BSC2085L Midterm Practical
1/348
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
349 Terms
Superior
Above or higher in position relative to another structure.
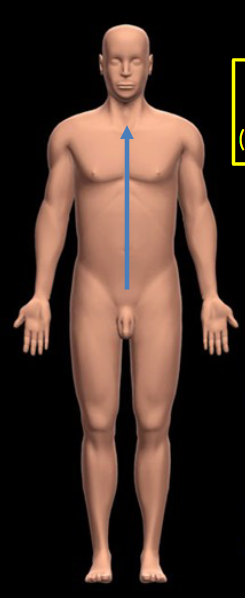
Inferior
Below or lower in position relative to another structure.
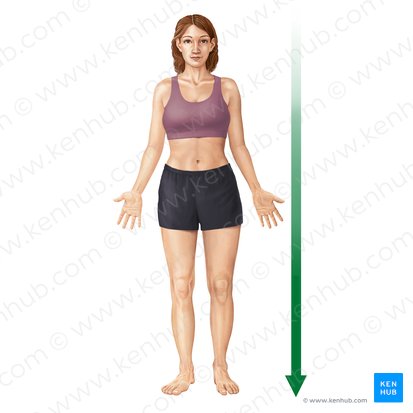

Medial
Closer to the midline of the body
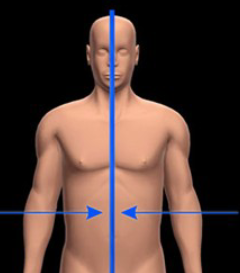
Lateral
Farther from the midline of the body
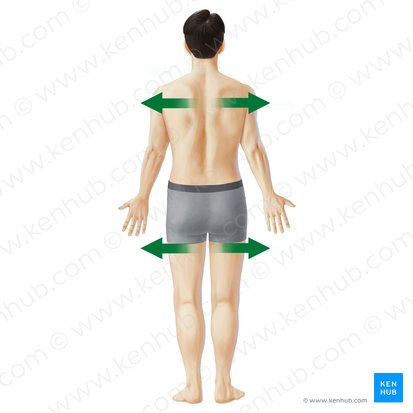
Superficial
Closer to the skin’s surface
Deep
Further from the skin’s surface
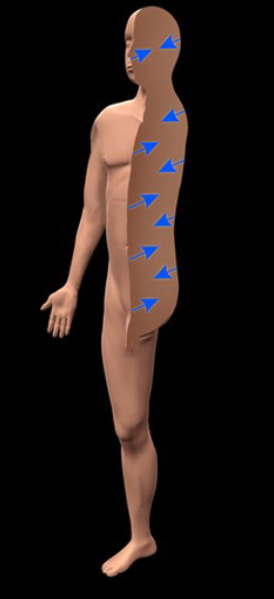
Dorsal
Back side of the body from the back
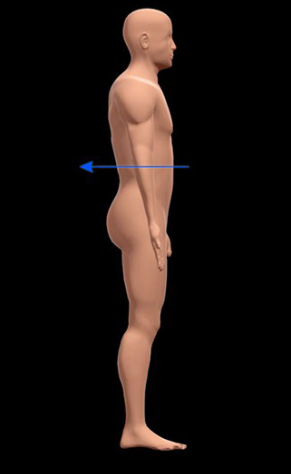
Ventral
Front side of the body from the belly

Anterior
The front part of the body.

