Cell Unit Test Review
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/96
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
1
New cards
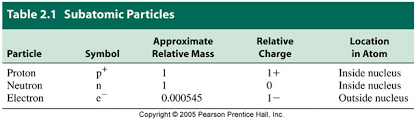
Location of the Three Atomic Particles
* neutron
* electron
* proton
* electron
* proton
2
New cards
Scientific Models
* representation of how something looks or works based on a hypothesis or theory
* 440 BC Democritus said atom was a solid, unbreakable ball
* 1898 Thomson said atoms have positive and negative charges
* 1911 Rutherford determined that atoms have a hard, massive center
* 1913 Bohr added to Rutherford’s model saying that electrons moved around the nucleus
* current one based on Einstein’s work (E=mc^2) = atom is made of a central, positively charged energy cloud and has an outer, negatively charged energy cloud.
* 440 BC Democritus said atom was a solid, unbreakable ball
* 1898 Thomson said atoms have positive and negative charges
* 1911 Rutherford determined that atoms have a hard, massive center
* 1913 Bohr added to Rutherford’s model saying that electrons moved around the nucleus
* current one based on Einstein’s work (E=mc^2) = atom is made of a central, positively charged energy cloud and has an outer, negatively charged energy cloud.
3
New cards
How to find number of atomic particles an atom has
\# of Protons = Atomic Number
\# of Electrons = Atomic Number
\# of Neutrons = atomic mass rounded to the nearest whole number
\# of Electrons = Atomic Number
\# of Neutrons = atomic mass rounded to the nearest whole number
4
New cards
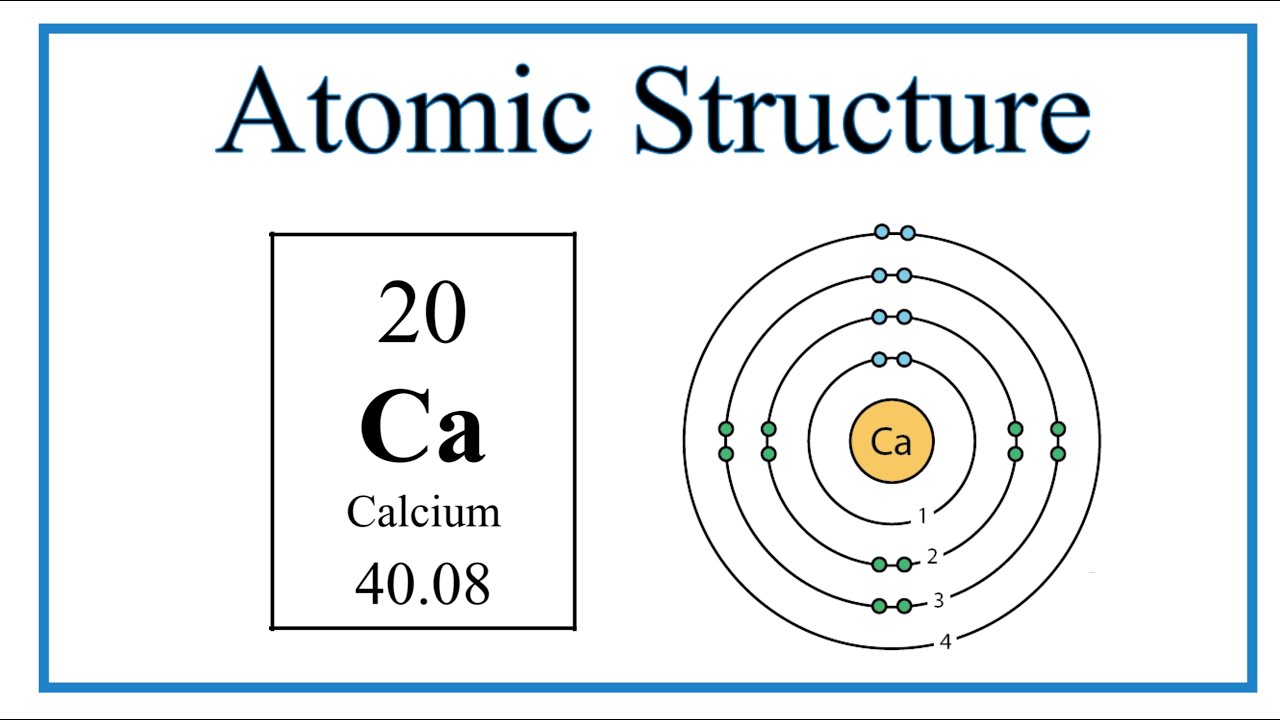
Bohr Model Example: Calcium
5
New cards
Why do atoms make bonds?
