CT REGISTRY- STUDY THIS AND YOU'LL PASS!! (excluding anatomy)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
how do you reduce beam hardening
1. Increase dose
2. Reduce collimation--Reduce slice thickness
3. Increase window width
At what level does the abdominal aortal bifurcate?
L4
What is the typical scan delay after injection of contrast media for studies of the liver?
30-45 seconds
What window settings provide the best tissue differentiation within the liver?
window width= 140, level= 60
What is the window settings that provide the best bone window for the pelvis?
window width=2000, window level=350
What mAs is typically used in routine CT exams of the abdomen?
200-300 mAs
What is the result of the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta?
The right and left common iliac arteries
What is the anode target angle?
12 degrees
At what level do the common carotids bifurcate into the internal and external carotid arteries?
C3-C4
The floor of the orbit is formed by the __________ bones.
maxillary and zygomatic
The lateral wall of the orbit is formed by the ___________ bones.
zygomatic and sphenoid
The medial wall of the orbit is formed by the _________ bones.
ethmoid and lacrimal bones
how do you calculate effective mAs?
mAs/pitch

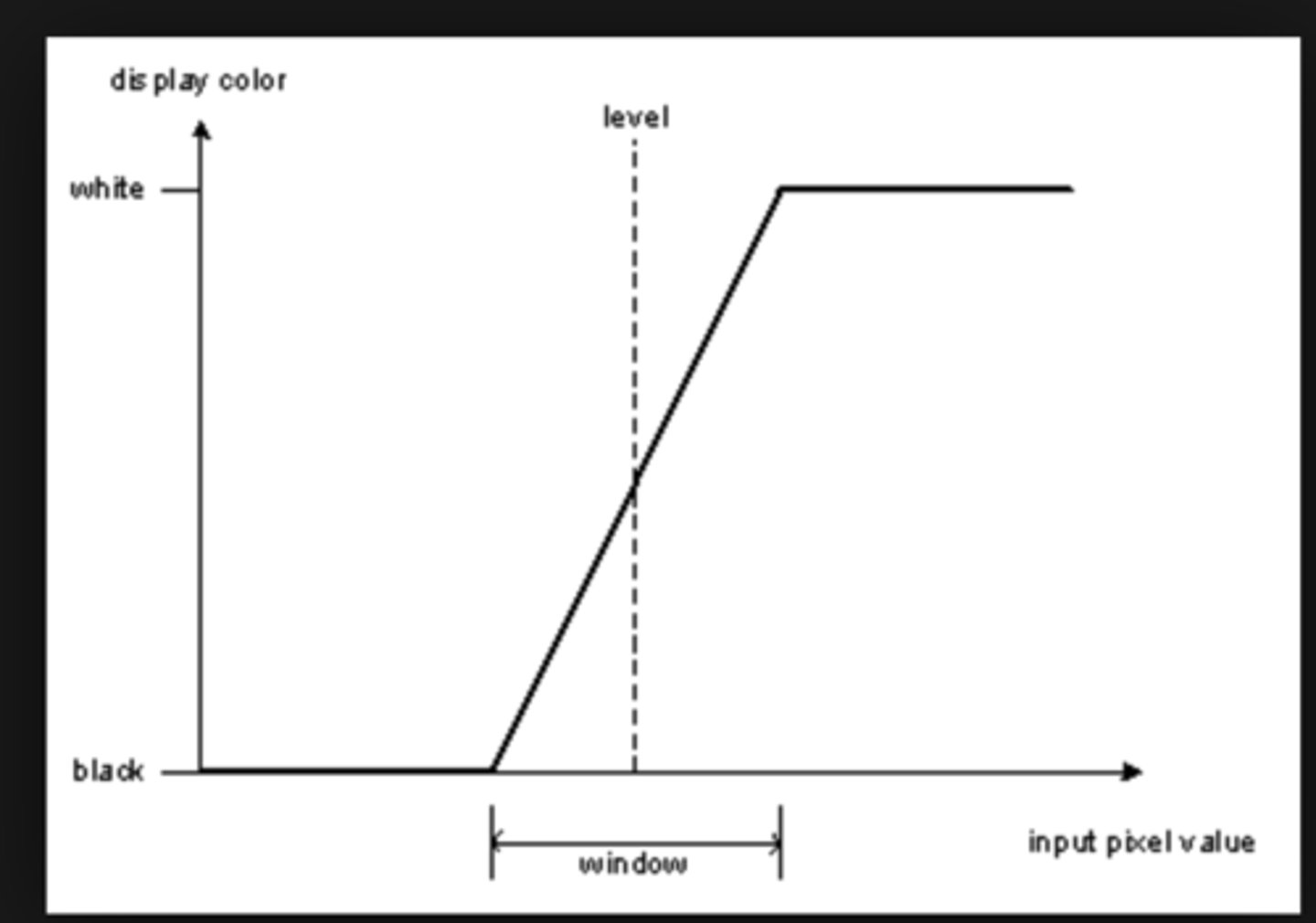
define window level and window width
LEVEL: a chosen midpoint in the grayscale
WIDTH: number of grayscale values above and below the level.