Posterior
Back side of the body.
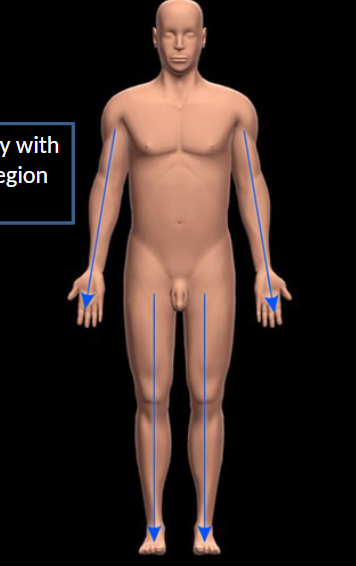
Proximal
Closer to point of attachment
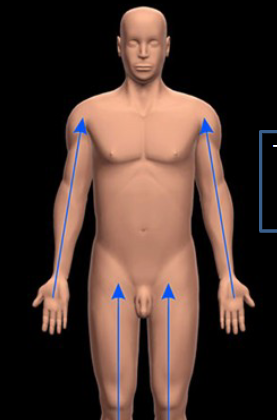
Distal
Further from the point of attachment.
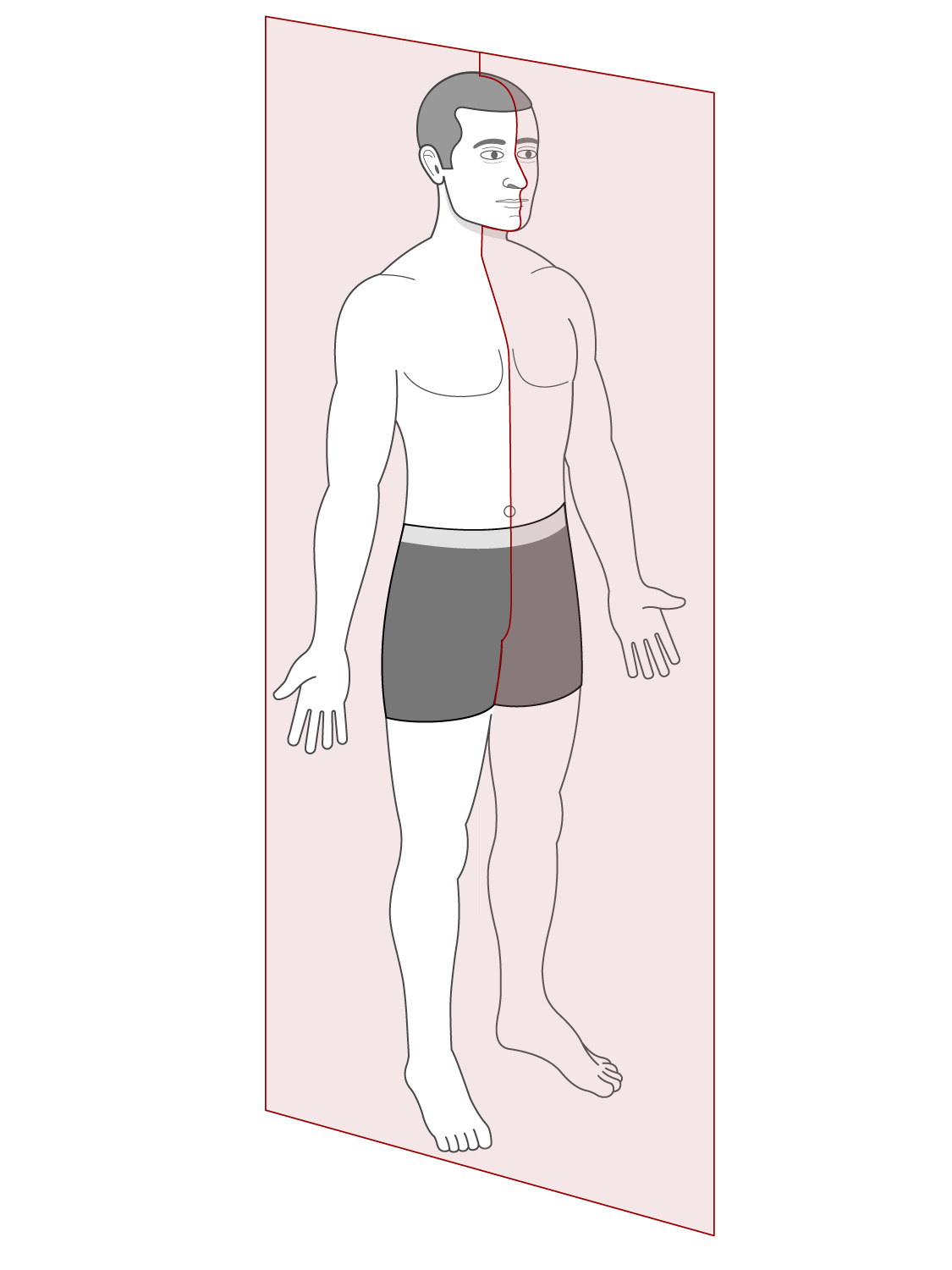
Sagittal Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into right and left sections.
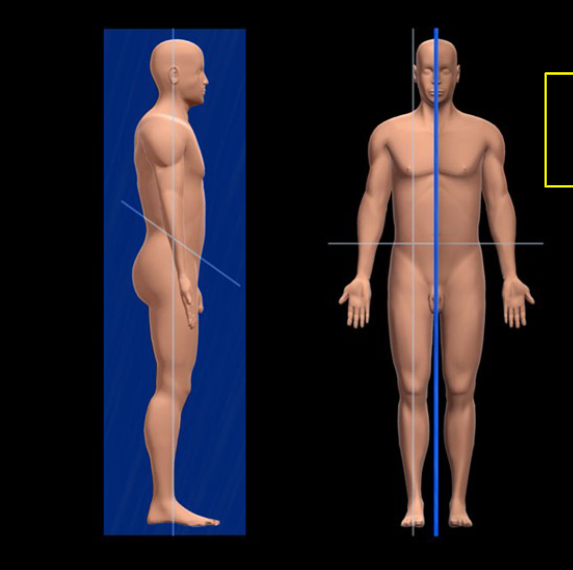
Midsagittal plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into equal right and left halves.
Parasagittal plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into unequal right and left sections.
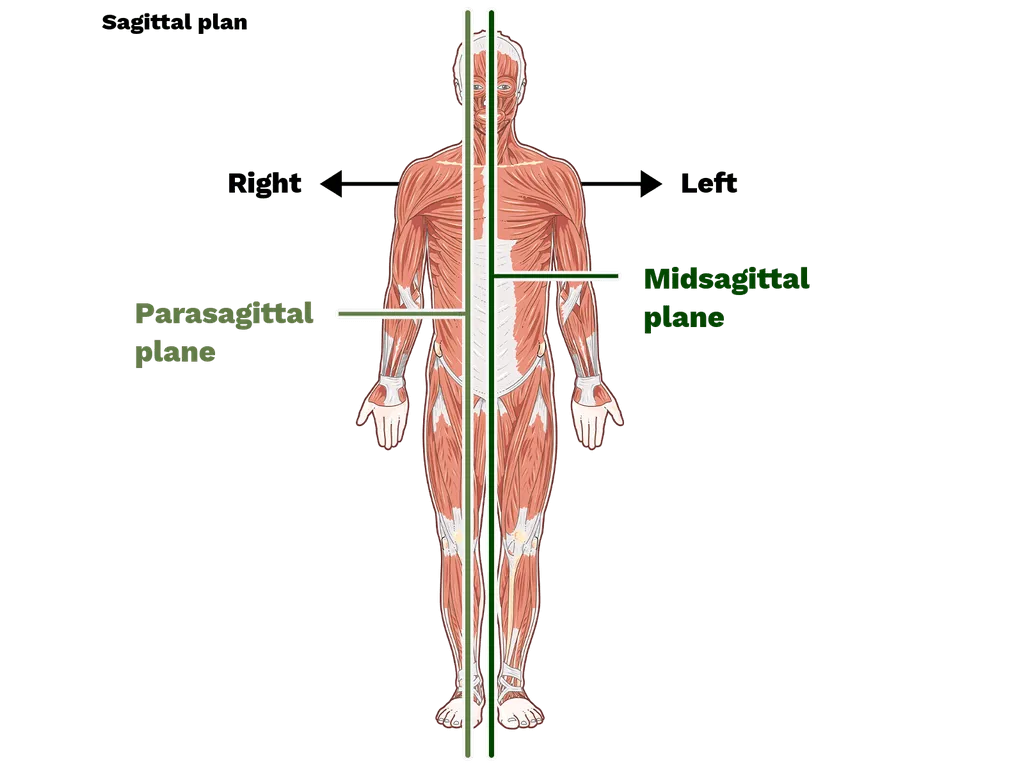
Frontal plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into front and back sections.
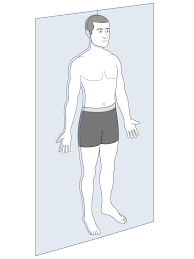
Transverse plane
Divides the body into upper and lower portions
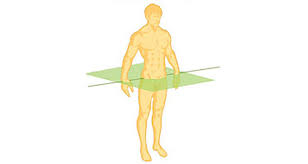
Oblique plane
A plane that cuts through the body at an angle, dividing it into non-standard sections.
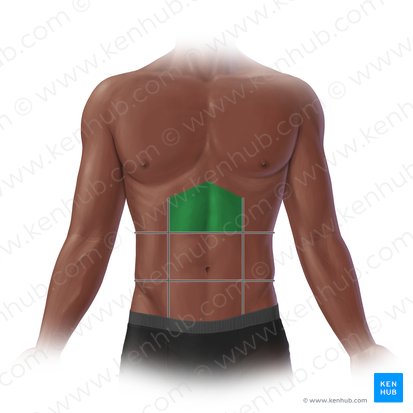
Right hypochondriac region
The area of the abdomen located beneath the right rib cage, containing organs such as the liver and gallbladder.
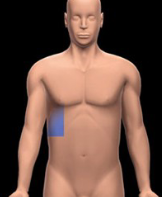
Right lumbar region
Between the right hypochondriac region and the right iliac region, containing parts of the large intestine and right kidney.
