CH2 - Waves and Measurements
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What are Electrodes?
Electrodes are sensors placed on the skin to detect electrical activity
12-lead EKG uses 10 electrodes: 4 limb + 6 chest (precordial) leads
Placement accuracy is key for reliable readings
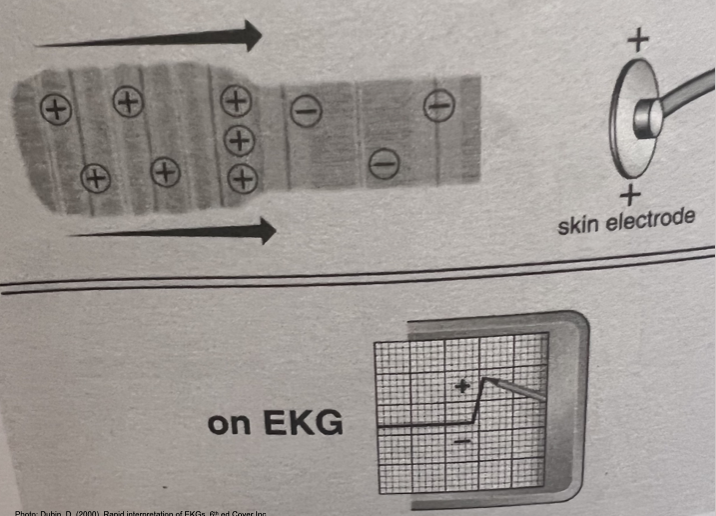
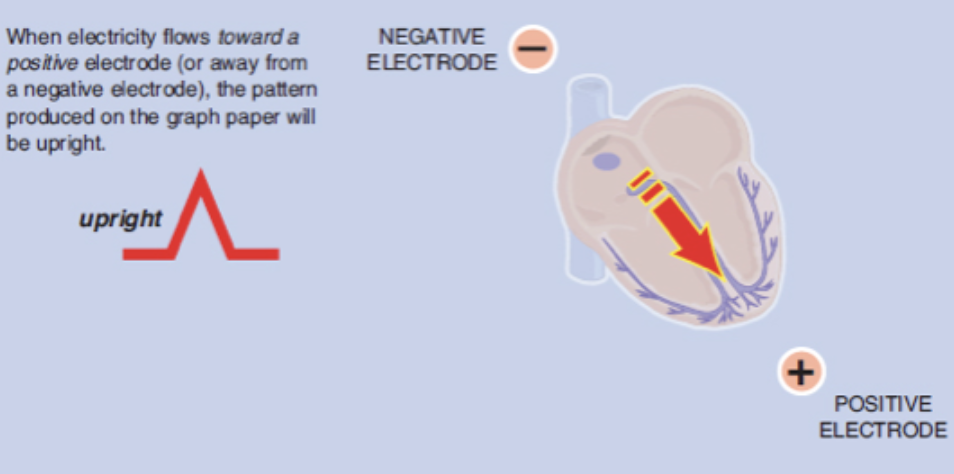
Rule of Electrical Flow
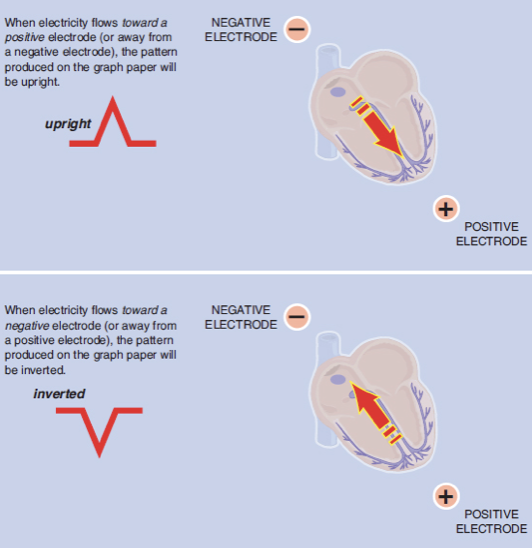
Electricity flows TOWARDS a positive electrode → positive (upright) deflection
Flows AWAY from positive electrode → negative deflection
Perpendicular flow → biphasic (equally up/down) waveform
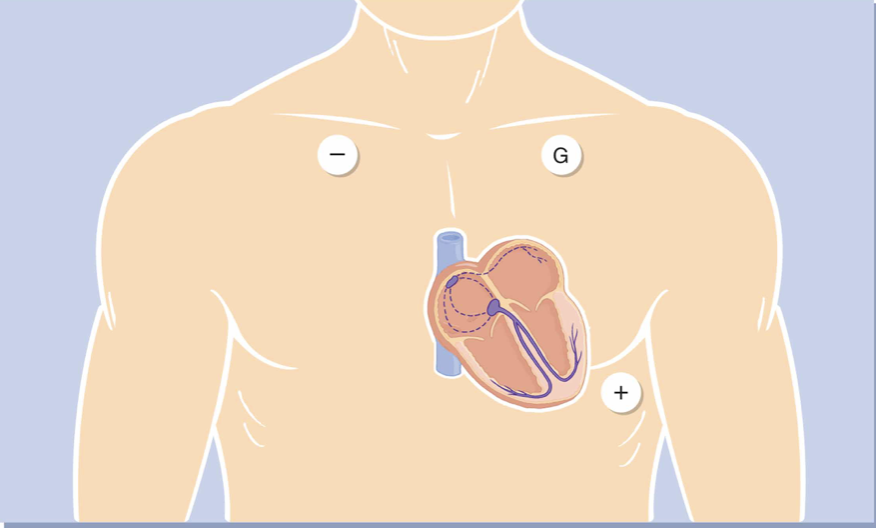
Which are the most common Monitoring Leads? Difference?
