Chest X-Ray (CXR) Interpretation
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
what 4 things must be done in order to read a CXR properly?
- make sure patient name is correct
- ensure XR is technically adequate
- perform a systematic evaluation
- compare to previous CXRs
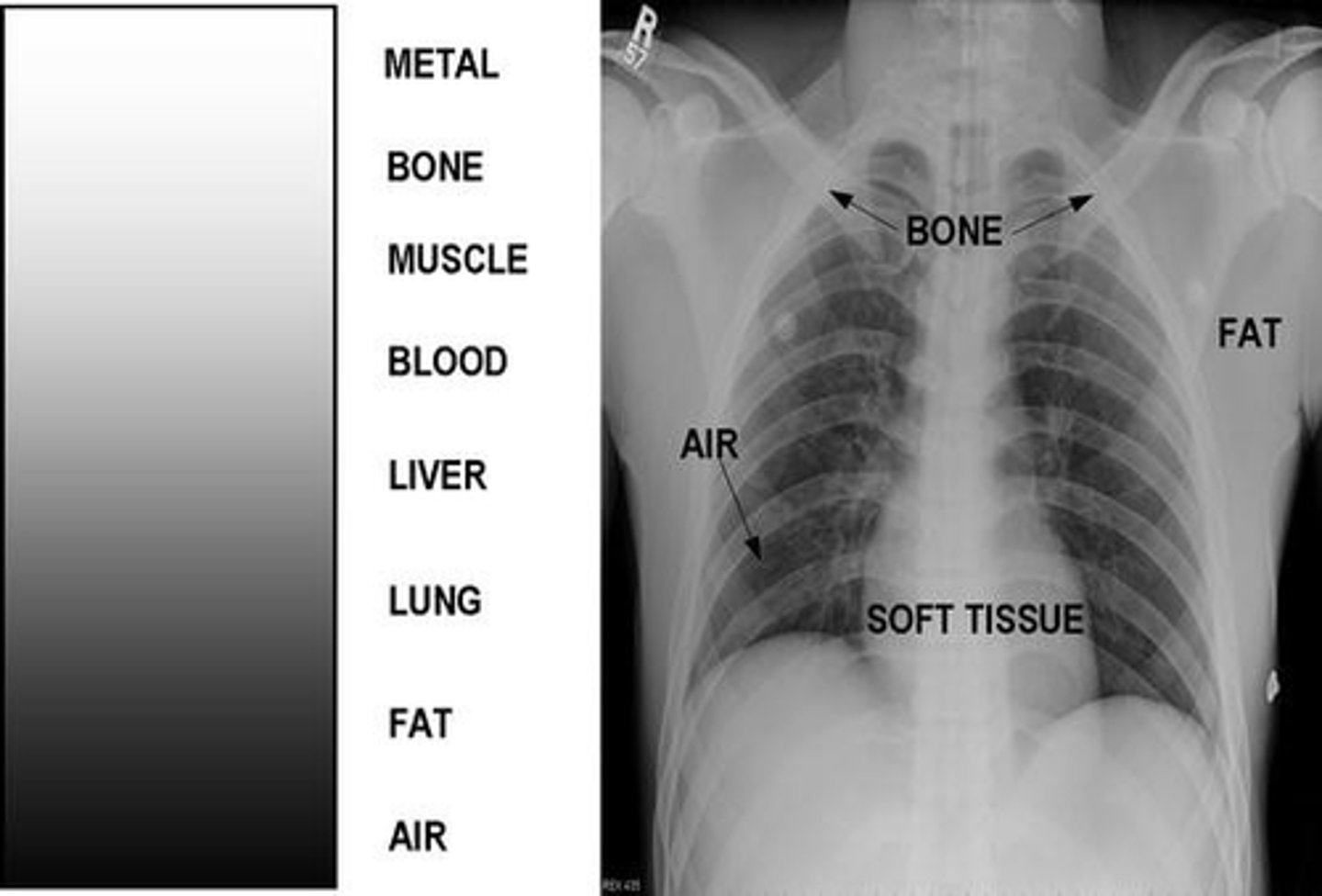
a dense structure will absorb ____ radiation (which leaves less energy available for exposure of the photographic emulsion)
more
1 multiple choice option
structures with little density (air) will appear ______________________ on the XR
"dark" or radiolucent
structures that are dense (metal or bone) will appear _____________________ on the XR
"white" or radiopaque
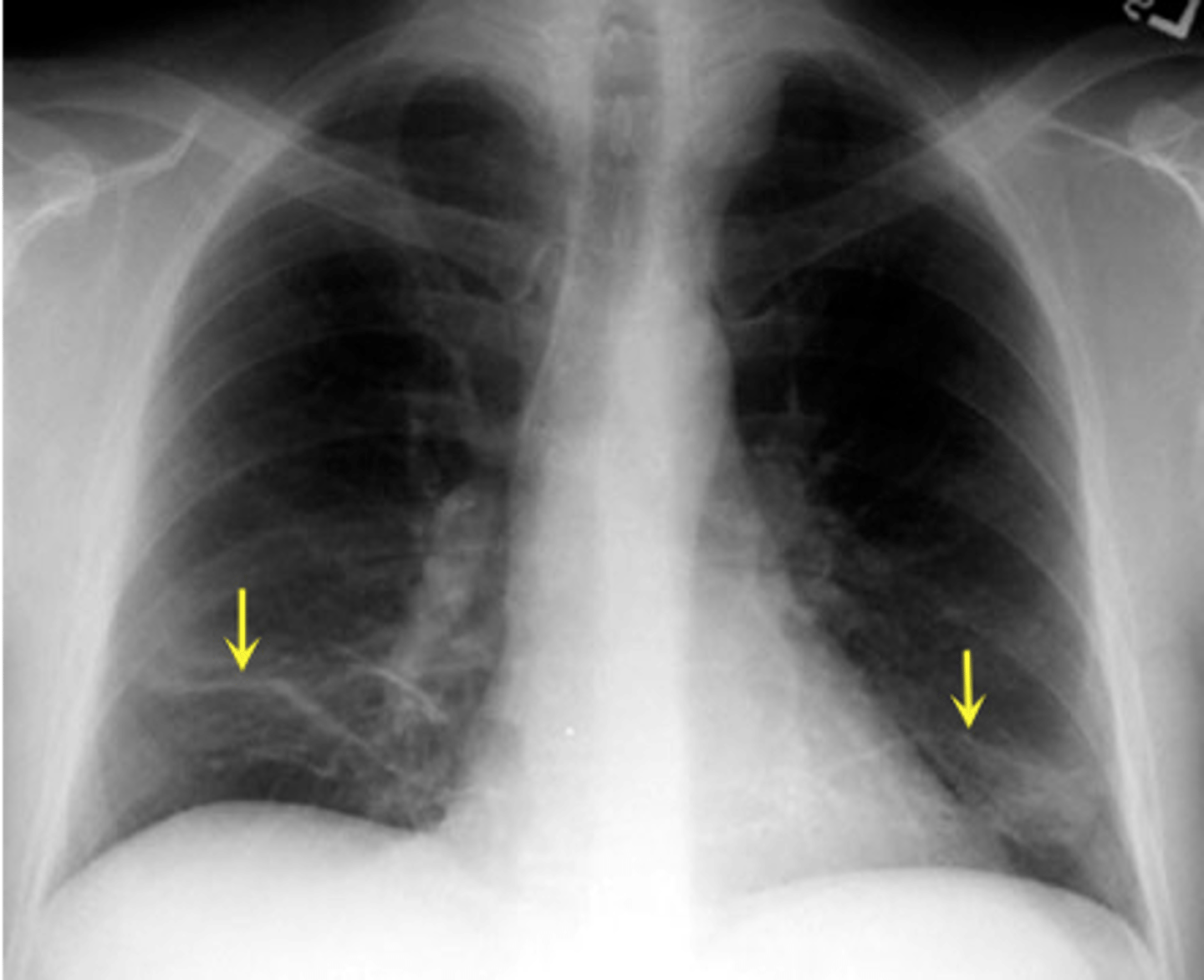
various densities on a CXR
types of CXR projections:
- posterioranterior ("PA")
- anteriorposterior ("AP")
- lateral
- decubitus
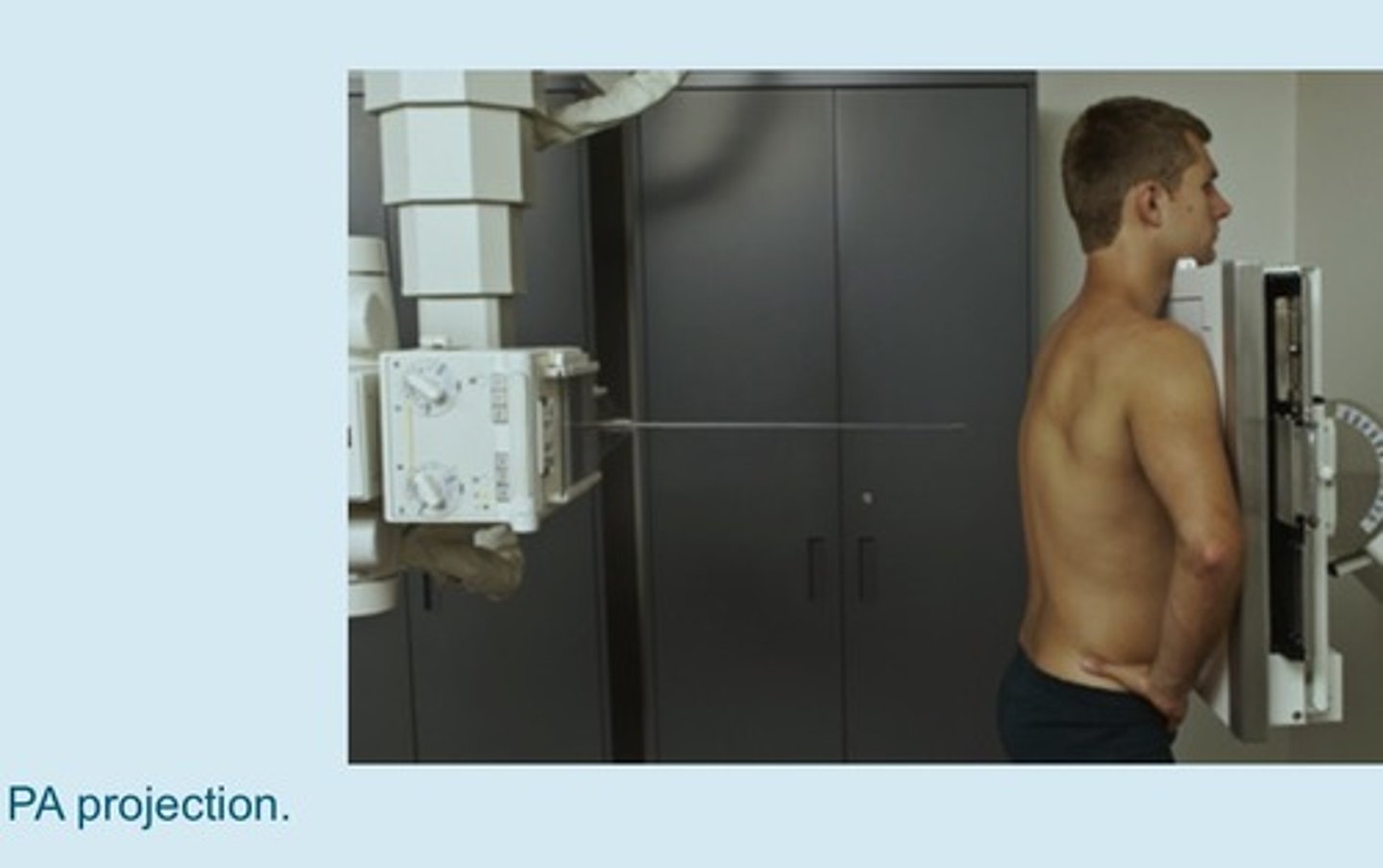
posterioranterior (PA) projection
patient faces the cassette
- done in radiology department
- beam passes "posterior-to-anterior"
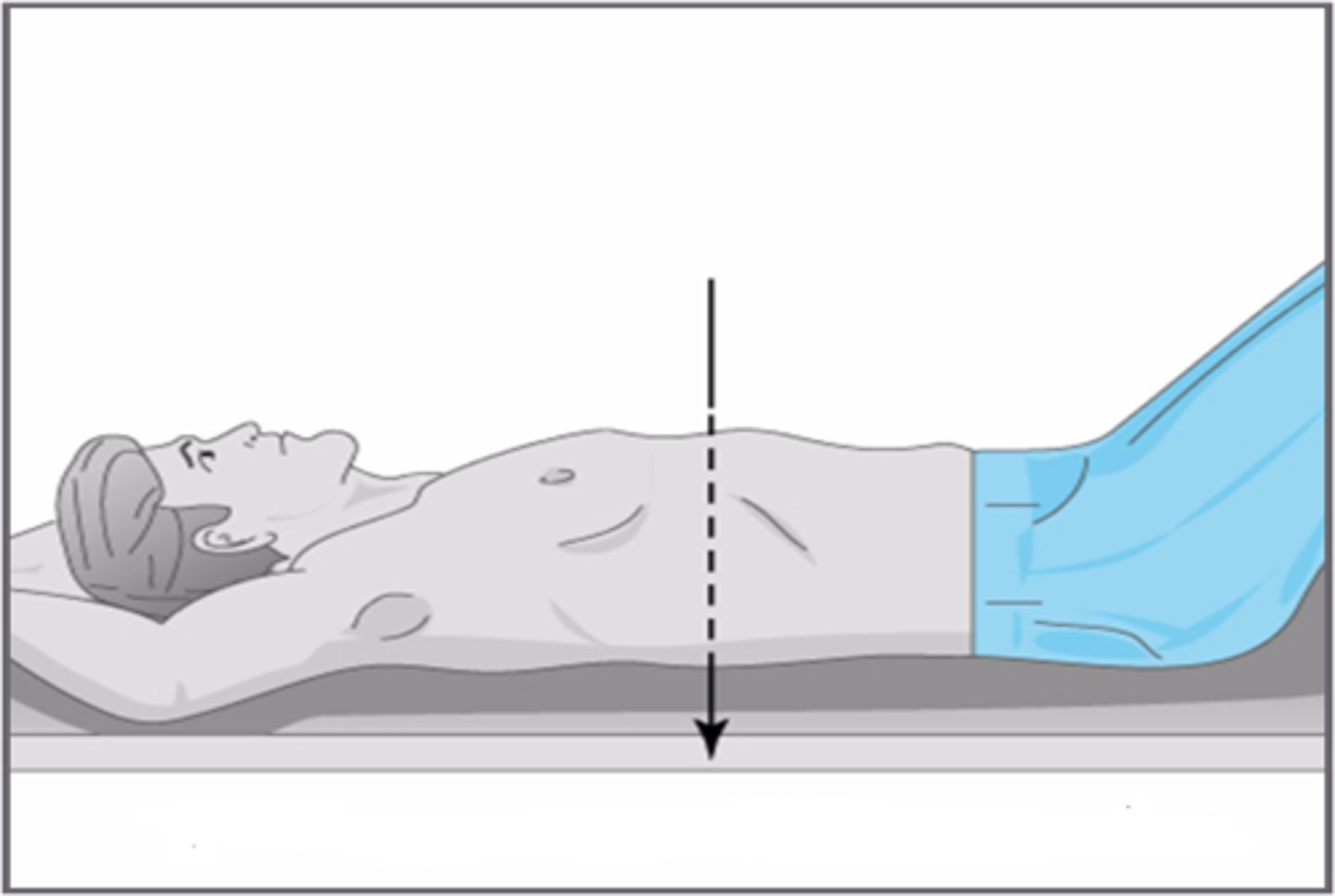
