AP Human Geography Unit 1 Review
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Who is considered to be the father of geography?
Eratosthones
Place
a human geographical term that means a location that has a significant meaning to a person
Site
The actual location of a settlement on the Earth, and the term includes the physical characteristics of the landscape specific to the area. Site factors include landforms, climate, vegetation, availability of water, soil quality, minerals, and wildlife.
Situation
the location of a place relative to its surroundings
Toponym
a name for a place
Sense of Place
the perception based on our emotional connection and association with a certain place
Proximity
indicates the degrees of nearness
spatial association
the relationship or connection between two or more phenomena that tend to occur in proximity to each other. It involves analyzing how the distribution of one phenomenon relates to the distribution of another phenomenon
spatial patterns
how and where different geographic features occur on the earth’s surface
4 types of spatial patterns
Absolute Distance
Absolute Direction
Clustering and Dispersal
Elevation
Absolute Distance
A distance that can be measured with a standard unit of length, such as a mile or kilometer
Relative Distance
Approximate measurement of the physical space between two places; for example, time
Absolute Direction
north, south, east west
Relative Direction
Describes one location in reference to another—left, right, forward, backward, up, down, directions
Clustering and Dispersal
how different phenomena are organized across an area
Elevation
the height of geographic features relative to sea level
map scale
the relationship between distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground
It is usually represented as a ratio such as 1:10000 where 1 unit on the map equals 10,000 units on the ground
map projection
a method by which the curved surface of the earth is represented on a flat map.
4 distortions a map can have
Shape
Distance
Relative Size
Direction
5 important map projections
Mercator
Peters
Goode Homolosine
Polar
Robinson
What is the Mercator Projection and what are the accuracies and inaccuracies of it?
a projection which is often used for navigation because it preserves angles, which is useful for plotting a straight-line course—the latitude and longitude lines meet at right angles
Accuracies:
Shape
Direction
Inaccuracies:
Relative Size
Distance
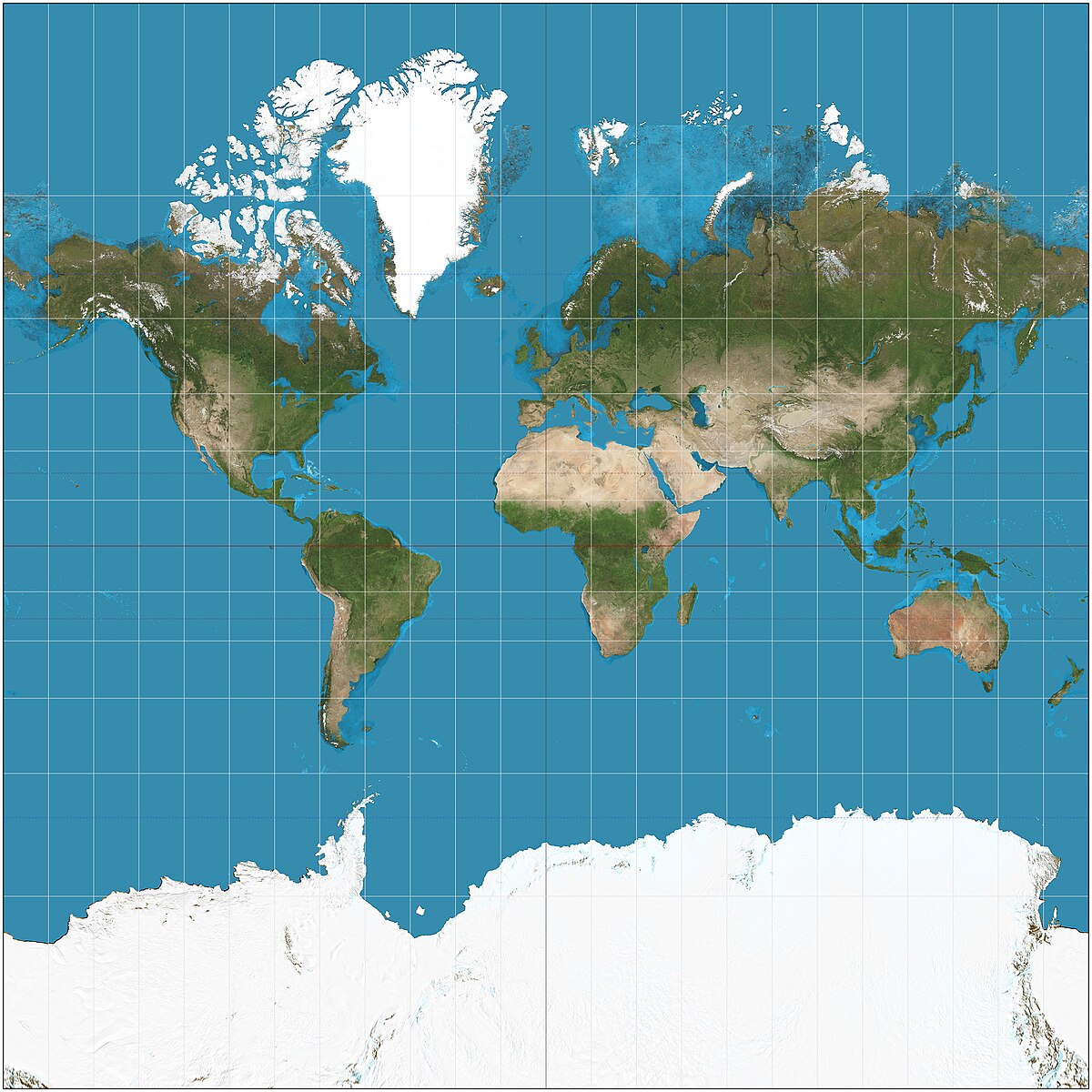
What is the Peters Projection and what are the accuracies and inaccuracies of it?