Lead II → best for rhythm
V1 → best for wide/narrow QRS
Each lead gives a different angle/view of the heart’s activity
Know the Electrode Placement for Monitoring Lead II
V1 → RIGHT Sternum
V2 → LEFT Sternum
V4 → LEFT under Nipple
V3 → BETWEEN V2 & V4
V6 → LEFT under Axillary
V5 → BETWEEN V4 &.V6
When a P wave originates in the SA node, it is expected to be smooth, rounded, and _____ in Lead II
Upright
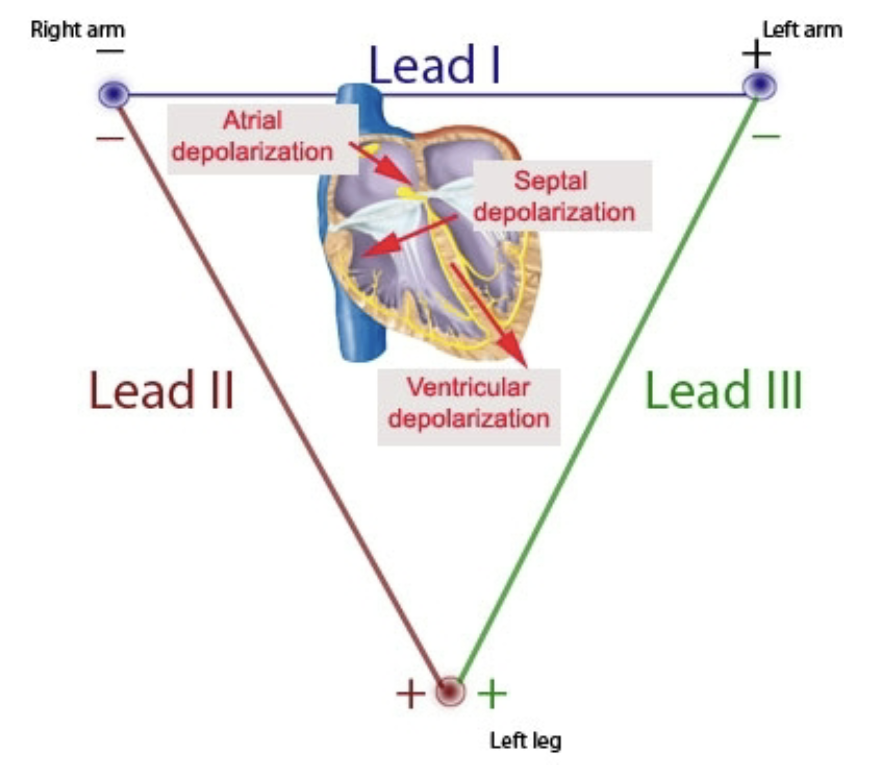
What explains why the QRS complex is typically upright in Lead II?
The mean electrical axis of ventricular depolarization is directed toward the left leg
Define Myocyte
Make up Myocardium
Contractile cells → pumps blood
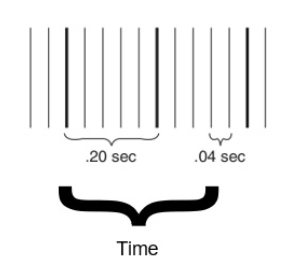
On a standard 12-lead EKG, what does one small box on the horizontal axis represent?
0.04 seconds
Know Graph Paper Basics
Small square = 0.04 sec (horizontally)/ 1mm (vertically)
Large square = 0.20 sec (5 small squares) / 5mm
What is the Speed EGK usually runs?