anteriorposterior (AP) projection
patient faces away from the cassette
- usually done w/ portable equipment
- beam passes "anterior-to-posterior"
- may have technical issues
- tends to magnify the image
which is more accurate PA or AP projection?
PA
1 multiple choice option
use _______ in comparing AP & PA films
caution
lateral projection
patient faces perpendicular to the cassette
- usually taken as part of the complete radiographic study of the chest
- labeled according to which side is closest to the XR camera
- obtained to show depth & locate densities
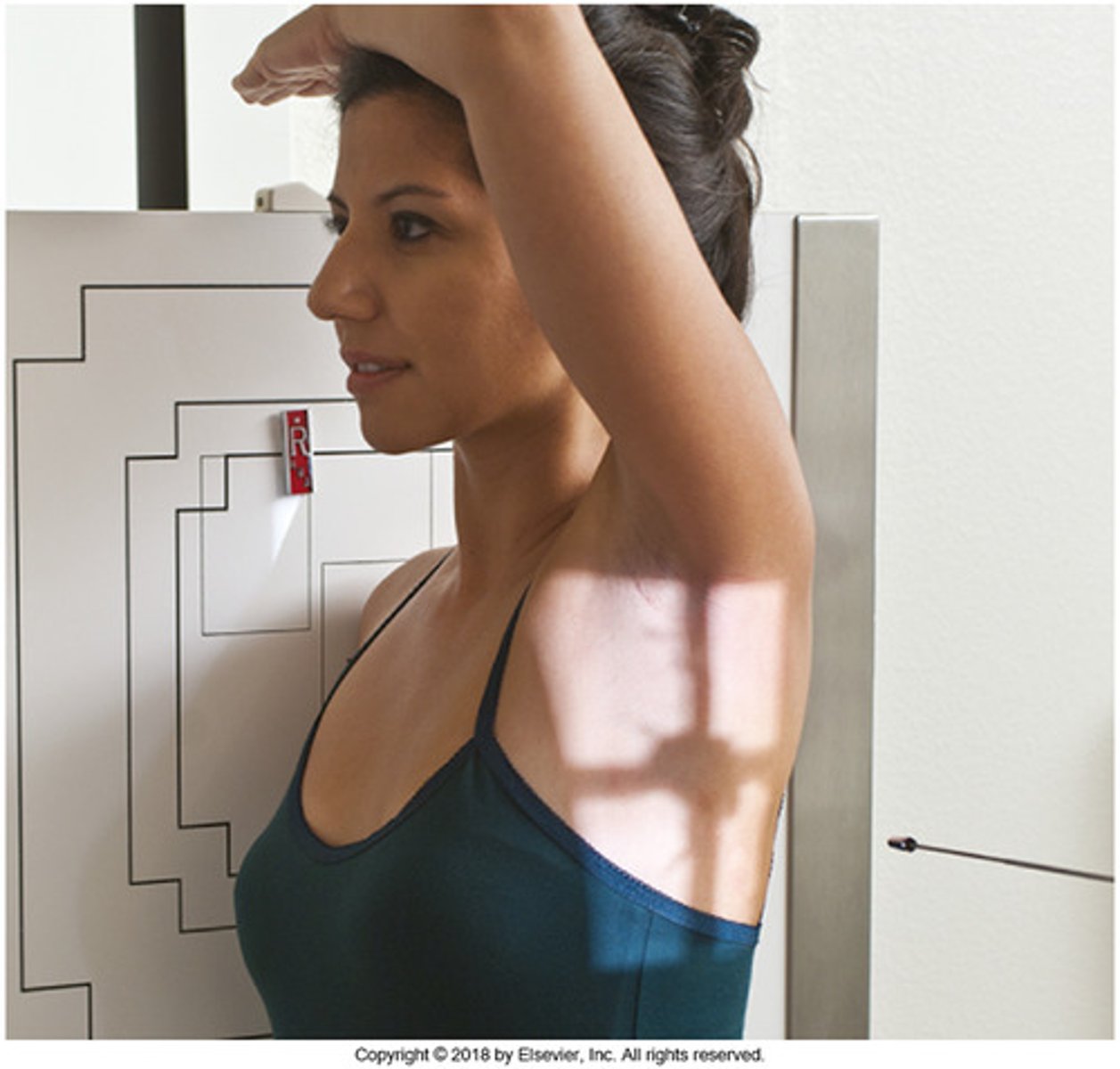

an ___________________ film together will provide more information than either film alone
anterior (AP) & lateral
decubitus projection
patient is placed recumbent on one side
- beam is placed parallel to the patient
- not routinely performed in CXR series; however, can be helpful when evaluating pleural effusion
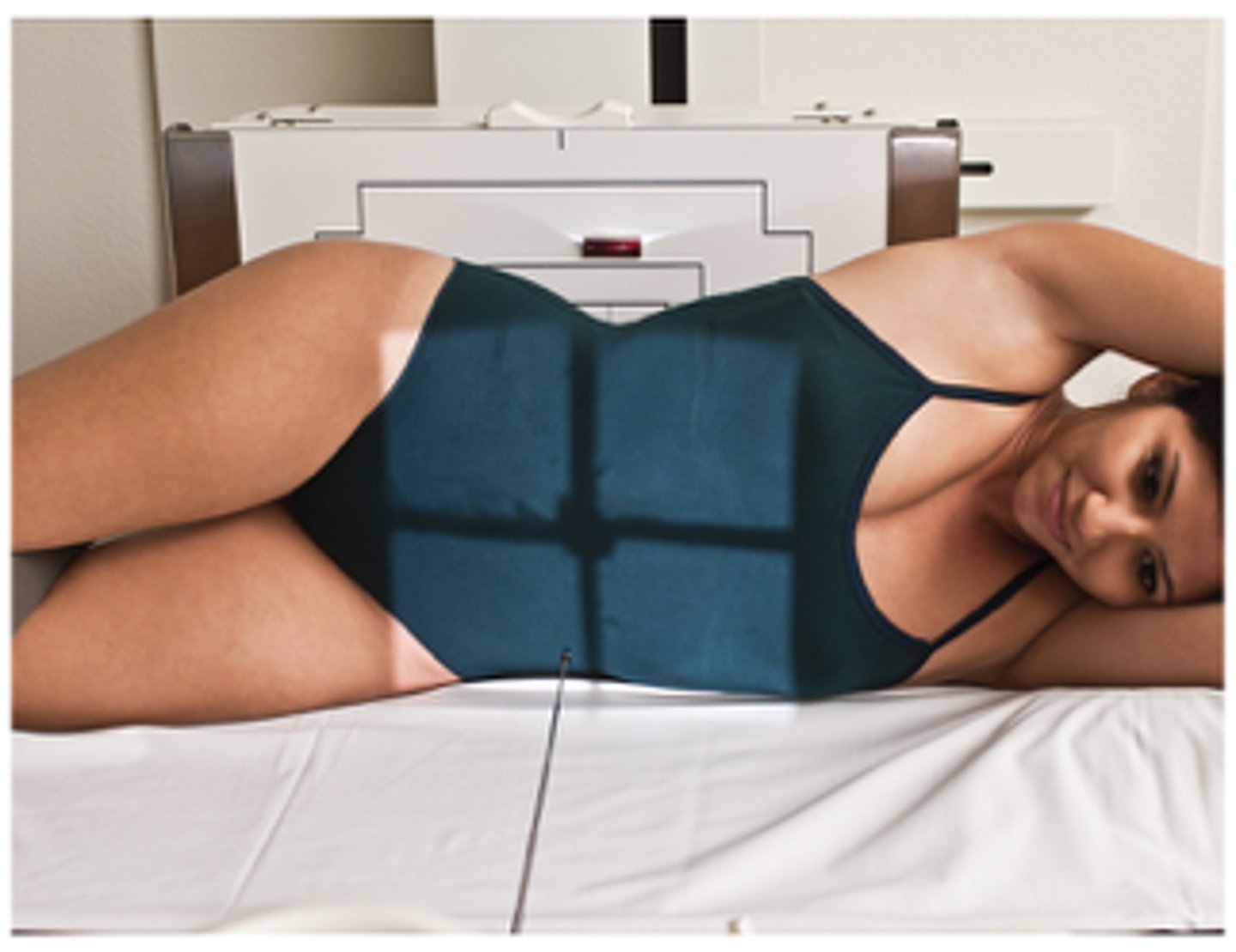

what should you check to ensure sufficient technical quality of an XR (to allow for accurate interpretation)?
