Earth Science Chapter 6, Running Water and Ground Water
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
water cycle
the continuous cycle of water from the surface, to evaporation, condensation, precipitation, runoff and infiltration, back to the oceans
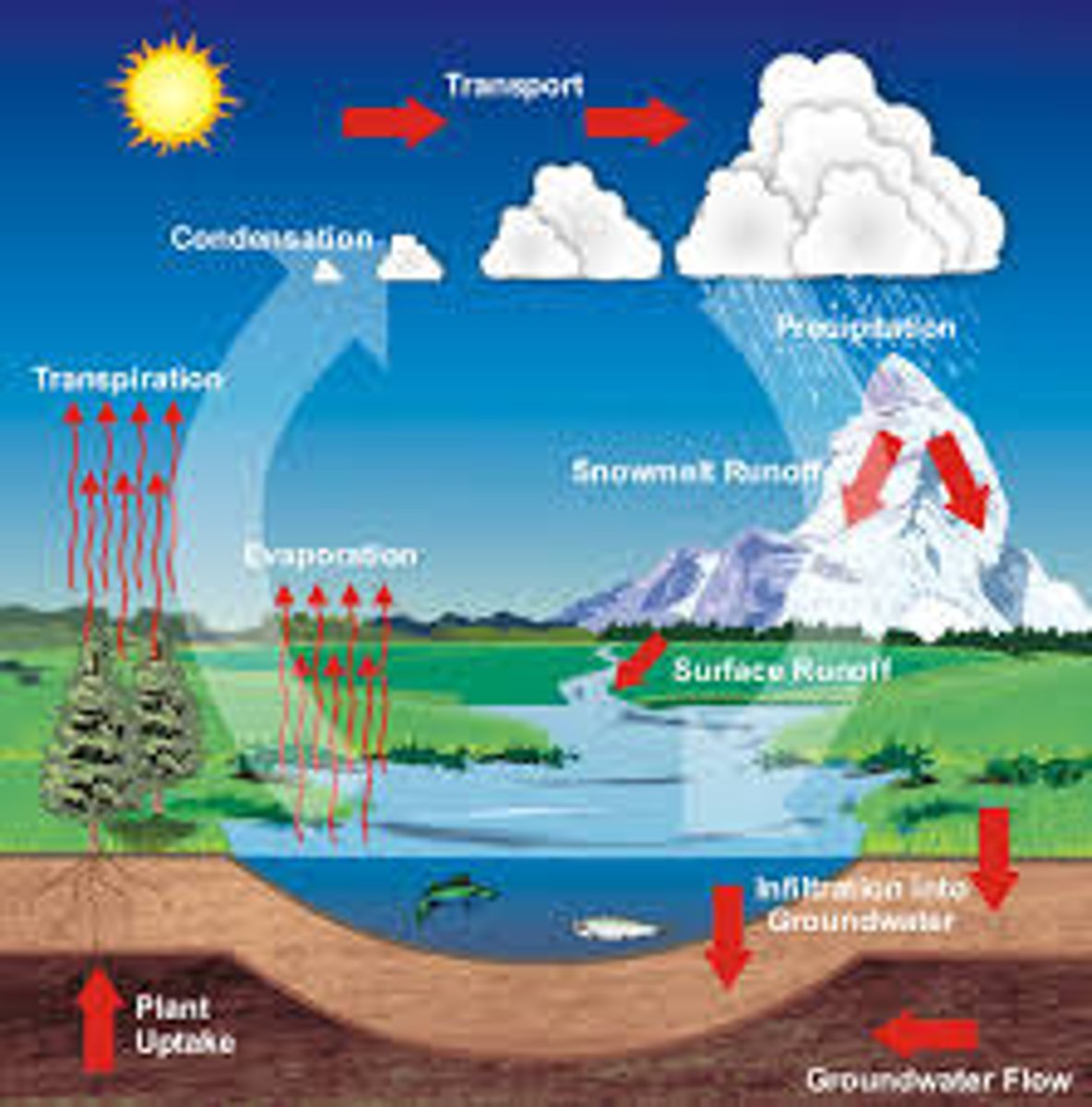