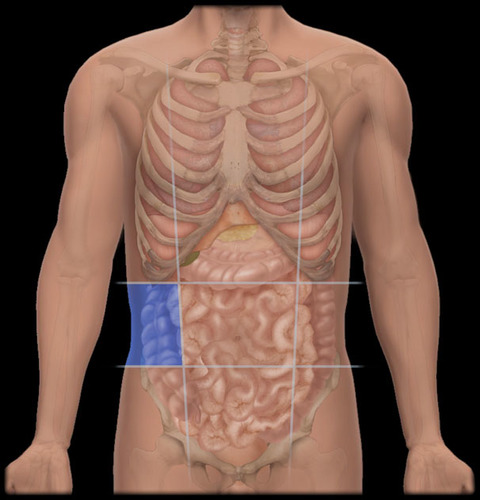
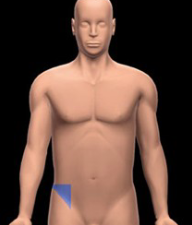
Right iliac region
Beneath the right lumbar region, containing the appendix and parts of the large intestine.
Epigastric region
Between the right and left hypochondriac regions, primarily containing the stomach, liver, and pancreas.
Umbilical region
Between the right and left lumbar regions, primarily containing the small intestine and parts of the colon.
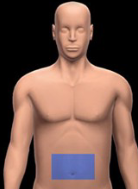
Hypogastric region
Beneath the umbilical region, containing the bladder and reproductive organs.
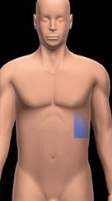
Left hypochondriac region
Beneath the rib cage on the left side, primarily containing the spleen, stomach, and part of the left kidney.
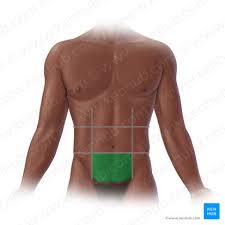
Left lumbar region
Left side of the lumbar region, primarily containing parts of the large intestine and left kidney.
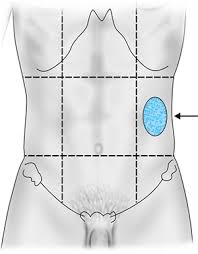
Left iliac region
Lower left area of the abdomen, primarily containing parts of the intestines and the left ovary in females.
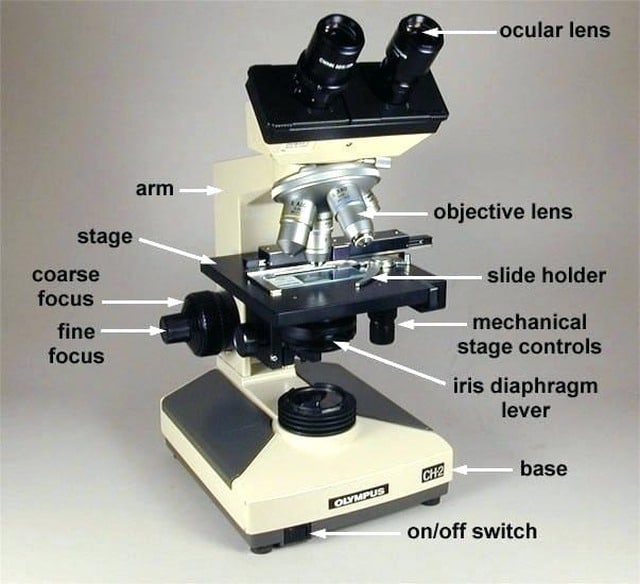
Base
The bottom part of a microscope that supports the entire instrument and contains the light source.

