Parietal lobes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Central sulcus (rolandic fissure)
Separates frontal and parietal lobes.
Lateral sulcus
Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes
Pareto-occipital fissure
Divided occipital and parietal lobes
Postcentral gyrus
In between the central and postcentral sulcus.
Receives somatosensory information from the entire body.
Posterior parietal lobes
Superior parietal lobule (SPL; little lobe)
Inferior parietal lobe (IPL)
In between these two is the intraparietal sulcus (IPS) which is a major sulcus.
Intraparietal sulcus (IPS)
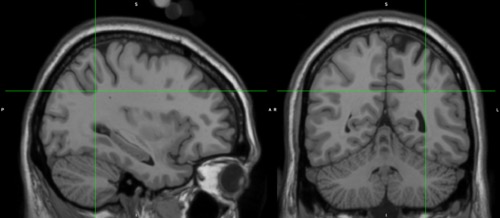
Summary of major antamoical subdivisions
Postcentral gyrus
Posterior parietal lobe (superior lobule
Summary of major functional subdivisions
- Primary somatosensory cortex (S1)
- Posterior parietal cortex: infraparietal sulcus and superior parietal lobule, right inferior parietal lobule, left anterior inferior parietal lobule, left posterior inferior parietal lobule.
Primary somatosensory cortex (S1)
Processing information about body sensations (e.g. touch, pain, proprioception)
Can be divided into at least 4 subdivisions (area 3a, 3b, 1 and 2)
Input: mainly from thalamus and motor cortex
Output: mainly to motor cortex and posterior parietal cortex.
Wilder Penfield (1930s to 50s)
Noted that some body parts have a larger dedicated area than others
Also known at the somatosensory homunculus
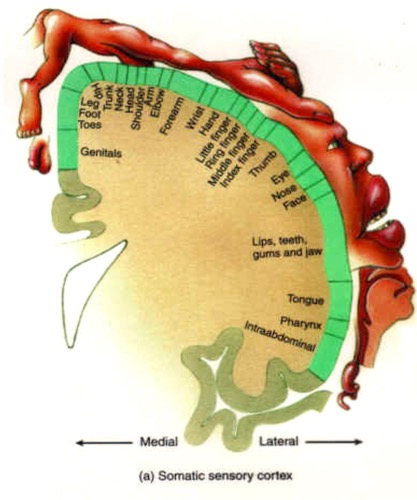
Why somatotopy is more complex
While there is clear somotatopy, it is not as simple as depicted by penfield,
Somatosensory cortex study (Kolansinski et al., 2016)
Our brain more wired than we assume, functional reoroganisation of S1 can occur within just 24 hours.
Kolansinski et al., showed this by an experiment where the little finger and ring finger were glued together.
Intrapariteal sulcus and superior parietal lobule
Visually guided actions.
Overarching concept
Vision for action - dorsal visual stream (Goodale, 2011, Ganel and Goodale, 2018)
Is there an object with which I can interact? What is its size and orientation? Objects in space, object relevance / attention.
Where is my body (arms, hands, eyes, finger) relative to the object? Reaching / grasping objects.
More anterior areas – coding in hand-centred coordinate system.
More posterior areas – coding in vision-centred coordinate system (retinotopy).
Classic neuropsychological sydndrome after bilateral lesions
Balint syndrome (Jackson et al., 2009)
Optic ataxia: deficit in visually guided reaching movements (Anderson et al., 2014)
Oculomotor apraxia: inappropriate fixation of gaze and difficulties in voluntarily shifting fixation to other objects.
Simultanognosia: impaired ability to perceive multiple items in a visual display.
Involvement in cognitive functions might derive from more primitive mechanisms
Visuospatial working memory: link to representing the location of objects, coding what is relevant.
Mental rotation/imagery: link to manipulating objects.
Arithmetics: link to moving eyes/hands to count, spatial layout (mental number line).
Right inferior parietal lobule
Detect salient events in the environment
Singh-Curry & Hussain (2009)
Detection and encoding of salient or novel events (bottom up attention, ie. up from stimuli via senses- brain interprets.
Key role in maintaining attention on current task goal as well as encoding of salient events so that task sets can be speedily reconfigured to deal with new challenges.
Left anterior inferior parietal lobe
Use objects in appropriate way, pantomime object use.
Left posterior inferior parietal lobule
Detect salient events in one’s thoughts.
Seghier (2012)
Semantic processing
Reading and comprehension
Default mode processing
Number processing
Memory retrieval
Theory of mind
Reynaud et al. (2016)
Understanding tool-use actions
Lesions in this area - Apraxia with possible impairments
Imitation of gestures
Communicative gestures
Real tool use.