AP Microeconomics Vocabulary
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
Scarcity
The fundamental economic problem of having seemingly unlimited human wants in a world of limited resources
Shortage
When the quantity demanded of a product exceeds the quantity supplied
Labor
The effort of workers
Land
Resources that come from nature, such as timber, water, minerals, horses, etc.
Capital
Manufactured goods used to make other goods and services, such as machinery, buildings, tools, etc.
Entrepreneurship
The risk taking, innovation and organization of resources for production
Factors of Production
Land, Labor, Capital, and Entrepreneurship
Human Capital
Training and education of workers
Market Economy
Economy in which production and consumption are the result of decentralized decisions by many firms and individuals; defined by private ownership of resources
Command Economy
Economy in which industry is publicly owned and there is a central authority making production and consumption decisions
Traditional Economy
What is produced and how it is produced is based on custom
Microeconomics
The branch of economics concerned with how individuals make decisions and how these decisions interact; focuses on choices made by individuals, households or firms - the smaller parts that make up the economy as a whole.
Macroeconomics
Focuses on economic aggregates that summarize data across many different markets
Positive Economics
Economic analysis used to answer questions about the way the world works; no value judgements
Normative Economics
Economic analysis saying how the world should work; value judgements added
Opportunity Cost
The value of the foregone option
Economic Growth
An expansion of an economy’s production possibilities
Comparative Advantage
Varied opportunity costs between people or nations
Absolute Advantage
Being best at producing something
Explicit Costs
Expenses involving a monetary payment
Implicit Costs
Non-monetary costs
Marginal
Additional; all decisions are made on this basis
Utility
Satisfaction
Diminishing Marginal Utlity
As a consumer purchases more of a good, the additional satisfaction falls for each additional unit consumed
Productions Possibilities Curve (PPF)
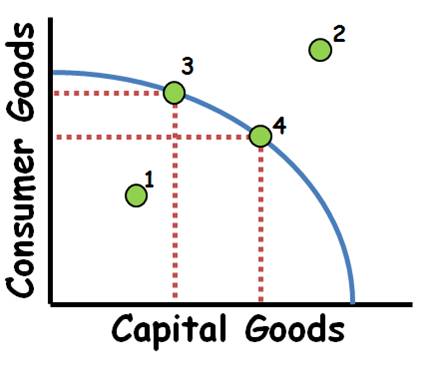
Market
An institution or mechanism which brings buyers (demanders) and sellers (suppliers) of particular goods and services together
Law of Demand
(Other things being equal) as the price increases, the corresponding quantity demanded falls; the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
Substitution Effect
The tendency of consumers to swap a similar, lower-priced product for a product that is relatively more expensive
Income Effect
Any increase or decrease in a consumer’s purchasing power caused by a change in price
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
As one continues to consume a given product, one will eventually get less additional utility (satisfaction) from each unit consumed
Demand Shifters
Tastes, Related Goods Prices, Income, Buyers, Expectations