Coarse-focus knob
The knob on a microscope used to make large adjustments in focus to bring the specimen into view.

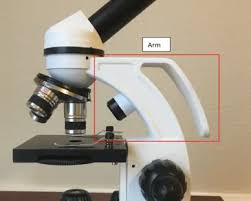
Arm
The part of a microscope that connects the eyepiece to the base and provides support, allowing for easy handling and positioning of the microscope.
Fine-focus knob
The knob on a microscope used to make small adjustments in focus for more precise viewing of the specimen.

Objective lenses
Lenses on a microscope used to magnify the specimen, typically ranging from low to high power.

Stage
The flat platform where slides are placed for observation, often equipped with clips to hold the slide in place.

Condenser
A lens system that focuses light onto the specimen, enhancing illumination and contrast.
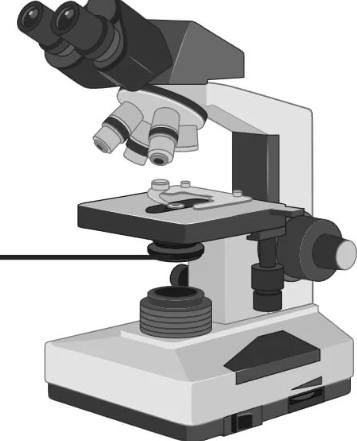
Scanning objective
Lowest power objective (4x)

Low power objective
An objective lens typically used at 10x magnification for initial examinations of a slide.
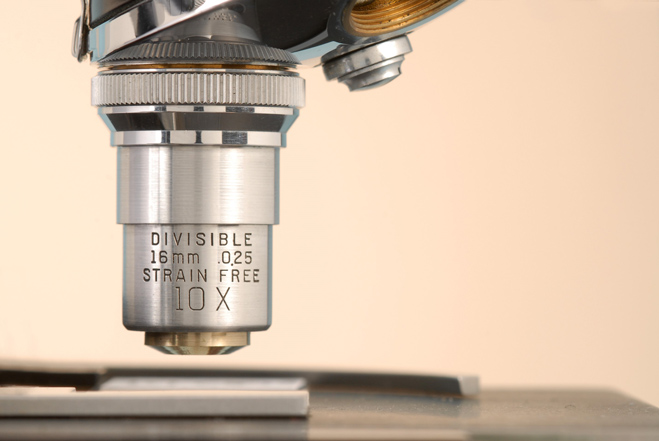

High power objective
An objective lens used for detailed viewing of specimens, typically at 40x.
Oil immersion objective
An objective lens used at 100x magnification
Ocular (eyepiece) lens
the lens at the top of the microscope that the viewer looks through, typically providing magnification of 10x or more.

Iris diaphragm lever
Ring that regulates the amount of light reaching the specimen, enhancing contrast and resolution.
Light source
The component that illuminates the specimen, enabling clearer visibility and detail during observation.

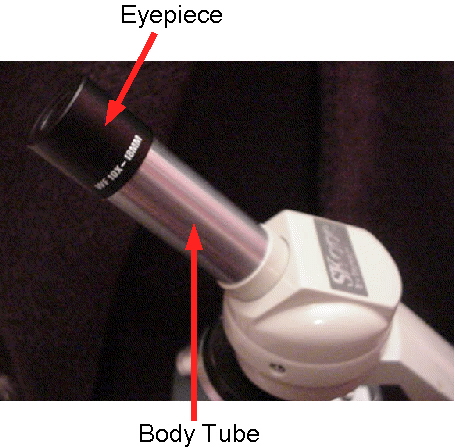
Body tube
Connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses, ensuring proper alignment of light and images.
Microscope power switch
The control that turns the microscope on or off, essential for activating the light source for observation.

Nosepiece
The revolving part of the microscope that holds the objective lenses and allows the user to switch between different magnifications.

Stage control knob
The knobs used to move the stage horizontally or vertically, enabling precise positioning of the specimen under the objectives.

Stage clip
Holds the slide in place on the stage to prevent movement during observation.

Light control knob
Adjusts the intensity of light passing through the specimen, enhancing visibility and contrast.