Atoms make bonds to balance their valence shells.
Either collect more electrons or drop electrons.
Become stable and decrease energy
Either collect more electrons or drop electrons.
Become stable and decrease energy
6
New cards
Types of Atomic Bonds
Covalent Bonds: two or more atoms share electrons
* most common
* strongest
Ionic Bonds: Ions of opposite charges are attracted and form a bond
Hydrogen Bonds: Weak attraction between hydrogen on one molecule and another atom on the same or different molecule
* most common
* strongest
Ionic Bonds: Ions of opposite charges are attracted and form a bond
Hydrogen Bonds: Weak attraction between hydrogen on one molecule and another atom on the same or different molecule
7
New cards
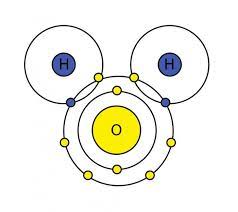
Bohr Model of Water
* show shared electrons
* show shared electrons
8
New cards
Define:
* atom
* molecule
* element
* compound
* atom
* molecule
* element
* compound
Atom: Smallest particle of an element that has the characteristics of that element
\
Element: simplest form of matter.
\
Molecule: Two or more atoms chemically combined
\
Compound: A molecule made of 2+ different types of atoms
\
Atoms are made of elements
Molecules and compounds are made of atoms
\
Element: simplest form of matter.
\
Molecule: Two or more atoms chemically combined
\
Compound: A molecule made of 2+ different types of atoms
\
Atoms are made of elements
Molecules and compounds are made of atoms
9
New cards
Molecule Models of:
* Sugar (monosaccharide)
* amino acid
* Sugar (monosaccharide)
* amino acid
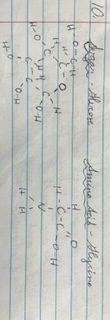
10
New cards
Molecule Models of:
* fatty acid
* glycerol
* nucleotide
* fatty acid
* glycerol
* nucleotide
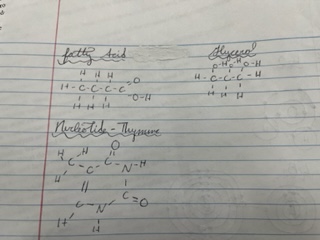
11
New cards
What elements comprise and what is the structure of a **single sugar**?
* rings of carbon and one oxygen
* each carbon has a hydroxyl group and a hydrogen bonded onto it
* each carbon has a hydroxyl group and a hydrogen bonded onto it
12
New cards
What elements comprise and what is the structure of an **amino acid**?
* carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
* building blocks of proteins
* made of an amino group, organic acid group, variable group
* building blocks of proteins
* made of an amino group, organic acid group, variable group
13
New cards
What elements comprise and what is the structure of a **fat/lipid**?
* made of carbon and oxygen with hydrogen bonded to each carbon
**Saturated Fats**
* have no double bonds
* had all the hydrogen atoms it can hold bonded to it
**Unsaturated Fats**
* one or more double bonds
* carbon doesn’t have all hydrogen possible bonded to it
**Saturated Fats**
* have no double bonds
* had all the hydrogen atoms it can hold bonded to it
**Unsaturated Fats**
* one or more double bonds
* carbon doesn’t have all hydrogen possible bonded to it
14
New cards
What elements comprise and what is the structure of a **nucleotide**?
* made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
* single or double ring structures of carbon and nitrogen with amine groups, methyl groups, or oxygen bonded to the rings
* single or double ring structures of carbon and nitrogen with amine groups, methyl groups, or oxygen bonded to the rings
15
New cards
What do the suffixes mean?
\-ose
\-ol
\-ase
\-ine
\-ose
\-ol
\-ase
\-ine
\- ose means sugar
\- ol indicates fat
\- ase indicates an enzyme
\- ine indicates an amino acid
\- ol indicates fat
\- ase indicates an enzyme
\- ine indicates an amino acid
16
New cards
What smaller molecules (monomers) make up this macromolecules (polymers)?