Complements
Goods typically consumed together
Normal Good
A product that people buy more of when their income is higher
Inferior Good
A product that people buy more of when income is lower
Law of Supply
(Other things being equal) as the price increases, the corresponding quantity supplied rises; the direct relationship between price and quantity supplied
Supply Shifters
Subsidies/Taxes, Technology, Other Related Goods Prices, Resource Costs, Expected Futures Prizes, Size of the Market
Price Elasticity
The measure of how responsive consumers/suppliers are to a change in price; %ΔQ/%ΔP
Total Revenue (TR)
Overall amount of money earned from the sale of a good or service; P * Qd
Price Effect
After a price increase, each unit sold sells at a higher price, which tends to raise revenue
Quantity Effect
After a price increase, fewer units are sold, which tends to lower revenue
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand
The effect of a change in a product’s price on the quantity demanded for another product; if positive, goods are substitutes, and if negative, complements; %ΔQdx/%ΔPy
Income Elasticity of Demand
Percentage change in quantity demanded which results from some percentage change in consumer incomes; if positive, normal goods, and if negative, inferior goods; %ΔQd/%ΔI
Consumer Surplus (CS)
The benefit buyers receive from paying less for a good than they were willing to; area above price and left of demand; Willingness to Pay - Price
Producer Surplus (PS)
Represents the benefit producers receive from selling goods or services at the market price, above the minimum price they would be willing to accept; below price and left of supply; P - Willingness to Sell
Economic Surplus
The total benefit to consumers and producers from a market transaction; CS + PS
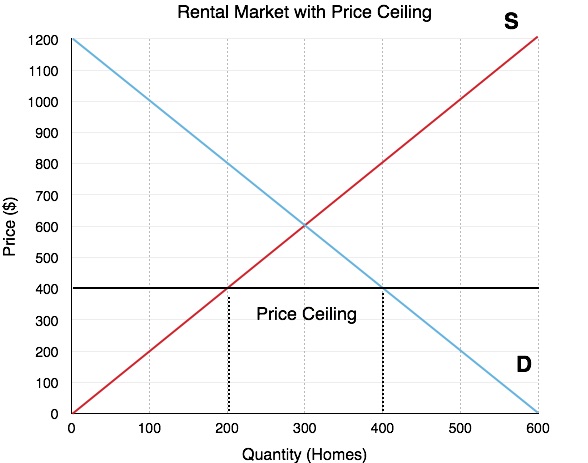
Price Ceiling
The legal upper limit (maximum) on the price that can be charged in a market
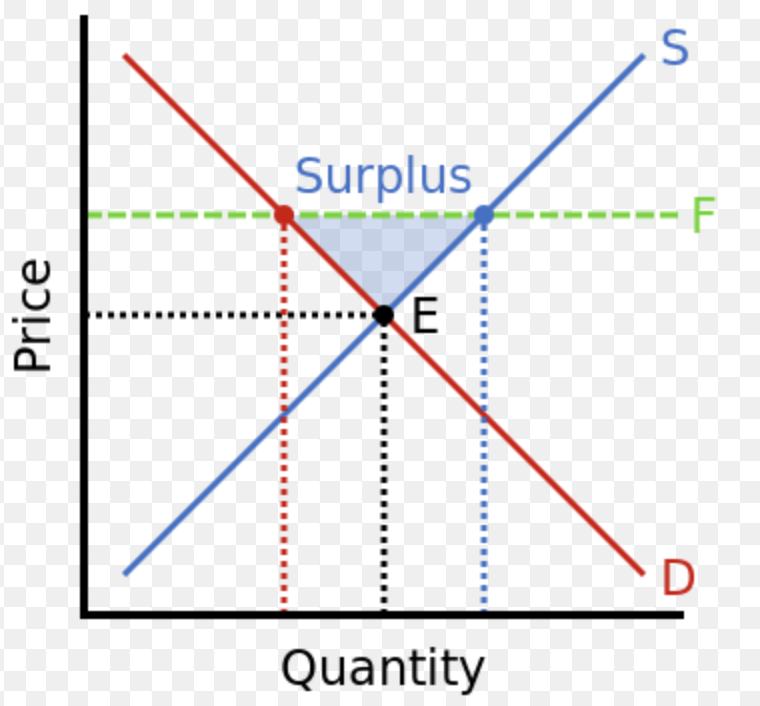
Price Floor
The legal lower limit (minimum) on the price that can be charged in the market
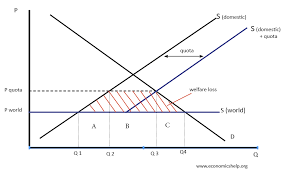
Quota
A restriction on the quantity that can be sold in the market
Deadweight Loss
Loss in economic efficiency and economic surplus
Tax
A financial charge a government imposes in a market
Excise Tax
Per-unit fee levied by the government
Lump-Sum Tax
Fee charged on a firm that is not dependent on quantity of units sold
Subsidy
A financial benefit given by the government to a firm or an individual
Tax Incidence
The division of the tax burden among affected parties
Variable Inputs
Factors of production that can be increased to increase production in the short run
Fixed Inputs
Factors of producation that cannot be increased in the short run to increase production, but can increase in the long run
Short Run
Time period that is too brief for a firm to alter its plant capacity
Long Run
A period of time long enough for a firm to change the quantities of all resources employed, including capital plant size.