- adequate inspiratory effort
- correct exposure conditions
- correct alignment
how do you know when a CXR has a "good"/adequate inspiratory effort?
when 9-10 ribs are seen above the level of the diaphragm
when can an expiratory CXR lead to?
over interpretation
- cardiac shadow may appear enlarged
- peripheral lung markings may look exaggerated
- false positive "infiltrates"
a poorly exposed CXR can also lead to errors, in the form of..
underpenetration or overpenetration
underpenetration = ________ than normal
"whiter"
- may exaggerate normal features & be overinterpreted
1 multiple choice option
overpenetration = ________ than normal
"blacker"
- may "burn out" important details (like a pneumonia) & thus be underinterpreted
1 multiple choice option
how do you know if an XR is properly exposed?
you will be able to see the vertebral bodies behind the heart shadow
improperly aligned film can make..
- the heart appear abnormally large
- mediastinum & pulmonary markings exaggerated
how do you know if a CXR is properly aligned?
the clavicles should be mirror images of each other
systematic approach for CXR interpretation:
- Airway (trachea) & Adenopathy (hilar)
- Bones (fractures/density, etc) & Breast (calcifications, asymmetry)
- Cardiac shadow (size & shape)
- Diaphragm (sharpness & costophrenic angle)
- Everything else (esp. soft tissue structures)
- Fields (lung infiltrates, vascularity)
zone I =
above & around lung fields
- bony structures (fractures, intercostal distance)
