Excretion
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
DRUG ELIMINATION
The irreversible removal of drug from the body by all routes of elimination.
Metabolism (Biotransformation) and Excretion (Renal)
How are drugs removed from the body?
DRUG EXCRETION
Final means of drug elimination, either as a metabolite or as unchanged parent drug.
DRUG EXCRETION
Drugs may be eliminated from systemic circulation by different pathways and then excreted through one or more of the excretory processes.
metabolite; unchanged parent drug
Final means of drug elimination, either as a ___________ or as _______________.
systemic circulation; excretory processes
Drugs may be eliminated from _____________ by different pathways and then excreted through one or more of the _________________.
Lungs
Perspiration
Bile
Intestine
Saliva
Milk
Kidneys
ROUTES OF DRUG EXCRETION
Excretion through Lungs
Pulmonary elimination
Excretion through Lungs
Removal of drug in a vapor state
Excretion through Lungs
The concentration of a volatile compound excreted through the lungs may also be correlated with the concentration of volatile compound in plasma (eg.: alcohol in breath)
Excretion through Lungs
Major pathway of volatile substances
passive diffusion; blood; alveolus
Excretion through Lungs follows ____________ (_______ to _______)
Excretion through Lungs
Only the non-ionized form of the drug is excreted
Excretion through Lungs
Examples: Anesthetic gases, ammonium chloride, camphor, chloroform, ethanol, iodides, and sodium carbonate
Excretion through Perspiration
Low-molecular weight, water-soluble electrolytes (eg.: sodium chloride)
Ditophal, an anti-leprosy drug, is largely excreted through perspiration
equals; exceeds
Ditophal concentration in sweat ____ to or even ______ the concentration in urine or feces
Excretion through Perspiration
Examples: p-aminohippuric acid (PAH), sulfonamides, thiamine, urea
Bile
produced by the liver, stored in the gallbladder, and release into the small intestine
Biliary Excretion
Requires that drugs have a molecular weight greater than about 300 and a strong polar group
passive diffusion, active transport, pinocytosis
Major pathways of Biliary Excretion
Biliary Excretion
Drugs are excreted as glucuronide conjugates of the parent compound
highly polar; increases; nearly 200
Glucuronide compounds are ____________
Formation of glucuronide ______ MW of parent conjugates by ___________
Biliary Excretion
Examples: cholesterol, chloramphenicol, diazepam, digitalis glycosides, doxycycline, estradiol, quinine, indomethacin, penicillin, steroids, streptomycin, strychnine, and tetracycline
Intestinal Excretion
Direct intestinal excretion via the feces
Substances that are poorly ionized in the plasma
Passive diffusion
What pathway is used in intestinal excretion?
Walls of capillaries to intestinal submucosa to intestinal lumen to eliminated in feces
What is the pathway for substances in passive diffusion of intestinal excretion?
Intestinal Excretion
Slow process for drugs that have slow biotransformation or slow urinary or biliary excretion
Salivary Excretion
Ability to detect unpleasant taste of drug in mouth long after the dose had been administered
T
T/F: In salivary excretion, the taste of the administered dose has been reported even, when the drug was administered by IV or rectal route
Excretion via Milk
Important since drugs can be passed with milk to nursing offspring
Passive diffusion and active transport
Major pathways of Excretion via Milk
6.6
pH of human milk
7.4
pH of plasma
F - ionized
T/F: Weak bases will have a tendency to be more nonionized in the acidic environment of milk than they would in more basic environment of plasma
Weakly basic drugs
Drugs with low therapeutic index
Tertracyclines
Sulfonamides
Drugs that should be avoided by nursing mothers:
Tertracyclines
It may cause deposition in the bones and teeth of newborn
Sulfonamides
It may cause hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn
F - less albumin and cannot metabolize bilirubin
T/F: Newborns have more albumin and can metabolize bilirubin.
T
T/F: Drugs with high affinity with proteins may displace bilirubin from binding sites.
The Kidneys
Kidney Function
Mechanisms of Renal Excretion
Major route of elimination for many drugs
Removal of metabolic waste products
Maintaining salt and water balance
Kidneys are the main excretory organ for:
Kidneys
Excretes excess electrolytes, water, and waste products while conserving solutes necessary for proper body function.
Secretion of renin, which regulates blood pressure
Secretion of erythropoietin, which stimulates red blood cell production
Endocrine functions of kidneys:
Renin
it regulates blood pressure
erythropoietin
it stimulates red blood cell production
Cortex
outer zone of the kidney
Medulla
inner region of the kidney
Nephrons
basic functional units of the kidney
1 to 1.5 million
Each kidney contains ____________ nephrons
Nephrons
Collectively responsible for the removal of metabolic waste and the maintenance of water and electrolyte balance
Cortical nephrons
have short loops of Henle that remain exclusively in the cortex
Juxtamedullary nephrons
have long loops of Henle that extend to the medulla
20% - 25%
Kidneys receive approximately ______________ of the cardiac output
renal artery
The kidney’s blood supply is supplied by blood via the ________, which subdivides into the interlobar arteries penetrating within the kidney and branching further into the afferent arterioles.
single nephron to Bowman’s capsule to glomerulus to efferent arterioles to peritubule capillaries and vasa recti
Each afferent arteriole in the kidneys carries blood toward a:
glomerulus
capillaries – where blood is filtered
Excretion Ratio (ER)
Effective Renal Plasma Flow (ERPF)
Tests to measure kidney function:
Excretion Ratio (ER)
Effective Renal Plasma Flow (ERPF)
These tests can be used to determine the rate of excretion of drug and clearance by the kidneys and monitor the changes in kidney function.