Calculation of total magnification
Multiplying the magnification power of the eyepiece by the magnification power of the objective lens used.
Mitochondria
Powerhouses of the cell, where ATP is produced through cellular respiration.
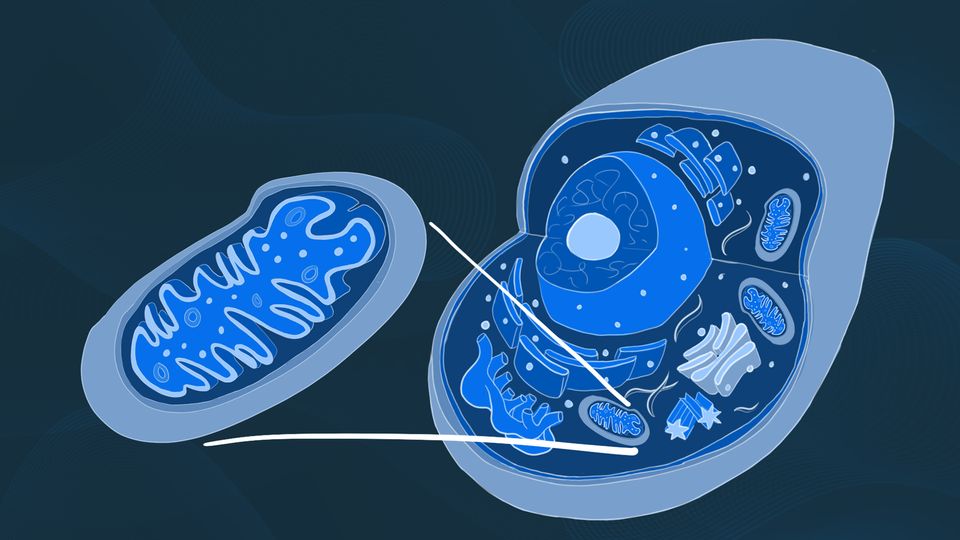
Golgi complex
A cell organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
Centrioles
Cell structures involved in cell division, helping to organize the mitotic spindle.

Bound ribosomes
Ribosomes that are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and are involved in the synthesis of proteins that are either secreted from the cell or incorporated into the cell's plasma membrane.
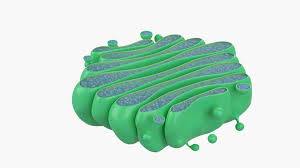
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
A type of endoplasmic reticulum that is involved in lipid synthesis, metabolism, and detoxification, lacking ribosomes on its surface.
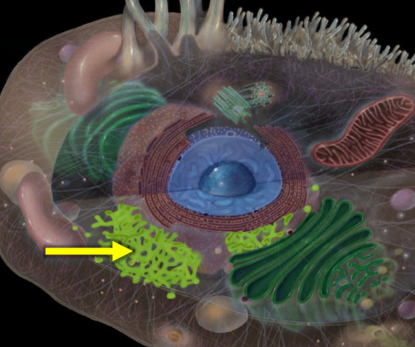
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
A type of endoplasmic reticulum that is studded with ribosomes, primarily involved in protein synthesis and processing.
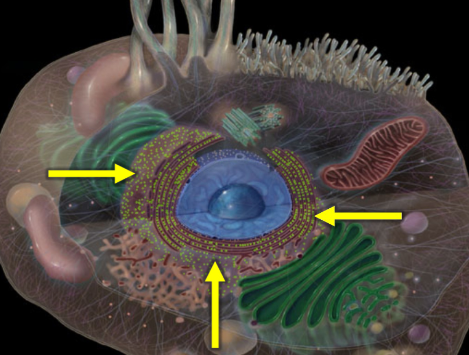
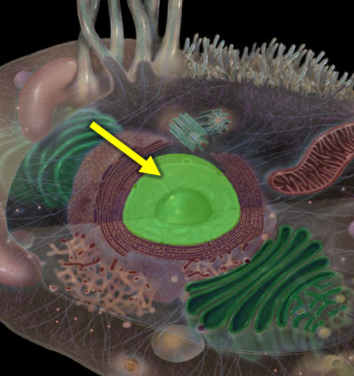
Nucleus
The membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell's genetic material and regulates gene expression, control of cellular activities.
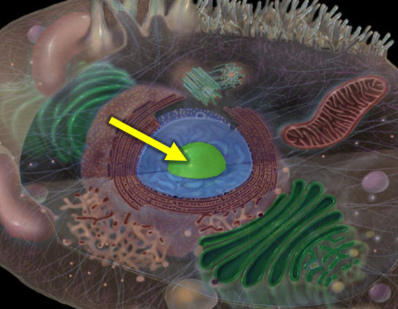
Nucleolus
A substructure within the nucleus responsible for ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosome assembly.
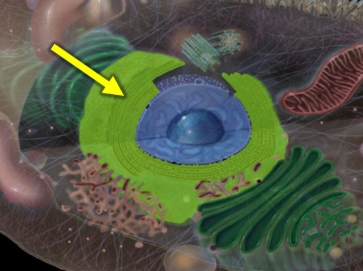
Nuclear envelope
A double membrane structure that surrounds the nucleus, separating its contents from the cytoplasm and regulating the transport of molecules in and out.
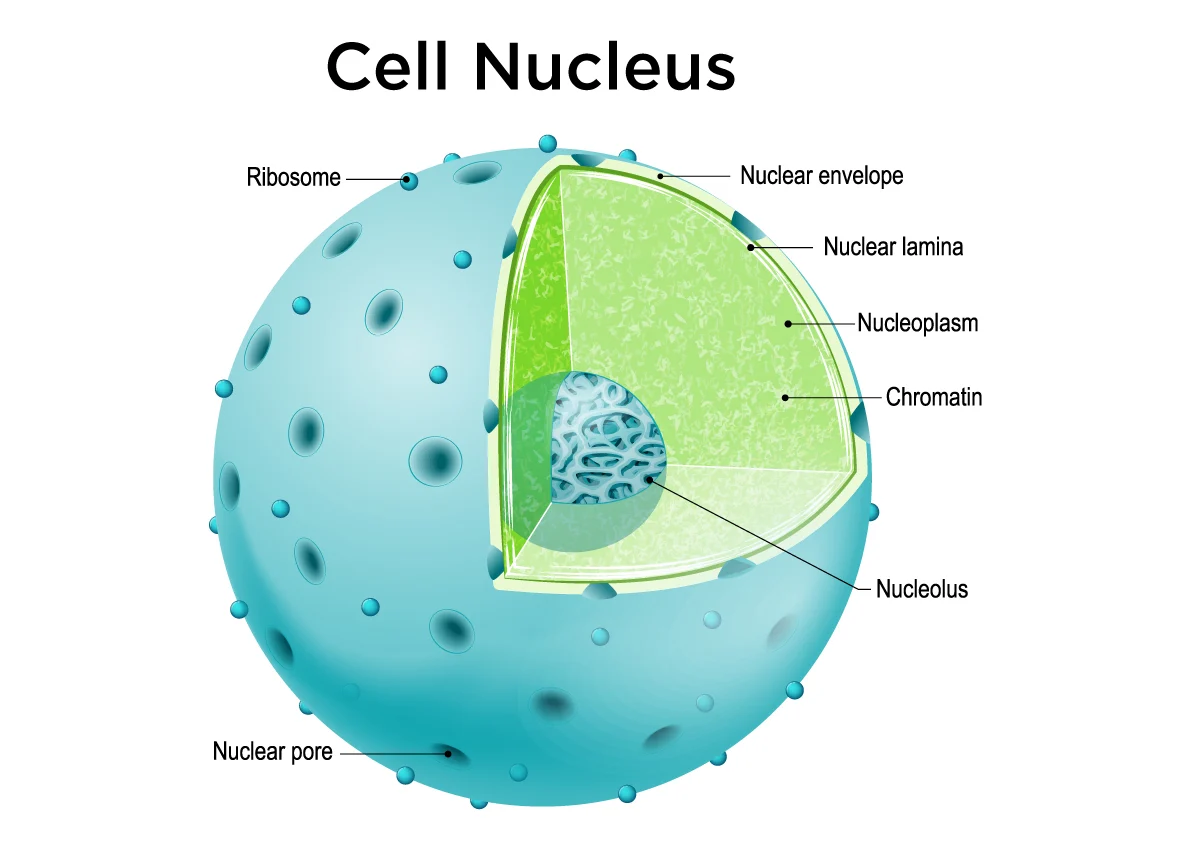
Nuclear pores
Small openings in the nuclear envelope that allow the transport of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
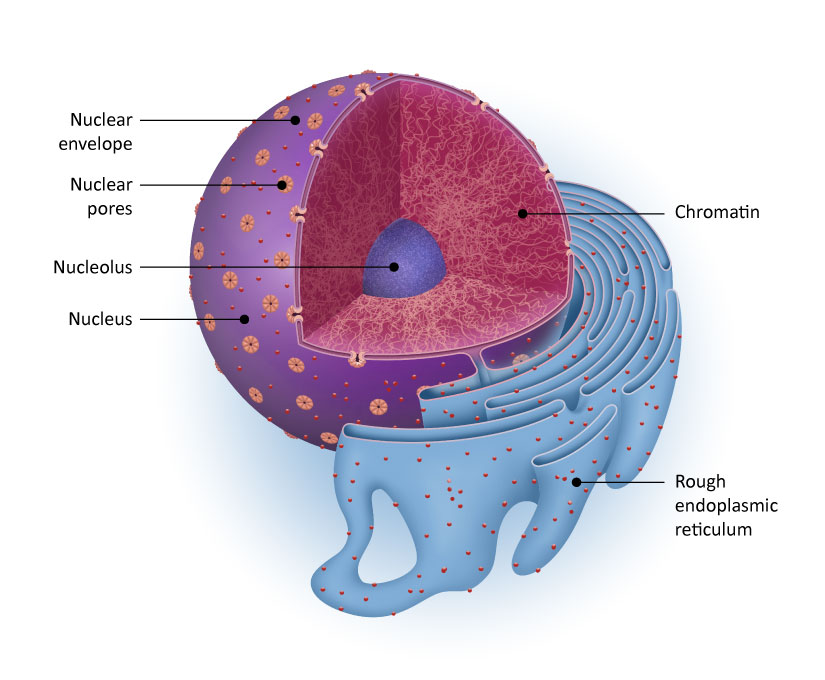
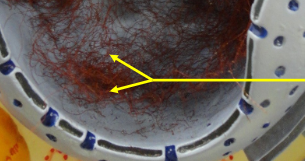
Chromatin
The material consisting of DNA and proteins that makes up chromosomes in the nucleus
Plasma membrane
The outer membrane of a cell that regulates the entry and exit of substances, providing structural support and protection.
Interphase
Cell prepares for division, including DNA replication and organelle growth.
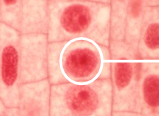
Prophase
The first stage of mitosis where chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and spindle fibers begin to form.
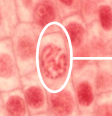
Metaphase
The second stage of mitosis where chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plane, ensuring proper separation during anaphase.
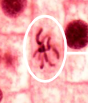
Anaphase
The stage of mitosis where sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell, ensuring each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes.
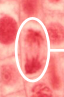
Telophase
The final stage of mitosis where sister chromatids reach the opposite poles, the nuclear envelope re-forms around each set of chromosomes, and the chromosomes begin to de-condense back into chromatin.
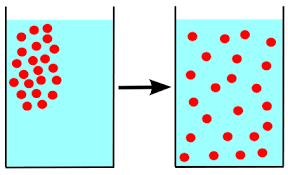
Diffusion
Molecules spread from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, resulting in the net movement until equilibrium is reached.
Tonicity
The measure of solute concentration in a solution relative to another solution, which affects cell shape and volume.
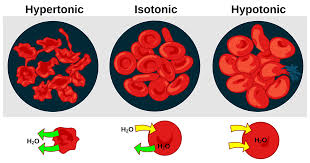
Hypertonic solution
A solution with a higher solute concentration compared to another solution, leading to water movement out of a cell, which may cause it to shrink (crenation)
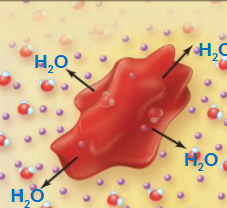
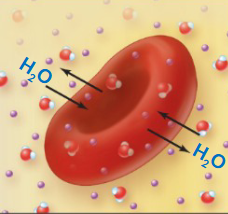
Hypotonic solution
A solution with a lower solute concentration compared to another solution, resulting in water movement into a cell, which may cause it to swell (hemolysis)
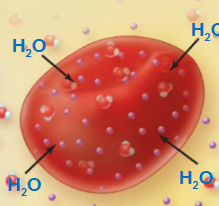
Isotonic solution
A solution with equal solute concentration compared to another solution, resulting in no net movement of water into or out of a cell. This maintains cell shape and volume.
Silver nitrate test
Turns into white cloudy streak in presence of salt