- soft tissue areas (densities/free air)
what should you look for in zone I?
- bony structures
- intercostal distance
- soft tissue structures
zone II =
below the lung fields
- diaphragm
- stomach bubble
what should you look for in zone II?
- diaphragm
- stomach bubble
zone III =
mediastinum, heart & lung fields
what should you look for in zone III?
- costophrenic angles (pleural effusion or pneumothorax)
- heart, mediastinum, & pulmonary vasculature (size, shape, hilum)
- lung tissue (opacities)
what is intercostal distance?
literally the height between one rib & the next
what will decrease intercostal distance?
loss of volume
what will increase intercostal distance?
hyperexpansion
______________ is a common soft tissue density seen on routine CXR of women; don't accidentally call this a pneumonia!
breast tissue
what may "flatten" the diaphragm?
- obstructive lung disease
- tension pneumothorax
what may elevate the diaphragm?
- tumors
- fluid
- fat
- pneumothorax
- atelectasis
free air under the diaphragm

what does a "backwards" heart & stomach bubble usually mean?
incorrectly labeled CXR
situs inversus =
reversal of peritoneal organs
dextrocardia =
"right-sided" heart
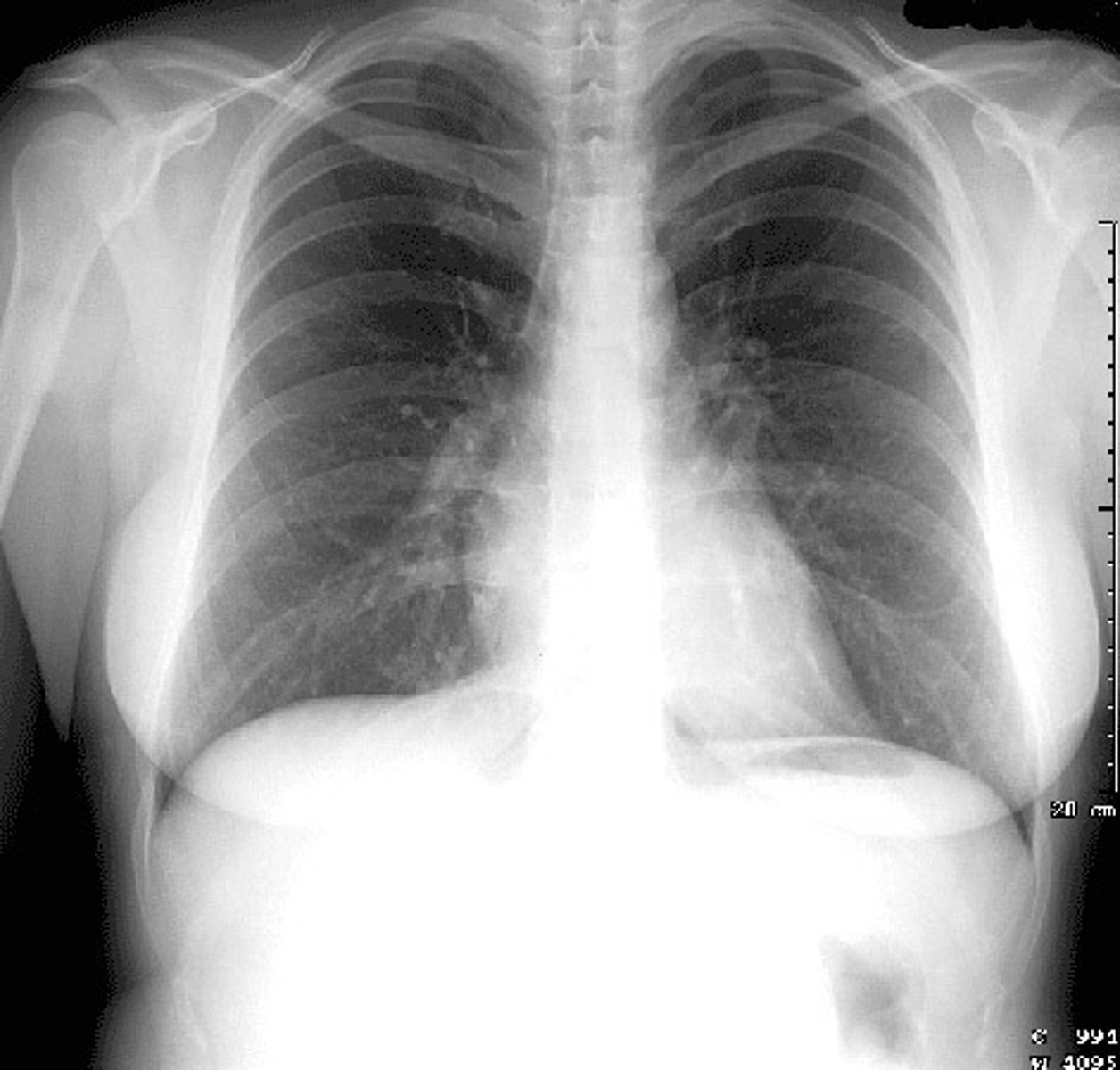
the costophrenic angles should be:
sharp & clear
w/ a pleural effusion (PE), the costophrenic angles are:
"blunted"
w/ a pneumothorax, the costophrenic angles show:
rim of air along the pleural surface
normal costophrenic angles
