Bacterial Transcription and translation
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is transcription?
information in DNA strand copied into mRNA
What is translation?
mRNA is decoded by a ribosome to produce a specific polypeptide or protein.
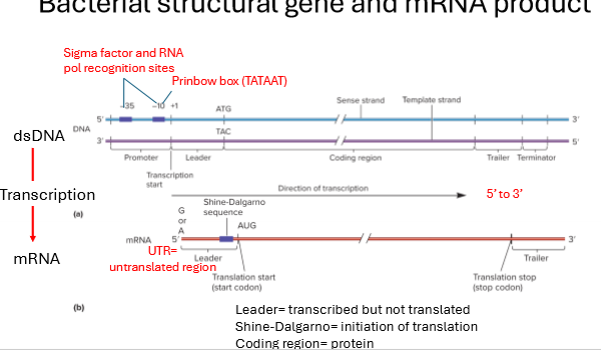
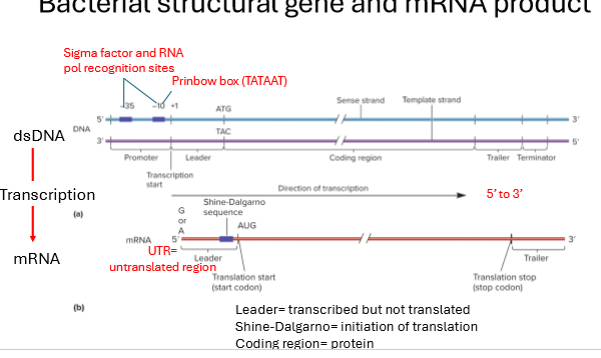
Describe the bacterial structural of a gene that help initiate transcription
regulatory structures/sequences upstream of the coding region that control expression. include promoter sequence
sigma factor and RNA polymerase recognition sites enable the specific binding of RNA polymerase
The Pribnow box (-10 box) - conserved TATAAT sequence, located 10 base pairs upstream from the transcription start site is essential for RNA polymerase binding and initiation of transcription.
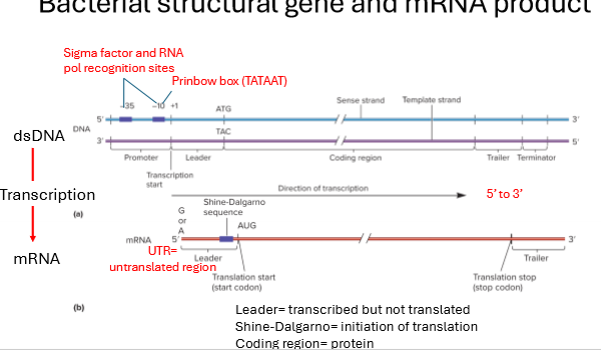