25 mm/sec
Vertical axis and Horizontal axis measure what on the EKG paper?
Vertical axis (Y) = voltage (amplitude), measured in mm or mV
Horizontal axis (X) = time, in seconds
If the R-R intervals across the strip are consitent, then the rhythm is considered _____
Regular
How to ACCURATELY measure Heart Rate?
6 second method: Count the number of R waves in a 6 second strip x 10
Used for regular or irregular rhythms
Small box method: HR = 1500/ # Small boxe
One Heartbeat =
P wave → QRS → T wave
Represents depolarization → contraction → repolarization → rest
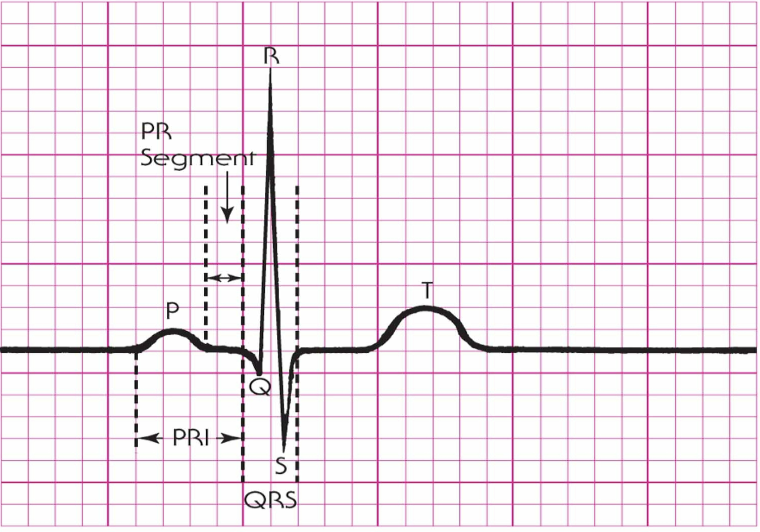
What describes the elements of a single cardiac cycle?
P Wave
PR Segment
PRI
QRS Complex
T Wave
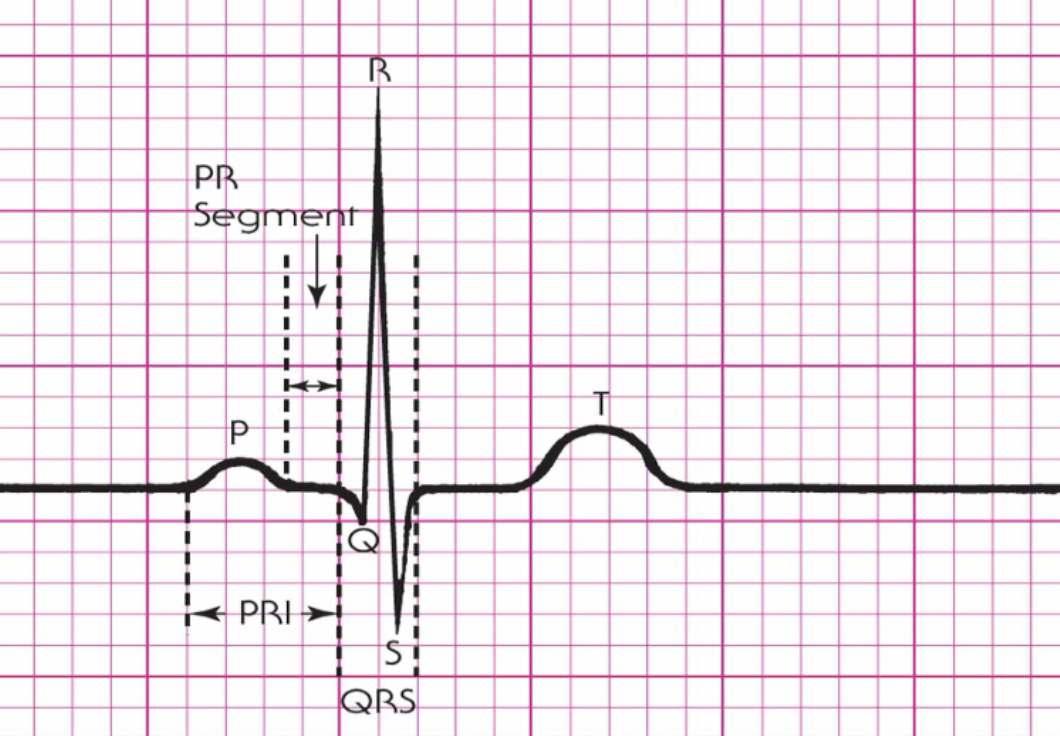
What happens during the PR interval on an EKG?