Benedict solution
turns YELLOW to GREEN to
ORANGE to RED in the presence of sugar when heated

Iodine solution
Turns “blue/black” in the presence of starch

Simple squamous epithelium
A single layer of flat cells found in areas such as the alveoli of lungs and lining of blood vessels, facilitating diffusion and filtration.
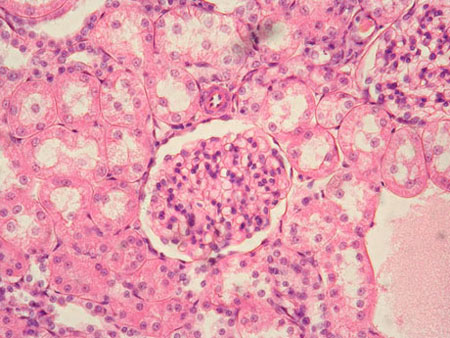
Simple cuboidal epithelium
A single layer of cube-shaped cells, commonly found in glands and kidney tubules, responsible for secretion and absorption.
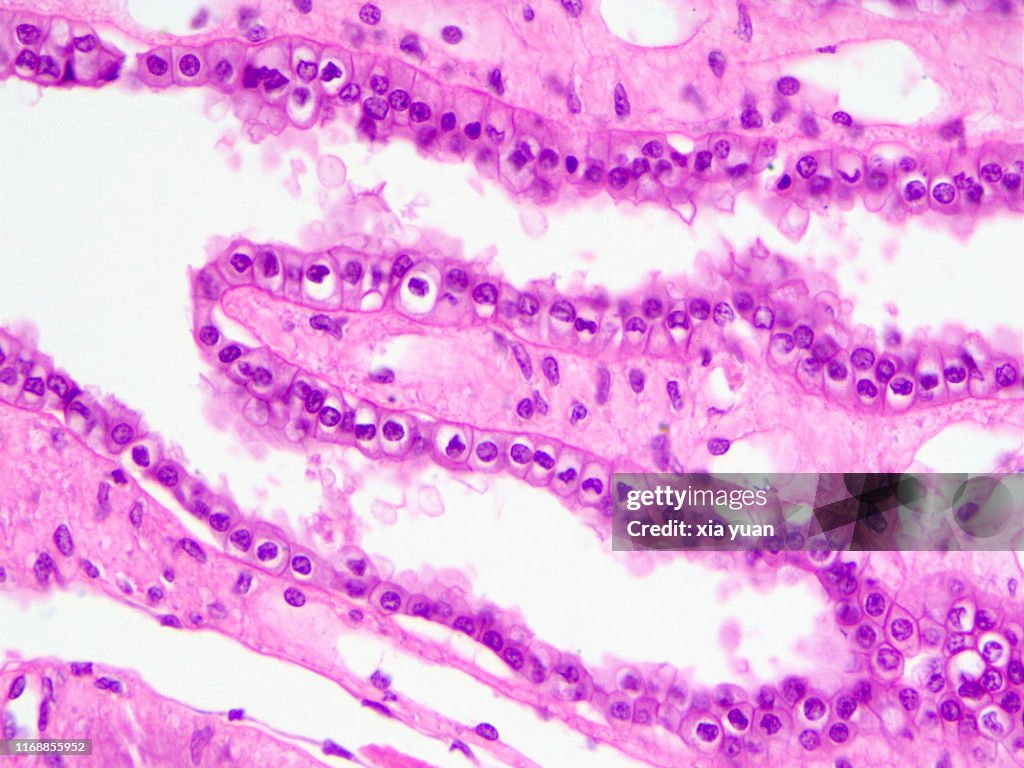
Simple columnar epithelium
A single layer of tall, column-shaped cells often found in the digestive tract, playing a key role in absorption and secretion.
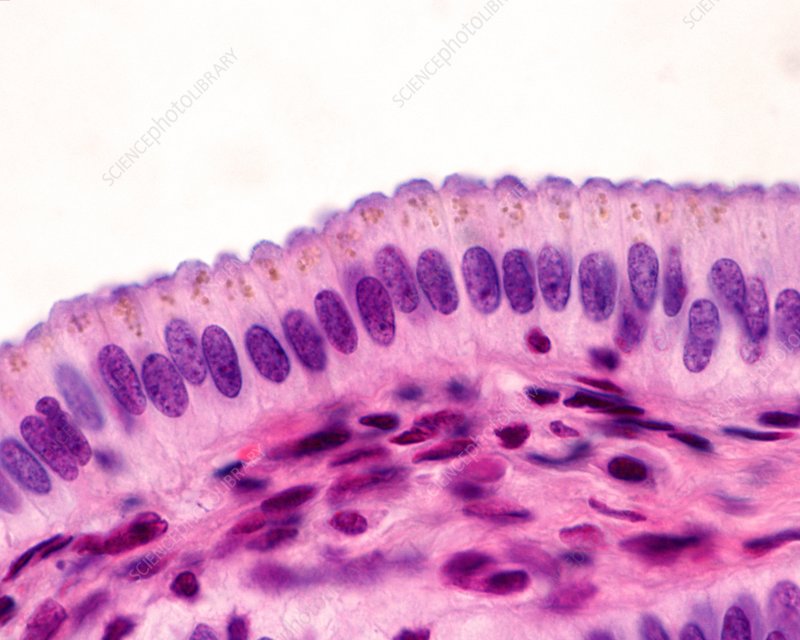
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
A type of epithelium that appears to be stratified due to varying cell heights but is actually a single layer of cells, often ciliated, found in the respiratory tract, aiding in secretion and movement of mucus.
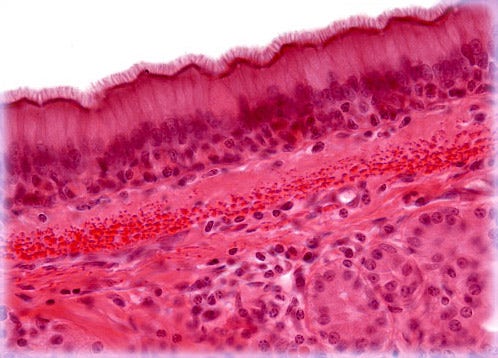
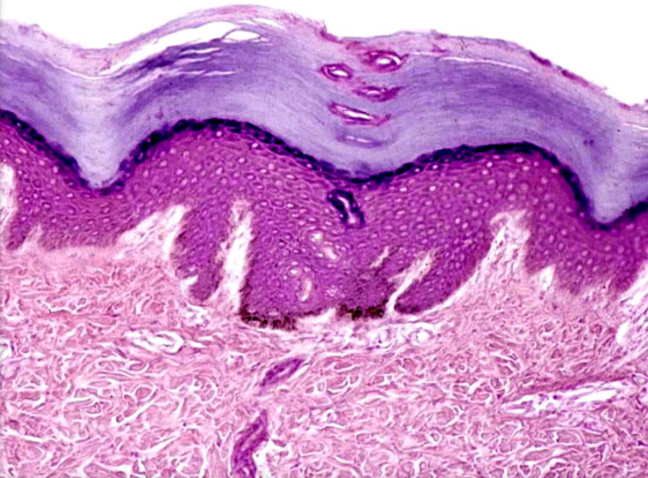
Stratified squamous epithelium (keratinized)
A multi-layered epithelium composed of flattened cells, providing protection against abrasion and found in areas such as the skin and mucous membranes.
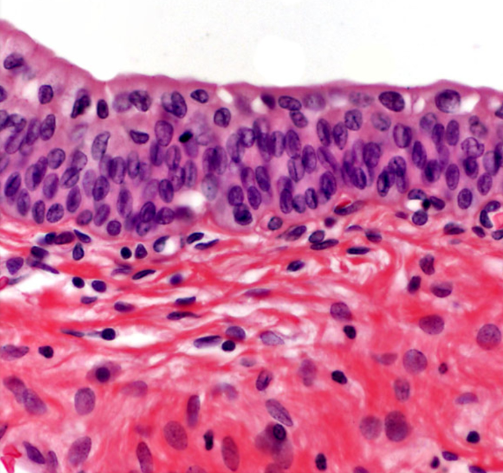
Transitional epithelium
A type of epithelium that can stretch and change shape, found in the urinary bladder and ureters, playing a crucial role in holding and accommodating urine.
Mesenchyme
Connective tissue that is loosely organized and contains stem cells capable of differentiating into various cell types, playing a crucial role in the development of organs and tissues.
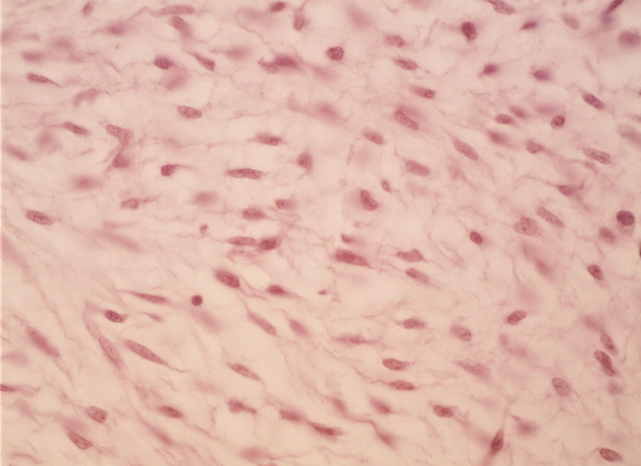
Areolar connective tissue
A loose connective tissue that provides support and elasticity; fibroblasts, elastic and collagen fibers
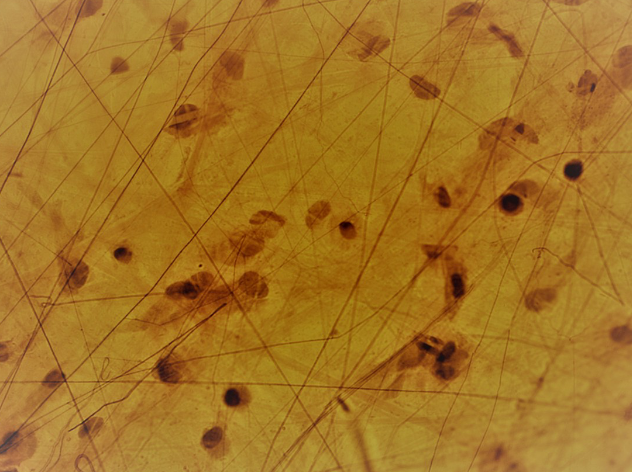
Reticular connective tissue