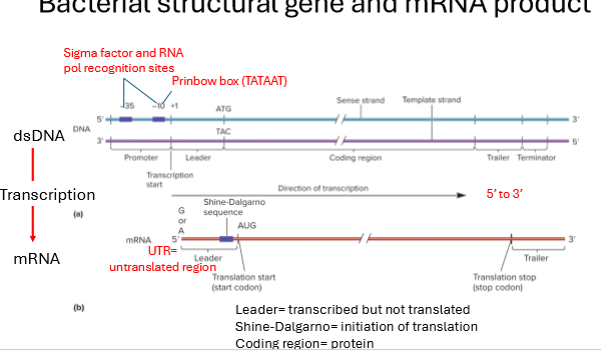
describe the flow from DNA to mRNA
dsDNA (double stranded)
transcription
mRNA
always 5’ to 3’
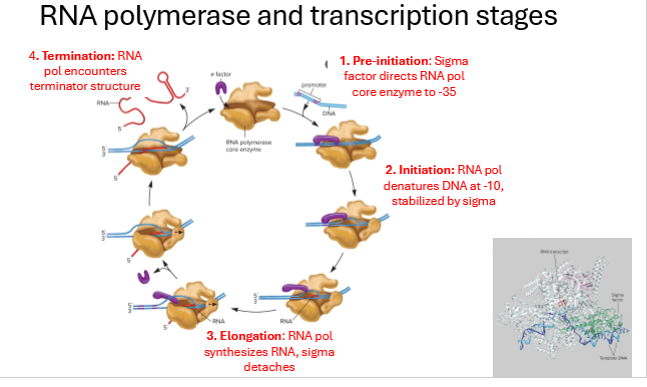
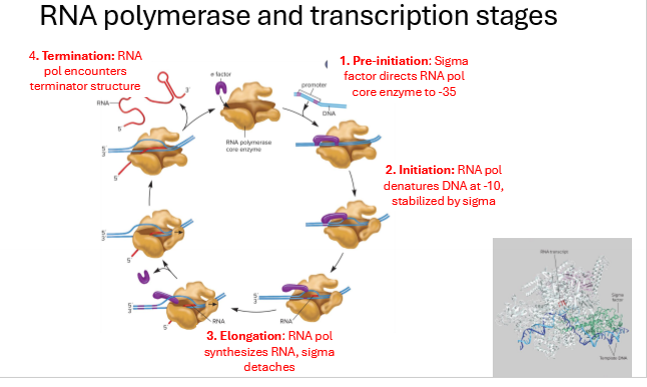
Descfribe the 4 stages of transcription
Pre-initiation - sigma factor directs RNA polymerase core enzyme to -35
Initation - RNA polymeraze denatures/separates DNA at -10 site, stabilized by sigma factor (protein subunit of RNA polymerase)
Elongation - RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA, sigma factor detaches
Termination - RNA polymerase encounters terminator sequence
What is the UTR?
untranslated region in mRNA
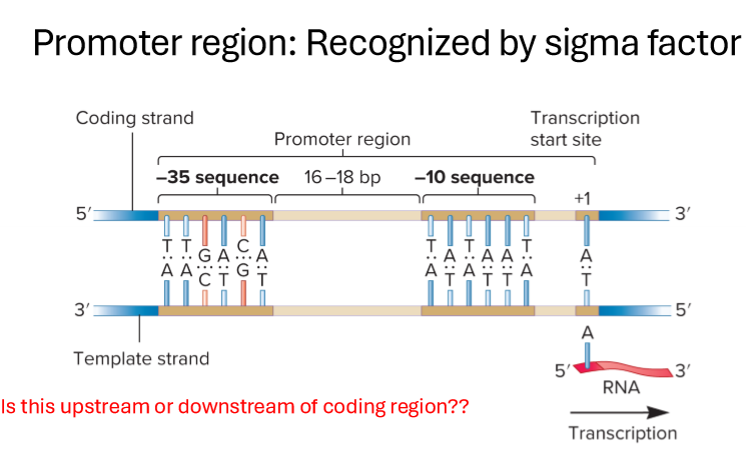
What is the promoter region?
region of DNA recognized by sigma factor, initiates transcription
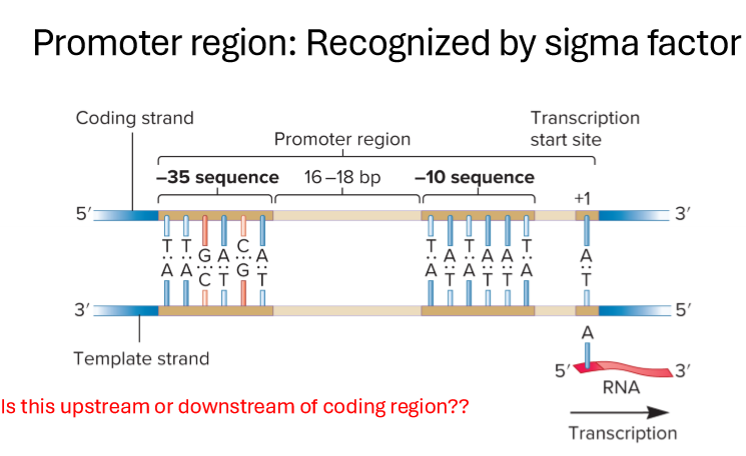
What is the promoter region and how does it work?