Atrial depolarization and conduction through the AV node
Normal: 0.12-0.20 sec
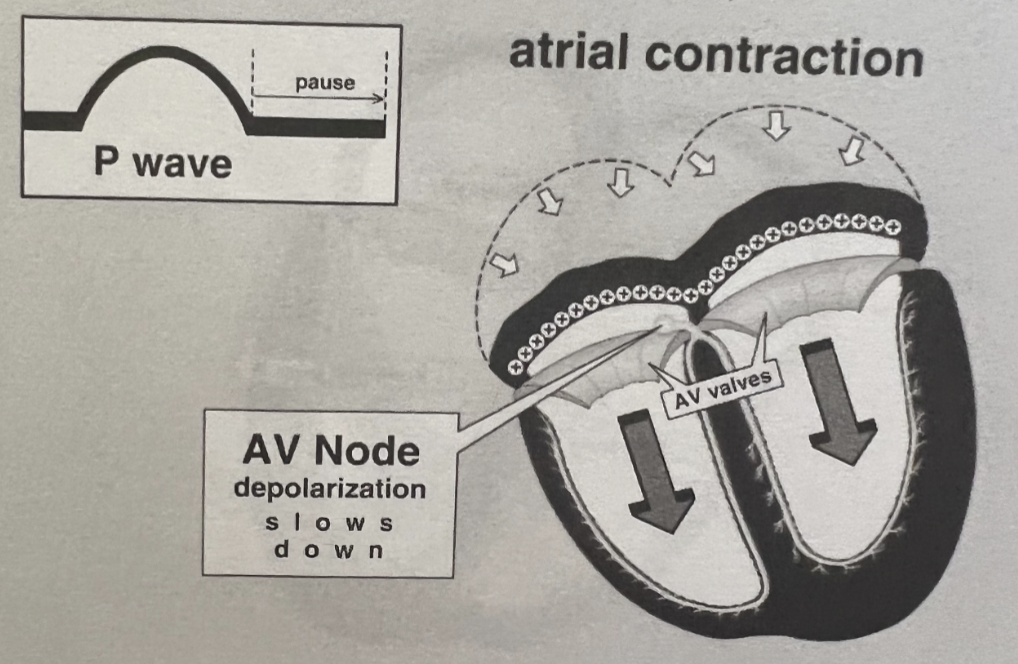
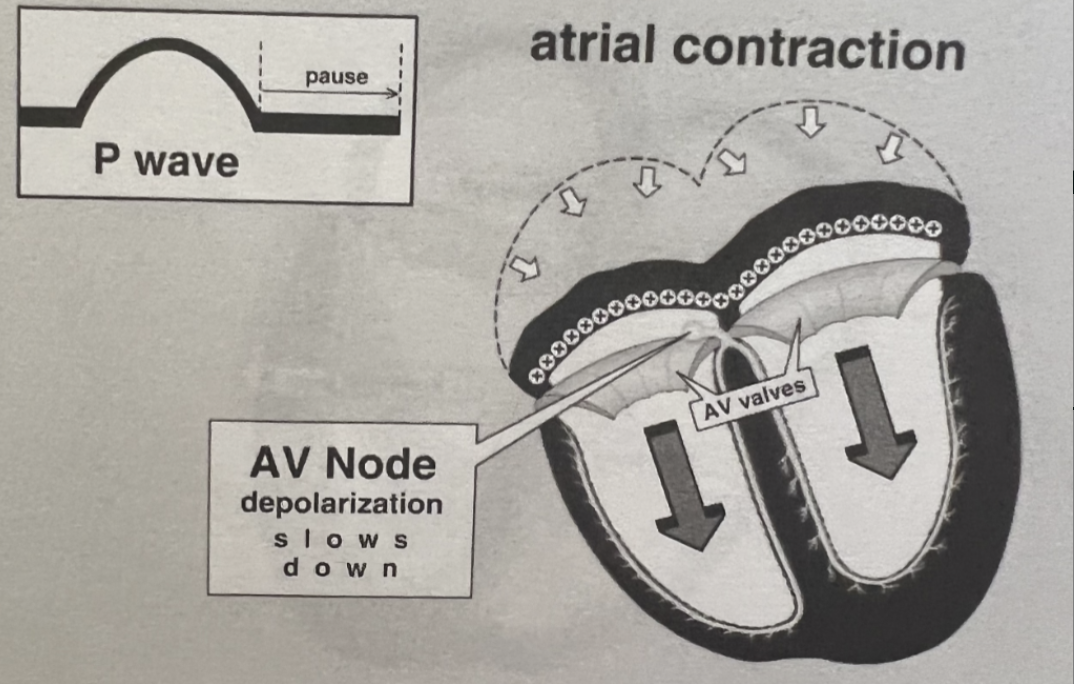
What is the Role of the AV Node?