A type of connective tissue that contains a network of reticular fibers and cells, providing a supportive framework for organs such as the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes.
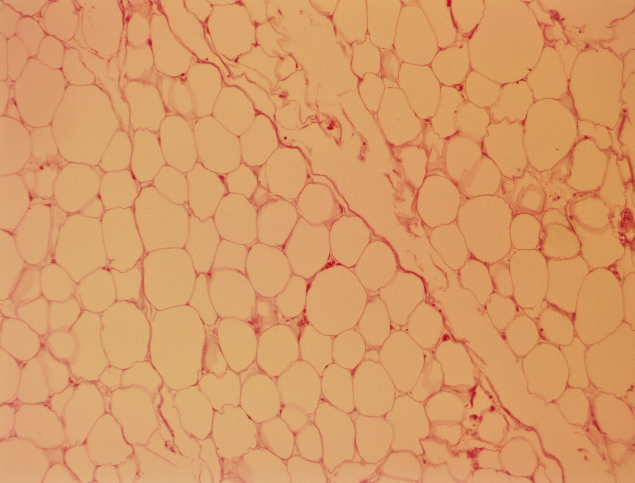
Adipose tissue
A specialized connective tissue that stores fat, providing insulation and cushioning for organs, as well as energy storage.
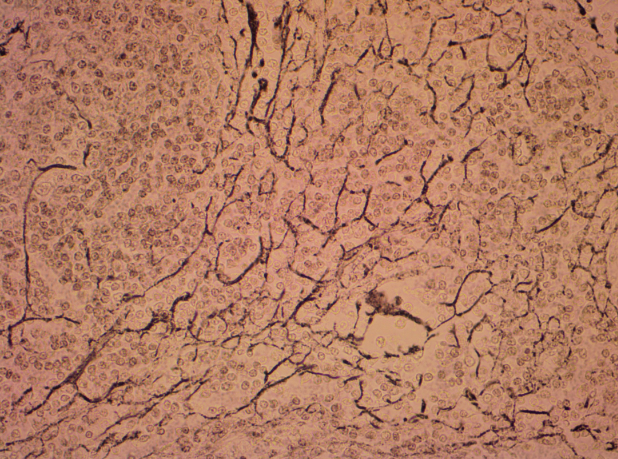
Dense regular connective tissue
A type of connective tissue organized into parallel collagen fibers, providing tensile strength and support, commonly found in tendons and ligaments.
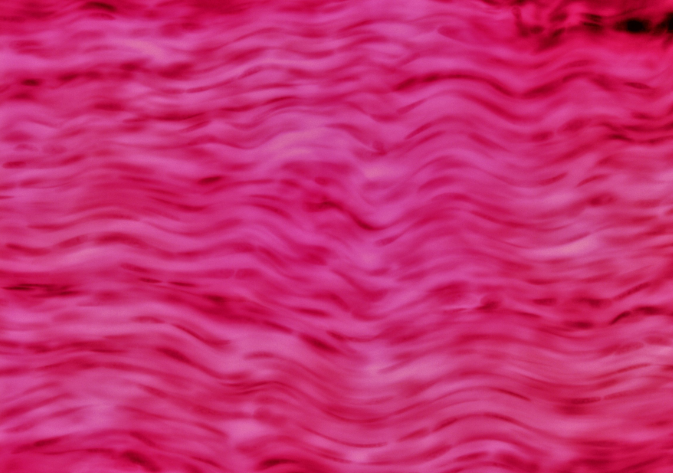
Dense irregular connective tissue
A type of connective tissue that consists of irregularly arranged collagen fibers, providing strength in multiple directions and support to areas such as the dermis of the skin (nonparallel collagenous fibers)
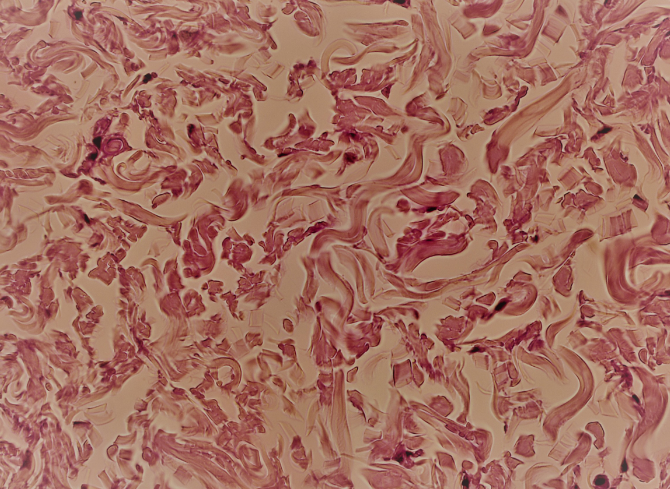
Elastic connective tissue
A type of connective tissue that contains a high concentration of elastic fibers, allowing for stretch and recoil. It is found in structures such as the walls of large arteries and the lungs.
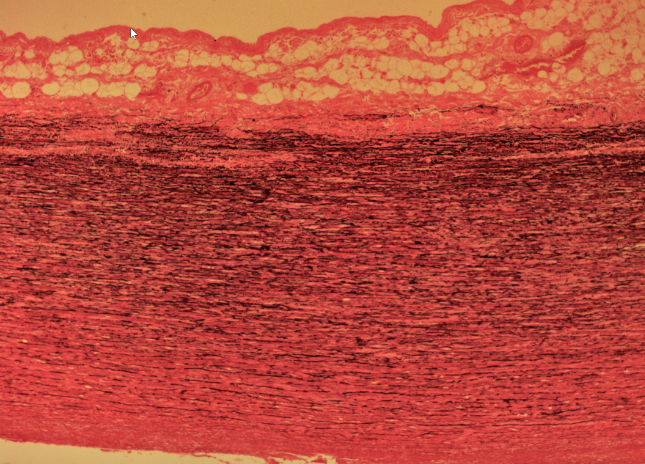
Hyaline cartilage
A type of cartilage characterized by a glassy appearance and a high content of collagen fibers, providing support with some flexibility. It is commonly found in joints, ribs, and the nose.
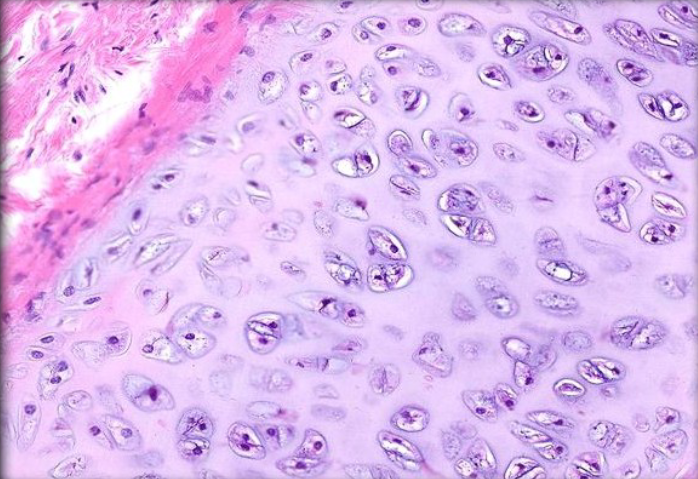
Fibrocartilage
A type of cartilage that contains dense bundles of collagen fibers, providing strong support and the ability to withstand pressure. It is found in areas such as intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis.
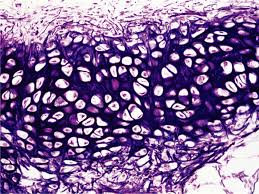
Elastic cartilage
A type of cartilage that is flexible and contains numerous elastic fibers, allowing it to maintain its shape while providing support (chondrocytes, lacunae)
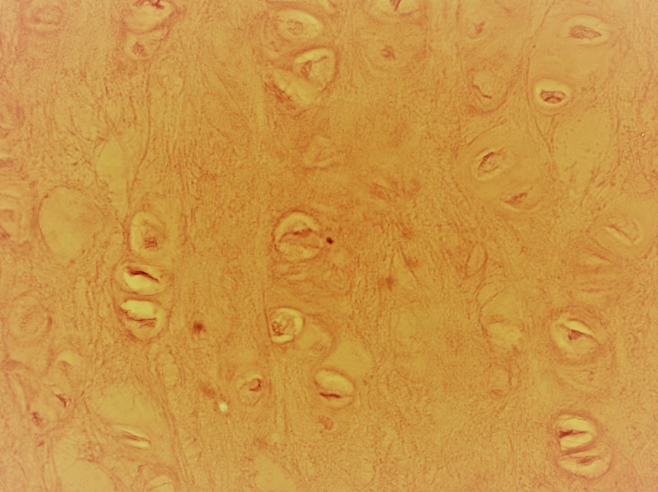
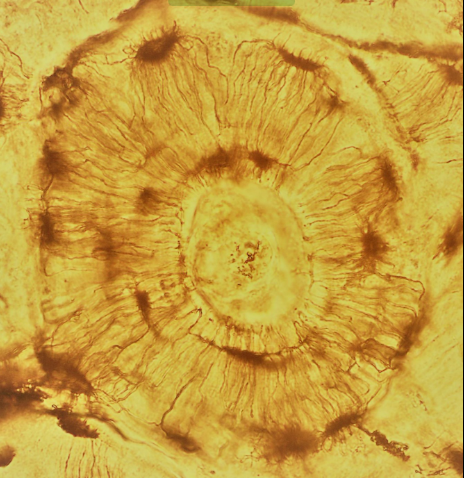
Bone tissue