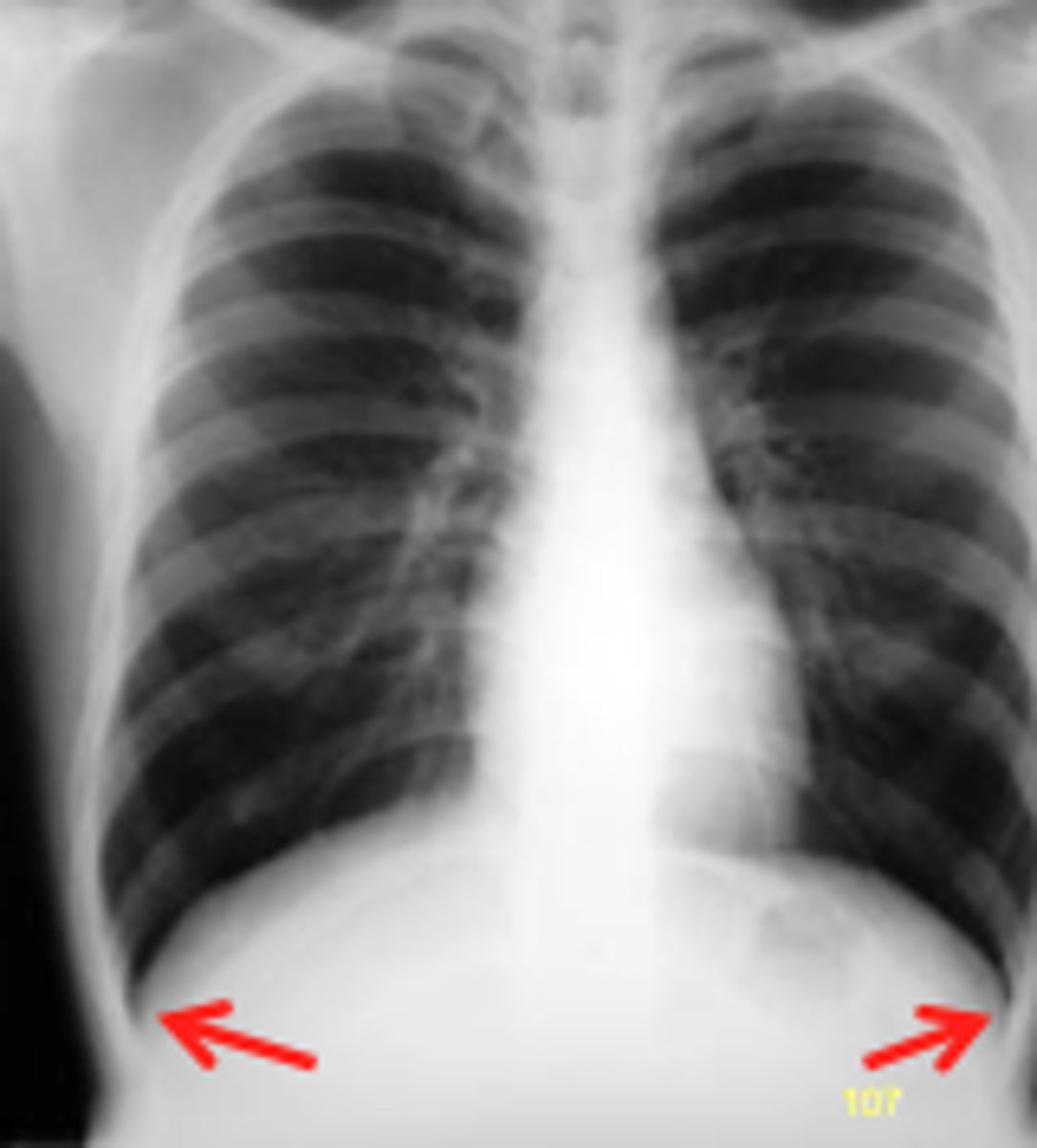
pleural effusion
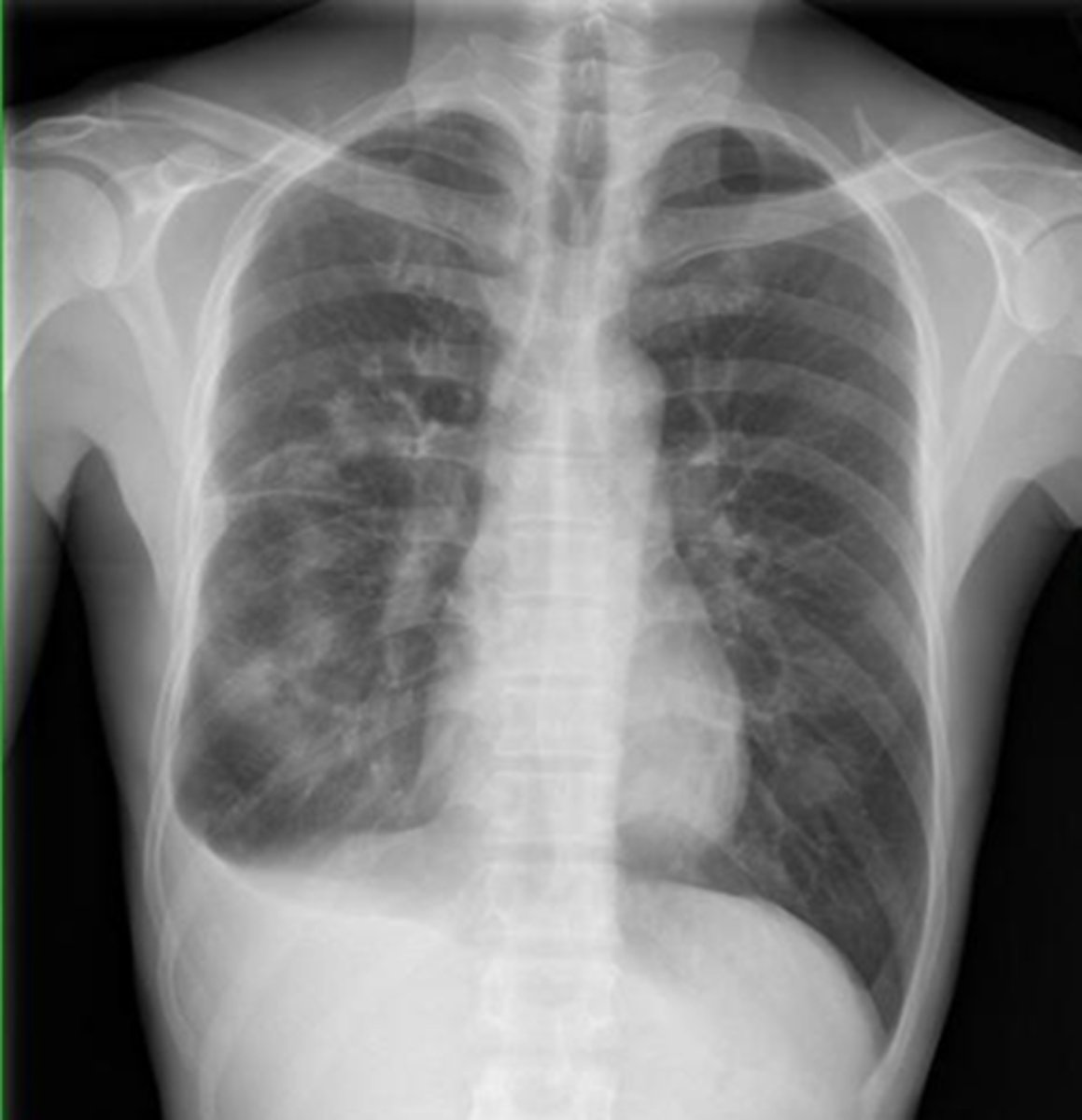
will you be able to see any pulmonary vessels, bronchial markings, or pulmonary parenchyma peripheral to a pneumothorax?
NO
1 multiple choice option
pneumothorax
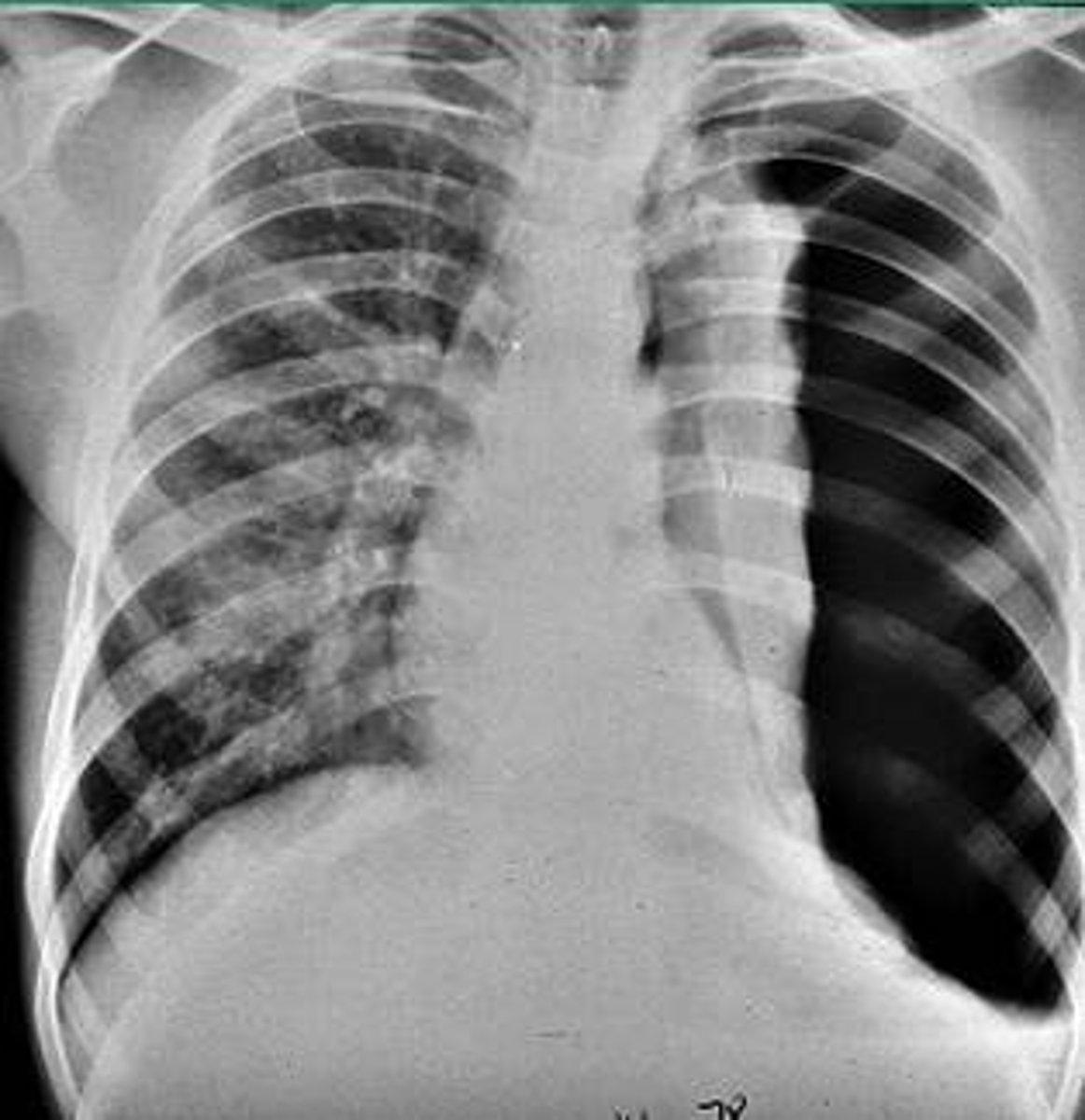
small pneumothorax =
minimal sx
large pneumothorax =
- diaphragm may be elevated
- intercostal distance may be decreased
- mediastinum can be shifted toward it
tension pneumothorax =
- intercostal distance may be increased (hyperexpansion)
- mediastinum & heart can be shifted away from it
in a large pneumothorax, the mediastinum can be shifted ________ it
toward
1 multiple choice option
in a tension pneumothorax, the heart & mediastinum can be shifted ________ it
away from
1 multiple choice option
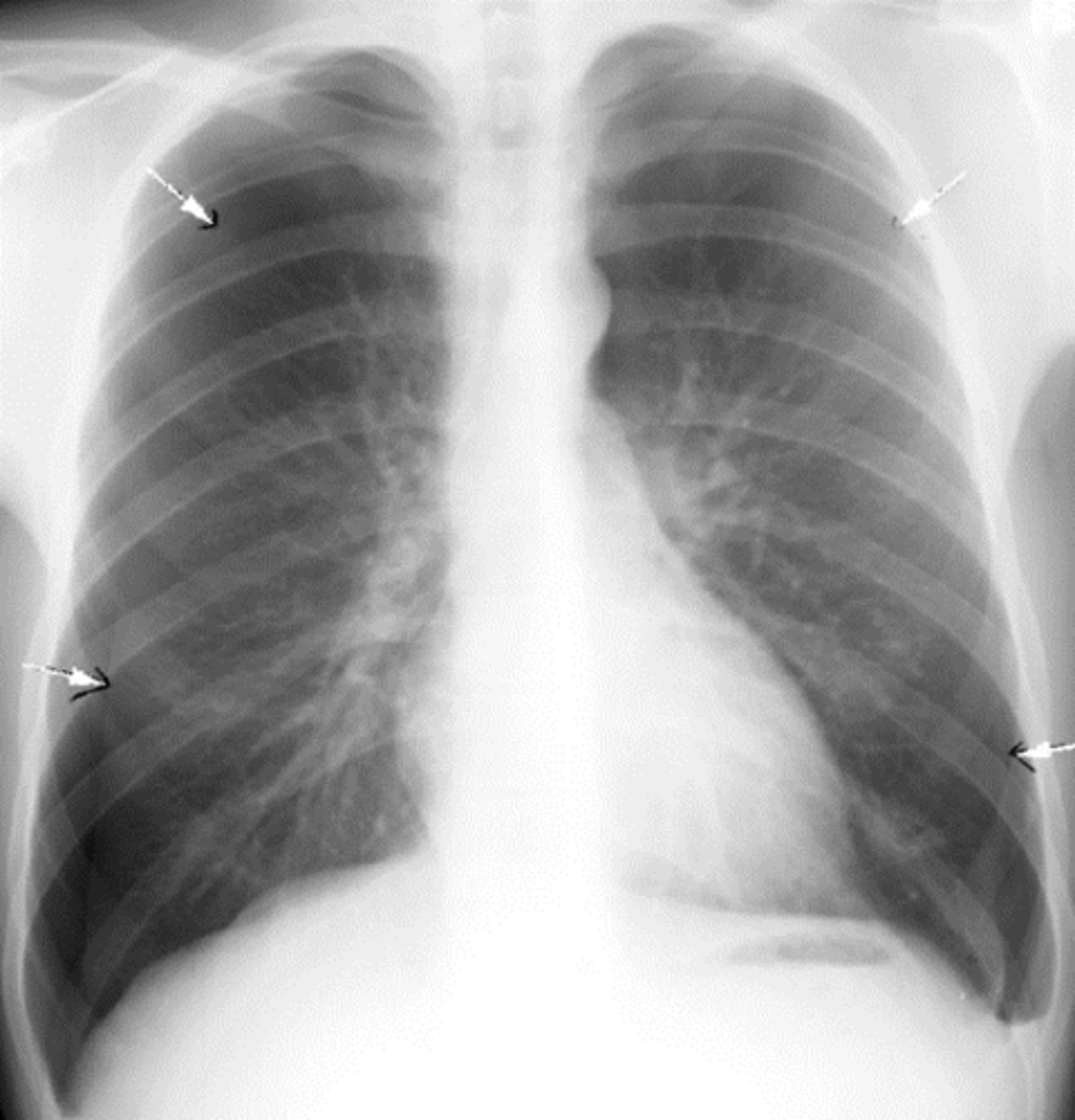
bilateral pneumothorax
tension pneumothorax
notice the trachea being pushed away
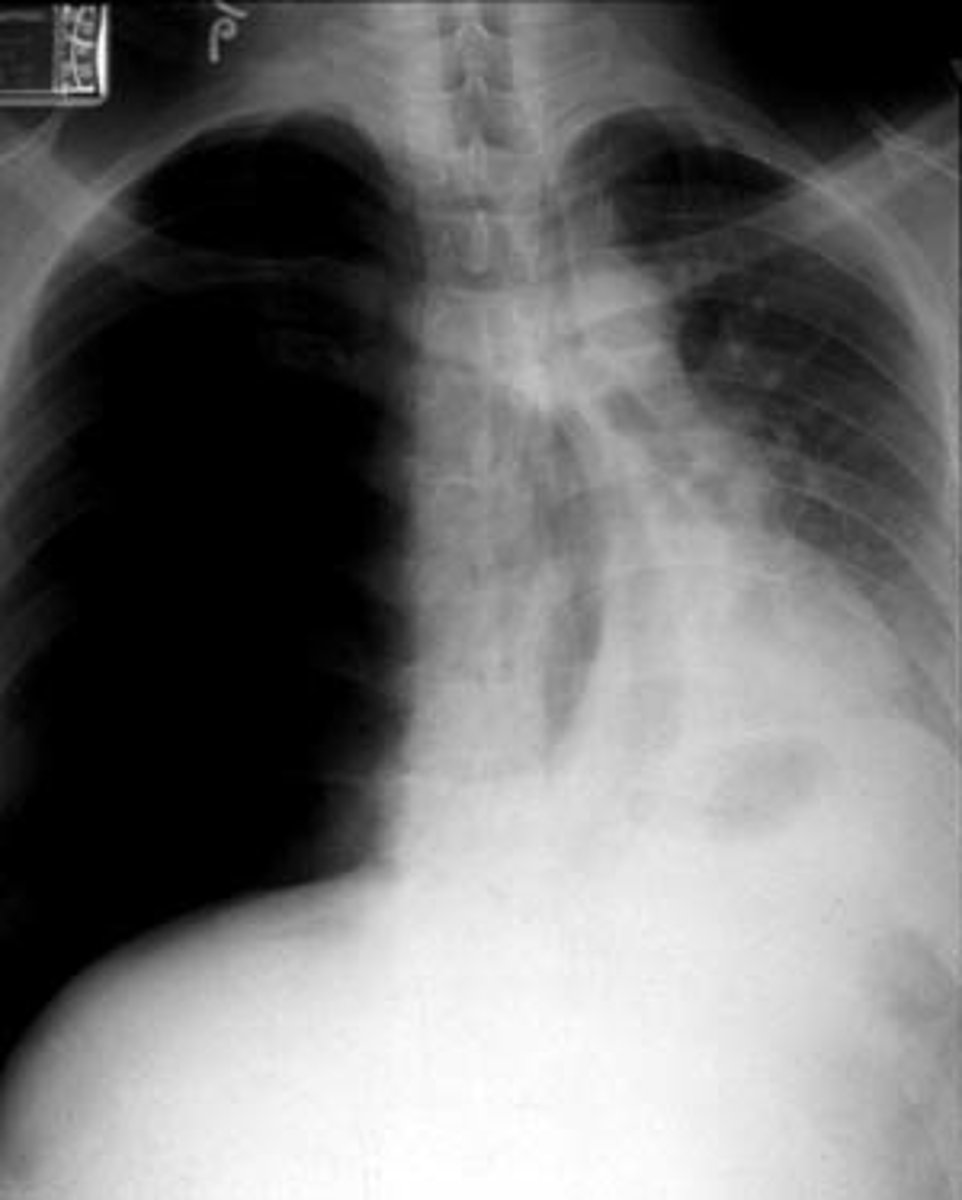
it is important to remember that the heart should be of appropriate..
size & shape
increased cardiac size =
cardiac dilation
while cardiac hypertrophy can be visible on CXR, it is better ascertained via..
EKG or echo
LVH
notice how the enlarged heart follows the contour of the diaphragm down toward the CP angle
- "weenie dog" heart
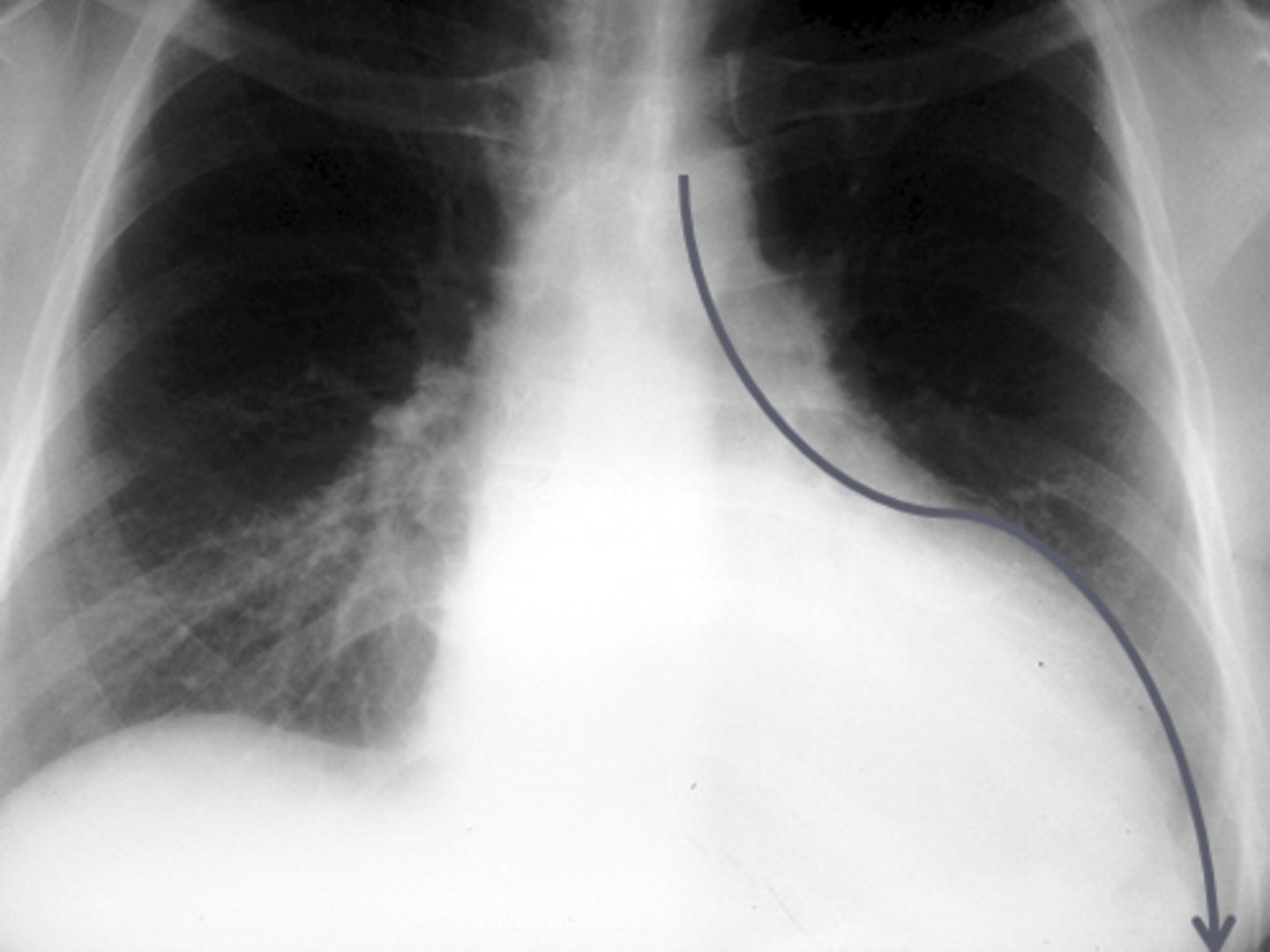
RVH
notice how the apex of the heart appears elevated or "picked up"
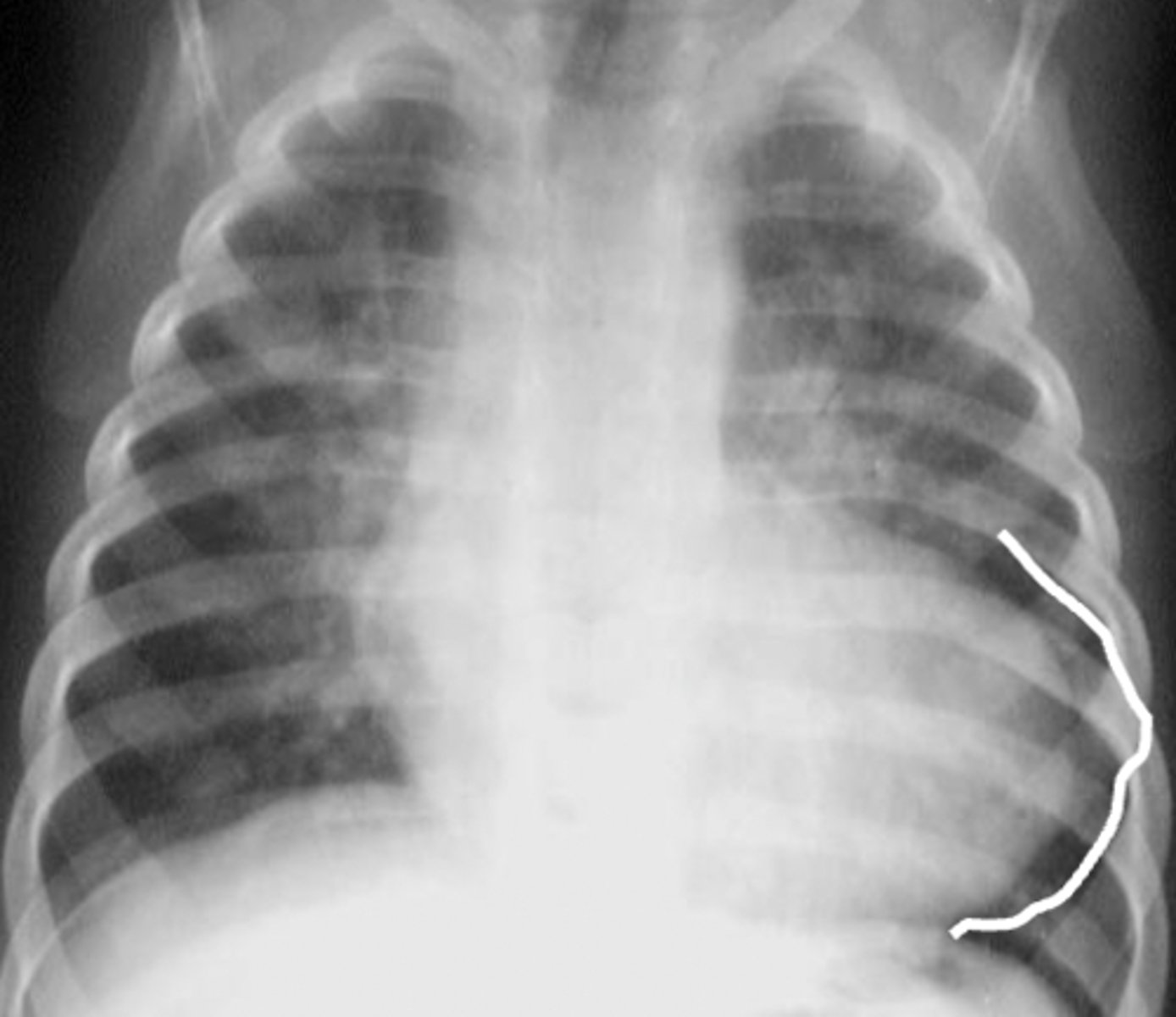
what does pediatric heart structure resemble?