- The width is DIVIDED in HALF and distributed above and below the level.
- Anything above the window is white
- Anything below the window is black
The wider the window the more grayscale values, the lower the contrast!
example:
Level 100, Width 300
White = >+250
Black = <-50
Level 100, Width 200
White = >+200
Black = <0
Level 100, Width 150
White = >+175
Black = <25
factors that affect spatial and contrast resolution
Spatial resolution:
1) focal spot
2) detector width (aperture)
3) reconstruction algorithm - bone>soft tissue
4) slice thickness - thinner is better
5) pixel/FOV/matrix
6) pitch - decreased pitch means no gaps
7) nyquist limitations
Contrast resolution: CNR
1) energy of X-rays - kVp - ↑ kVp ↓ contrast
2) number of X-rays - mA - ↑ mA ↓ mottle
3) slice thickness - thicker is better
4) reconstruction method - iterative > filtered
5) reconstruction algorthith - soft tissue>bone

Give window levels for brain, lung, abdomen, bone
Brain: W80,L+40
Lung: W1500, L-400
Abdomen: W400, L+50
Bone: W1600, L+500
What is beam hardening?
what are the two types of beam hardening artifact?
how do you compensate for it?
1) as the X-ray beam passes through an object, lower energy photons are removed (like filtration!) leaving a "harder beam" of high energy photons. This causes two artifacts:
2) Cupping: the center of a round object is darker than the periphery due to hardening of the beam 360 degrees around the object. happens in the head
3) Streak: these are dark bands that occur in between two dense objects - nearly all the photons are removed in a line between the two objects
4) fixes:
A) Filtration: pre-hardening the beam to remove low energy photons
B) Calibration: using a phantom to set a compensated mA/kVp
C) Correct software: iterative reconstruction may help
D) Avoidance: tilting the gantry of positioning the patient to avoid areas that may cause hardening.
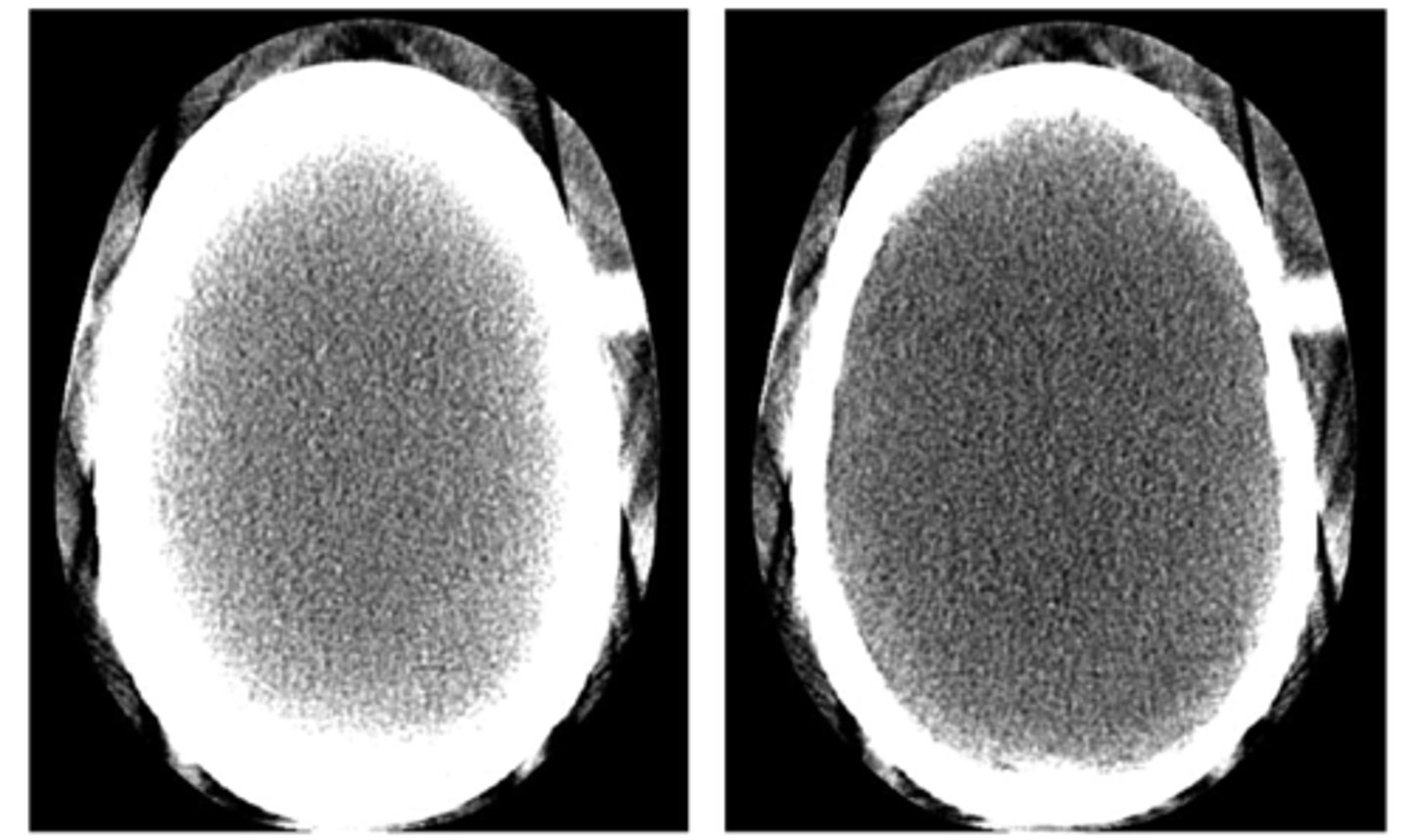
ring artifact
Calibration error or defective detector cause consistently erroneous reading at each angular position, resulting in a circular artifact
is the focal spot large or small?
large 0.6-1.2 - so as not to overheat the anode from such a high mA
Which of the following will result in an increased voxel size: B increased slice thickness
A)decreased reconstruction FOV B) increased slice thickness C) increased matrix D) none of these