A type of connective tissue characterized by a mineralized matrix, providing structural support and protection to the body while housing bone marrow for blood cell production.
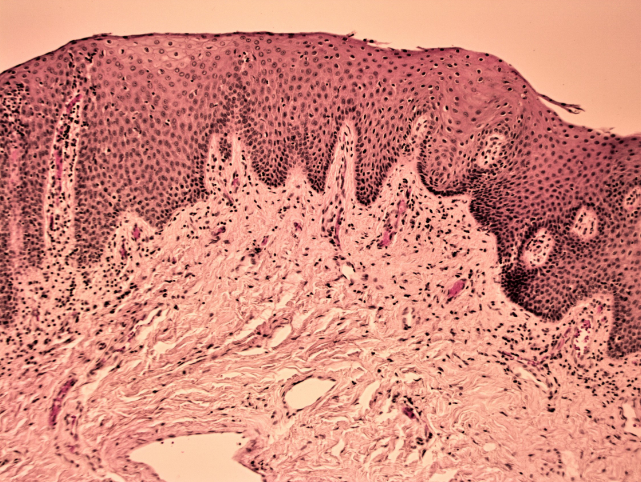
Stratified squamous epithelium (nonkeratinized)
A type of epithelial tissue composed of multiple layers of cells, with the outermost layer remaining moist. It is found lining body cavities and organs such as the mouth, esophagus, and vagina.
Epidermis
The outermost layer of skin, composed of stratified squamous epithelium that provides a protective barrier against environmental factors.
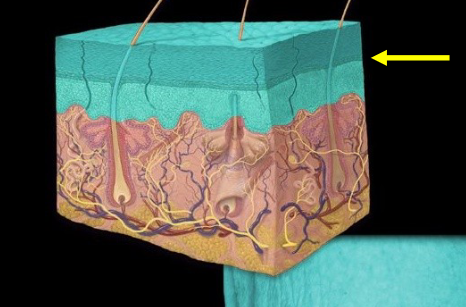
Dermis
The layer of skin located beneath the epidermis, consisting of connective tissue that provides strength and elasticity, containing blood vessels, nerves, and hair follicles.
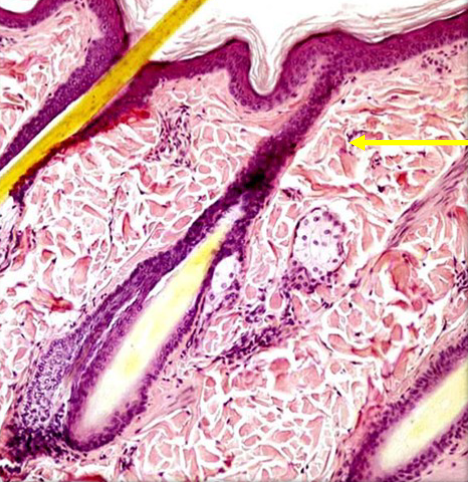
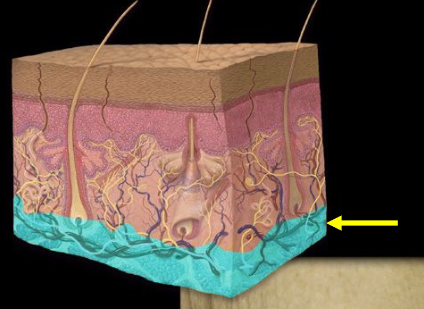
Hypodermis
The deepest layer of skin, also known as subcutaneous tissue, composed of loose connective tissue and fat, providing insulation and cushioning for underlying structures.
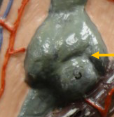
Arrector pili muscle
A small muscle located at the base of hair follicles that contracts in response to cold or fear, causing the hair to stand upright, also known as "goosebumps."

Sebaceous oil glands
Glands in the skin that secrete an oily substance called sebum, which helps to lubricate and protect the skin and hair.
Sudoriferous sweat glands
Glands that produce sweat to regulate body temperature and eliminate waste.
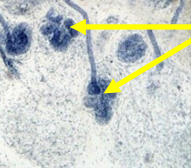
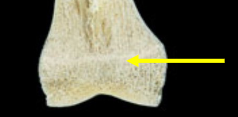
Epiphysis
The rounded end of a long bone that is involved in the formation of joints and growth plates.
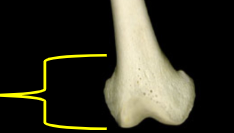
Diaphysis
The long, tubular shaft of a long bone that provides structural support and houses bone marrow.
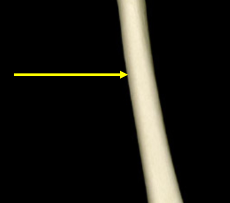
Epiphyseal line
A remnant of the growth plate in a long bone that represents the fusion of the epiphysis and diaphysis once growth has ceased.