transpiration
evaporation of water from plants

runoff
water that does not infiltrate into the ground, but rather, flows along the surface, flowing into rivers and streams

infiltration
water that is absorbed by soil. Some of this water will become ground water
hydrosphere
all the water on the Earth

oceans
bodies of water containing 97.2% of all the water on Earth

glaciers
non-ocean portion of the hydrosphere, containing 2.15% of all the water on Earth
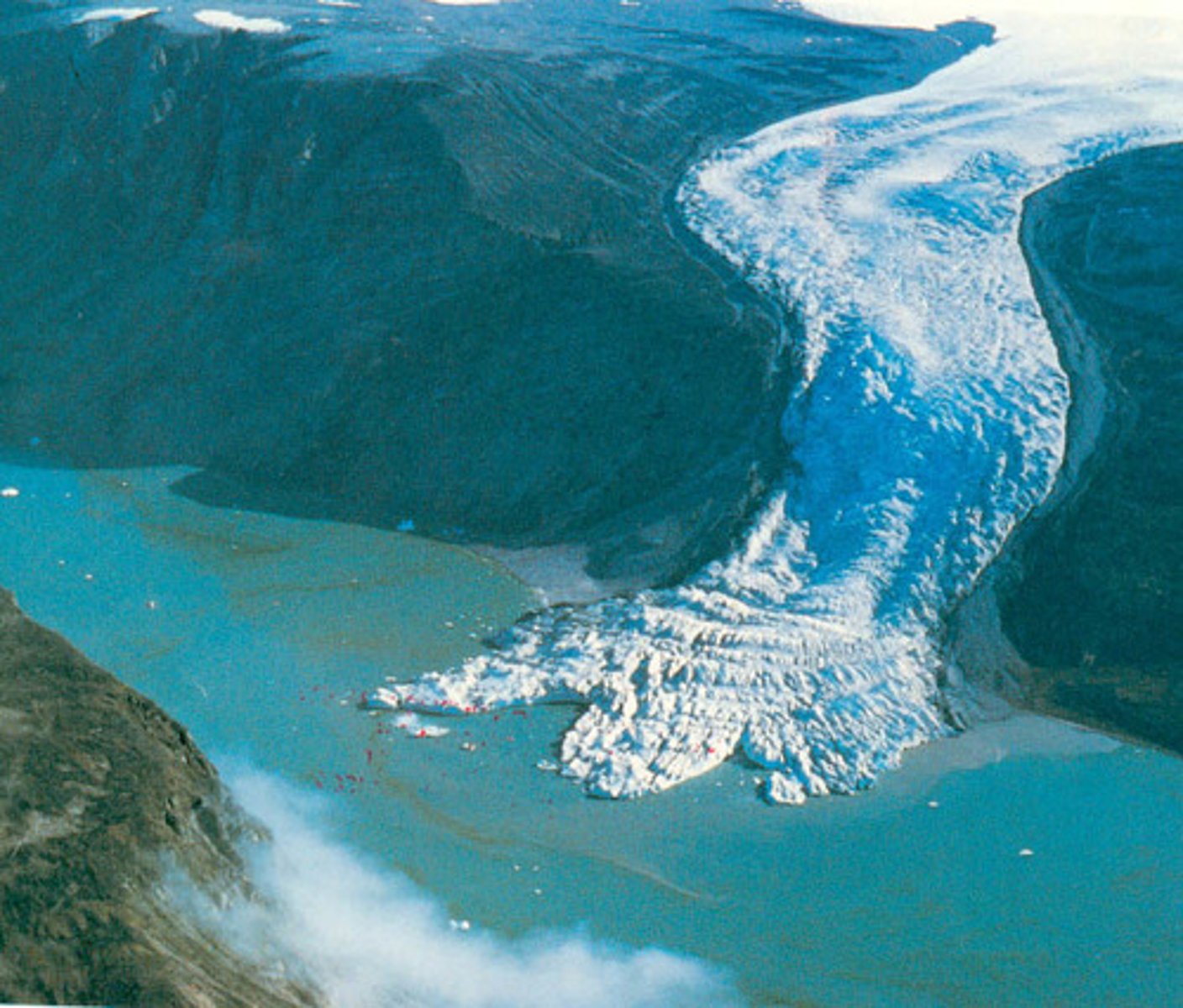

groundwater
water underground, in the zone of saturation. Contains about .62% of all the water on Earth