* starch (polysaccharide)
* starch (polysaccharide)
* made of glucose
* two glucose molecules do a dehydration reaction to become maltose to become starch
* two glucose molecules do a dehydration reaction to become maltose to become starch
17
New cards
What smaller molecules (monomers) make up this macromolecules (polymers)?
* fat
* fat
* made of glycerol and three fatty acids
* bonded by an ester bond
* bonded by an ester bond
18
New cards
What smaller molecules (monomers) make up this macromolecules (polymers)?
* proteins
* proteins
* made of amino acids
* bonded with a peptide bond
* bonded with a peptide bond
19
New cards
What smaller molecules (monomers) make up this macromolecules (polymers)?
* DNA
* DNA
* made of nucleotides
* important for storing energy
* 3 carbon of sugar has hydroxyl group
* important for storing energy
* 3 carbon of sugar has hydroxyl group
20
New cards
Chemical Groups
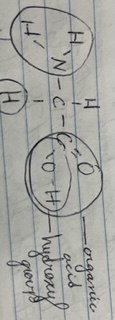
21
New cards
What is an enzyme?
What is it made of?
How are enzymes the workers of the cell?
What is it made of?
How are enzymes the workers of the cell?
* catalyst made of proteins
* called “workers of the cell” because they
* increase the speed of the chemical reactions but **aren’t used up/changed in the reaction**
* each enzyme **works on a specific substrate**/has a specific job
* called “workers of the cell” because they
* increase the speed of the chemical reactions but **aren’t used up/changed in the reaction**
* each enzyme **works on a specific substrate**/has a specific job
22
New cards
What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory and what does it have to do with the speed of the reaction?
* KMT states all matter vibrates/moves and increasing energy (heat) will increase vibration (movement).
* if the substrates/enzymes move faster, they will collide at an increased rate
* increases the rate of reactions
* if the substrates/enzymes move faster, they will collide at an increased rate
* increases the rate of reactions
23
New cards
How does induced fit/lock and key method work?
1. enzyme and substrate join together
2. enzyme “tweaks” the substrate so a bond is made/broken
3. enzyme and substrate break apart
\
Reaction happens much faster with enzymes than without
24
New cards
**Hydrolysis Reaction**
* **breaks apart** molecules
* catabalesm
* two molecules that had been joined + a water molecule are split apart with water joining the now separated molecules as OH groups
* catabalesm
* two molecules that had been joined + a water molecule are split apart with water joining the now separated molecules as OH groups
25
New cards
**Dehydration Reaction**
* **bonds 2 molecules together**
* removes H20 (water)
* an anabolism
* an H is removed from one molecule and an OH from another molecule and the two molecules are joined together at an O
* results in a macromolecule and a water molecule
\
**DEHYDRATION = JOINING by REMOVING WATER**
* removes H20 (water)
* an anabolism
* an H is removed from one molecule and an OH from another molecule and the two molecules are joined together at an O
* results in a macromolecule and a water molecule
\
**DEHYDRATION = JOINING by REMOVING WATER**
26
New cards
Hydrolysis vs. Dehydration
Hydrolysis = macromolecules become smaller
Dehydration = smaller molecules become bigger/macromolecules
Dehydration = smaller molecules become bigger/macromolecules
27
New cards
**pH Definition**
*negative log of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution*
\
* acidic = more H+ than OH-
* basic/alkaline = more OH- than H+
* neutral = equal number
\
* acidic = more H+ than OH-
* basic/alkaline = more OH- than H+
* neutral = equal number
28
New cards
pH ranges
>7 = Acidic
7= Neutral
7= Neutral
29
New cards
What conditions does amylase work best and is it the same for all enzymes?
* amylase should work best in warm areas with a neutral to basic pH
* working better at warmer temperatures is the same for all enzymes because of KMT
* working better at warmer temperatures is the same for all enzymes because of KMT
30
New cards
What occurs in the cell cycle between mitotic divisions?
The cell goes through three other phases. Synthesis (S), Gap 1 (G!) and Gap 2 (G2).
31
New cards
What happens in Gap 1?
* cell experiences metabloic changes to prepare the cell for division
* cell builds more contents and doubles all contents except chromosomes
* at restriction the cell is committed and can’t get back
* cell builds more contents and doubles all contents except chromosomes
* at restriction the cell is committed and can’t get back
32
New cards
What happens in synthesis?
