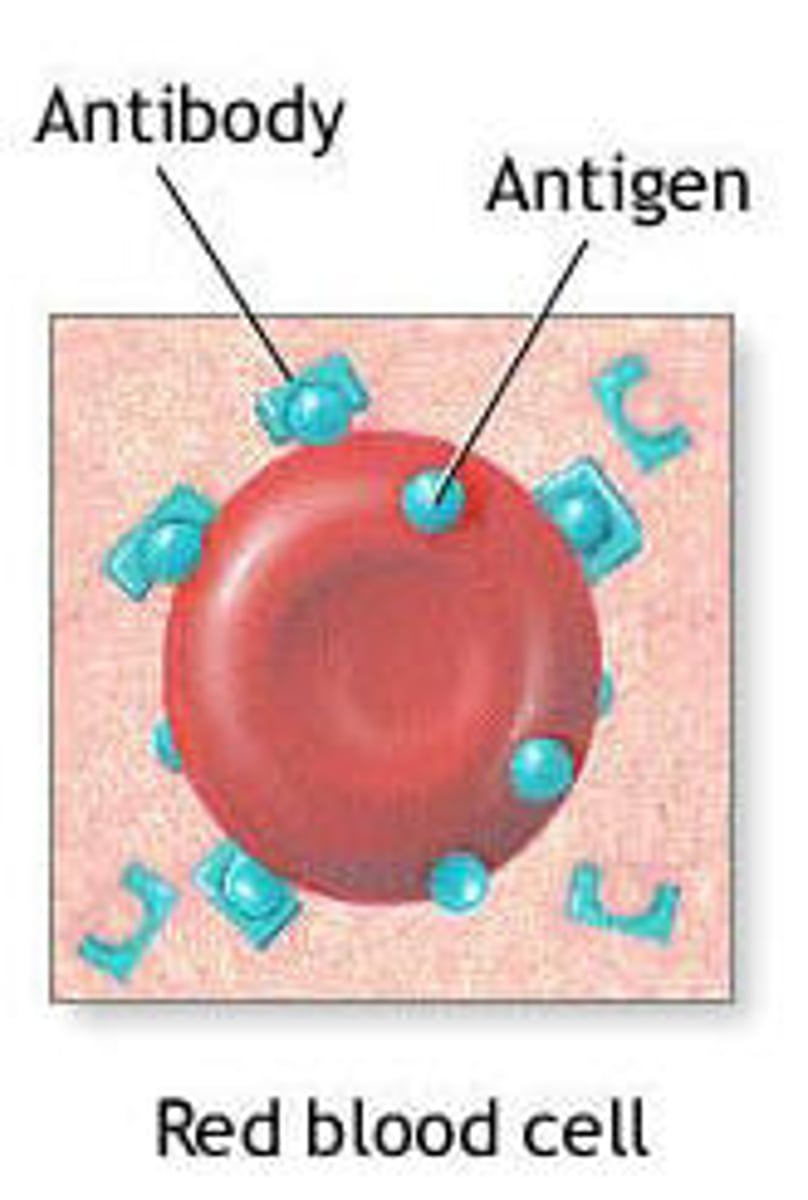
antigen
any non-self molecule (triggers antibody production)
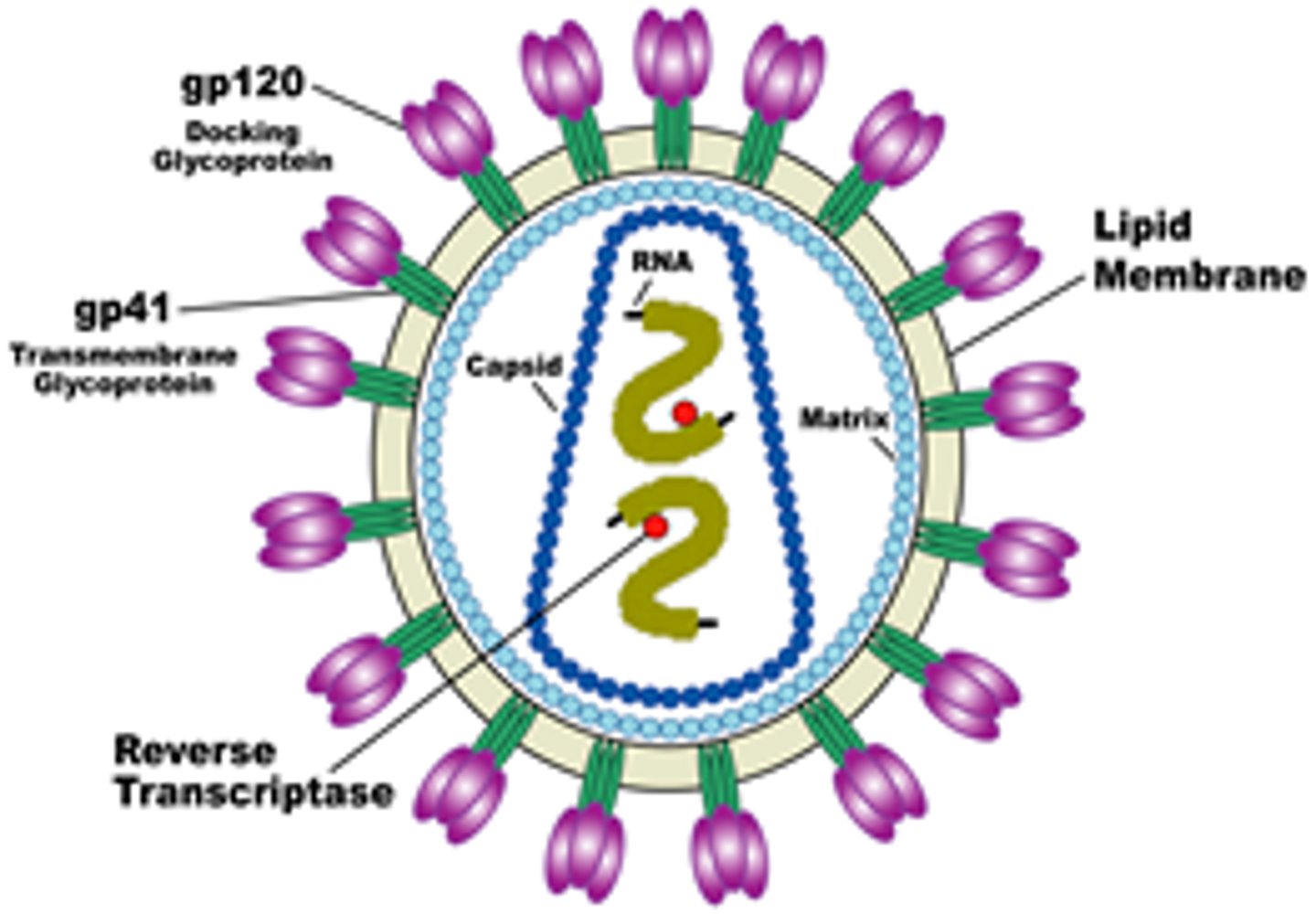
retrovirus
RNA virus (example: HIV, influenza) that reproduces by transcribing its RNA into DNA using REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE & inserting DNA into the host cell's genome