a rounded isoceles triangle
tetralogy of fallot (TOF)
transposition of the great vessels
what are the 3 divisions of the mediastinum?
- anterior (front of heart)
- middle
- posterior (behind the heart)
what is the hilum?
the space medial to each lung that transmits the bronchi & pulmonary vessels, & contains lymph nodes
widened mediastinum
aortic aneurysm
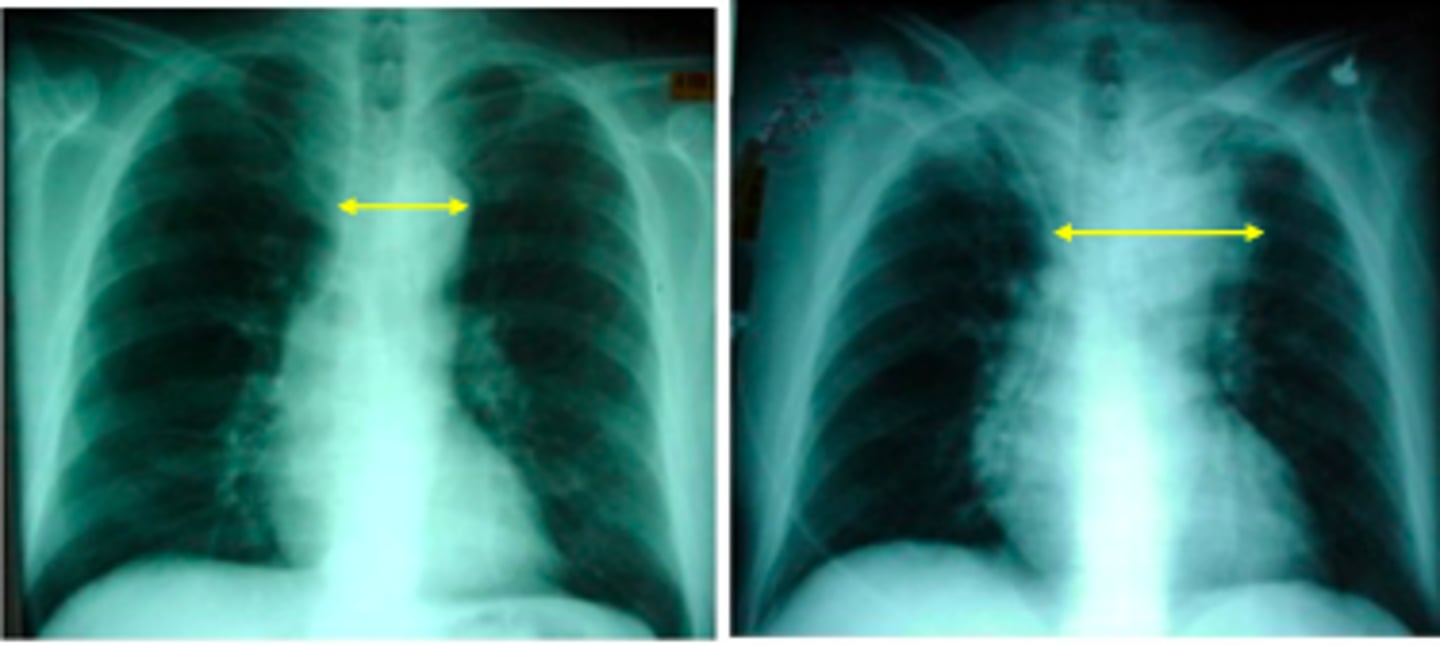
alterations in peripheral vasculature may be secondary to:
- congestive heart failure (CHF)
- congenital heart disease (CHD)
what does cardiogenic pulmonary edema develop from?
increased pulmonary pressure w/ resultant exudate formation in the interstitium & alveolar spaces
what are some findings that may be seen on CXR w/ cardiogenic pulmonary edema?
- cephalization
- fluid in fissures
- peribronchial cuffing
- kerley-b lines
- large hila w/ indistinct borders
- alveolvar edema
areas for infiltrates of pneumonia:
- interstitial
- lobar
- alveolar
- atelectasis