gradient
the slope or steepness of a stream channel
stream channel
the course that the water in a stream flows

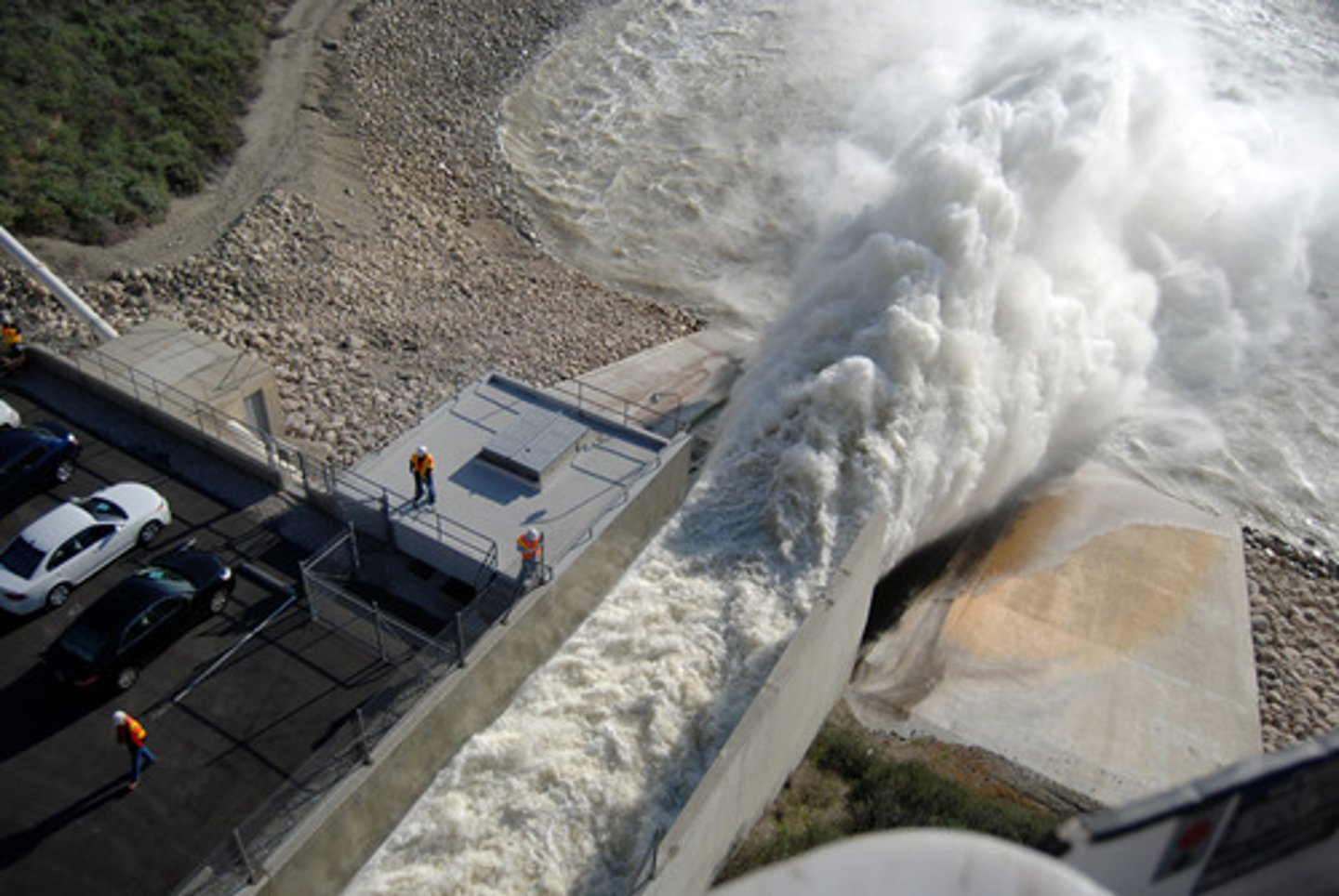
discharge
the volume of water flowing past a certain point in a given amount of time (example: 2,000 liters per minute)