Acts as a gatekeeper between atria and ventricles
Slow conduction allow time for:
Atrial contraction (atrial kick)
Ventricular filling
Can act as a backup pacemaker if SA node fails
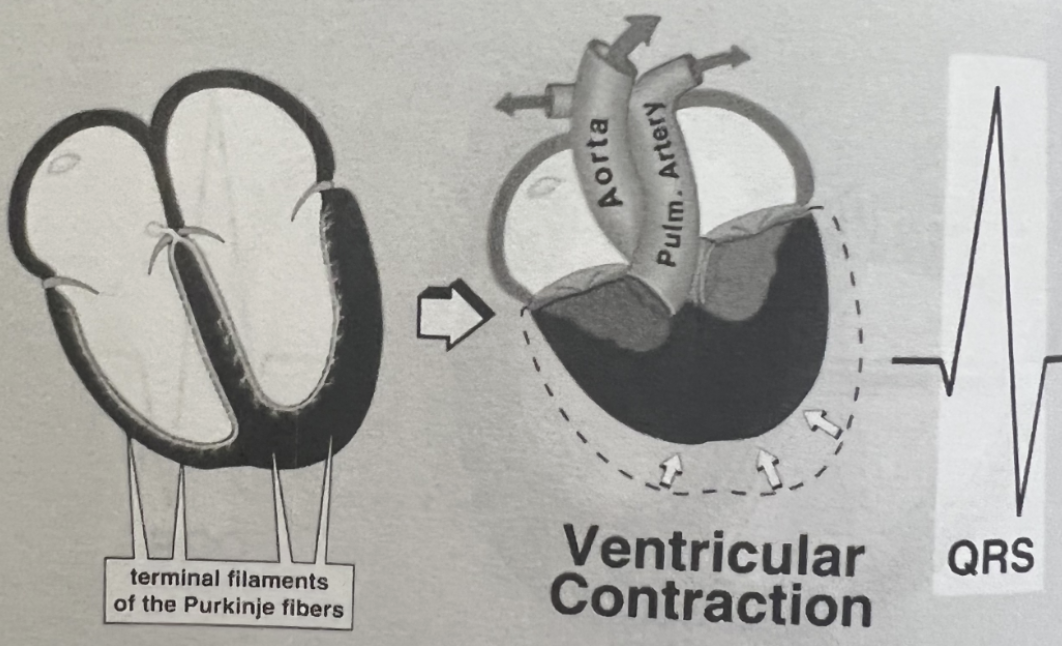
What happens during the QRS Complex on an EKG?
Start to end of ventricular depolarization
Normal: <0.11 sec
The T wave on an EKG represents which electrical event?
Ventricular repolarization
The P wave, QRS Complex and T wave on an EKG represents which electrical event?
P wave
→ Atrial Depolarization
Contraction
QRS complex