a projection developed to challenge the Euro-centric Mercator Projection. It depicts continents according to their true size
Accuracies:
Relative Size
Inaccuracies:
Shape
Distance
Direction
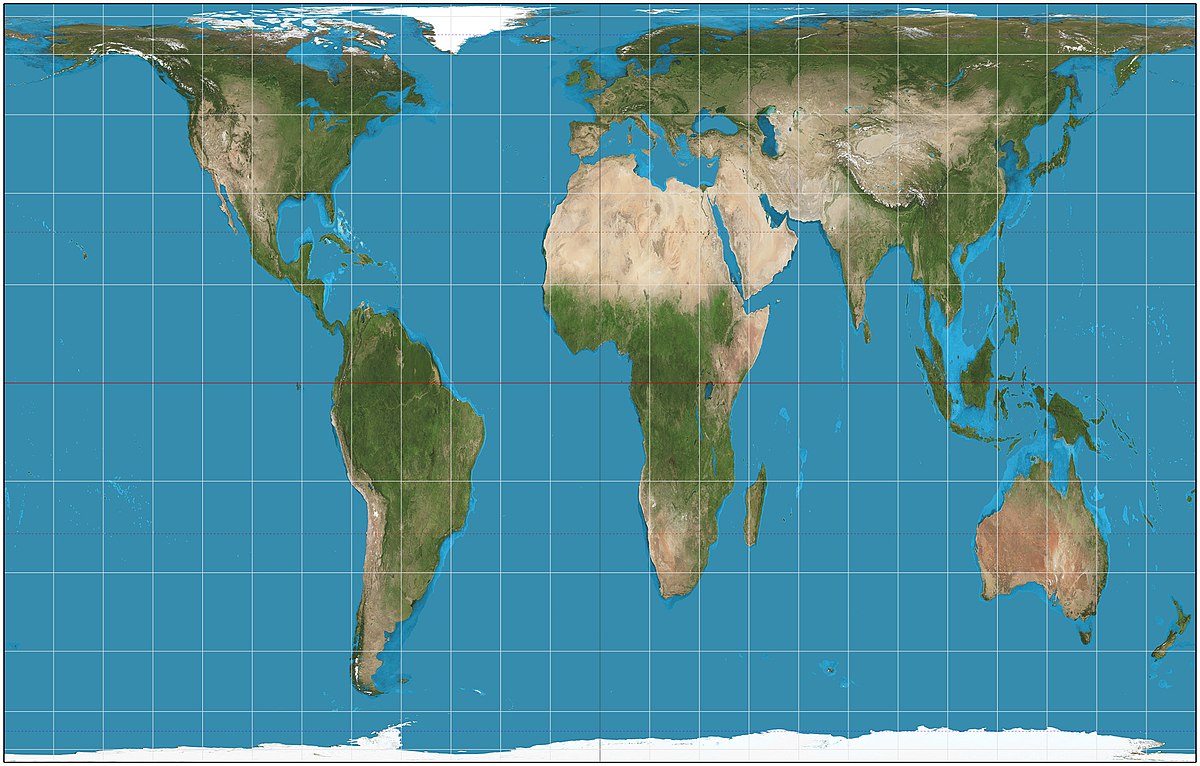
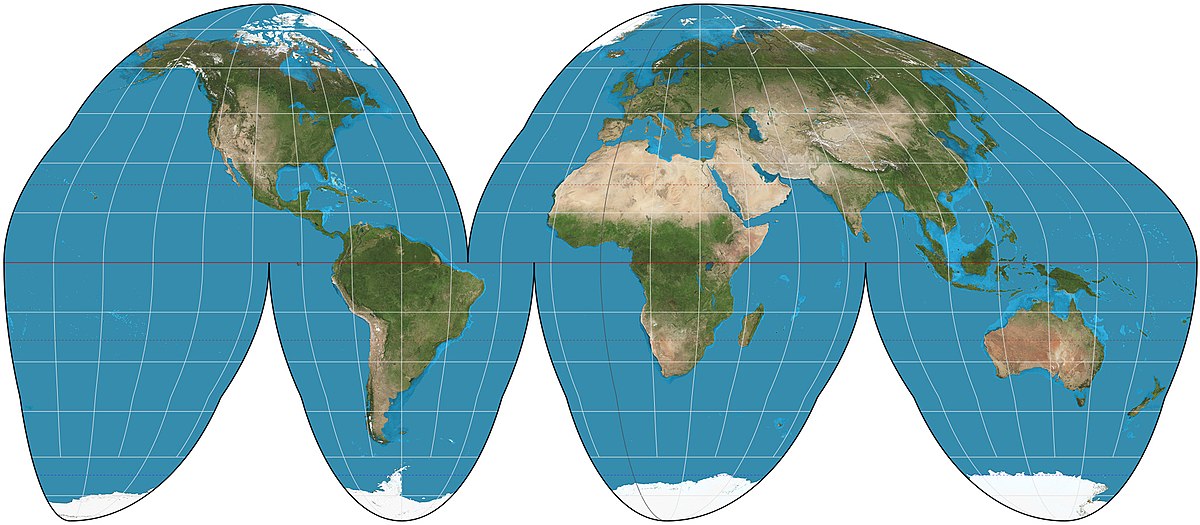
What is the Goode Homolosine Projection and what are the accuracies and inaccuracies of it?