* the cell constructs a second full set of chromosomes through DNA synthesis
* each chromosome is now made of two sister chromatids
* each chromosome is now made of two sister chromatids
33
New cards
What happens in Gap 2?
* cytoplasmic materials are assembled
* cell checks for errors and makes repairs
* then the cell can move onto mitosis
* cell checks for errors and makes repairs
* then the cell can move onto mitosis
34
New cards
What are G1, S, and G2 called collectivly?
Interphase
35
New cards
What are the phases of mitosis?
1. interphase
2. metaphase
3. anaphase
4. telophase
5. cytokinesis
36
New cards
What happens in interphase?
Interphase is **stage one** of **mitosis**.
* chromosomes duplicate with copies remaining attached
* chromosomes duplicate with copies remaining attached
37
New cards
What happens in prophase?
Prophase is **stage two** of **mitosis**.
* nucleolus and nuclear envelope break apart
* spindle begins attaching to the chromosomes
* nucleolus and nuclear envelope break apart
* spindle begins attaching to the chromosomes
38
New cards
What happens in metaphase?
Metaphase is **stage three** of **mitosis**.
* the chromosomes are pulled to the center of the cell
* aligns with the equatorial plane
* the chromosomes are pulled to the center of the cell
* aligns with the equatorial plane
39
New cards
What happens in anaphase?
Anaphase is **stage four** of mitosis
* the two identical chromatids of each chromosome seperates
* pulled by centromeres to the opposite ends of the cell
* the two identical chromatids of each chromosome seperates
* pulled by centromeres to the opposite ends of the cell
40
New cards
What happens in telophase?
Telophase is **stage five** of mitosis.
* spindle breaks down
* allows chromosomes to spread out
* nuclear envelope and nucleolus are reforming
* cytoplasm may be starting to divide
Basically reversing prophase
* spindle breaks down
* allows chromosomes to spread out
* nuclear envelope and nucleolus are reforming
* cytoplasm may be starting to divide
Basically reversing prophase
41
New cards
What happens in cytokinesis?
Cytokinesis is the **last stage/stage six** of mitosis
* actual cell division
* divides into two identical daughter cells
* nucleus and nucleolus are evident
* chromatin are not
* cells are identical to parent cell, but 1/2 the size
* actual cell division
* divides into two identical daughter cells
* nucleus and nucleolus are evident
* chromatin are not
* cells are identical to parent cell, but 1/2 the size
42
New cards
What is mitosis?
* type of nuclear division
* results in 2 exact copies of DNA and then 2 identical daughter cells (formed during cytokinesis)
* occurs in somatic (body cells)
* occurs to maintain body cells to perform their function
* allows cells to repair, develop, grow
* results in 2 exact copies of DNA and then 2 identical daughter cells (formed during cytokinesis)
* occurs in somatic (body cells)
* occurs to maintain body cells to perform their function
* allows cells to repair, develop, grow
43
New cards
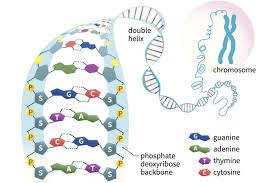
What is DNA?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
* genetic material for all living things
* formed in the nucleus
* double helix
* made of phosphate and sugar
* sides of the ladder
* paired bases
* Adenine and Thynine (AT)
* Guanine and Cytosine (GC)
* genetic material for all living things
* formed in the nucleus
* double helix
* made of phosphate and sugar
* sides of the ladder
* paired bases
* Adenine and Thynine (AT)
* Guanine and Cytosine (GC)
44
New cards
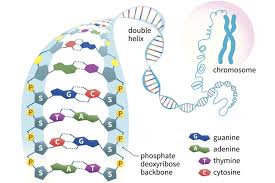
What monomers make up DNA? How are they arranged?
Nucleotides
* made of sugar/deoxyribose
* phosphate
* bases
* made of sugar/deoxyribose
* phosphate
* bases
45
New cards
How are the “steps” of the ladder bonded? (paired bases)
* covalent bonds
46
New cards
How are the uprights of the ladder bonded? (phosphate and sugar)
* hydrogen bond
47
New cards
Where does DNA replication occur?
* nucleus
48
New cards
When does DNA replication occur?
* S phase of interphase
49
New cards
What happens in DNA replication?
* exact copies of DNA are made
* like copying a book
* like copying a book
50
New cards
What are the steps of DNA replication?