region of DNA recognized by sigma factor, initiates transcription
ATG pattern to start
sigma recognizes -35 portion of DNA, helps RNA polymerase bind to template
sigma and RNA polymerase “open” dsDNA at -10 with helicase
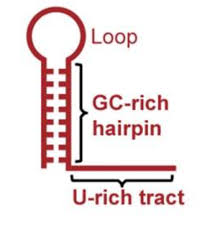
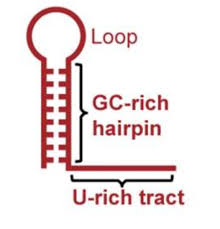
What is intrinsic termination?
mechanism in bacterial transcription where RNA polymerase detects A-rich terminator sequence in the newly synthesized RNA that signal it to stop transcription
cause formation of a hairpin loop
destabilizes bonds and releases RNA polymerases
Describe the initaiton of transcription
region of DNA recognized by sigma factor, initiates transcription
sigma recognizes -35 portion of DNA, RNA polymerase binds to template
sigma and RNA polymerase “open” dsDNA at -10
sigma released during transcription
different sigma factors with different binding sequences bind different promoters
What are the mechanisms for termination of transcription?
intrinsic termination - step loop secondary structure
rho factor dependent terminatino
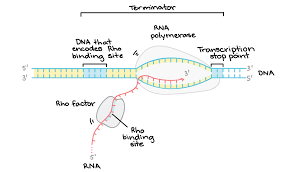
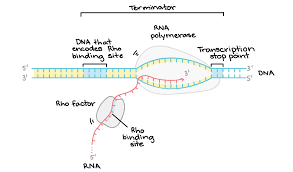
What is rho factor dependent termination?
termination of transcription mechanism
rho protein binds to rho recognition site in mRNA and chases RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase pauses
rho catches up, separates RNA-DNA hybrid using helicase
What is translation?
The process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA sequences, where ribosomes read the mRNA codons and tRNA molecules bring the corresponding amino acids.
Describe the structure of tRNA
amino acid attaches at 3’ end
antiocodon at bottom, contains 3 nucleotides complementary to mRNA codon, allowing tRNA to read mRNA and deliver correct polypeptide
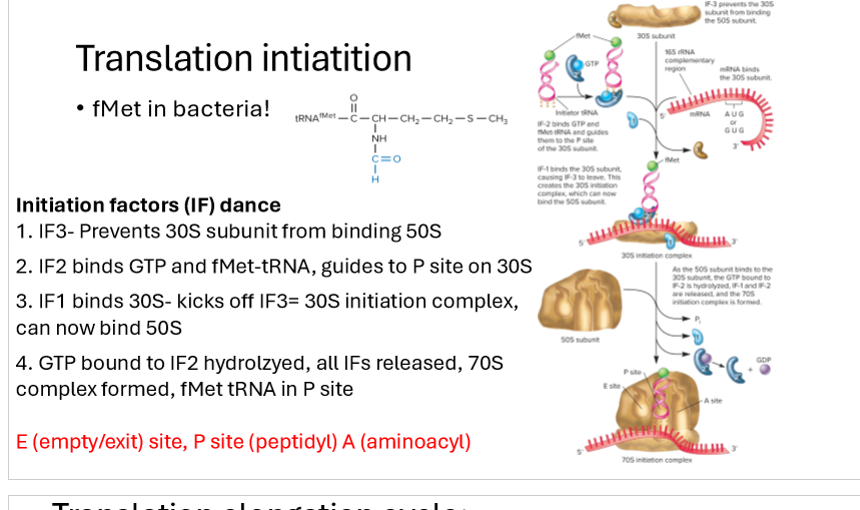
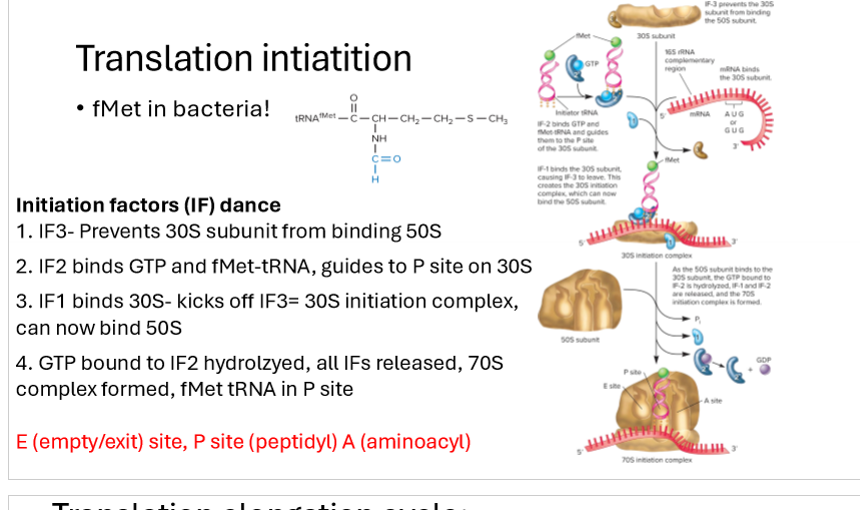
What are the steps of translation initiation?