Plant Capacity
A firm’s maximum potential level of output
Total Product (TP)
The total quantity of output produced by a certain amount of inputs
Marginal Product (MP)
The additional output produced by one more unit of a variable input, often labor; ΔTP/ΔQL
Average Product (AP)
The average quantity of output produced by one unit of a variable input, often labor; TP/L
Fixed Costs (FC)
Expenses whose total does not vary with changes in short-run output
Variable Costs
Expenses which change with the level of output
Total Cost (TC)
VC + FC
Marginal Cost (MC)
The additional expense of producing one more unit of output; ΔTC/ΔQ
Average Fixed Cost (AFC)
FC/Q
Average Variable Cost (AVC)
VC/Q
Average Total Cost (ATC)
AVC + AFC or TC/Q
Spreading Effect
The larger the output, the greater the quantity of output over which fixed cost is distributed, leading to lower AFC
The Diminishing Returns Effect
The larger the output, the greater the amount of variable input required to produce additional units, leading to higher AVC
Increasing Returns to Scale
Output is increasing at a faster rate than all inputs
Decreasing Returns to Scale
Output is increasing at a slower rate than all inputs
Constant Returns to Scale
Output is increasing at the same rate as all inputs
Economies of Scale
Long run ATC decreases as output increases
Diseconomies of Scale
Tong run ATC increases as output increases
Constant Returns to Scale
Long run ATC is constant as output increases
Sunk Cost
An expense that has been incurred in the past and cannot be recovered
Profit (π)
TR-TC
Explicit Cost (a.k.a accounting costs)
An expense that involves actually laying out money
Implicit Costs
Does not require an outlay of money; it is measured by the value, in dollar terms, of the benefits that are foregone
Normal Profit (a.k.a. zero profit)
When economic profit is equal to zero
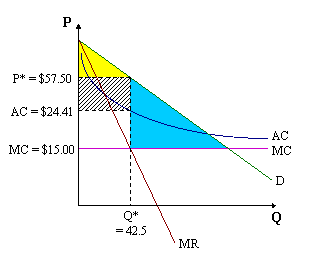
Monopoly
A firm that is the only producer of a good has no close substitutes in that market; high barriers to entry; price makers; unique products; allocatively and productively inefficient