1. enzymes open up the double helix
1. breaking hydrogen bonds between the bases
2. Enzymes separate the base pairs and expose the bases to the nucleoplasm
1. nucleoplasm contains more nucleotides
3. other enzymes bring in new nucleotides with the correct paired bases to the open DNA helix
4. nucleotides are covalently bonded together
1. forms sugar/phosphate backbone
5. as enzymes move down the DNA strands, two identical double helixes are formed
1. one goes to each cell
51
New cards
Why do bases pair?
* allows DNA to be copies accurately *every time it is replicated*
52
New cards
Where does transformation occur?
* ribosomes
* cytoplasm
* cytoplasm
53
New cards
When does transformation occur and what is it?
* Happens as DNA replication occurs
* is DNA being copied into mRNA
* is DNA being copied into mRNA
54
New cards
What are the steps of transformation?
1. initiation
1. ribosomes, tRNA, and mRNA come together
2. tRNA anticodons align with H-bonds mRNA codon
3. start codon is methionine
2. Elongation
1. second tRNA with a second anticodon attaches to the next mRNA codon
\
Then the ribosome moves down the RNA by one codon
\
3. a third tRNA aligns
1. amino acids 1 and 2 are bonded and the original tRNA is released
1. tRNA goes back to cytoplasm for another amino acid
continues for the length of the mRNA
\
4. Termination
1. stops the process
2. once ribosome reaches a “stop” codon the protein is complete
1. mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA are released
Multiple rRNAs can read the mRNA at once
* each makes a copy of the protein
55
New cards
Where does transcription occur?
* in the nucleus
56
New cards
What are the steps of transcription?
1. Helicase opens DNA helix
1. breaks hydrogen bonds for one gene length
1. bases are exposed to nucleoplasm
2. enzyme brings in the complimentary RNA nucleotides
1. sugar and phosphate are covalently bonded
3. DNA closes, mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm or on the endoplasmic reticulum.
57
New cards
Why is it ensured that the correct amino acid will be put into a protein?
* base pairing
58
New cards
What is meiosis?
* cell division in which the number of chromosomes in each daughter cell is reduces to 1/2 the number in the parent cell
* produces **gametes** (sex cells)
* haploid
* produces **gametes** (sex cells)
* haploid
59
New cards
Somatic vs. Gametes
**Somatic**: diploid, body cells
**Gametes**: haploid, sex cells
**Gametes**: haploid, sex cells
60
New cards
Chromosome
* rod shaped structure
* visible during mitosis and meiosis
* contains one long DNA molecule and proteins
* visible during mitosis and meiosis
* contains one long DNA molecule and proteins
61
New cards
Gene
* section of DNA found on chromosomes
* contains information for one protein or trait
* contains information for one protein or trait
62
New cards
Allele
* alternate forms of a gene or two genes on homolgous chromosomes
* contains information for the same trait
* contains information for the same trait
63
New cards
Heterozygote
* pairs of genes for a given trait
* alleles are **different**
* alleles are **different**
64
New cards
Homozygote
* pairs of genes for a given trait
* alleles are **identical**
* alleles are **identical**
65
New cards
Phenotype
* physical characteristics of a trait
* how gene is expressed
* how gene is expressed
66
New cards
Genotype
* gene combination for a trait
67
New cards
Homologous chromosomes
* pairs of chromosomes
* have DNA that codes for the same traits
* same genes in the same sequence
* one pair from each parent
* have DNA that codes for the same traits
* same genes in the same sequence
* one pair from each parent
68
New cards
variation
* individuals with a wide variety of traits
69
New cards
Crossing over
* exchange of gentic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis
70
New cards
Gametes
* sperm or egg
* produces in the gonads
* produces in the gonads
71
New cards
What is a dominant trait?
* trait expressed in phenotype, expressed physically
72
New cards
What is a recessive trait?
* contained in genotype but is __not__ expressed physically
73
New cards
What is an autosomal trait?
* trait controlled by any chromosome that is __not__ a sex chromosome
74
New cards
What is a sex linked trait?
* trait in which the gene is on a sex chromosome (usually X chromosome)
75
New cards
Zygote
* fertilized egg
76
New cards
Embryo
* germ laywes are formed but organs are not
77
New cards
Fetus
* organs are designated
* pre-natal
* pre-natal
78
New cards
How are zygotes, gametes, and fetuses related?