Fmet amino acid on end of first tRNA
Initiation factor IF3 prevents small ribosome subunit (30s) from binding to large subunit (50s)
IF2 binds GTP and fmet-tRNA, guides them to P site on 30s subunit
IF1 binds 30s, kicking off IF3, kicking off !F3 initiation complex so it can bind 50s
GTP bound to IF2 hydrolyzed, all IFs released
70s complex formed, fMet TRNA in P site and A site open
What are the steps of the translation elongation cycle?
Binding - EF-Tu binds GTP and tNA, brings to A site
Transpeptidation - peptide bond forms between p site and a site amino acids
Translocation - peptide chain on A site, tRNA noves to p site, other leaves out the E site
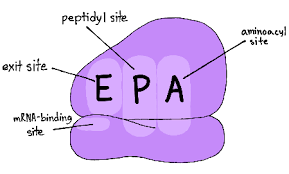
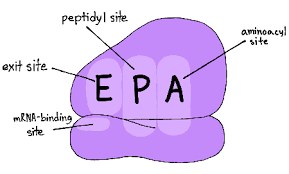
What are the p site, A site, and e site?
sites in ribosome for translation
A site - arrival - entrypoint for incoming tRNA carrying an amino acid
p site - peptide bond formed between new amino acid and chain; first tRNA binds here during initiation of translation
E site - exit - empty tRNA exits
What is transpeptidation?
transfer of growing polypeptide from P site to A site, peptide bond formed
How is translation terminated
release factor proteins bind to UAA/UAG/UGA stop codons
polypeptide released
ribosome dissociates
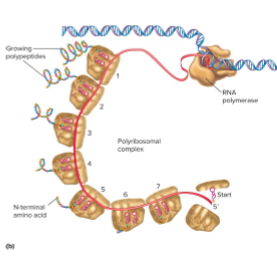
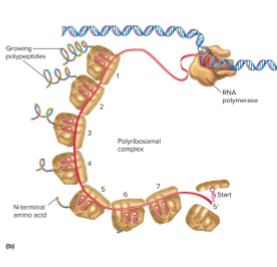
What is couple transcription and translation in bacteria?
translation starts before transcription is finished
Multiple ribosomes attach to a single mRNA strand simultaneously, called a polyribosome
allows bacteria to respond quickly to environmental changes by rapidly producing proteins.
Describe how bacteria translocate proteins to outside
signal peptides at the amino terminal of protein act as tag for secretion
most bacteria use SEcA system with SEC protein pushing protein out of a membrane channel
some use TAT system
Where does transcription of DNA start in bacteria?
ATG promoter region, called -35 region. sig
What is fMet?
modified amino acid used exclusively by bacteria to initiate protein synthesis during translation.
Why is translocation (secretion or inserting in membrane) protein to the ourside important?
can occur during host pathogens interactions
What is the leader sequence in mRNA ?
mRNA region thats transcribed but not translated before the start codon
What are the 3 primary regions of mRNA and their functions?
leader - transcribed but not translated
shine-dalgarno - site within leader region where translation begins
coding region - protein region
What is the Shine-Dalgarno sequence?
site in mRNA leader sequence where translation begins