If a tissue with a CT number of +300 appears white on the image, which of the following are the window width and window level selected: A)window level =0, window width =500 B)window level= +300, window width= 500 C)window level =+100, window width =1000 D)none of these
A) window level =0, window width =500
What is the volume of a voxel if a slice thickness of 3 mm, a 512x512 matrix & a reconstruction field of view of 25.6cm are used A) 0.75mm³ B)1.5mm³ C) 6.0mm³ D)none of these
A. Solve this by finding the pixel size first FOV/matrix size ... that is 0.5 ... now square that 0.25 .... multiply that by slice thickness and you get 0.75
Which of the following parameters is responsible for partial volume averaging: A) matrix size B) kVp C)slice thickness D) patient dose
C
Voxel equation
pixel area x section thickness
What is interpolation?
Mathematical method for taking SPIRAL data and viewing it as AXIAL images
Bone windows
2000-4000 WW
200-400 WL
Lung windows
1400-1600 WW
(-)400-600 WL
Modular Transfer Function?
graphical representation of SPATIAL RESOLUTION measured in lp/cm, tells how small you can scan without blurring
Decrease partial volume averaging?
Reduce slice thickness
Which portion of the pancreas is the most common site for tumors?; and where located?
The head of the pancreas. It is located approximately at T12
LUNG WINDOW
(-) IS AIR
2000 WW and -200 WL =
The Hounsfield unit that is -1000 most likely represents which of the following?
Air
Relative to CT topography, slice thickness is best represented by which of the following axes?
Z axis
What unit is the basis for exposure based on ionization in air?
mR or C/kg
What radiation unit considers the biological effectiveness of radiation exposure?
mrem or mSv
"Fan" beam technology first historically came on the scene with which acquisition geometries?
Second
"Rotate-rotate" applies to which of the following geometries?
Third
In CT what imaging plane is the pituitary best visualized?
coronal
The third ventricle of the brain communicates with the fourth ventricle through the
Cerebral aqueduct
refers to an excessive Amount of nitrogenous materials in the blood and is a symptom of renal failure.
Azotemia
Which paranasal sinus is usually the last to fully develop?
Frontal
What is the average annual radiation dose?
2 rem
10 rem converted to Sieverts is what?
0.1 Sv
convert 10 mSv to Sv
0.01 sV
annual limit for adult occupational effective dose?