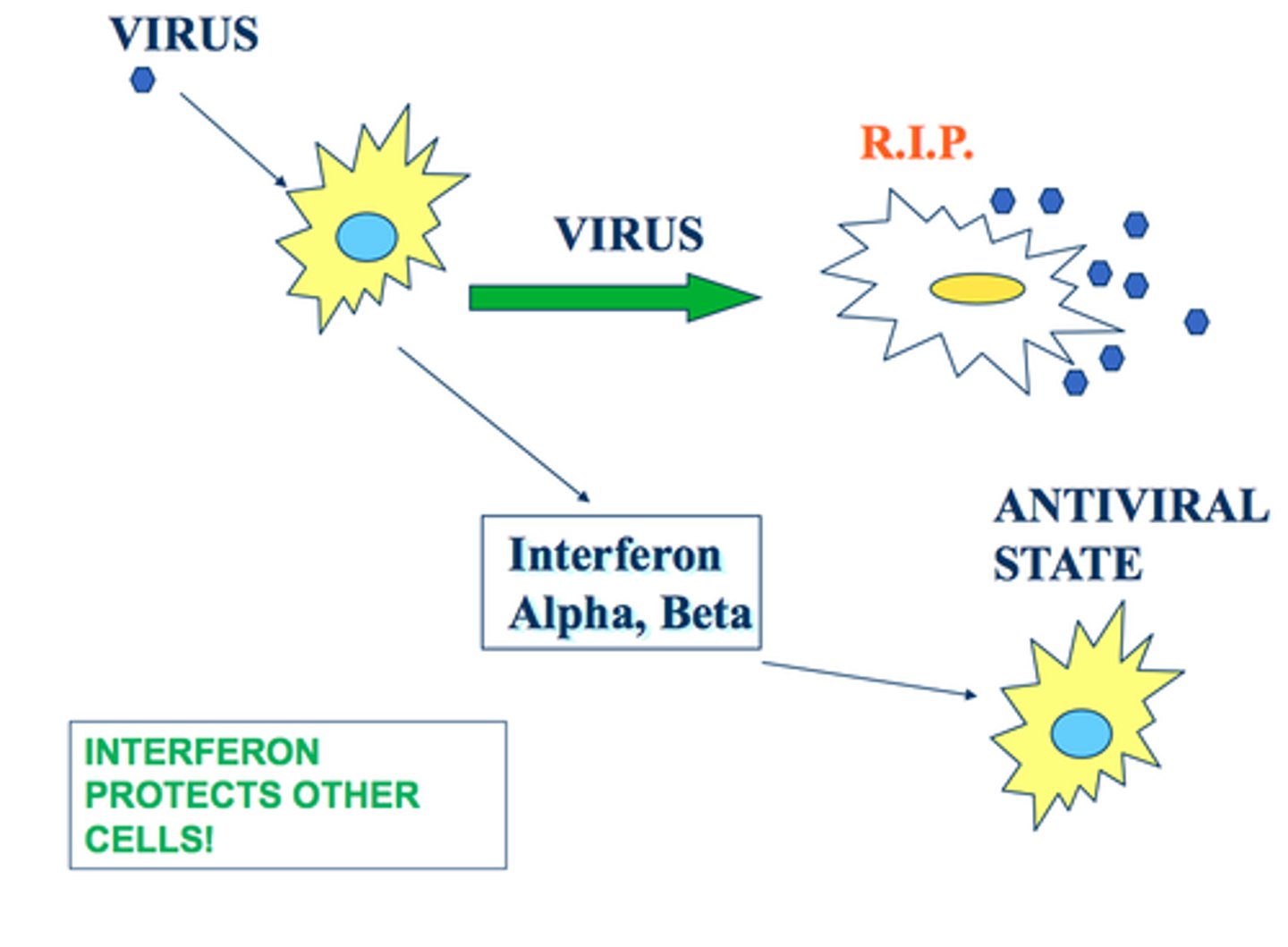
interferon
signaling protein/class of cytokine released by infected cells that warn nearby cells (incl. immune cells)
antibiotics
kill bacteria by - blocking ability to repair DNA, preventing replication, weakening cell wall
- DO NOT WORK ON VIRUSES bc they lack a metabolism