a type of equal-area map projection that minimizes distortion of land masses. It achieves this by breaking up the Earth's surface into separate regions and projecting them individually, resulting in more accurate representation of both shape and area.
Accuracies:
Relative Size
Inaccuracies:
Shape
Distance
Direction
What is the Polar Projection and what are the accuracies and inaccuracies of it?
a type projection which views the earth from the north or south pole
Accuracies:
Direction
Inaccuracies:
Shape
Distance
Relative Size
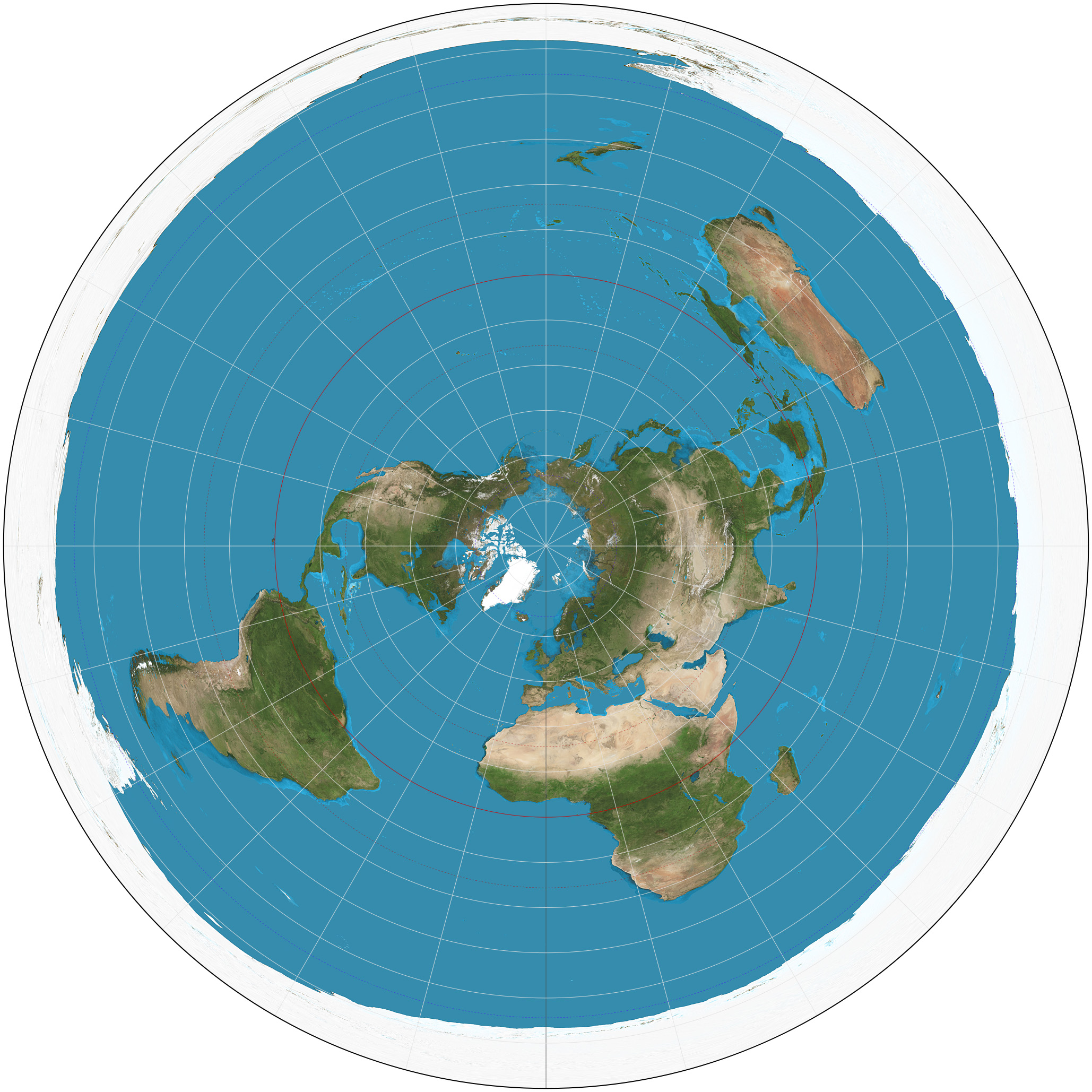
What is the Robinson Projection and what are the accuracies and inaccuracies of it?
