Redox reactions
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is oxidation?
It is the loss of electrons; The increase in +ve charge and the decrease in -ve charges
What is reduction?
It is the gain of electrons
What elements does Group 1 have?
hydrogen (H), lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr).
What elements does Group 2 have?
beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra)
What elements does Group 13 have?
boron (B), aluminium (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), and thallium (Tl)
What elements does Group 17 have?
fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At)
What is an oxidising agent?
Any substance that reduces itself to oxidize others
What is an reducing agent?
Any substance that oxidize itself to reduces others
What are disproportionate reactions?
A type of reaction in which an element undergoes oxidation and reduction reactions at the same time
What does a pyro reaction mean?
It is a type of reaction in which water is removed
What is n factor and what is its formulae?
It is the gain/loss of electrons per molecule
OR the number of H⁺ or OH⁻ ions replaced/reacted (in acid-base)
OR the total positive/negative charge exchanged (in salts)

What is the formula for equivalent mass?
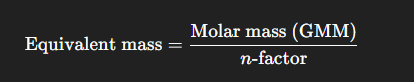
How would you find out the n factor for disproportionate reaction
n factor(oxidation)* n factor(reduction) / n factor(oxidation) + n factor(reduction)
(This sure does look like a weighted average)
What is the range of oxidation from period 3 onwards?
From (n) to (n-8)
where,
n → number of valence electrons
What are equivalents
It is the measurement of the reactivity of a compound
What are the formulas for calculating equivalent mass
Molar mass/ n factor
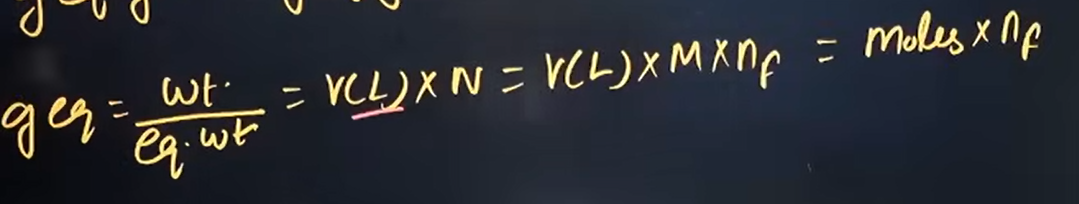
Tell everything about K2Cr2O7; What is the indicator used for this compound; What is the product that is formed of K2Cr2O7 after the reactions; What compounds does it react with and what does it do to them?
It is an excellent oxidising agent in an acidic medium
Cr2O7-2 + H -> Cr3 + H2O
The indicator use is K3[Fe(CN)6] or Diphenylamine
![<ul><li><p>It is an excellent oxidising agent in an <strong><em>acidic medium</em></strong></p></li><li><p>Cr<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub><sup>-2 </sup>+ H -> Cr<sub>3</sub> + H<sub>2</sub>O</p></li><li><p>The indicator use is K<sub>3</sub>[Fe(CN)<sub>6</sub>] or Diphenylamine</p><p></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ba7fdce9-b668-432d-a44b-c4c1df278510.png)
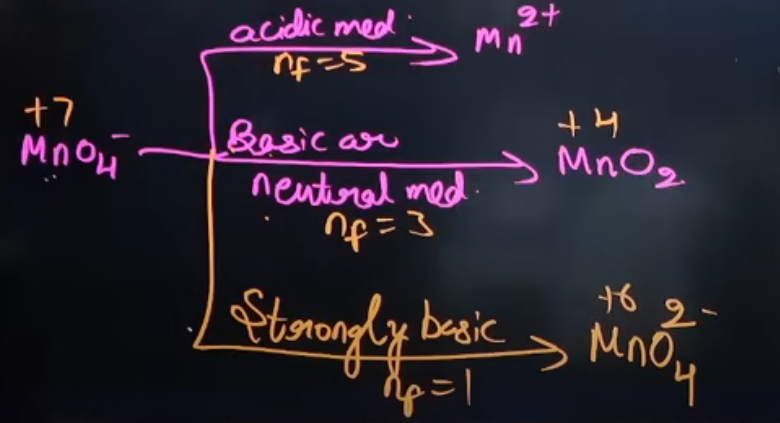
Tell everything about KMnO4; What is the product that is formed of KMnO4 after the reactions; What compounds does it react with, and what does it do to them?
It is an excellent oxidising agent in an acidic, basic and neutral medium
It reacts with the same compounds and gives the same results as K2Cr2O7
It also gives water as a product
Tell everything about I2; What is the product that is formed of I2 after the reactions; What compounds does it react with, and what does it do to them?
It is a good oxidizing agent
I2 + 2e- = 2I2 → because 2 Iodine need 2 electrons
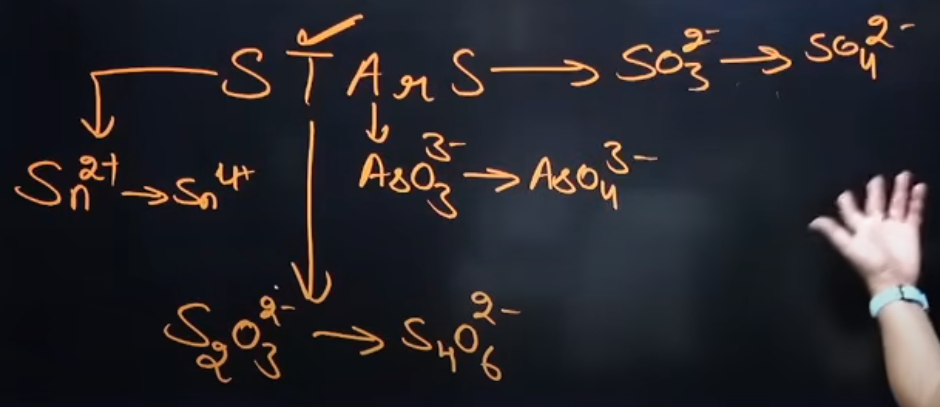
What is I- ?
It is a compound that is a very good reducing agent