* Gametes are sex cells which combine to become a fertilized egg
* after cell replication the zygote becomes an embryo
* cells continue to replicate and the embryo becomes a fetus
* after cell replication the zygote becomes an embryo
* cells continue to replicate and the embryo becomes a fetus
79
New cards
What are Mendel’s Four Principles of Inheritance?
1. traits are controlled by paired factors (genes) with one from each parent
2. a dominant gene masks a recessive gene hiding its presence
1. 2 types of dominance
1. complete
2. incomplete
3. paired genes are separated in the parents when gametes are formed during meiosis (segregation)
4. Independant assortment
1. all different genes are distributed to the gametes in a random order
80
New cards
How did Mendel test his theory?
* bred thousands of pea plants
* found purebred pea plants od the same tupe resulted in offspring with the same genotype
* tested interbred pure plants of two types they were tall 100% of the time with genotype of Tt
* when 2 crossbreds were interbred, 75% were tall, 25% were short
* found purebred pea plants od the same tupe resulted in offspring with the same genotype
* tested interbred pure plants of two types they were tall 100% of the time with genotype of Tt
* when 2 crossbreds were interbred, 75% were tall, 25% were short
81
New cards
How is recombinant DNA formed?
* formed when DNA fragments of more than one organism are combined
82
New cards
How is recombinant DNA formed?
* A plasmid and recipicient are needed
* gene is cut out of both (same gene, different alleles)
* leaves “sticky ends”
* DNA from plasmid is input into the recipicient
\
needs to be in a vector, for example a retrovirus
* gene is cut out of both (same gene, different alleles)
* leaves “sticky ends”
* DNA from plasmid is input into the recipicient
\
needs to be in a vector, for example a retrovirus
83
New cards
Metabolism
Sum of breaking down and building up processes in the body
84
New cards
Anabolism
Building up processes
* mitosis, photosynthesis, making macromolecules
* mitosis, photosynthesis, making macromolecules
85
New cards
Cell Diagram Examples
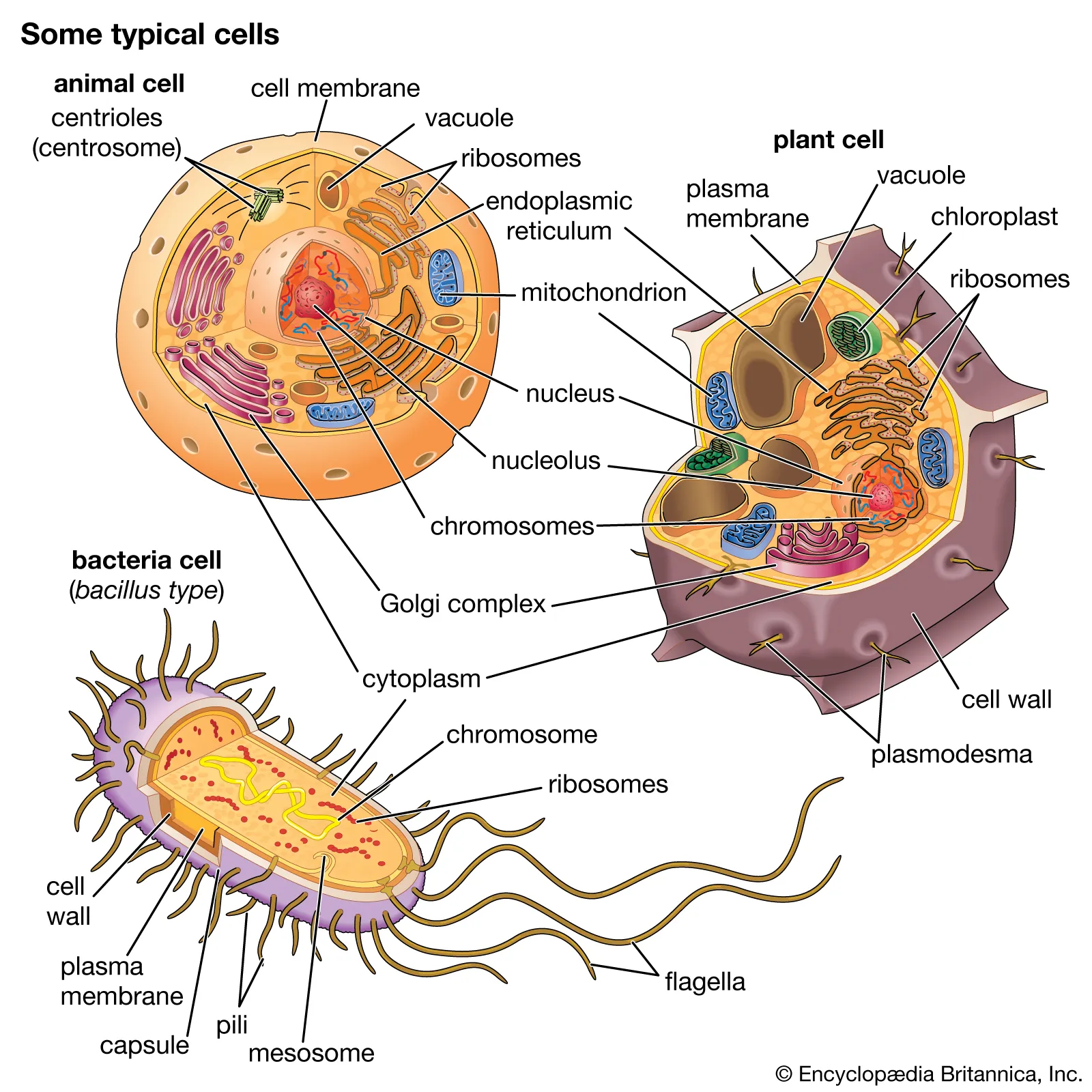
86
New cards
Endothermic creatures
* control own body temperature