0.05 Sv
annual limit of occupational lens dose
0.15 Sv
annual limit of shallow dose equivalent to skin/extremities
0.5 Sv
occupational exposure to embryo/fetus during pregnancy
0.5 mSv
total effective dose equivalent to public
--also average background radiation
1 mSv
Mild reactions to iodinated intravenous contrast media include
nausea, vomiting, mild urticaria, and a warm flushed sensation
Moderate reactions?
Dyspnea, Hives (urticarial); wheezing (mild bronchospasm); change in pulse; facial edema; vasovagal response; hypo- or hypertension
Severe reactions?
Severe bronchospasm; anaphylaxis; Drowsiness; headache; fever/chills, Shock, pulmonary edema
Osmolality
Concentration of a solution in terms of number of dissolved particles per unit of water
Non-ionic intravenous contrast media such as Omnipaque should have an average osmolality of
750 mOsm/kg water
What drugs are administered for moderate reaction to injection of iodinated contrast medium
Antihistamines
Epinephrine
Prothrombin measures the amount of time necessary for a person's blood to coagulate
normal limits: between 10 and 14 seconds
why use an autoclave?
The use of an autoclave for sterilization involves heat and steam under pressure to eliminate microbes.
1 rem= 1 rad
When measuring the radiation dose from x-rays, rads and rems are equivalent. The units of Sv and rem are used to measure any kind of ionizing radiation where 1 Sv =100rem. The units of rad and Gy are used to measure specifically x-ray radiation where 1 Gy = 100 rads.
When performing a multi-slice CT study, the slice thickness may be ___________ to cover the region of interest, in order to minimize the dose to the patient.
Due to radiation penumbra, a multiple slice study results in a greater patient dose than the same number of individual slices. By covering a specific region of interest with fewer slices (increase in slice thickness) the resulting radiation overlap from adjacent slices is reduced, reducing the dose to the patient.
A given CT exam yields a CTDI of 4.5 rads, with a slice thickness of 10mm, and a 2mm gap between slices, the MSAD for this exam is ________ rads.
The MSAD is equal to the CTDI X the ratio of the slice thickness to the table increment. With a 2mm gap and a 10mm slice the table increment will be 12mm. The MSAD = (4.5 rads) X (10mm/12mm)
--3.75 rads
Calulate the DFOV for an image with a 320 2 matrix and a pixel dimention of .75 x .75 mm.
A)36cm B)12cm C)24cm D)48cm
Answer: C
*The formula for DFOV is pixel dimension x the matrix size. 320 x .75 mm = 240mm or 24 cm DFOV
The units rad and rem are equivalent when measuring radiation dose used in CT x-ray radiation.
True or False
Answer: True
*When measuring the radiation dose only from x-rays, rads and rems are equivalent. The units Sv and rem measure any kind of ionizeing radiation (1 Sv = 100 rem). The units rad and Gy measure specifically x-ray radiation
(1 Gy = 100 rads
Non-ionic contrast media include
iopamidol (Isovue), Iohexol (Omnipaque), and iopromide (Ultravist)
What is the normal pulse rate for an adult?
70-100 bpm
What is the average normal adult respirations per minute?
12-20
Which of the following iodinated contrast media may NOT be used for an intrathecal injection?
Iohexol(Omnipaque), metrizamide(Amipaque) and iopamidol(Isovue) are all non-ionic contrast agents that may be used for intrathecal injection. Meglumine is not considered safe for an intrathecal injection.
A patient arrives with a central venous line in place. Which type of central venous line may be used for a CT examination requiring the administration of iodinated contrast media with an automatic injector?
none.. indwelling catheters or central venous lines cannot withstand the pressure produced by an automatic injector
The total quantity of radiation dose received by the patient from a CT scan series is termed
MSAD(multiple-scan average dose) quantifies the amount of exposure to a patient from a series of CT scans. MSAD is calculated using a series of equations based on the CTDI(CT dose index). The radiation quantity per scan is measured using an ionization chamber.
Average pulse rate for an infant is
100-180 bpm
General signs of shock include:
rapid breathing, tachycardia, hypotension, weak pulse, pallor, cyanosis, and cold, clammy skin.
What is the average range for activated partial thromboplastin time?
28-34 seconds
The average radiation dose to the pituitary gland during a CT head is
2 rads
A CT exam is done with a slice thickness of 10mm, and a 2mm gap is between the slices, the pitch is 1:2 and the total scan time is 5 seconds. What is the table increment for this exam?
*The table increment is determined by adding the slice thickness with the gap between the slices. 10mm + 2mm = 12mm table increment. The other information given is just that other information to distract you.
What is medical asepsis?
The reduction in number of infectious agents but not the complete elimination of all organisms.
