Exam 2 - Pathophysiology
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Words to know
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Sodium electrolyte range
135 and 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L)
Maintaining fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contraction
Hyponatremia
Cause: excessive water intake and diuretics
Symptoms: headache, confusion, coma
Tx: 3% NS and fluid restriction
Hypernatremia
Cause: excessive salt intake
Symptoms: lethargy, irritability, seizure, weakness
FRIED: Fatigue, Restlessness, Increased reflexes, Extreme thirst, Dry mouth and skin
Tx: rehydrate with D5W and increase water intake
Potassium electrolyte range
3.5 to 5.0 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L)
Hyperkalemia
Cause: excessive K+ intake, renal dysfunction and ACE inhibitors
Symptoms: cardiac arrythmias (peaked T), cramping, diarrhea, & irritability
Tx: Limit intake of K+ rich foods, loop diuretics, insulin, dialysis and Kayexalate
Hypokalemia
Cause: loop & thiazide diuretics, IV administration of insulin
Symptoms: WALT: weakness, arrhythmias (U wave), lethargy and thready pulse
Tx: PO and IV potassium and increased K+ in the diet 2
Calcium electrolyte range
Ca+ 8.5-10.5 mg/dL
Hypercalcemia
Cause: overactive thyroid gland and cancer
Symptoms: N/V, constipation, and thirst
Tx: decrease calcium in the diet, increase mobility and phosphorous
Hypocalcemia
Cause: diuretic use, and removal of parathyroid glands
Symptoms: numbness, tingling, Chvotek’s sign, tetany, Trousseau’s sign
Tx: increase Ca+ in the diet, and IV/PO calcium
Magnesium electrolyte range
Mg+ 1.5-2.5 mEq/L
Hypermagnesemia
Cause: excessive mg+ intake (laxatives and antacids), and renal dysfunction
Symptoms: muscle weakness, bradycardia, asystole, tremors and slow reflexes
Tx: Dialysis, increase fluid intake, and stopping medications that contain Mg+
Hypomagnesemia
Cause: diuretics, undernutrition, long-term alcohol use disorder, NGT suction, diarrhea, administration of tube feedings or parenteral nutrition
Symptoms: N/V, weakness, tremors, tetany, leg cramps, seizures, change in mental status, hyperactive DTRs, change in mental status, respiratory paralysis
Tx: Increase Mg+ in the diet, and PO/IV magnesium
Chloride electrolyte range
Cl - 98-108 mmol/L
Hyperchloremia
Cause: often seen in metabolic acidosis, hypernatremia, increased chloride retention from by the kidneys, and hyperparathyroidism
Symptoms: tachypnea, weakness, lethargy, decreased cognition, coma
Tx:IVF and diuretics
Hypochloremia
Cause: seen often in metabolic alkalosis, excessive use of loop diuretics, NGT suction, kidney disease, severe V/D
Symptoms: fatigue, weakness, respiratory distress, numbness and tingling, muscle cramps, confusion
Tx: Saline solution administration
Phosphorus electrolyte range
PO4- 2.5 – 4.5 mg/dL
Hyperphosphatemia
Cause: impaired kidney excretion, hypoparathyroidism, Excessive Vitamin D, excessive phosphate in diet, DKA
Symptoms: hyperreflexia, anorexia, muscle weakness, decreased mental status
Tx: With normal kidney function: volume repletion with saline and diuresis with a loop diuretic such as furosemide or bumetanide
Hypophosphatemia
Cause: administration of calories to malnourished patients (refeeding syndrome), ETOH withdrawal, hyperventilation, diuretic use, GI absorption problems
Symptoms: muscle weakness, slurred speech, dysphagia, irritability, confusion, seizures, coma
Tx: oral phosphate supplementation and bioactive vitamin D (calcitriol)
Serum osmolality normal range?
275 - 295 mOsm/kg (milliosmoles per kilogram)
BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) normal range?
10 - 20 mg/dL
Dehydration lab values?
Hct (more than 3xHgb)
BUN > 20
Specific Gravity > 1.030
Serum Osmolality > 295 mOsm/kg water
Serum sodium > 145 mEq/L
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
Serum Potassium and Sodium

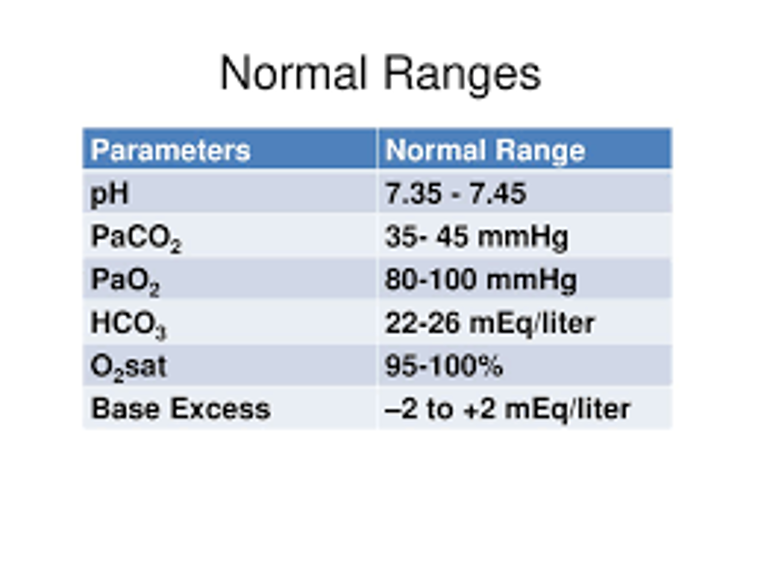
ABG Analysis
pH = 7.35 - 7.45
PaCO2 = 35mmHg - 45mmHg
HCO3 = 22mEq/L - 26mEq/L
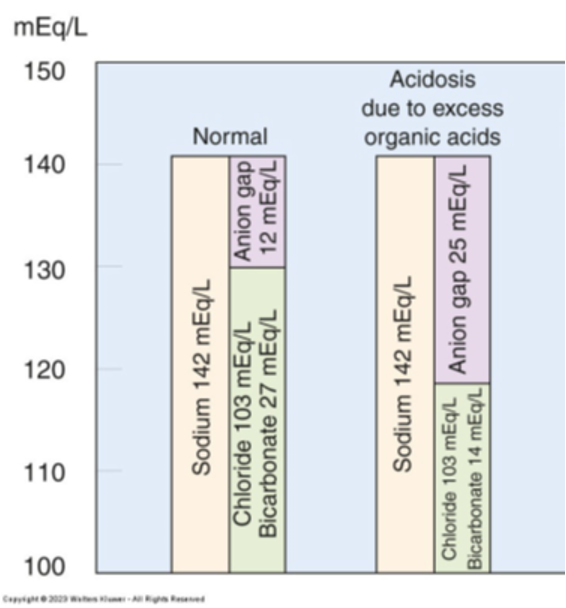
Anion gap normal range?
8 - 12 mEq/L