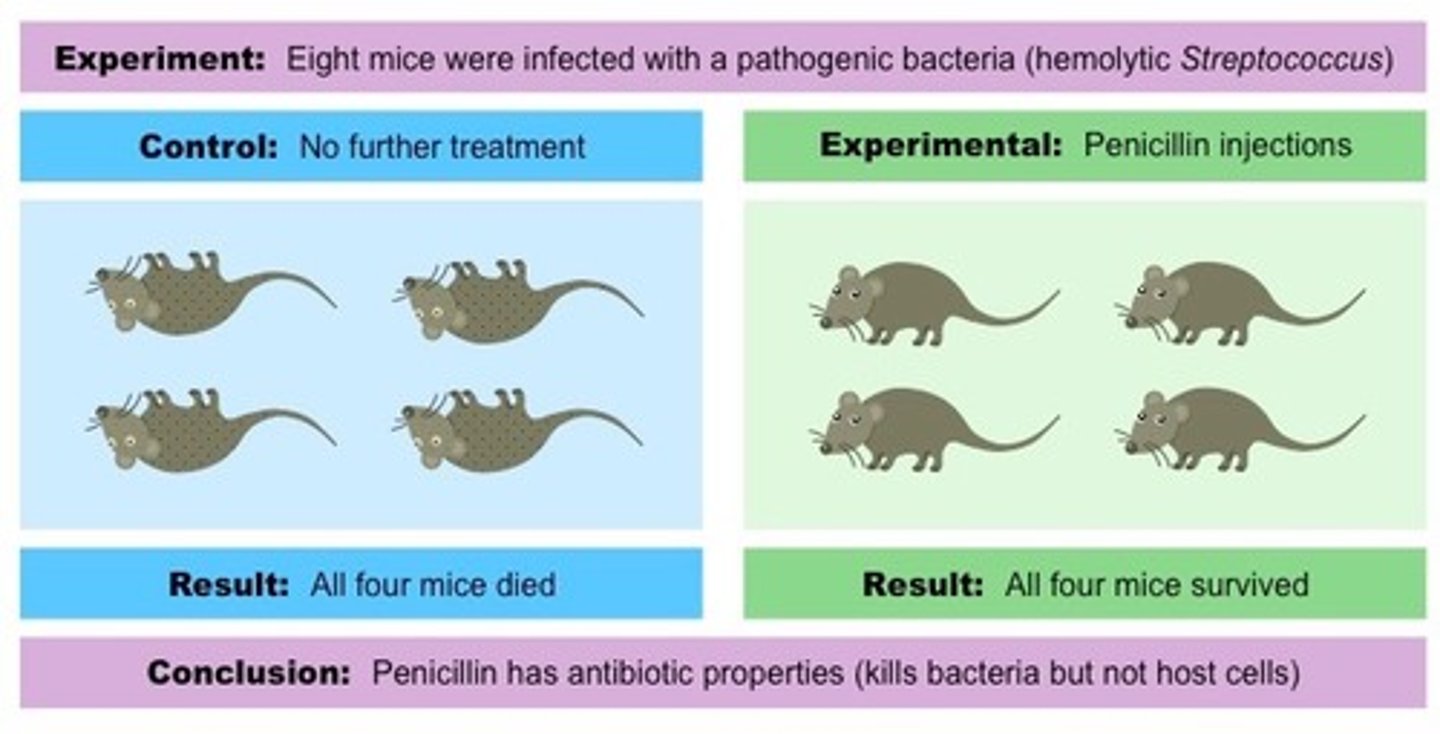
Fleming, Florey, and Chain
developed penicillin
Fleming: discovered penicillin but failed to make it practical to use
Florey & Chain: proved penicillin could kill bacteria in both mice & humans
WWII need for penicillin = Allies collaborated to mass produce