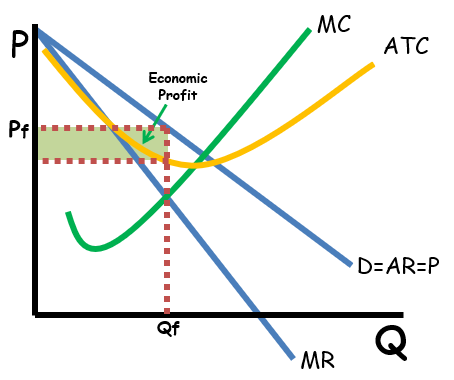
Natural Monopoly
Economies in which there is a sole provider of a good; experiences economies of scale; allocatively and productively inefficient
Oligopoly
A few large firms produce almost all of the total output of the industry; products may be identical or differentiated; high barriers to entry; top 4 firms need a Concentration Ratio of 40% or higher to be considered one; allocatively and productively inefficient
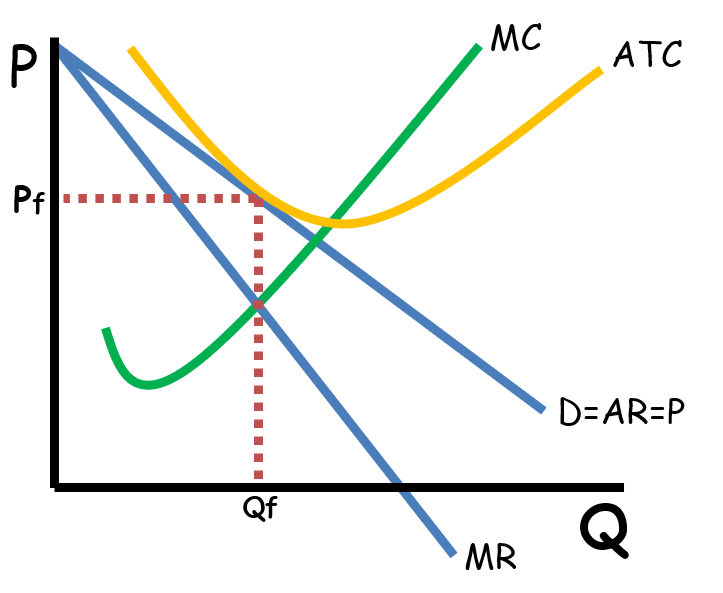
Monopolistic Competition
Market with no barriers to entry; limited price control; differentiated products; and many competitors
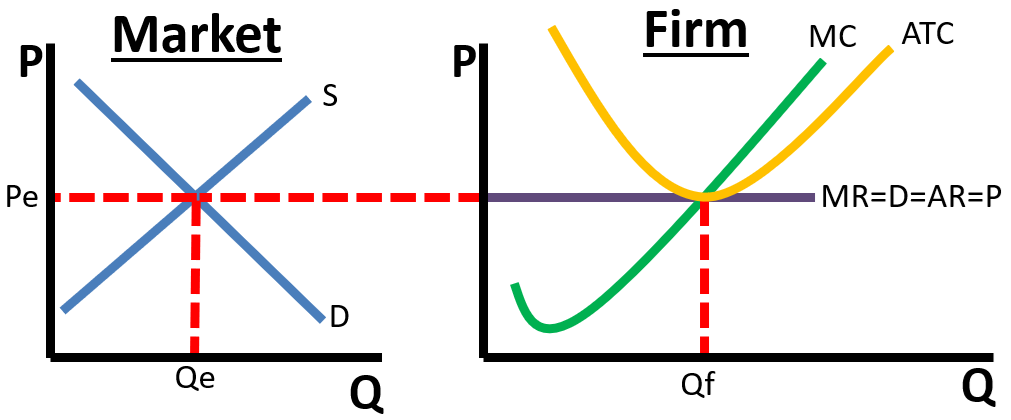
Perfect Competition
Market with perfectly elastic demand; no barriers to entry; price taking; differentiated product; and many competitors; allocatively and productively efficient
Allocative Efficiency
Everyone who wants a product gets it; P = MC
Productive Efficiency
When a firm produces a good at the lowest possible price; P = min of ATC
Excess Capacity
The difference between what a firm produces and what it is capable of producing (i.e. productive efficiency)
Interdependence
When the actions of one firm affect those of another
Cartel (Overt Collusion)
Members openly join and scheme to restrict output and gain monopoly prices
Tacit Collusion
Unspoken understanding that firms will act together
Game Theory
Arises from interdependence; companies must take the possible responses of other companies into account when planning a course of action
Dominant Strategy
A choice that maximizes satisfaction regardless of the other’s action
Nash Equilibrium
Outcome where each has made the best decision possible, given the actions of the other
Payoff
Outcome of a strategic decision
Best Outcome
Combination of strategies that yields the highest joint profit
Price Differentiation
When the same product is sold to different consumers at different prices; P = MR
Marginal Factor/Resource Cost (MFC/MRC)
The additional expense paid by the firm when it hires an additional worker or other resources; W *