tributary
a stream that empties into another stream
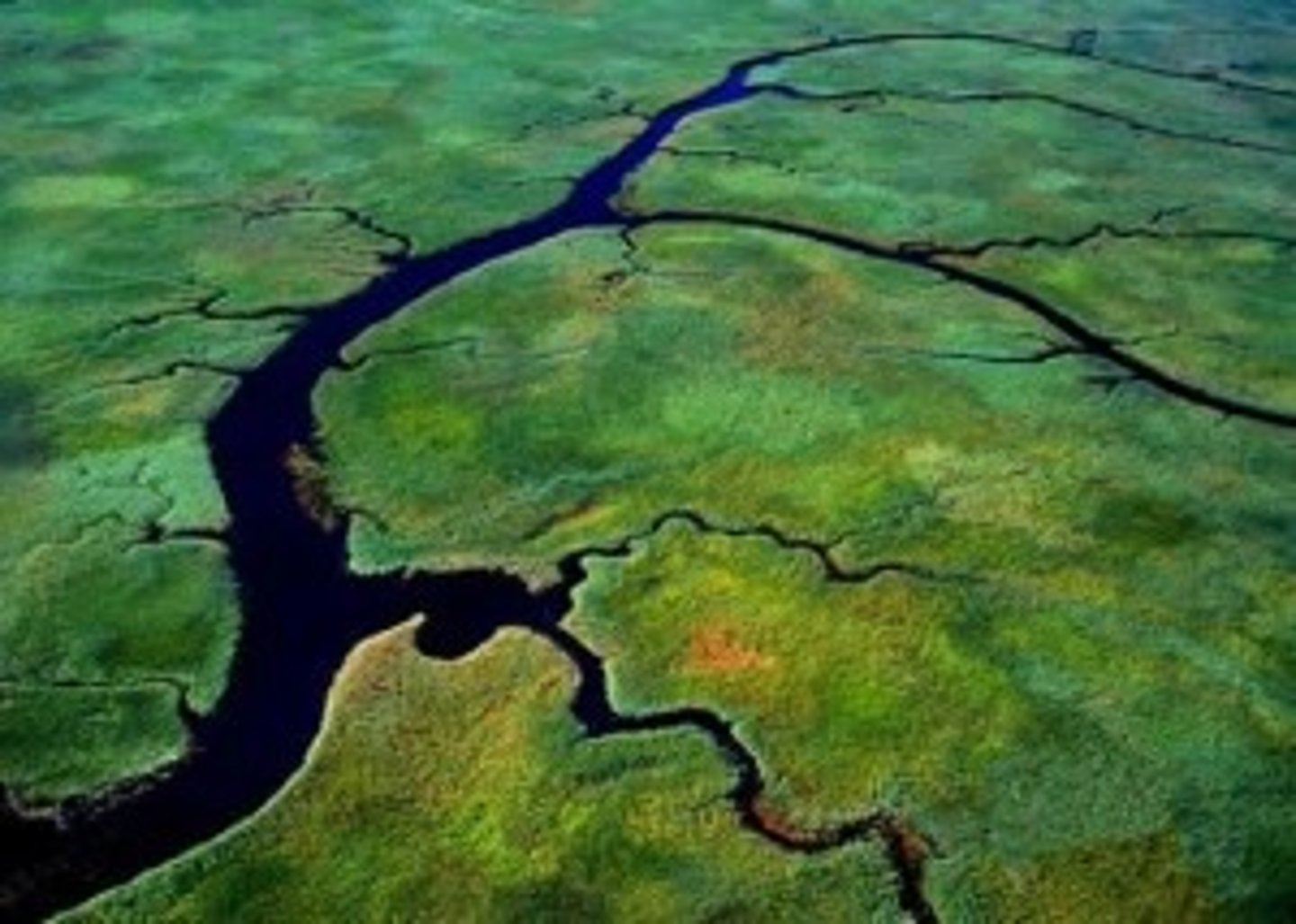

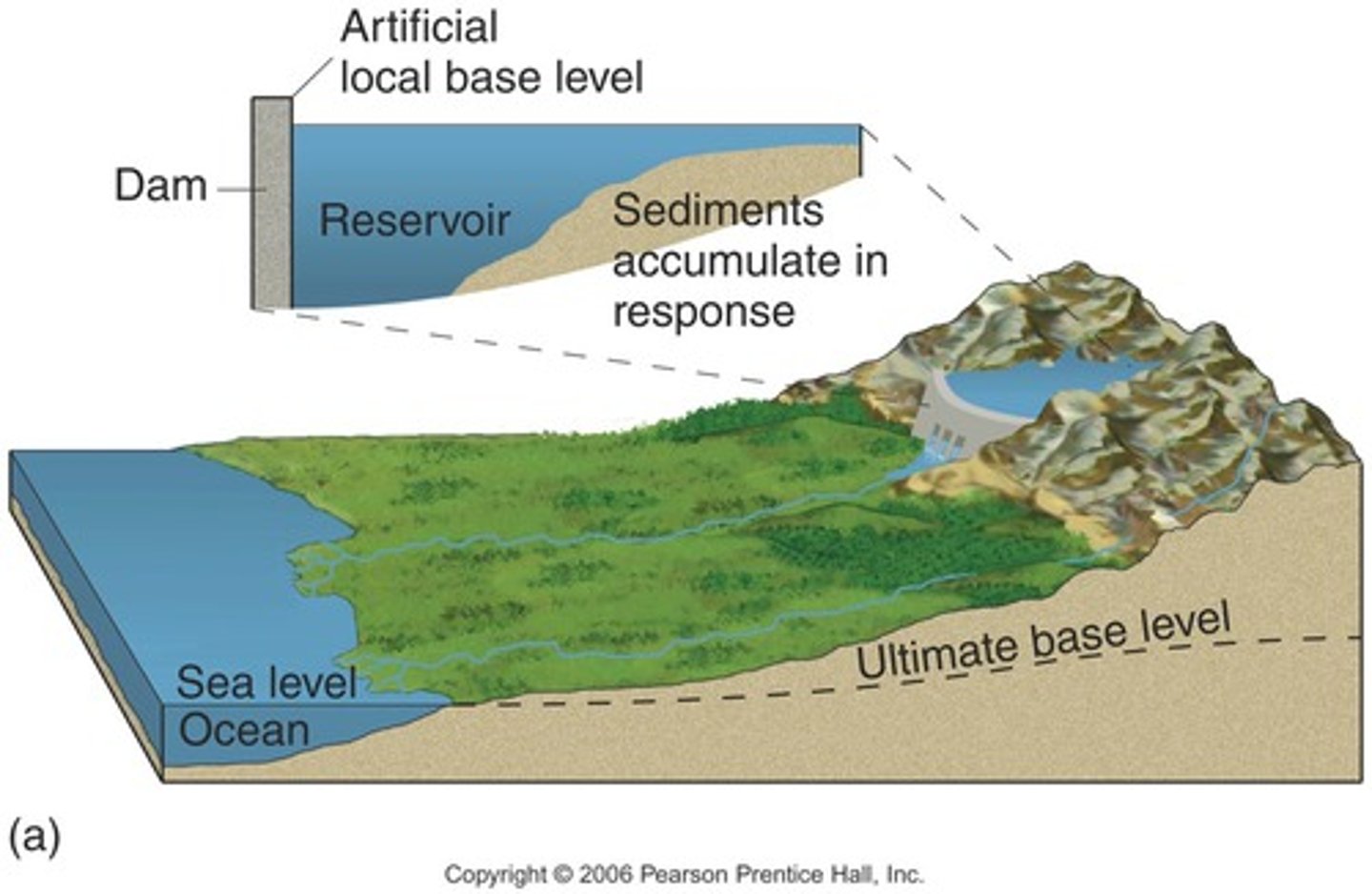
base level
the lowest level to which a stream can erode. It is the level of the body of water the stream empties into, such as the ocean.