a compromise projection, meaning that it tries to balance out some of the distortions inherent in all map projections
Inaccuracies:
Shape
Distance
Relative Size
Direction
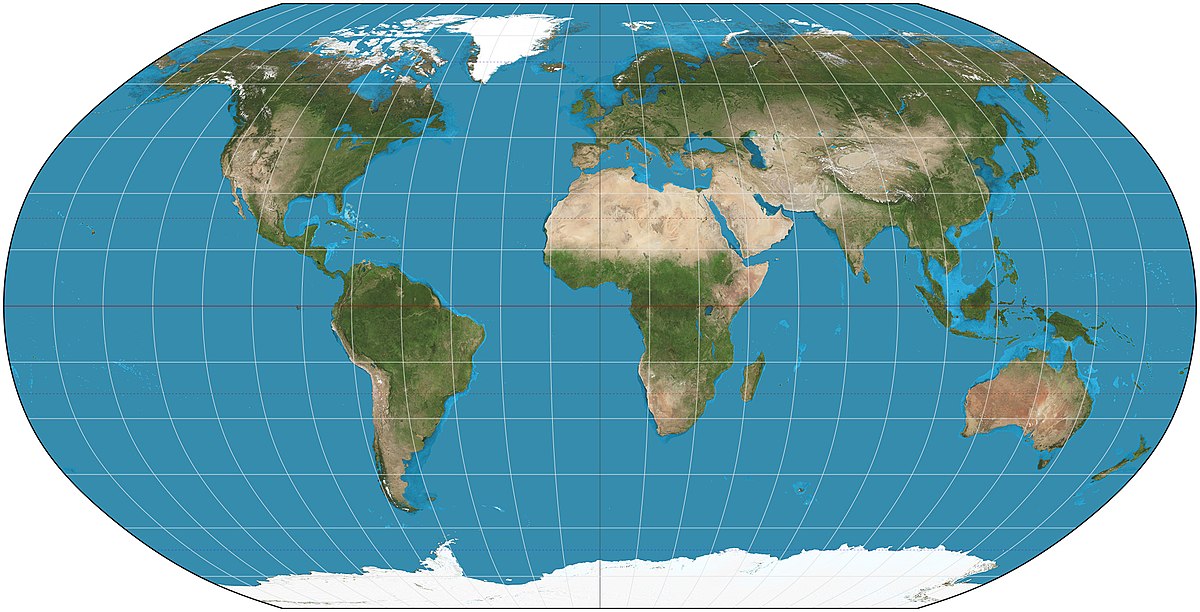
equal-area maps
types of projection preserves the area of land masses, but distorts shape and distance
latitude
lines from the East to West and measuring distance north or south
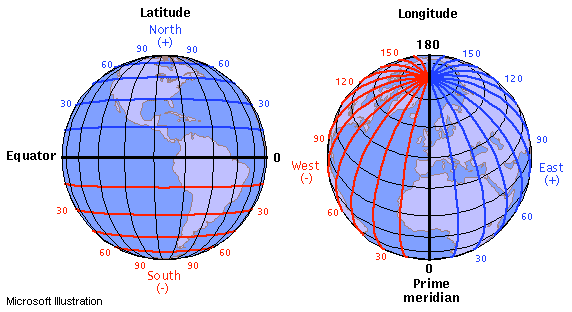
longitude
lines from the North Pole to the South Pole and measuring distance east or west
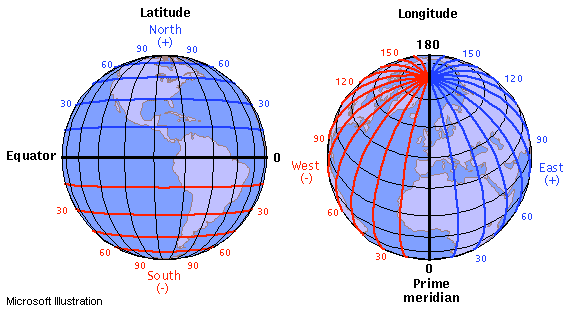
coordinates of a map
(latitude (N or S), longitude (E or W))
equator
an imaginary line that circles the glob exactly halfway between the north and south pole
the equator is designated 0° and the poles as 90° N and90° S
meridian
lines of longitude. from the North Pole to the South Pole and measuring distance east or west
prime meridian
an arbitrarily-chosen meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°
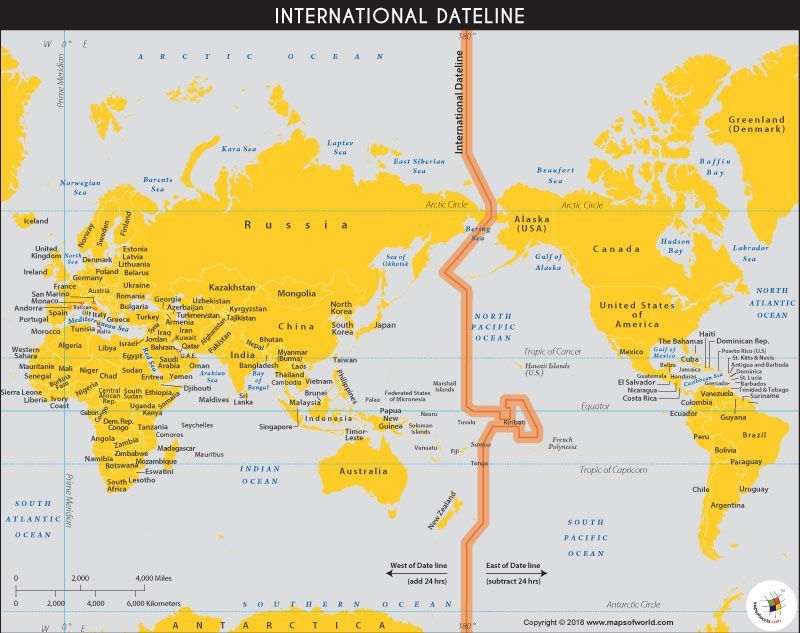
International Date Line
The line between the South and North Poles that is the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific Ocean, roughly following the 180.0° line of longitude and deviating to pass around some territories and island groups. Think of it as the anti-prime meridian
ghost towns
abandoned settlements
Reference Maps
