BIO 251 Exam 1
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
211 Terms
Microbiology
The study of microorganisms
Microbes are
ubiquitous (everywhere)
Bacteria
single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus; prokaryotes
Archaea
Domain of unicellular prokaryotes that have cell walls that do not contain peptidoglycan
Protozoa
one-celled organisms that are more complex than bacteria
Fungi
A kingdom made up of nongreen, eukaryotic organisms that have no means of movement, reproduce by using spores, and get food by breaking down substances in their surroundings and absorbing the nutrients
Helminths
parasitic worms
Viruses
tiny particles, smaller than bacteria and other pathogens, which must invade living cells in order to reproduce; when they invade, the cells are damaged or destroyed in the process releasing new particles to infect other cells
Algae are
autotrophic protists
Eukaryotic
A cell characterized by the presence of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can be unicellular (protists) or multicellular (fungi, plants and animals).
Prokaryotic
An organism whose cells do not have an enclosed nucleus, such as bacteria.
Theory of Evolution
states that organisms change and develop over time to adapt an increase rate of survival
Photosynthesis
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars
Biotechnology
The manipulation of living organisms or their components to produce useful products.
genetic engineering
The direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes.
Recombinant DNA
DNA produced by combining DNA from different sources
Bioremediation
The use of living organisms to detoxify and restore polluted and degraded ecosystems
Pathogens
disease causing agents, such as bacteria and viruses
infectious disease
A disease that is caused by a pathogen and that can be spread from one individual to another.
Cellular Organization
All living things are composed of one or more cells
Organelles are
like tiny organs within cells.
spontaneous regeneration
The mistaken idea that living things can arise from non living sources
Abiogenesis
spontaneous generation
Biogenesis
the production of living organisms from other living organisms
Leeuwenhoek
1670's ; father of modern microbiology; first to observe living cells
sterile
no living microbes
aseptic technique
method used to make the environment, the worker, and the patient as germ-free as possible
Germ Theory of Disease (Koch's Postulates)
1) the suspected pathogen should be present in all cases of the disease animals and absent from the healthy animals.
2) the suspected pathogen should be grown in pure culture
3) cells from a pure culture of the pathogen should cause disease in healthy animal
4) the pathogen should then be reisolated and shown to be the same as the original
Macromolecules are
polymers built from monomers
Monomer
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
Carbohydrates
Broken down to glucose to provide energy.
Monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
Disaccharide
A double sugar molecule made of two monosaccharides bonded together through dehydration synthesis. (maltose)
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides (lactose, sucrose)
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Triglycerides
an energy-rich compound made up of a single molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. (fats, oils)
Phospholipids
a lipid consisting of a glycerol bound to two fatty acids and a phosphate group. (membrane components)
Waxes
A type of lipid molecule consisting of one fatty acid linked to an alcohol; functions as a waterproof coating on many biological surfaces such as apples and other fruits.
Steroids (cholesterol)
Minor component of all animal cell membranes; precursor of bile salts, vitamin D, and steroid hormones.
Proteins
Chains of amino acids
Amino acids
a simple organic compound containing both a carboxyl (—COOH) and an amino (—NH2) group.
nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
RNA
A single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along genetic messages
Pentoses
5 carbon sugars
Hexoses
6 carbon sugars
Glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues. When its level is low, we feel hunger.
Fructose
a hexose sugar found especially in honey and fruit.
Maltose
glucose + glucose
Lactose
glucose + galactose
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms
Agar
a gel-like polysaccharide compound used for culturing microbes; extracted from certain red algae
peptide bond
The chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
nitrogen base, pentose sugar, phosphate group
3 parts of a nucleotide
Purines
Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidines
Cytosine and Thymine
Chitin
A chemical that provides both toughness and flexibility
peptidoglycan
A protein-carbohydrate compound that makes the cell walls of bacteria rigid
Lipopolysaccharide
LPS is a phospholipid layer with sugars. Many of these sugars act as antigens and allow us to differentiate strains of bacteria. Plays an important role in endotoxic shock.
