Indirect cost allocation - Blanket Rate
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover the key vocabulary related to overhead allocation and costing methods discussed in the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
direct cost
For mango juice of T3H, 2 mangoes are required for each juice bottle, and it takes 5 minutes to produce a juice. If price/mango is £0.50 and the labour cost/hour is £14, then the direct cost will be
Direct materials: 2 mangoes @ £0.50 = £1.00
Direct labour: 5 minutes @ £14 = £1.17
Direct cost = £1.00 + £1.17 = £2.17
cost allocation
Cost allocation is the process of identifying, accumulating, and assigning costs to costs centres such as departments, programs, and a branch of a company by using a parameter, called allocation base.
cost centre
A cost centre is a department that is responsible for the costs within their control.
There will be a manager assigned to every cost centre to ensure somebody is ultimately accountable for the state of affairs in that department.
A cost centre is a place where costs are collected and analysed
Main function is to track expenses/costs.
Blanket Rate
A method of absorbing overhead costs using the same absorption rate throughout the entire organization, regardless of product or department.
This simplifies budgeting and reporting by applying a single rate per unit produced or service provided, ensuring consistency across different cost centres.
to calculate blanket rate we use Overhead Absorption Rate (OAR)
OAR = manufacturing overhead / allocation base
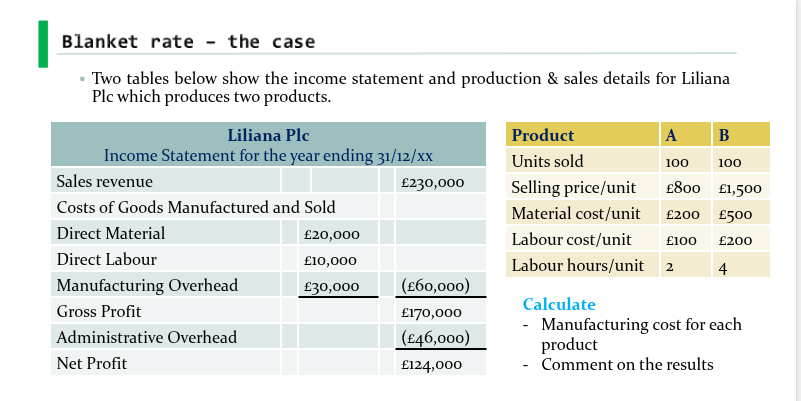
blanket rate - numerical explanation
Manufacturing Cost = DM + DL + MOH
We know:
MOH = £30,000
We need to allocate this amount to Products A and B
The question is how to do that
We need an allocation base = Units sold and labour hours
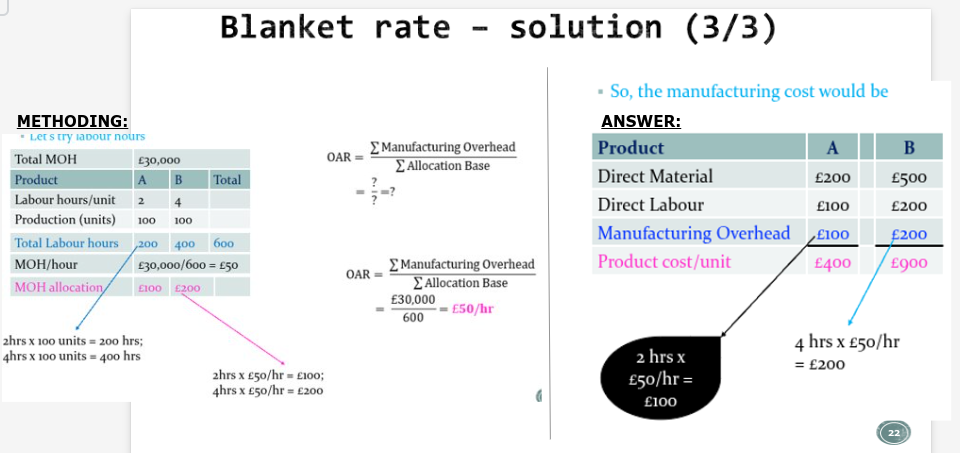
OAR = manufacturing overhead / allocation base
= 30,000 / 600 = £50 an hour
ANSWER = £100 MOH for product A and £200 MOH for product B
Cost Object
Any item for which costs are measured and assigned.
Contribution Margin
The difference between total revenue and total variable costs.
Cost Centre
A department or section responsible for controlling its costs.
Allocation Base
A measure used to assign costs to cost objects, such as machine hours or labour hours.
Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
A method of allocating overhead costs based on activities that drive costs.
Sales Value Method
A method of allocating administrative overhead based on a percentage of total revenue.
Overhead Absorption Rate (OAR)
A rate used to allocate manufacturing overhead costs to units produced.
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
A financial modeling tool used to analyze the relationship between costs, volume, and profit.