→ Ventricular Depolarization
Contraction
T wave
→ Ventricular Repolarization
Going towards resetting
U wave
→ Sometimes seen with hypokalemia
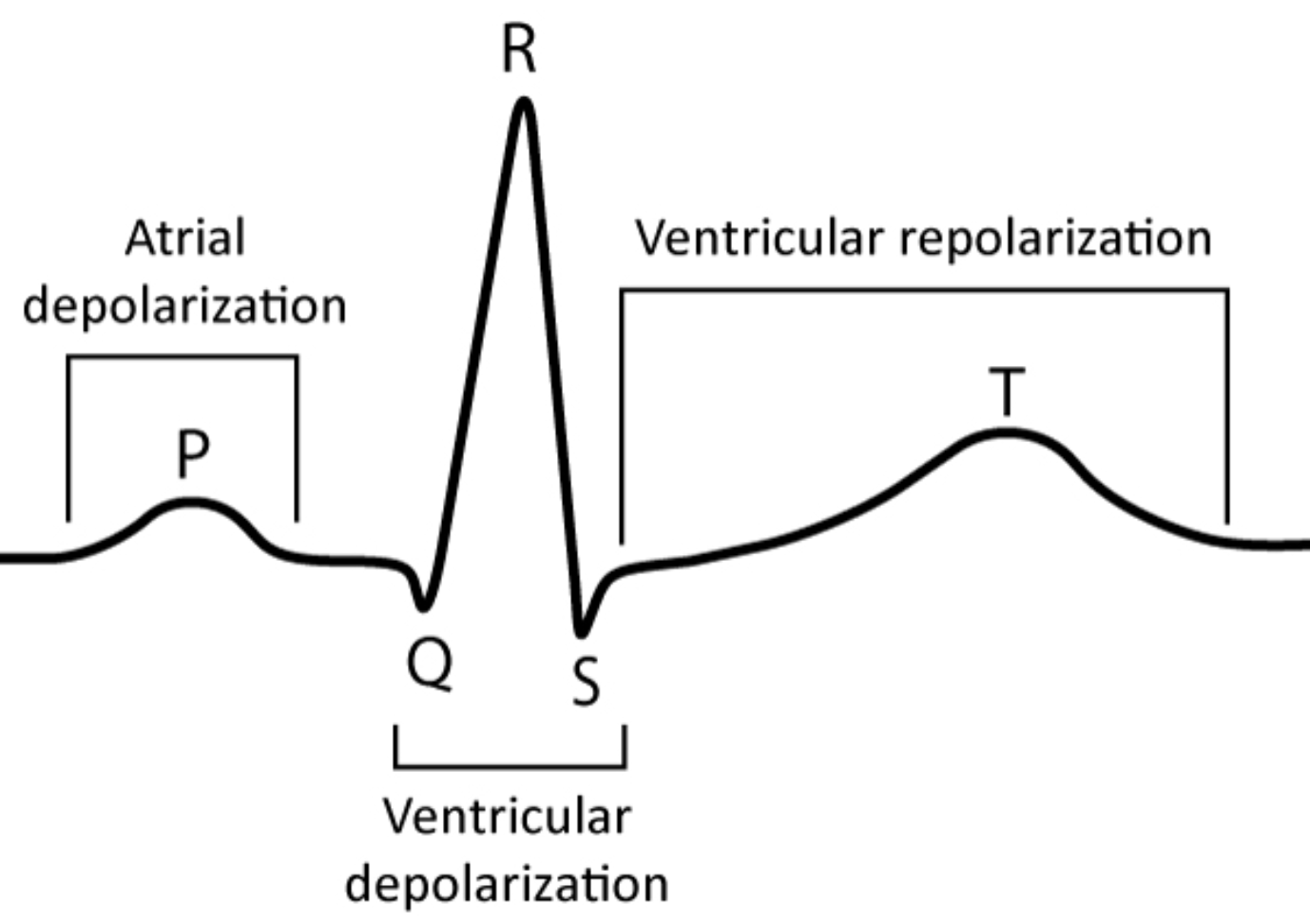
Describe ST segment
End of QRS to start of T wave
Look for elevation/depression
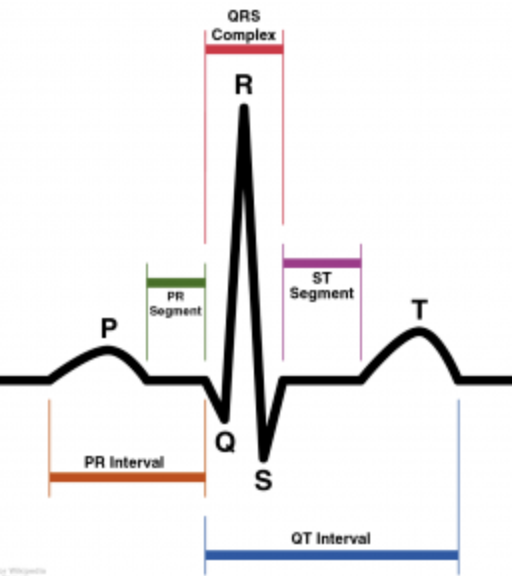
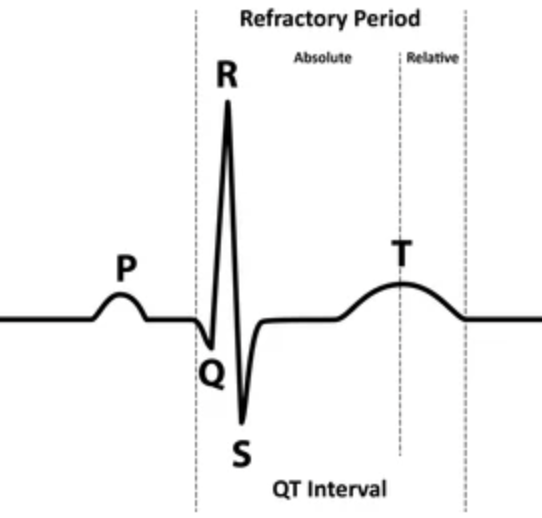
The QT interval represents what event in the cardiac cycle
Ventricular depolarization and repolarization
Beginning of QRS to end of T wave
Varies with HR
Normal: MEN - <0.45sec; WOMEN: <0.46