Excretion Ratio (ER)
Describes the fractional decrease in concentration of drug in the plasma due to removal of the drug by the kidney
Excretion Ratio (ER)

no drug is excreted through the kidneys
If ER = 0
no drug is excreted through the kidneys
If CV = CA
100% of drug is excreted through the kidneys
If ER = 1
100% of drug is excreted through the kidneys
If CV = 0
Effective Renal Plasma Flow (EPRF)
Also known as clearance
Effective Renal Plasma Flow (EPRF)
A measure of the amount of drug excreted in urine as function of concentration of drug in the plasma
Effective Renal Plasma Flow (EPRF)
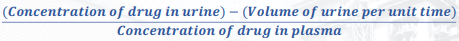
Effective Renal Plasma Flow (EPRF)

amount of drug in urine per unit time
(concentration of drug in urine) - (volume of urine per unit time)
Renal Excretion
Major route of elimination for many drugs that are: ̶
Non-volatile
Water-soluble
Of low molecular weight
Slowly biotransformed by the liver
GLOMERULAR FILTRATION
ACTIVE TUBULAR SECRETION
TUBULAR REABSORPTION
The processes by which a drug is excreted via kidneys may include any combination of the following:
Glomerular Filtration
A passive process by which water and small-molecular-weight ions and molecules diffuse across the glomerular-capillary membrane into the Bowman’s capsule and then enter the proximal tubule
water; small-molecular-weight ions and molecules; glomerular-capillary; Bowman’s capsule; proximal tubule
Glomerular Filtration is a passive process by which ____ and ________________________ diffuse across the __________ membrane into the ______________ and then enter the _____________
Glomerular Filtration
Molecules with MW < 20,000 can pass through irrespective of the charge
shape
In glomerular filtration, if MW > 20,000; the _______ of the molecule becomes the determining factor for filtration
readily filtered
Glomerular filtration:
Glomerular hemoglobin (MW = 64,500),
almost completely unfiltered
Glomerular filtration:
Elongated serum albumin (MW = 68,000)
50,000
In glomerular filtration, upper limit of filterable MW = ______
T
T/F: In glomerular filtration, drugs that are associated with plasma proteins are not filtered
increase; increase; longer
______ free portion of drug in plasma, ______ glomerular filtration
A drug that is excreted exclusively by glomerular filtration and is highly plasma protein-bound, has _________ half-life, unless it undergoes relatively extensive biotransformation.
GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE (GFR)
The amount of fluid filtered from blood into glomerular capsule per unit time
131 ± 22 mL/min
Normal Range of GFR
Total surface area available for filtration
Permeability of the filtration membrane
Net filtration pressure
FACTORS INFLUENCING GFR:
Net filtration pressure (NFP)
it greatly affects the GFR
NFP
GBHP - (CHP + BCOP)
increase; increase; increase; increase; decrease
___ arterial BP = ___ glomerular filtration = ___ GFR
Dehydration: ___BCOP = ___ filtrate
Active Tubular Secretion
Drug is passed from blood into the glomerular filtrate
Active transport process
Requires energy input because drug is transported against a concentration gradient
capacity-limited; saturated
The carrier-system in active tubular secretion is __________ and may be _______________
Active Tubular Secretion
Specificity for chemical structure
Competitive secretory transport mechanism
Active Tubular Secretion
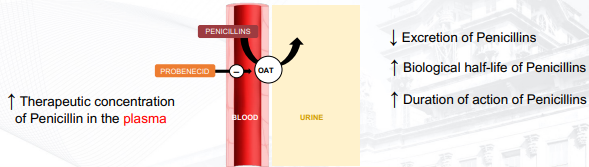
Accounts for the fact that certain plasma protein-bound drugs are rapidly eliminated from the body essentially by renal excretion
Active Tubular Secretion
The kidney dissociates the drug-protein complex
For weak acids: ORGANIC ANION TRANSPORTER (OAT)
For weak bases: ORGANIC CATION TRANSPORTER (OCT)
Active renal secretion systems:
ORGANIC ANION TRANSPORTER (OAT)
Active renal secretion systems for weak acids
ORGANIC CATION TRANSPORTER (OCT)
Active renal secretion systems for weak bases
Active Tubular Secretion
Principle of competition has been employed to provide a longer biological half-life for some drugs (Example: Penicillin)
Tubular Reabsorption
Reclamation process
Tubular Reabsorption
Occurs after the drug is filtered through the glomerulus
Tubular Reabsorption
Can be an active or passive process involving transporting the drug back to the plasma
Tubular Reabsorption
This process can significantly reduce the amount of drug excreted
pH of the fluid in the renal tubule (i.e. urine pH)
pKa of the drug
The reabsorption of drugs that are weak acids or weak bases is influenced by: