CH 20 - Markups and Average Cost Pricing
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What are markups
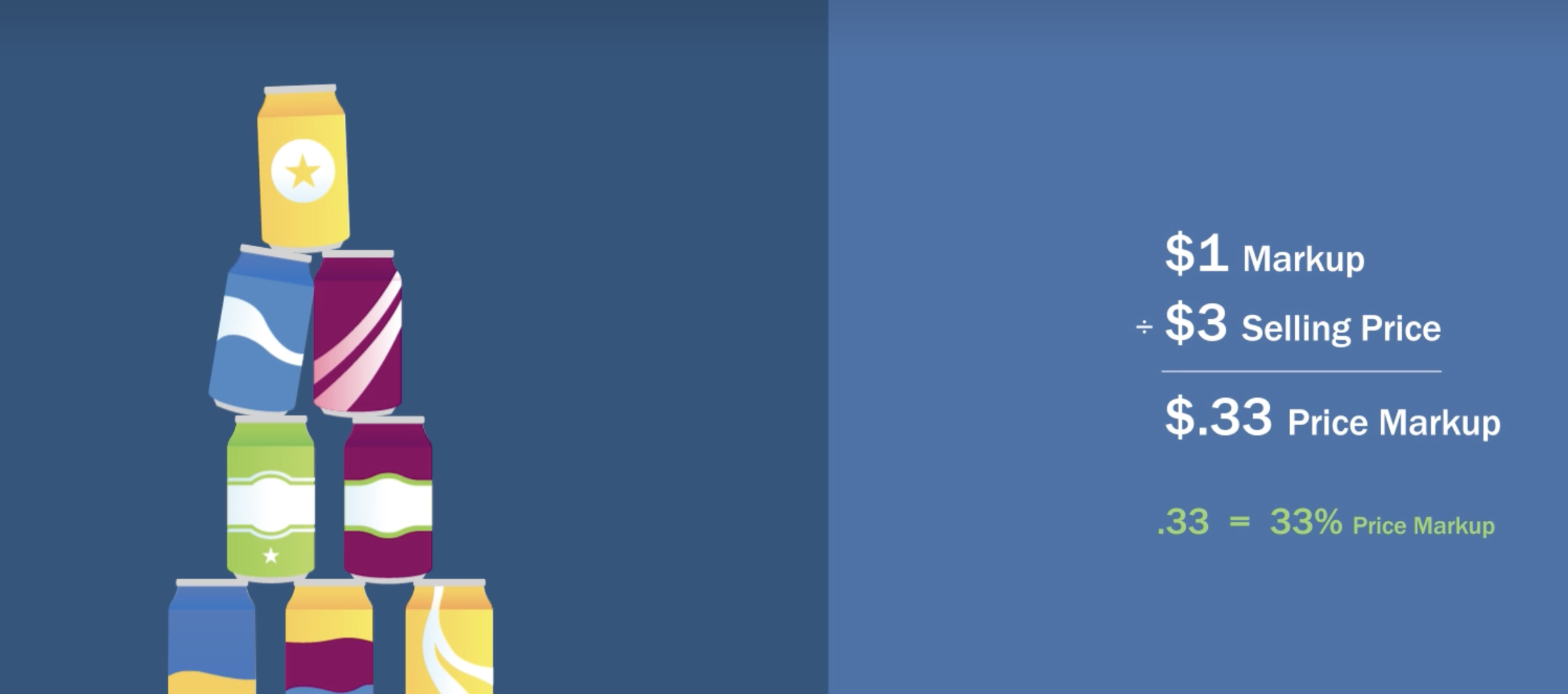
are we marking up the cost or the price. Price is the industry standard because as a percentage it appears to be lower

What is a cost markup

What is the price markup

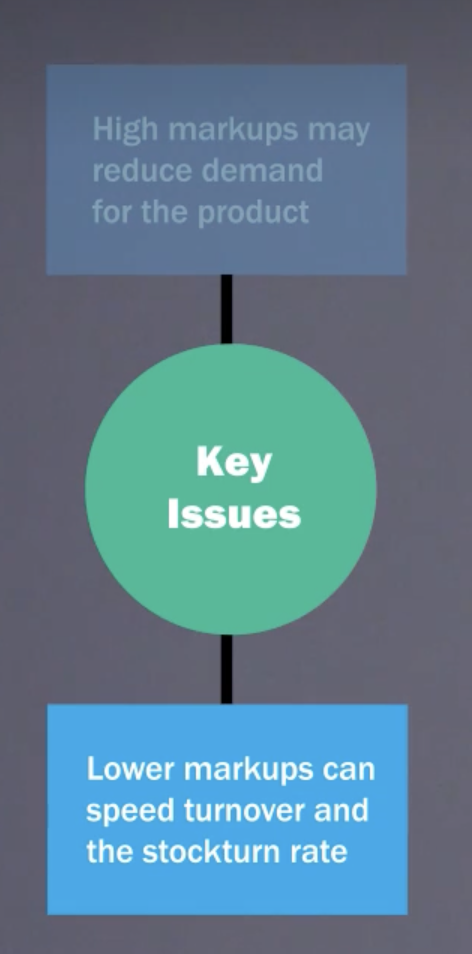
What are the key issues with mark ups
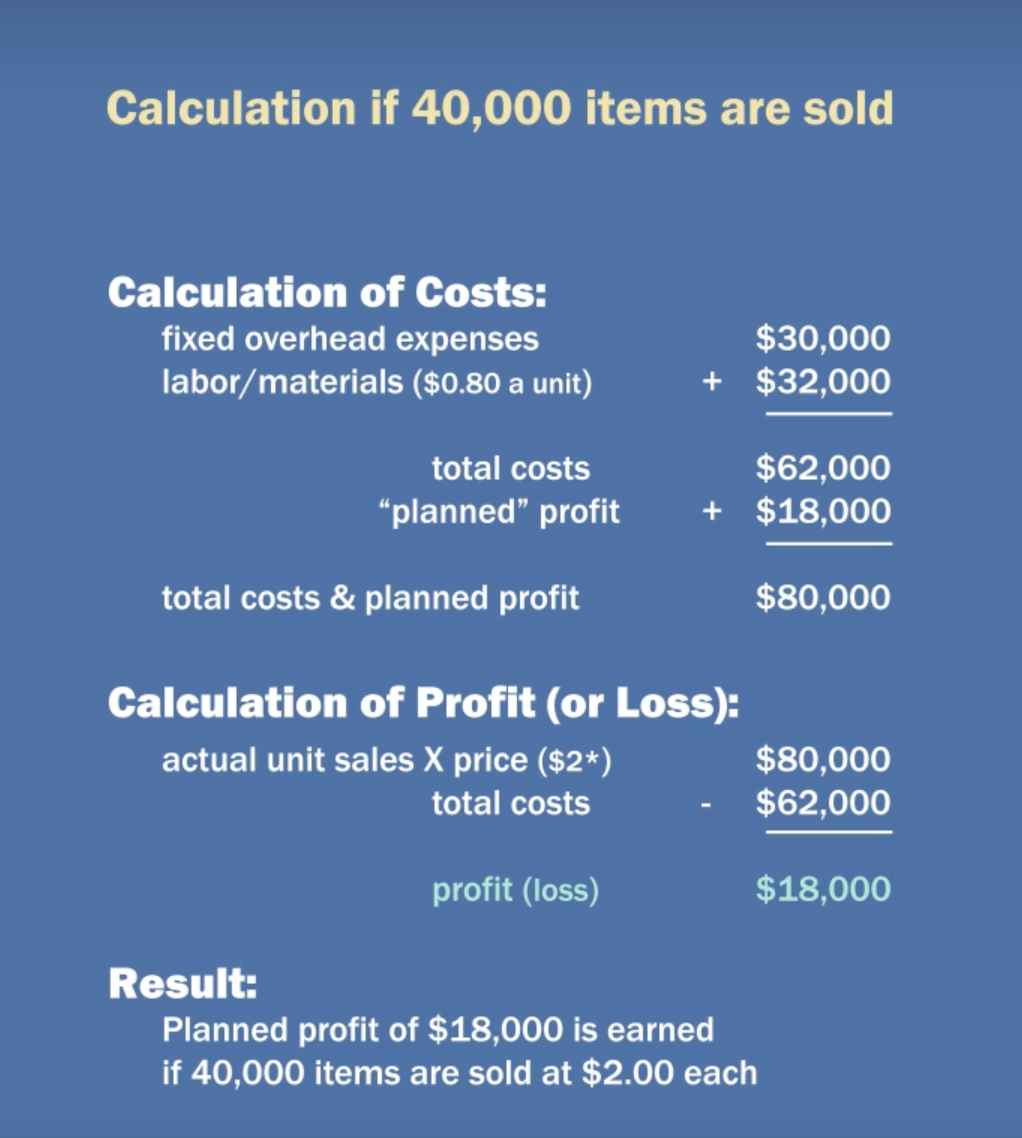
what is avg cost pricing

How to calculate avg cost pricing
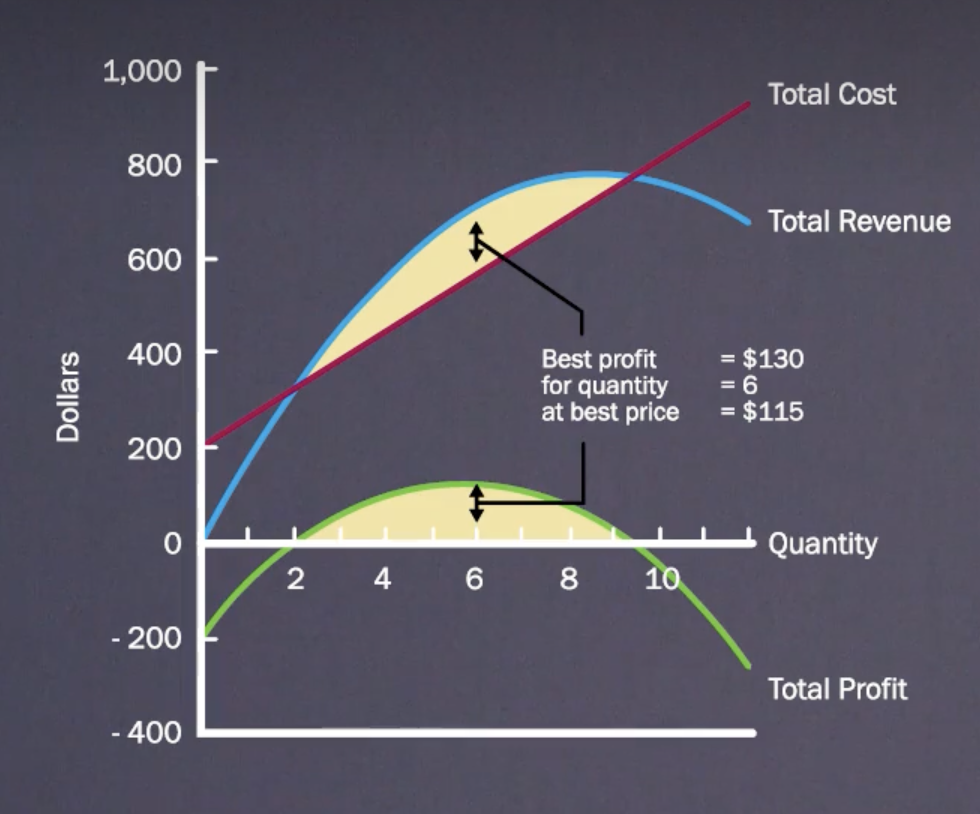
What is the break even formula

how to calculate fixed cost contribution per unit

if we make more we sell more
not true
what is the main idea of marginal analysis

dif between avg cost pricing and marginal
avg cost = the more you sell the more you make
marginal = there is optimum (range)
understanding price sensitivity
are they substitute ways of meeting the need
easy to compare prices
who pays the bill
how great is the total expenditure
what the hell effect
how sig is the end benefit
is there already a sunken investment
what is value in use pricing