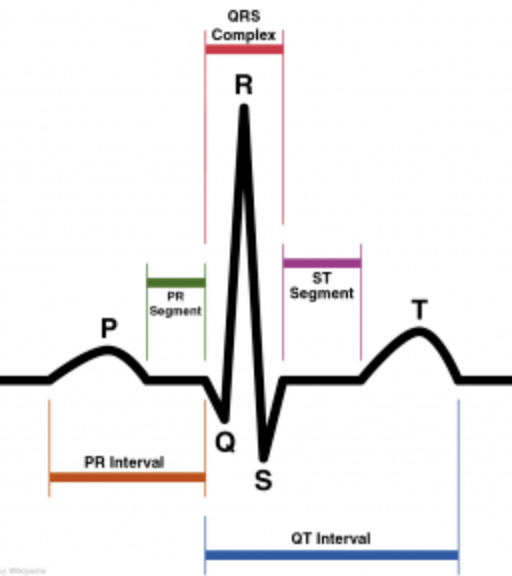
Key Measurements
P wave
<0.12 sec, <2.5 mm tall
PRI
0.12-0.20 sec
QRS
<0.12 sec
QT Interval
MEN <0.45sec
WOMEN: <0.46
Should be less than half the R-R interval
What can cause artifact on an EKG tracing?
Caused by patient movement, loose electrodes, and electrical interference
Can mimic arrhythmias - ALWAYS CHECK THE PATIENT
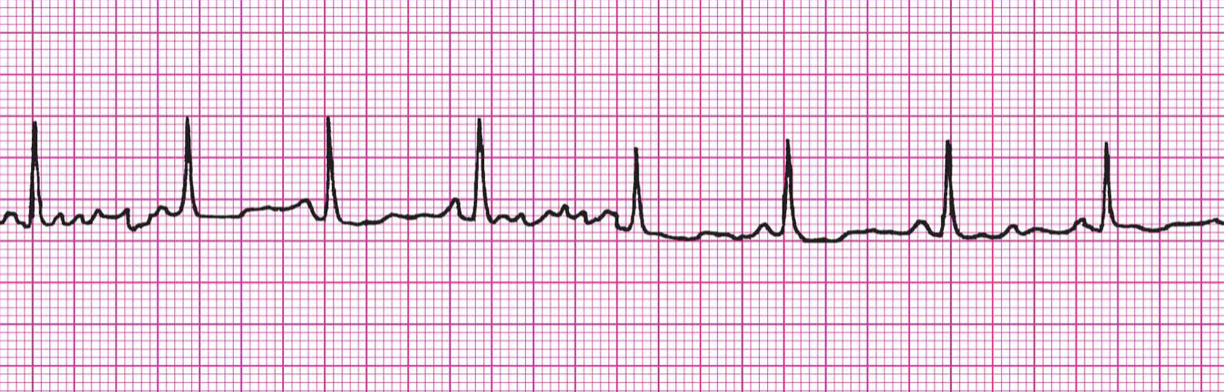
What example of Artifact/Interference is this?
Artifact: Muscle Tremors
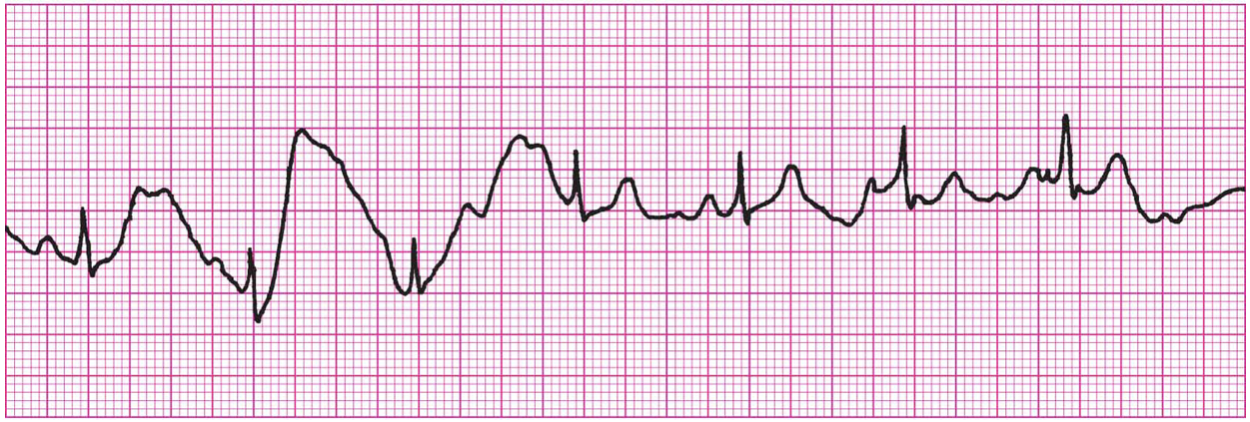
What example of Artifact/Interference is this?