what are some common etiologies for interstitial infiltrates (pneumonia)?
- viruses
- atypical bacterial (mycoplasma, chlamydia)
interstitial infiltrates have a _____________________ appearance
diffuse, "honeycomb"
mycoplasma is AKA..
"walking pneumonia"
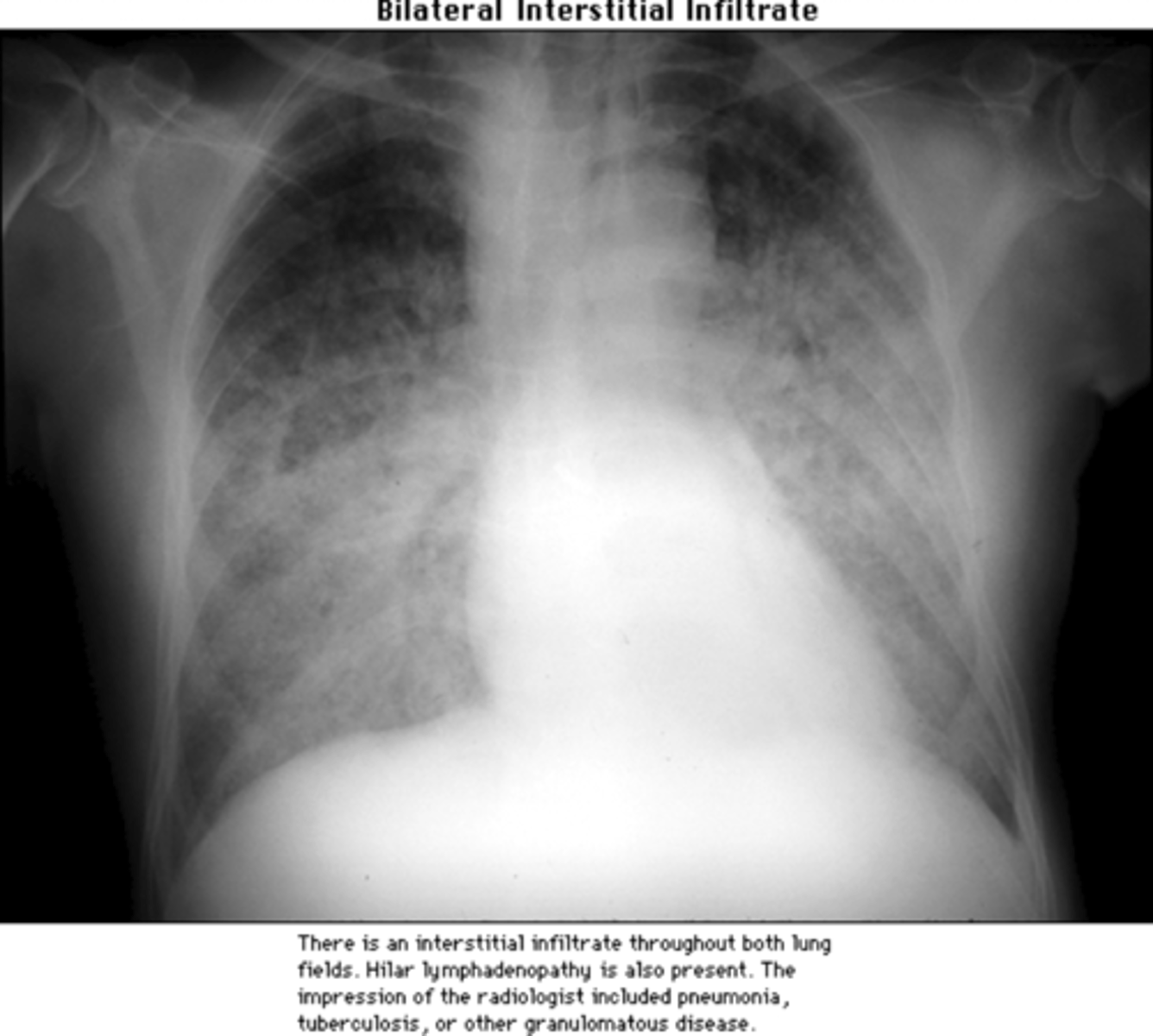
bilateral interstitial infiltrate
notice how it looks like "fog" or a general heaviness throughout the lung fields
- heart borders are still well defined
mild interstitial infiltrate
notice how the interstitial markings are increased & look like prominent "scratch" marks throughout both upper lung fields
- heart borders are reasonably well maintained
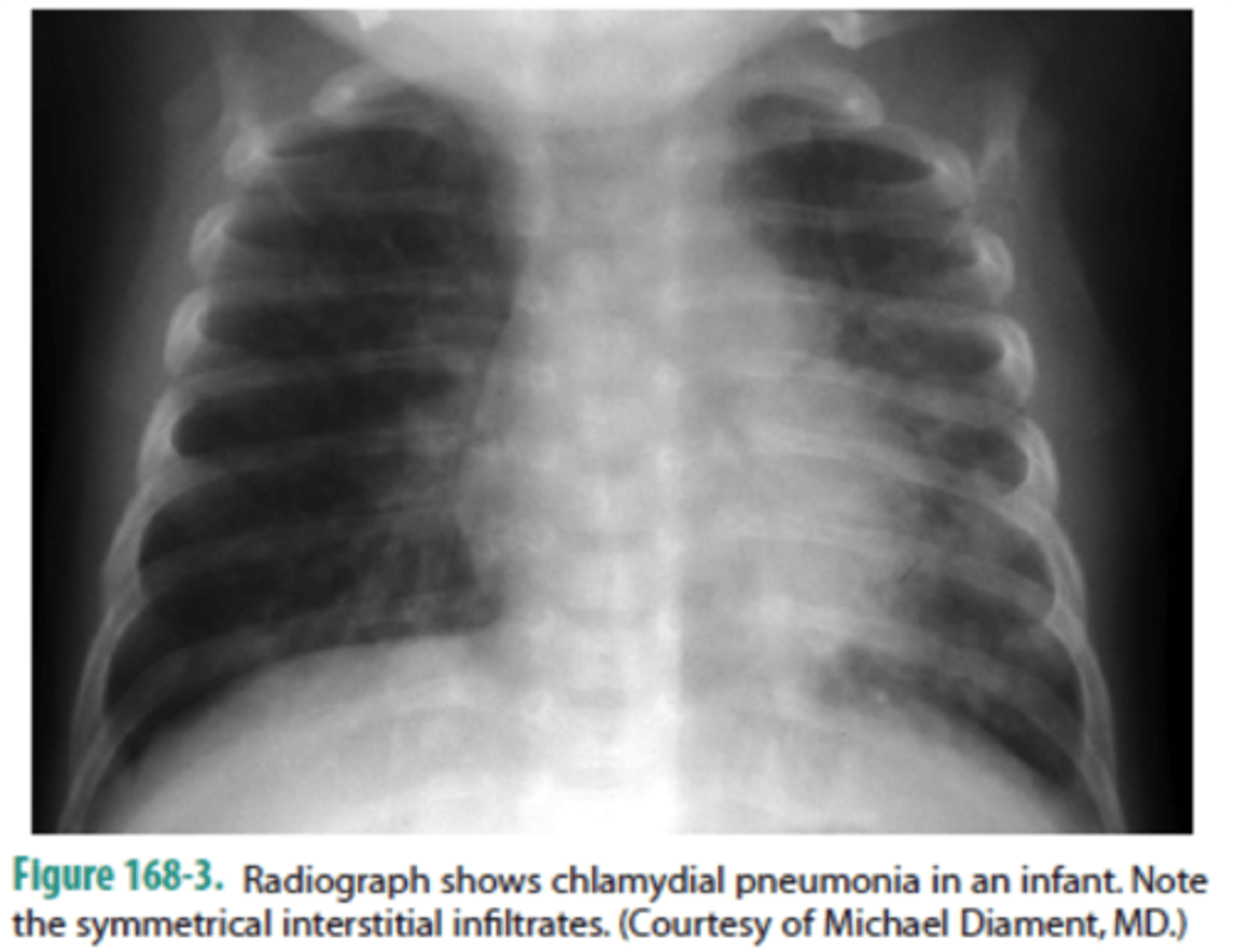
chlamydia pneumonia
notice the "shaggy" heart borders w/ an overall "dirty" appearance to the lung fields
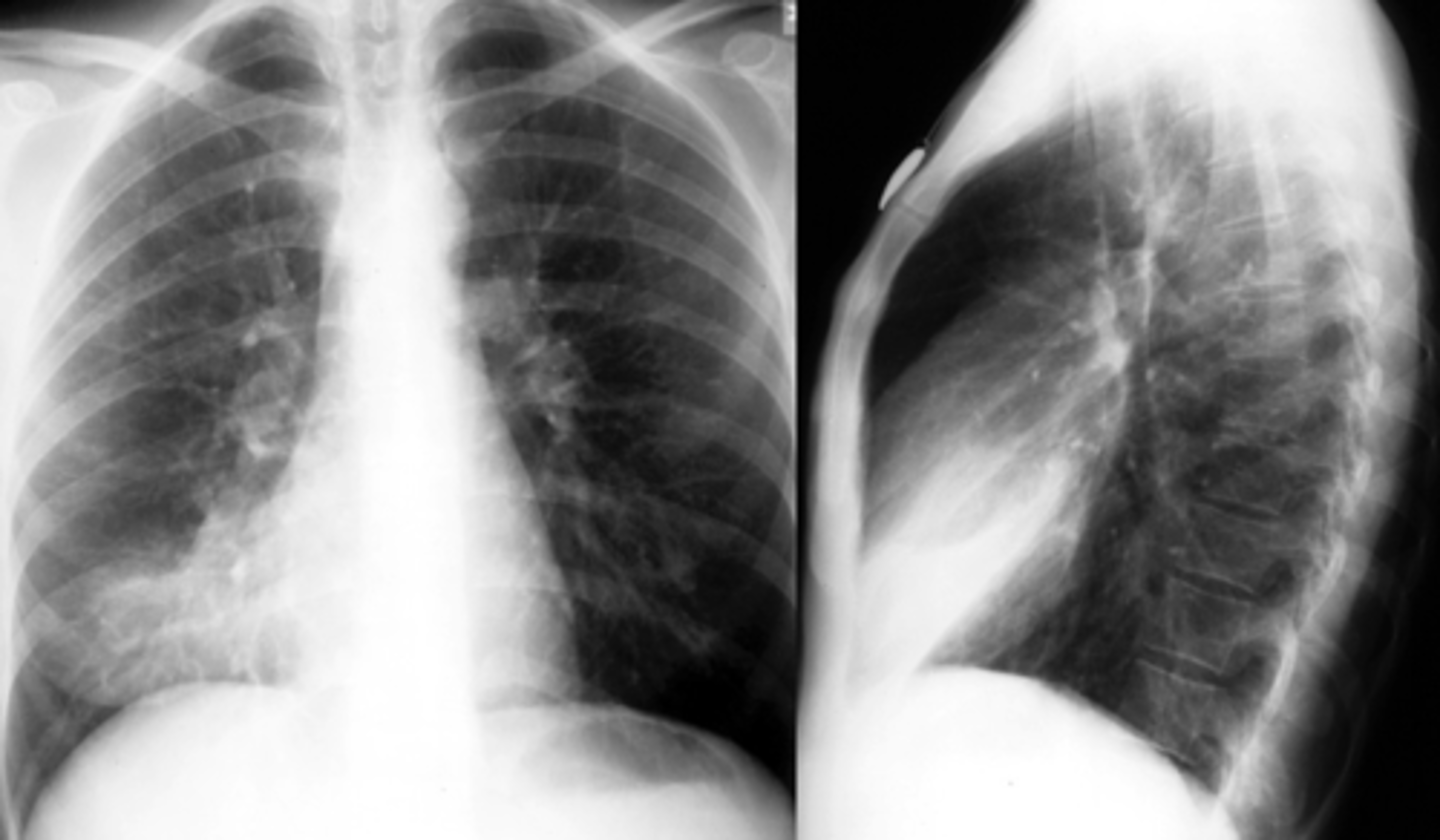
characteristics of lobar infiltrates:
- segmental
- "silhouette sign"
lobar infiltrates are usually _________ pneumonias
bacterial
3 multiple choice options