emphasize the location of geographic features
Thematic maps
aim to show data through graphics, colors, lines and more.
Political Maps
show and label human-created boundaries and designations, such as countries, states, cities, and capitals
Is a political map a reference map or thematic?
reference
Physical Maps
show and label natural features, like mountains, rivers, and deserts
Is a physical map a reference map or thematic?
reference
Road Maps
show and label highways, streets, and alleys
Is a road map a reference map or thematic?
reference
Plat Maps
show and label property lines and detail of land ownership
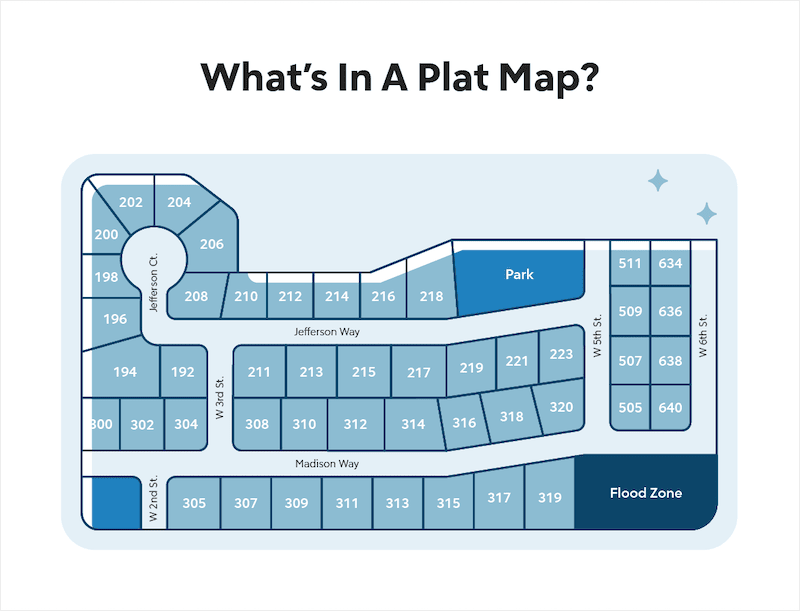
Is a plat map a reference map or thematic?
reference
Choropleth Maps
use various colors, shades of a color, or patterns to show the location and distribution of spatial data

Dot Distribution Maps
A type of thematic map that uses a point symbol to visualize the geographic distribution of a large number of related phenomena. Dot density maps are a simple yet highly effective way to show density differences in geographic distributions across a landscape
Graduated Symbol Map
A map with symbols that are scaled proportionately according to the value of the data attribute they represent; each data value is symbolized to show its location in the progression of smaller to larger data values.
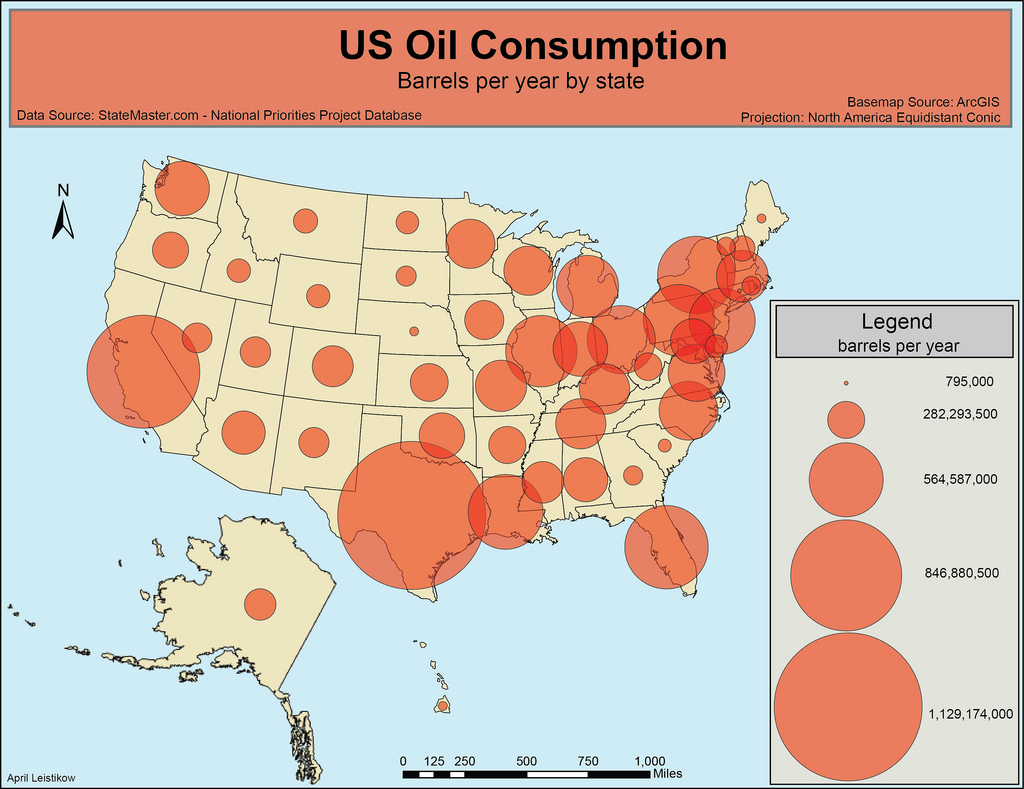
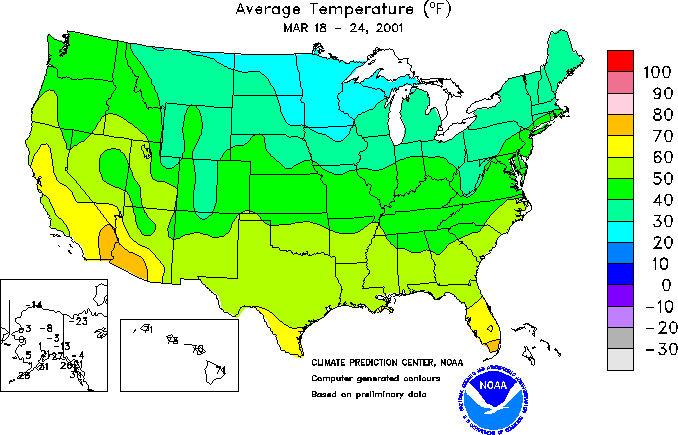
Isoline Maps
Isolines are lines drawn on maps connecting data points of the same value
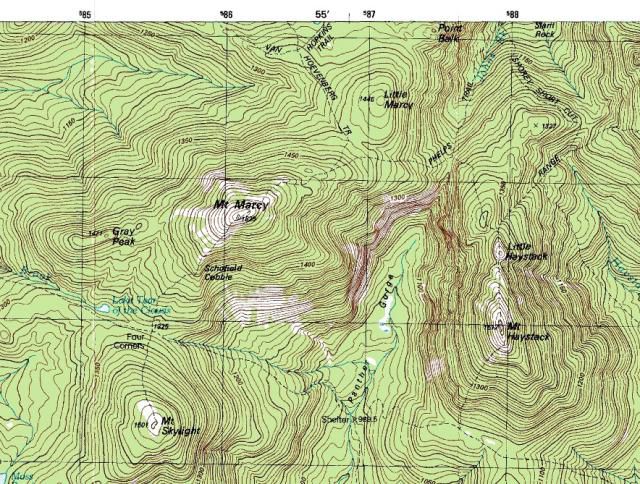
Topographic Maps
a type of isoline map that contours lines to show different elevations
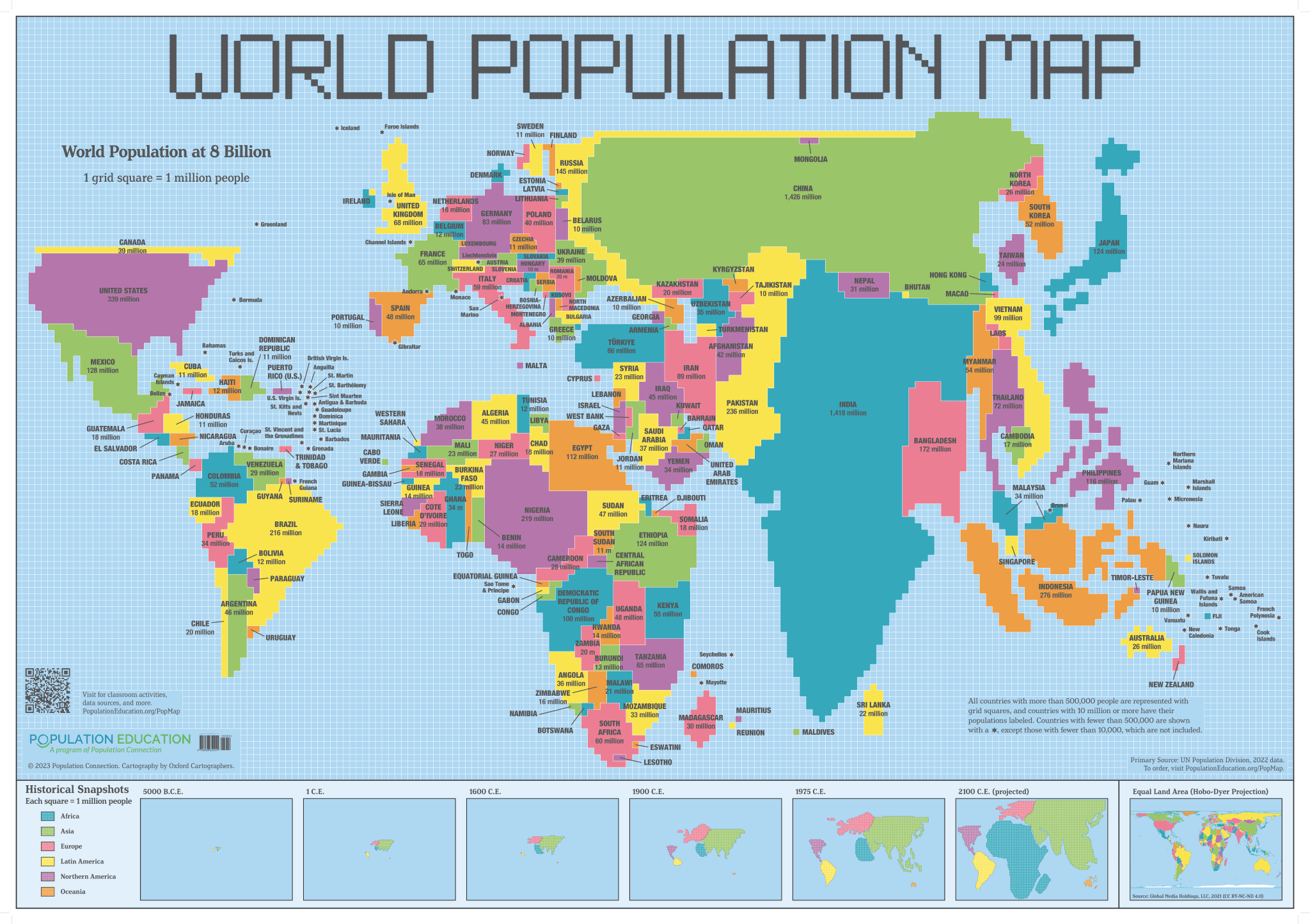
Cartograms
maps in which the size of a region is distorted in order to convey some variable
Why do government’s conduct censuses?
they gather data that is used to inform policy decisions
2 types of Data
Quantitative
Qualitative
Quantitative Data
numbers-based info—counting things
Qualitative Data
characteristics or qualities of a place—data that is descriptive and can't be measured or expressed in numerical terms
Time-Space Compression
the way that the world is seemingly getting smaller, or compressing, as a result of improved transport, communications, and reducing local diversity.
spatial interactions
the movement and flows involving human activity. This could include migration, trade, or communication over a specific space.
Friction of Distance / Distance Decay
as the distance between two places increases, the interaction between those two places decreases.
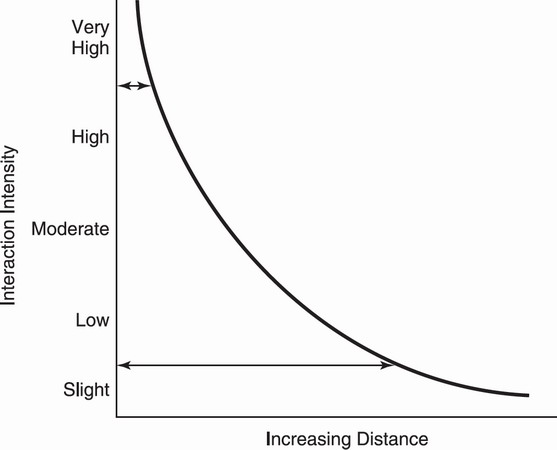
density
the number of people who live in a defined land area (usually square miles or square kilometers)
distribution
the way something is spread out or arranged over a geographic area
4 prominent types of distributions
Linear
Circular
Geometric
Dispersed
Random
Linear Distribution
Phenomena are arranged in straight line, such as the distribution of towns along a railroad line.
