Week 1
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is the main solvent in cells?
H2O (water)
What are common solutes found in cells?
Glucose, amino acids, ions (sodium ions, potassium ions), chloride, calcium.
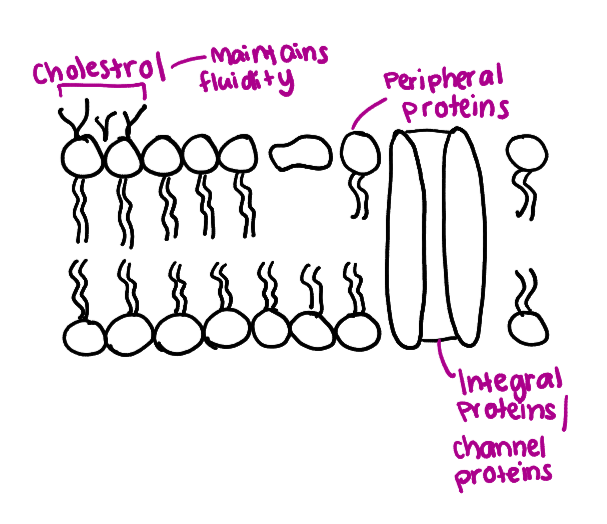
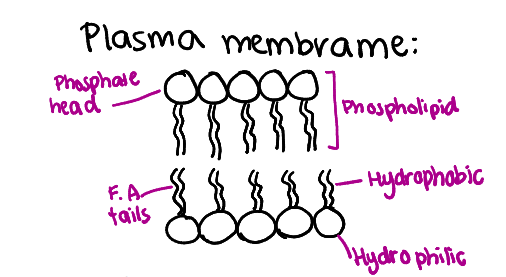
What is the structure of the plasma membrane?
A phospholipid bilayer consisting of hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
What does it mean for a membrane to be selectively permeable?
It controls what substances can enter or exit the cell.
What type of molecules can easily pass through the phospholipid bilayer?
Non-polar substances and small uncharged molecules.
What is the difference between polar and non-polar molecules?
Polar molecules have an uneven distribution of electrons (creating a dipole), while non-polar molecules have an even distribution.
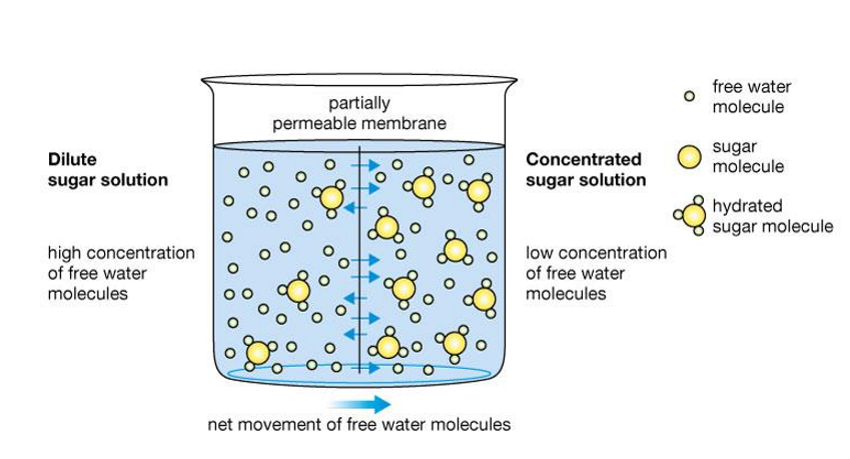
What process does osmosis refer to?
The movement of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
What is a hypotonic solution?
A solution with a lower solute concentration.
What is a hypertonic solution?
A solution with a higher solute concentration.
What is an isotonic solution?
A solution with the same solute concentration as another.
What is simple diffusion?
The passive movement of small, uncharged molecules across the plasma membrane from high to low concentration.
What is facilitated diffusion?
The process of transporting specific ions or molecules across a membrane with the help of transport proteins.
What role do aquaporins play in a cell?
They facilitate the movement of water through the cell membrane.
What happens during equilibrium?
Concentration of solutes is equal on both sides of the membrane.
How do transport proteins impact facilitated diffusion?
They selectively allow specific ions or molecules to pass more quickly than through simple diffusion.
Label/draw basic plasma membrane
Visually explain osmosis
Draw/label more detailed plasma membrane, including transport proteins