what is the "silhouette" sign?
infiltrate that has a lobar distribution
- heart border in that specific lobe will appear "hazy" or indistinct
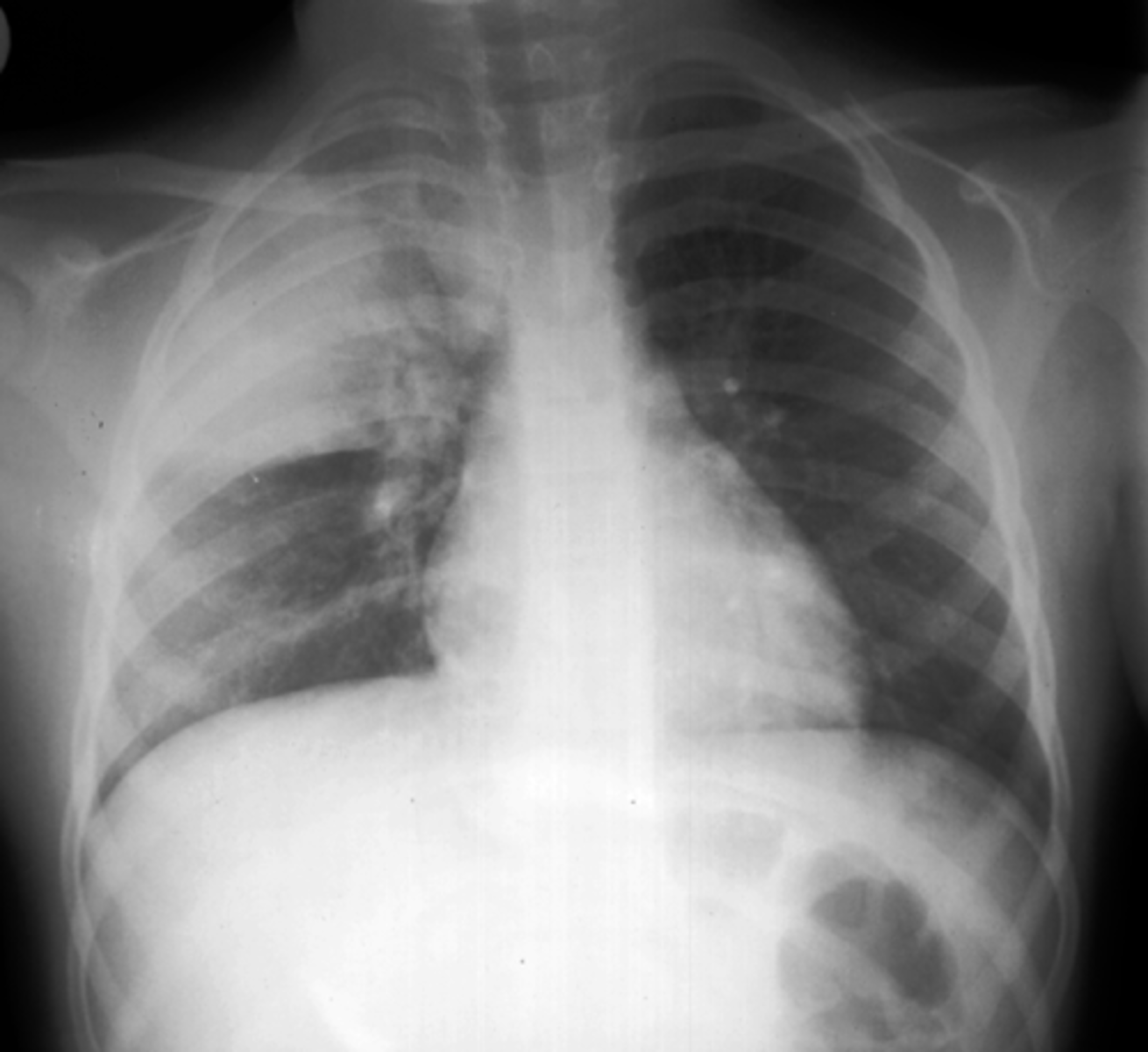
right middle lobe pneumonia
note the classic silhouette sign here
- what should be a sharp, well defined R heart border is "lost" due to superimposition of the infiltrate
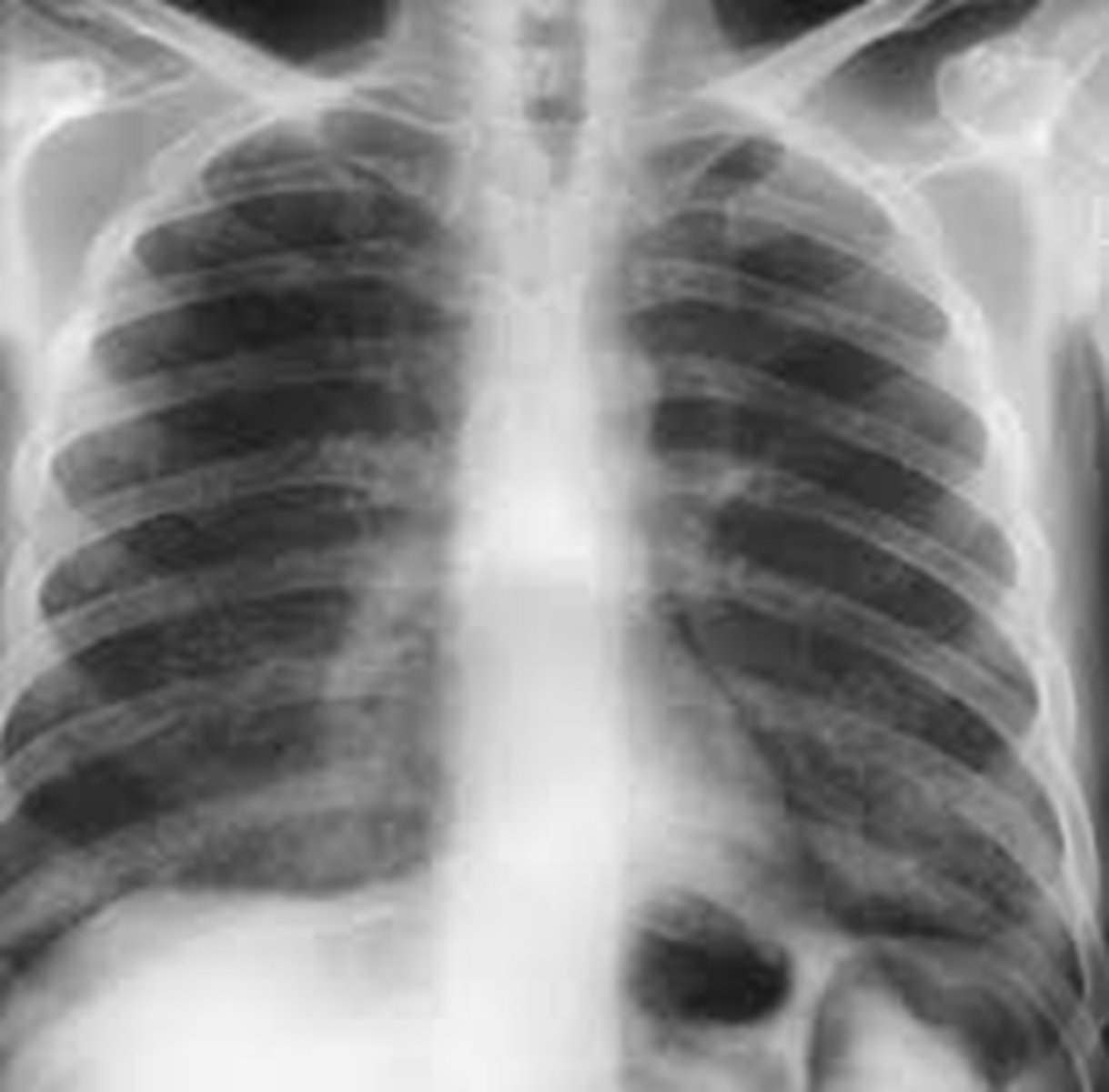
right upper lobe pneumonia
left lower lobe pneumonia
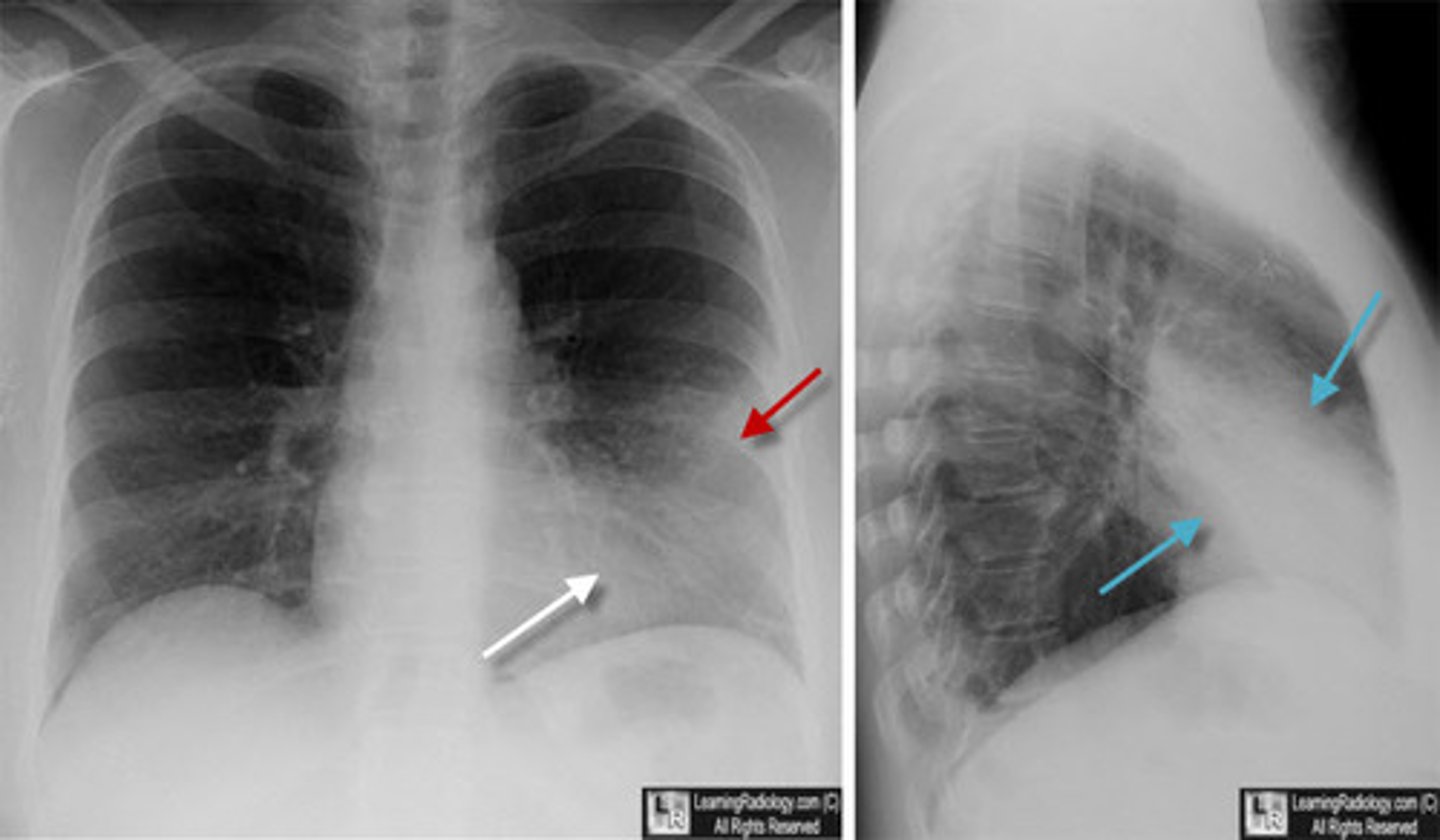
which lobes are involved in this pneumonia?
RUL
RML
RLL
LLL
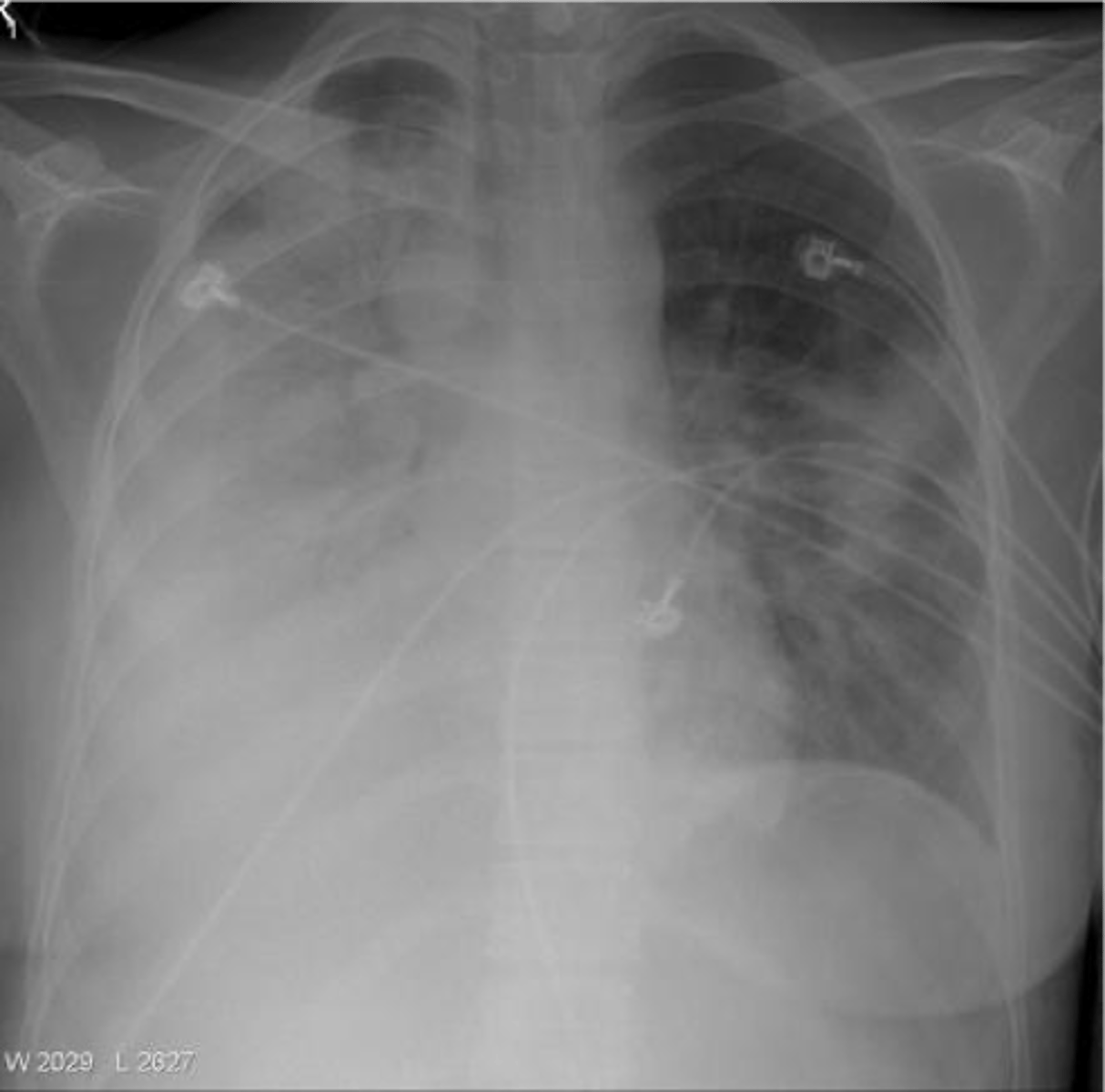
alveolar infiltrates have a _____________________ appearance
"fluffly," cotton ball
alevolar infiltrates **don't have to know
idk if this is the best pic, see notes instead
what can atelectasis result from?
not being ventilated due to:
- compression (effusion)
- obstruction (mucus plug, tumor)
- contraction (scarring)
how can you look for atelectasis?
check intercostal distance
"plate like" atelectasis