Complete cardiac diastole correspond to which portion of the cardiac cycle on a electrocardiogram (ECG)?
T-wave
Gas accumulating within a degenerating intervertebral disk is termed
vacuum effect
Following the intravenous administration of iodinated contrast media, a hepatic hemangioma may become _________ and may no longer appear on the CT image.
isodense -- The diagnosis of hemangioma is confirmed on CT by evaluation of its pattern of enhancement. Hemangiomas enhance from the periphery inward, until they become isodense with the surrounding hepatic tissue. Once isodense, the hemangioma attenuates the beam in the same way as the hepatic tissue. The CT numbers of the hemangioma and hepatic tissue become equal and the structures may become impossible to differentiate.
During CT examination of the larynx, the patient is often instructed to phonate the letter "E" in order to properly evaluate the
vocal chords
The exaggeration of displayed calcification within the coronary arteries during a cardiac MDCT study is referred to as
Blooming- refers to the potential overestimation of vessel calcification due to partial volume artifact
What describes a condition in which cerebral ischemia is caused by systematic hypertension?
Vasovagal reaction
Patients whose posterior descending artery branches from the right coronary artery, and whose left posterior ventricular braches arise from the left circumflex artery are said to be
codominant - 7% of the population is said to be codominant... which means the PDA is supplied by the RCA.. and the left posterior ventricular braches arise from the LCX
Which of the following window settings would optimally display CT colonography images?
level= -400 width= 1600
CT colonography images are best displayed in wide "lung-type" window setting
A CT scanner with a limiting resolution of 15 lp/cm can resolve an object as small as..
0.3 mm
The minimum object size that a CT scanner can resolve may be calculated by taking the reciprocal value of the scanner's limiting resolution. The reciprocal of 15 lp/cm is 1/15 lp/cm. This is equivalent to 10/15 lp/mm, which equals 0.6 mm/lp. Because a line pair is equivalent to a line and the space adjacent to it, this value may be divided in half to provide the minimum object that this scanner can resolve..0.3
The total length of a CT scan may be calculated by multiplying the scan time by the aperture size
An example: If the scan time is 15 seconds and the aperture size(slice thickness) is 1.0cm(10mm) the length of the scan will be 150mm.
An abnormal density of the liver is found to be a fatty infiltrate. The CT number for this area would most likely be in the range of ..
-100 Hounsfield units
What is the HU of a pulmonary nodule?
+200 hu
The radiologist has requested a CT examination to identify the thymus gland in a young pre-puberty patient. The thymus gland is located
anteriosuperior portion of the mediastinum
To best image a possible Schwannoma found within the Schwann cells of the eighth cranial nerves, CT examinations should include which of the following
internal auditory canal
CT examination of the liver for hepatic tumor evaluation should NOT be performed during which of the following phases of contrast enhancement?
Equilibrium phase
The correct orientation for viewing CT images on the monitor is which of the following?
Cross sectional anatomy is viewed from the perspective of looking up from the patient's feet to the head and the image oriented with the left side of the patient on the right side of the viewer.
Some CT scanners allow the CT technologist to outline an anatomic area on a series of cross-sectional images and then define the outlined area on the localizer(scout) image. This is called
correlation
A bolus injection of iodinated contrast media is administered to a patient scheduled for a CT examination of the liver, a delay of ________ should be applied
45 second delay will allow the portal vein to become completely opacified
An acoustic neuroma would be found in which of the following cranial nerves?
eighth cranial nerve
When performing a dynamic CT study of the chest the interscan delay used would be
4 seconds (shortest possible)
CT images acquired in a plane which divides the body into dorsal and ventral sections are considered ____________ images
coronal
A CT examination of the liver shows an abnormal finding of reduced density, which of the following is most likely the cause?
A fatty infiltrate - they greatly reduce the density of the liver
To best demonstrate a tumor of the liver the CT scan should be performed during which of the following phases of contrast enhancement?
Non-equilibrium phase-- Bolus phase, dynamic phase and equilibrium phase will not provide the best contrast enhancement needed for liver tumor evaluation.
A contrast enhanced CT examination of the chest is completed, when viewing the image it appears small, making evaluation of the anatomy difficult. To improve image quality which of the following technical changes may be made?
Decreased DOV---The image was obviously reconstructed in a display field of view larger than necessary. The image appears small because of this error. The DFOV chosen for an image should be slightly larger than the diameter of the area of interest.
_____________ a specialized technique which uses narrow section widths and a low-resolution algorithm for image reconstruction.
High resolution CT
What is used to combat brachycardia during a vagal reaction to contrast?
Atrophine