Energy Types and Conservation in Physics and Chemistry
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is energy associated with?
Movement, changes in matter, and the potential to move or change.
What happens without a source of energy?
There is no change or movement; things remain constant.
What are the two states of energy?
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy.
What is kinetic energy?
The energy associated with motion.
How is kinetic energy calculated?
KE = 1/2 mv², where m is mass and v is velocity.
What are the two types of kinetic energy?
Heat Energy (random movement) and Work Energy (systematic movement).
What is heat energy?
A special form of kinetic energy related to the random movement of atoms and molecules.
How is temperature related to heat energy?
Temperature measures the average speed of moving atoms or the amount of heat in matter.
What is the direction of heat flow?
Heat flows from high energy (hot) temperatures to low energy (cold) temperatures.
What is work energy?
Kinetic energy that performs systematic movement, such as flow or volume change.
What is potential energy?
Stored energy that has the potential to form kinetic energy.
What are the three potential energy fields?
Gravitational Field, Magnetic Field/Electric Field, and Potential Chemical Energy (Gibbs Free Energy).
How is potential energy determined in a gravitational field?
By the mass of an object and the distance it can move towards the center of gravity.
What is the formula for potential energy?
Potential Energy = Mass x Distance.
What characterizes an exothermic process?
Potential energy is converted to kinetic energy, releasing energy.
What characterizes an endothermic process?
Kinetic energy is converted to potential energy, requiring energy input.
What does the Law of Conservation of Energy state?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only change states or forms.
What is the relationship between potential and kinetic energy during conversion?
The amount of kinetic energy produced equals the amount of potential energy given off.
What is Gibbs Free Energy?
The potential energy associated with molecules stored in chemical bonds.
How do high energy molecules differ from low energy molecules?
High energy molecules, like sugar and oxygen, have more Gibbs Free Energy than low energy molecules, like carbon dioxide and water.
What is the role of energy in changes of matter?
All changes in matter require energy, including movement, chemical changes, and phase changes.
What is the relationship between energy and matter interactions?
All energy comes from the interactions and transformations of matter.
What is chemistry?
The study of matter and energy interactions, including defining matter types and controlling interactions.
What is an example of energy conversion in nature?
The conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy as systems move from high to low potential energy levels.
What is the efficiency of energy conversion in the human body?
The human body is about 20% efficient, with most energy from food producing heat.
What is the significance of thermal equilibrium?
Energy flows until temperatures are equal throughout the matter.
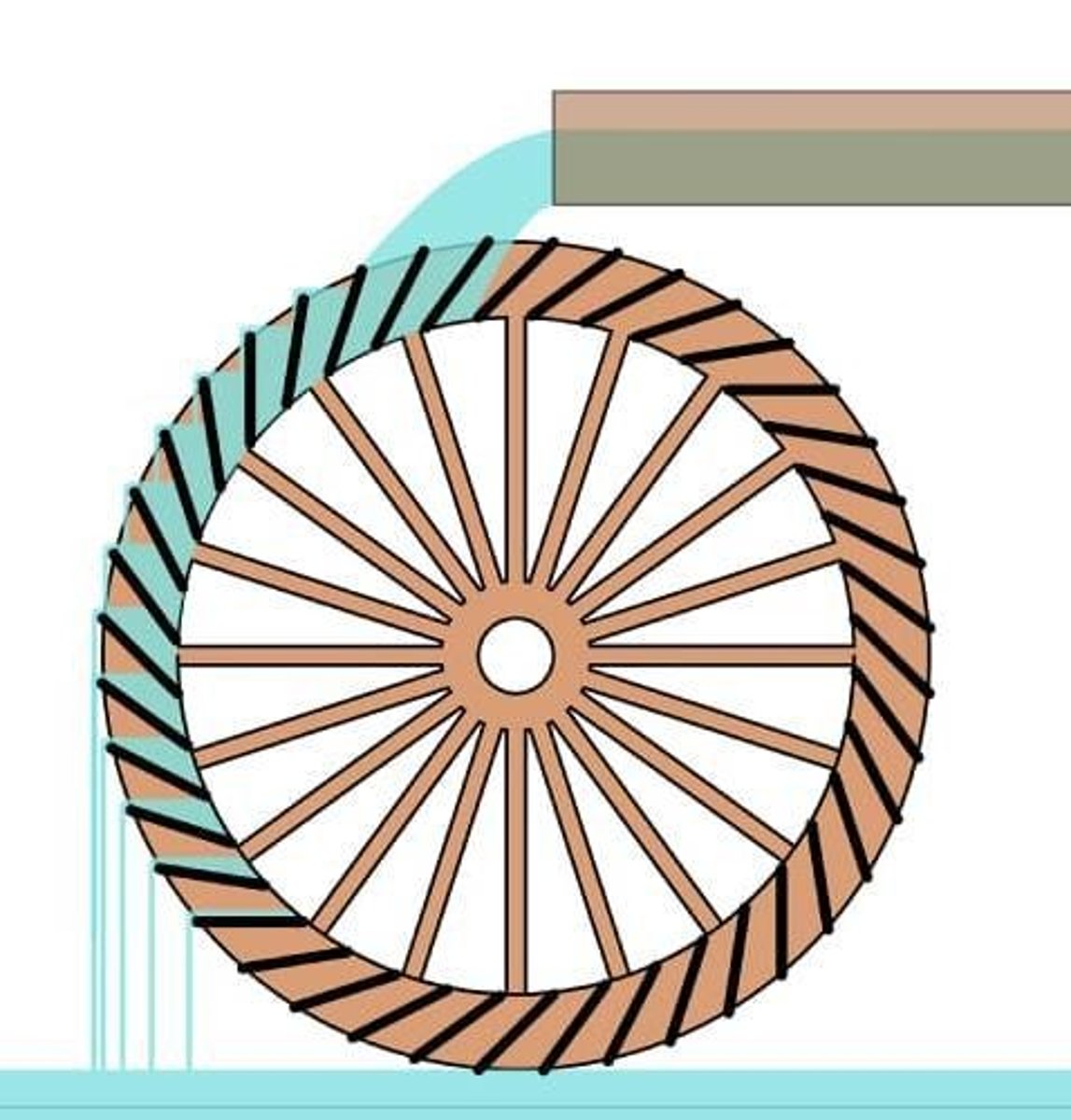
What is the importance of the water wheel in energy conversion?
It demonstrates the conversion of potential energy (stored water) to kinetic energy (flow and rotation).