* mammals and fish
* insulation is used to prevent heat loss
* uses metabolism to make heat
* mammals and fish
* insulation is used to prevent heat loss
* uses metabolism to make heat
87
New cards
Exothermic
* gets body temperature from the environment
* fish, amphibians, reptiles, invertebrates
* no insulation
* dependant on outside temperatures
* fish, amphibians, reptiles, invertebrates
* no insulation
* dependant on outside temperatures
88
New cards
Where does photosynthesis take place?
In the palisade mesophyll inside choroplast
89
New cards
What is photosynthesis?
* light energy is converted into chemical energy stored in bonds of glucose
* 2 different phases
* 2 different phases
90
New cards
What is the summary reaction of photosynthesis?
\
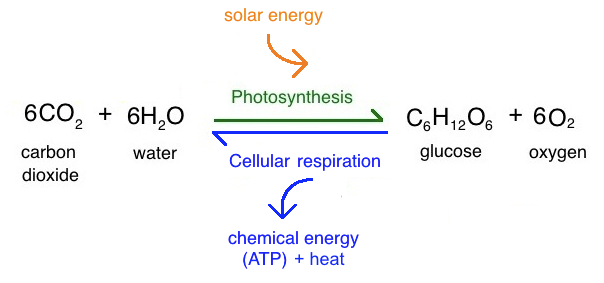
91
New cards
What are the two phases of photosynthesis?
Light reaction
Dark reaction
Dark reaction
92
New cards
What is the light reaction of photosynthesis?
* converts H20 and light energy into oxygen
* water is split releasing H+, e- and O2.
* H+ and e- are kept for next reaction
* O2 is released
* water is split releasing H+, e- and O2.
* H+ and e- are kept for next reaction
* O2 is released
93
New cards
What is the dark reaction of photosynthesis?
* converts CO2 into glucose
* inorganic carbon (CO2) is converted into organic carbon (glucose) which is stored as energy
* inorganic carbon (CO2) is converted into organic carbon (glucose) which is stored as energy
94
New cards
What is ATP?
**A**denosine **T**ri**p**hosphate
* energy source for all activities in living things
\
To release energy from ATP, **last phosphate is broken off**
* energy source for all activities in living things
\
To release energy from ATP, **last phosphate is broken off**
95
New cards
Where is cellular respiration and glycolysis taking place?
* mitochondria of the cells
* all cells
\
Takes place in almost all organisms
* except some yeast and bacteria
* all cells
\
Takes place in almost all organisms
* except some yeast and bacteria
96
New cards
What happens in glycolysis?
* glucose is split and **2ATP** is captured
* occurs in cytoplasm
* occurs in cytoplasm
97
New cards
What is the summary equation for glycolysis?
C6 H12 O →2C3 H4 O3 4H + E (**2ATP**)