auction pricing

what is leader pricing

what is bait pricing

what are reference prices

what is psychological pricing

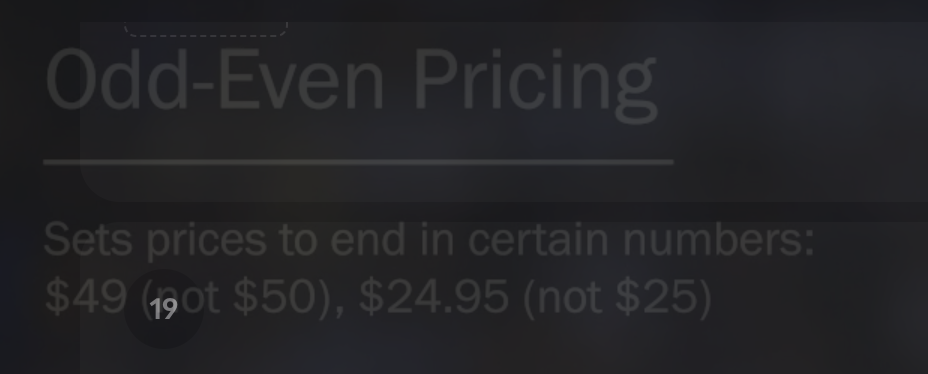
what is odd even pricing
what is price lining

what is demand backwards pricing

what is prestige pricing

what is subscription pricing

what is full line pricing

what is market orientated pricing
differences in price should be reasonably reflect differences in versions

what is firm oriented pricng

what are complimentary product pricing

A markup is the dollar amount added to the cost of products to get the selling price.
true: Markup is a dollar amount added to the cost of products to get the selling price.
By definition, a markup of $1 on a cost of $2 translates to a markup of 40 percent.
false: Unless otherwise stated, markup (percent) means percentage of selling price.
Firms with high markups and low turnover rates may earn lower profits than firms with low markups and high turnover rates.
true: Some retailers try to speed turnover to increase profit, even if this means reducing their markups. The markup combines with the stockturn rate to determine what the product actually earns
Average-cost pricing guarantees that the firm will earn enough to at least cover its costs.
false: Average-cost pricing does not make allowances for cost variations as output changes. So it's easy to lose money with average-cost pricing.
A major problem with average-cost pricing is that it does not allow for cost variations at different levels of output.
true: The basic problem with the average-cost approach is that it doesn't consider cost variations at different levels of output.
Ignoring demand is the major weakness of average-cost pricing.
true: Ignoring demand is the major weakness of average-cost pricing.
Break-even analysis is particularly accurate because it recognizes that the demand curve is downward sloping.
false: The break-even graph, with its straight-line total revenue curve, makes it seem that any quantity can be sold at the assumed price. This usually isn't the case, however.
The price that maximizes profit is the one that results in the greatest difference between total revenue and total cost.
true: The price that maximizes profit is the one that results in the greatest difference between total revenue and total cost.
The greater the total expenditure, the less price sensitive customers are.
false: Customers tend to be more price sensitive when the total expenditure is greater.
Psychological pricing involves setting prices that end in certain numbers, while odd-even pricing is setting prices that have special appeal to target customers.
false:Psychological pricing means setting prices that have special appeal to target customers, while odd-even pricing is setting prices that end in certain numbers.
The price most consumers expect to pay for a product is called the leader price.
false: The price most consumers expect to pay for a product is called the reference price.
One major difference between leader pricing and bait pricing is that bait pricing is criticized as unethical, while leader pricing is not.
false: Extremely aggressive and sometimes dishonest bait-pricing advertising has given it a bad reputation.
Price lining tends to result in faster turnover, fewer markdowns, quicker sales, and simplified buying.
true: Price lining has several advantages. Sales may increase because they can offer a bigger variety in each price class, and it's easier to get customers to make decisions within one price class. Stock planning is simpler because demand is larger at the relatively few prices. Price lining can also reduce costs because inventory needs are lower.
With complementary product pricing, different price levels are set on different products because the products are targeted at different market segments.
false: Complementary product pricing is setting prices on several products as a group, which may lead to one product being priced very low in order to increase profits from another product—thus increasing the product group's total profits.
Product-bundle pricing may encourage customers to spend more and buy products that they would not buy otherwise.
true: Product-bundle pricing is setting one price for a set of products. Firms that use product-bundle pricing usually set the overall price so that it's cheaper for the customer to buy the products at the same time than separately.