Glycocalyx
The external surface of a plasma membrane that is important for cell-to-cell communication
Glycerol
A three-carbon alcohol to which fatty acids are covalently bonded to make fats and oils.
primary protein structure
sequence of amino acids
secondary protein structure
occurs when the sequence of amino acids are linked by hydrogen bonds
tertiary protein structure
3D folding pattern of a protein due to side chain interactions
Cysteine
An amino acid with a sulfur atom that joins together two peptide strands
quartenary protein structure
protein consisting of more than one amino acid chain
Antibodies
Specialized proteins that aid in destroying infectious agents
double helix
The form of native DNA, referring to its two adjacent polynucleotide strands wound into a spiral shape.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
compound used by cells to store and release energy
guanosine triphosphate (GTP)
an energy transfer molecule similar to ATP that releases free energy with the hydrolysis of its terminal phosphate group
Taxonomy
The scientific study of how living things are classified
nomenclature
naming system
binomial system of nomenclature
System of naming a species by the combination of the genus name and a specific epithet.
domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
taxonomic categories from top to bottom
beneficial relationships
many relationships between microorganisms and humans
Viruses are not
cells
Woese-Fox System of Taxonomy
place all organisms into three domains: eukarya, bacteria, and archaea
Bacteria Anatomy
Rods
Round
Spirals
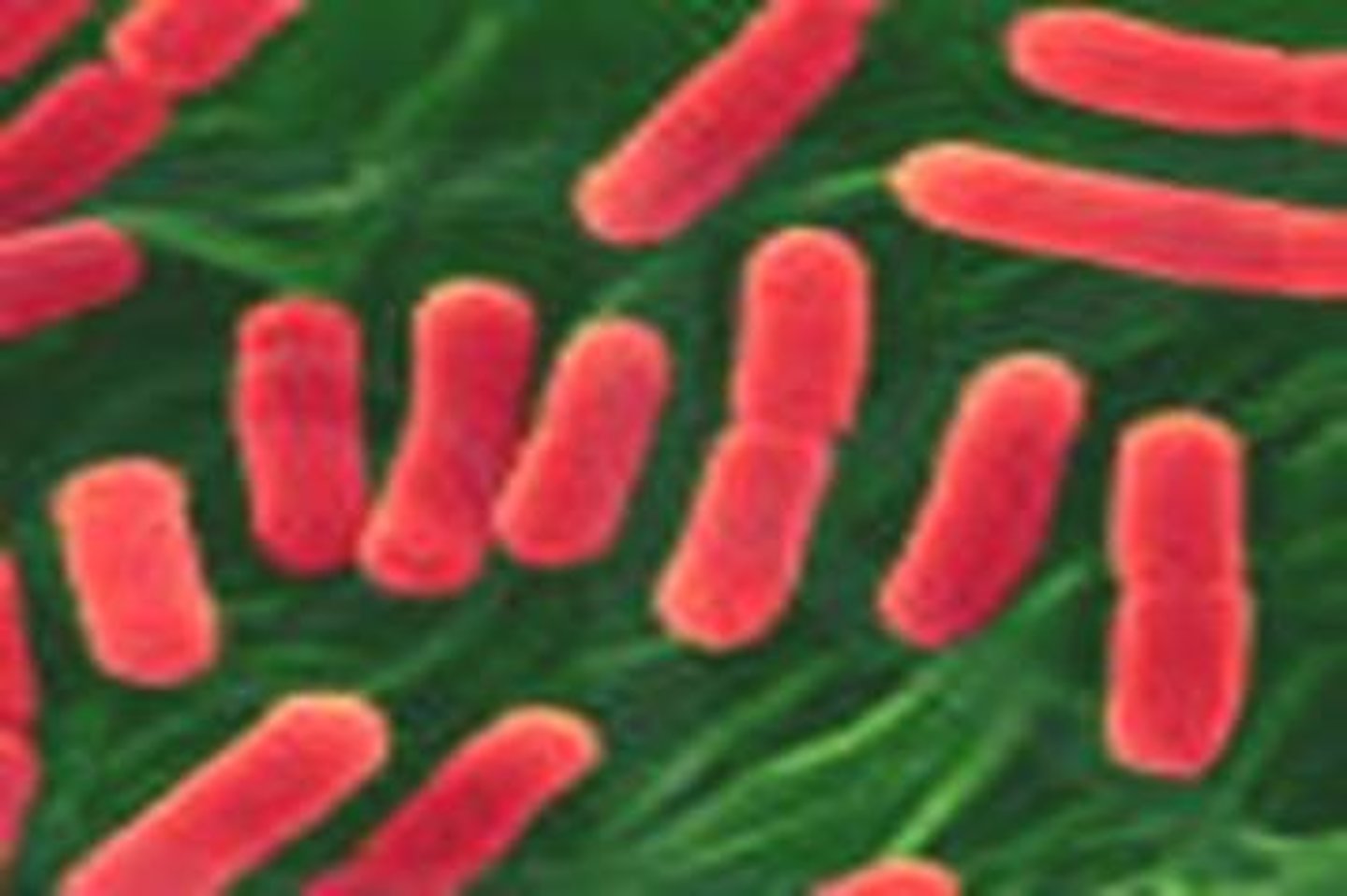
Rods (bacilli)
bacteria with a rod shaped morphology
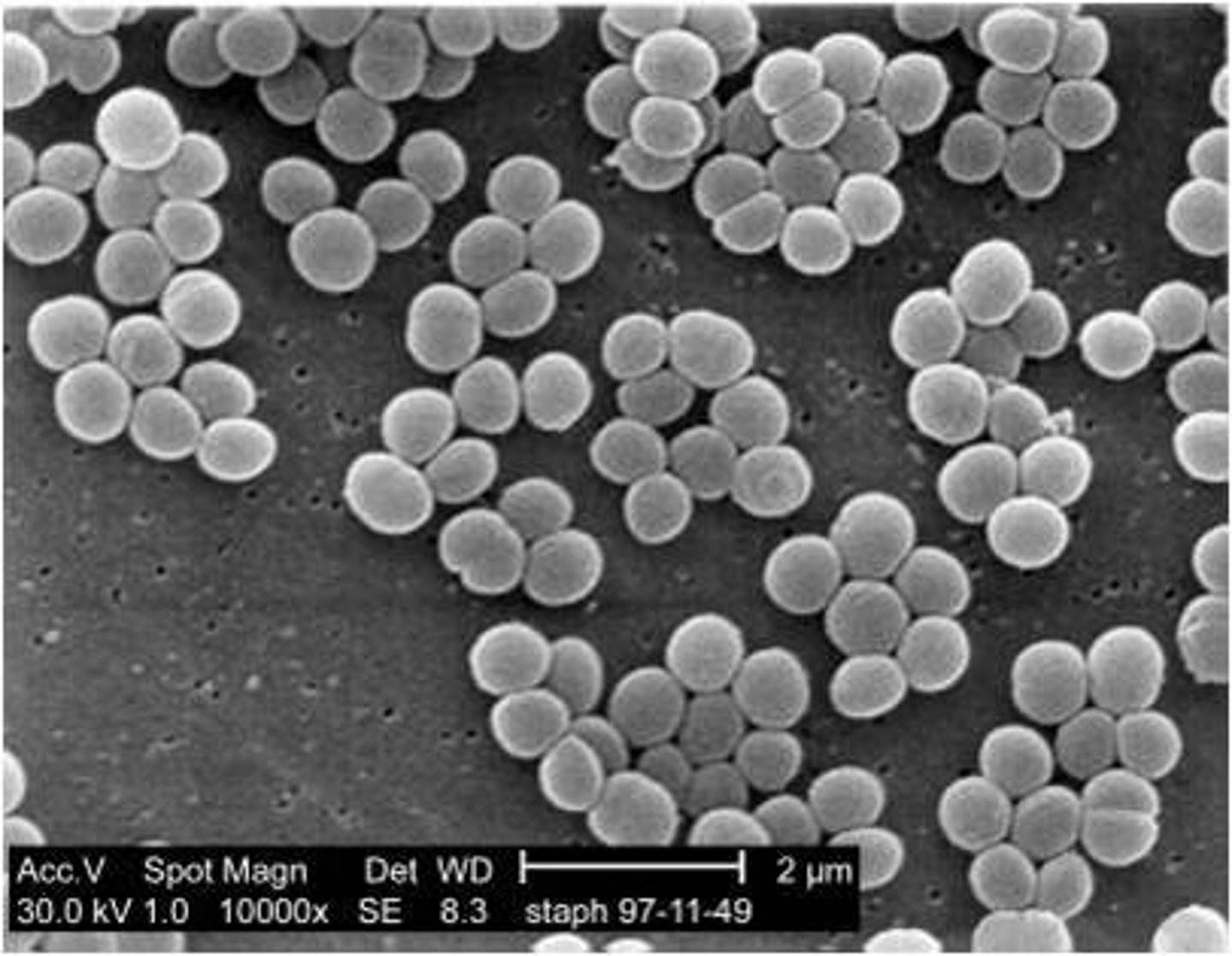
round bacteria
cocci
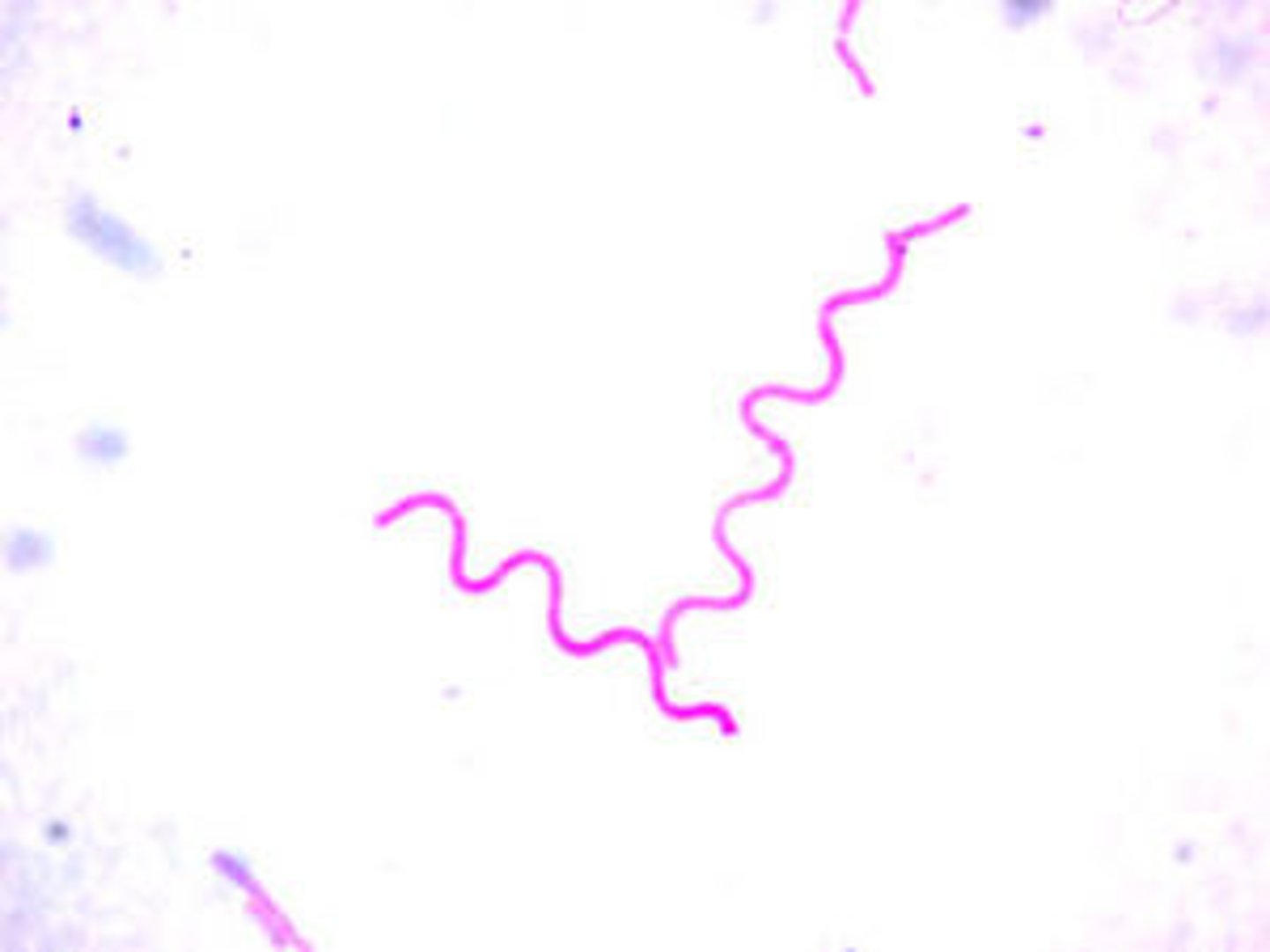
spiral bacteria
spirilla
cell (cytoplasmic) membrane
a thin sheet of lipid and protein that surrounds the cytoplasm and controls the flow of materials into and out of the cell pool
Bacterial chromosome or nucleoid
composed of condensed DNA molecules. DNA directs all genetics and heredity of the cell and codes for all proteins
ribosomes in bacteria
70s ribosomes are different from eukaryotic ribosomes 80s - attack site for some antibiotics such as tetracycline and gentamicin
Cytoplasm of bacteria
contains a single chromosome
Nanotubes
intercellular connections that pass material from one cell to the next
Endospore
A thick-walled protective spore that forms inside a bacterial cell and resists harsh conditions.
intracellular membranes
compartmentalize functions within the cell
S layer protein
used for protection
Fimbriae
attachment structures on the surface of some prokaryotes
outer membrane of bacteria
contain phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides
the cell wall of bacteria is made up of
peptidoglycan
Cytoskeleton (bacteria)
Some bacteria produce long polymers of protein similar to eukaryotic actin:
-arranged in helical shape
-contribute to cell shape
-have also been identified in archaea
-unique to non-eukaryotic cells-may be a potential target for antibiotic development
Pilus (bacteria)
used to draw another bacteria in close to transfer DNA to it
inclusion/granule
stored nutrients such as fat, phosphate, or glycogen deposited in dense crystals or particles that can be tapped into when needed
bacterial microcompartments
protein coated packets used to localize enzymes and other proteins in the cytoplasm
Plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome
Flagellum (bacteria)
rotating filament present in some bacteria that pushes the cell forward
Pleomorphism
variations in size and shape among cells of a single species