Dispersed Distribution
Phenomena are spread out over a large area such as the distribution of large malls in a city.
Circular Distribution
Phenomena are equally spaced from a central point, forming a circle, such as distribution of the homes of people who shop at a particular store.
Geometric distribution
Phenomena are in a regular arrangement, such as the squares or blocks formed by roads in the Midwest.
Random Distribution
Phenomena appear to have no order to their position, such as the distribution of pet owners in a city.
Human-Environmental Interaction
the dual relationship between humans and the natural world are at the heart of human geography
Types of Human-Environmental Interaction
Use of Natural Resources
Sustainability - using non-renewable resources so they will continue to be available in the future
Land Use -
cultural ecology
the relationship between culture and the environment, dealing with human adaptations to various environments
Built Environment
the tangible human creation on the landscape
environmental determinism
A philosophy of geography that stated that human behaviors are a direct result of the surrounding environment
possibilism
The concept that the natural environment places constraints on human activity, but humans can adapt to some environmental limits while modifying others using technology.
field observation
the act of physically visiting a location, place, or region and recording, firsthand, information there
aerial photography
taking of photographs of the ground from an elevated position off Earth's surface.
formal region
Areas where everyone in that region shares common attributes or traits like language, climate or political system. Formal regions are primarily used to determine and outline political, cultural and economic regions.
functional region
defined by a social or economic function that occurs between a node or focal point and the surrounding areas
vernacular region
An area that people believe exist as part of their cultural identity
GPS
This system uses data from satellites to pin-point a location on earth and help people find their way to a destination.
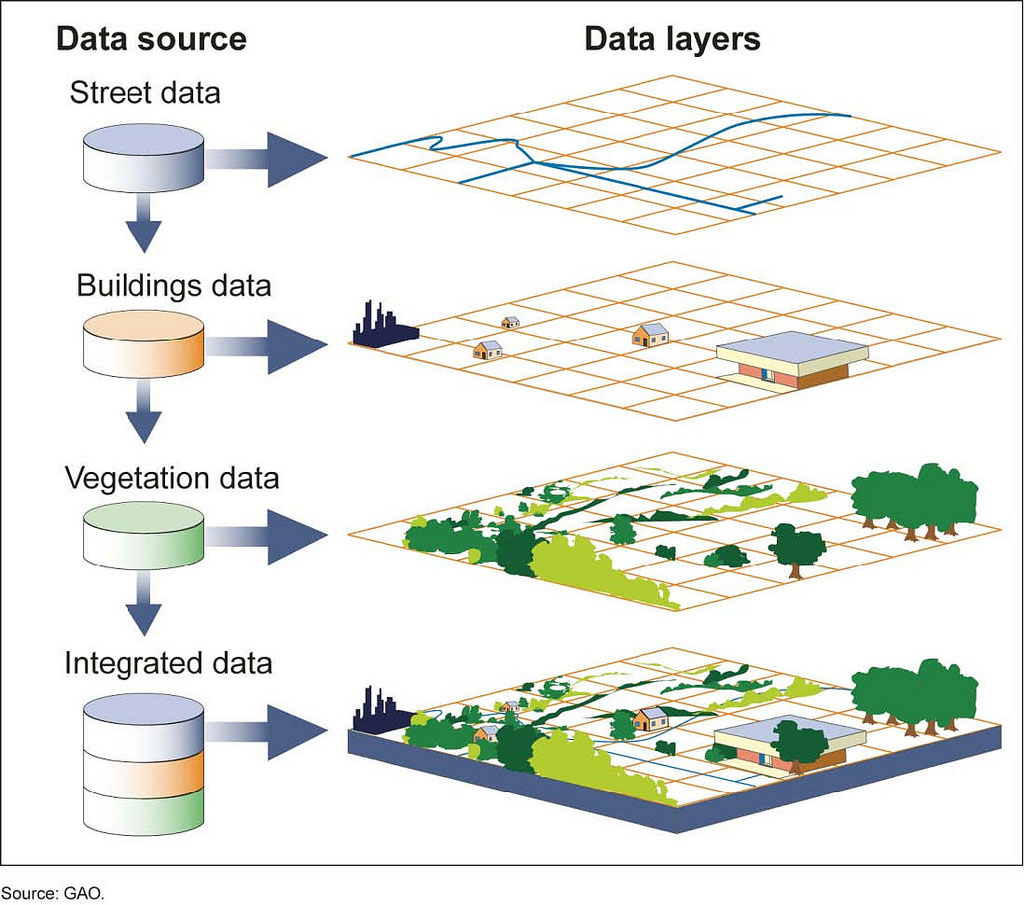
GIS
a collection of computer hardware and software that permits spatial data to be collected, recorded, stored, retrieved, manipulated, analyzed, and displayed to the user.
Remote Sensing
the process of detecting and monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by measuring its reflected and emitted radiation at a distance