Artifact: Patient movement
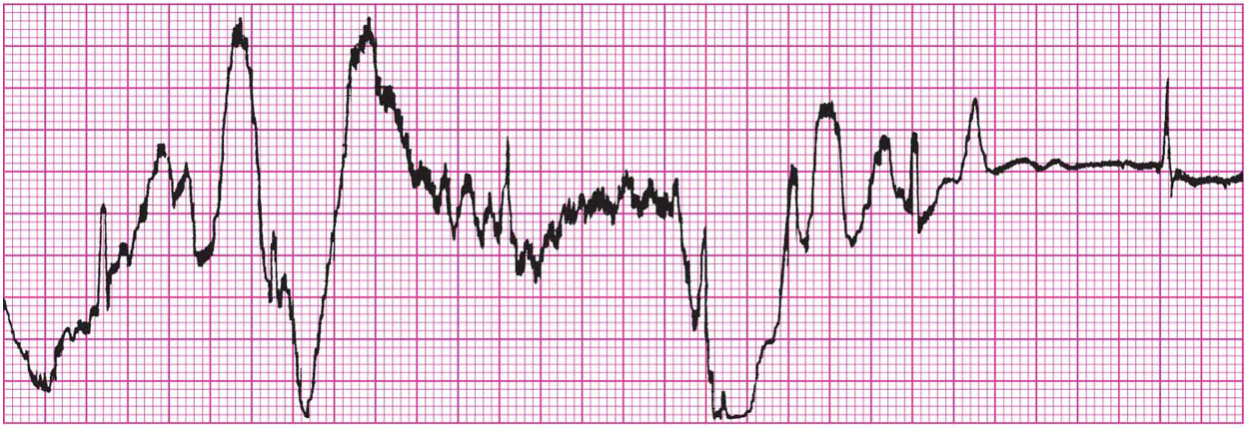
What example of Artifact/Interference is this?
Artifact: Loose Electrode
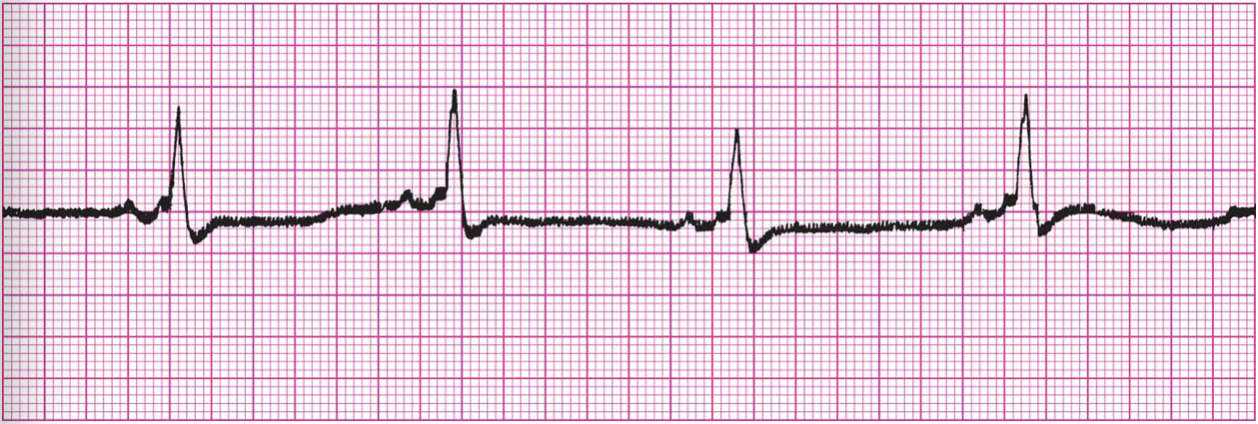
What example of Artifact/Interference is this?
Artifact: 60-Cycle Interference
Explain Refractory Periods
Absolute
No stimulus can cause a new depolarization
QRS → peak of T
Relative
A strong enough impulse can trigger another beat (downward slope of T wave)
Dangerous time
R-on-T phenomenon