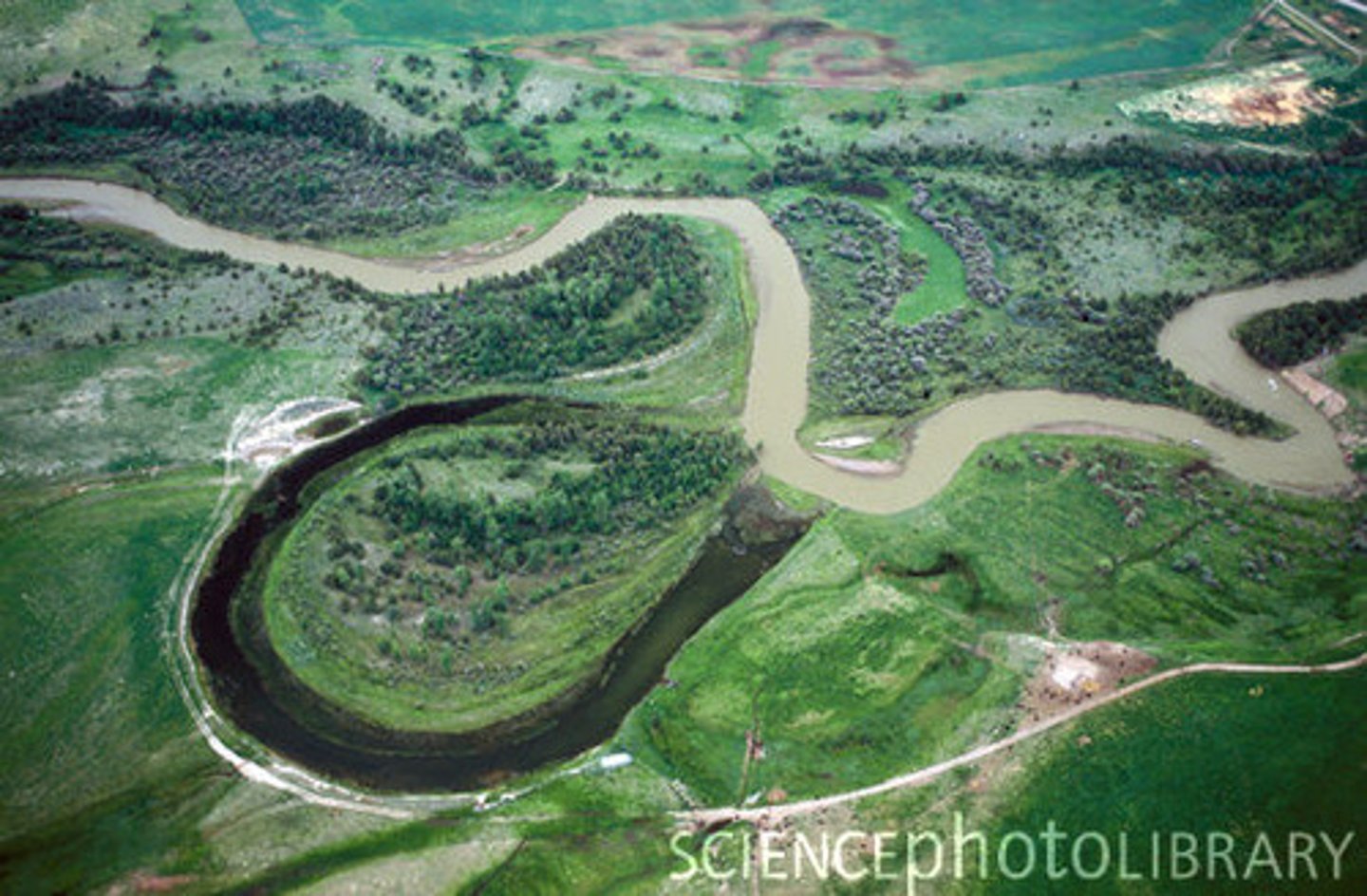
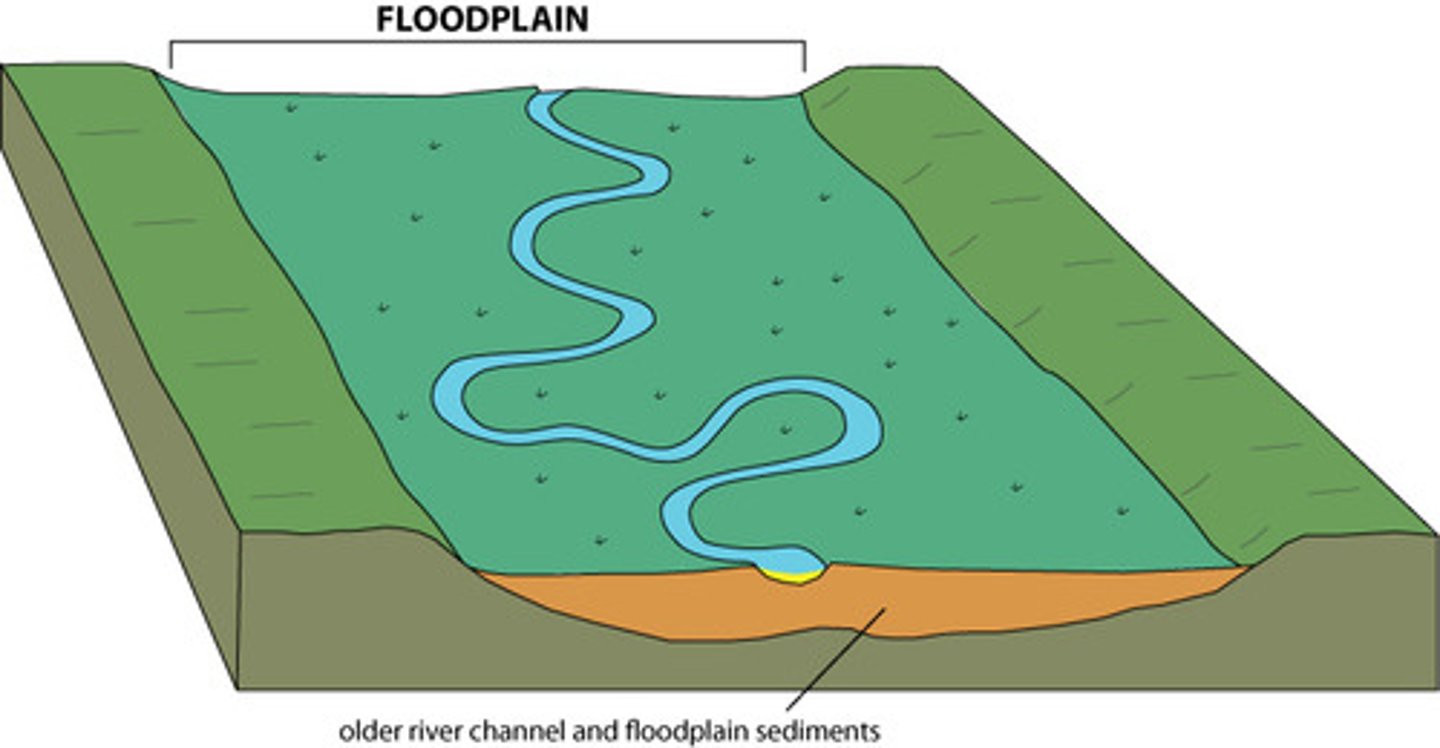
meander
a bend in a stream flowing through a broad, flat valley,
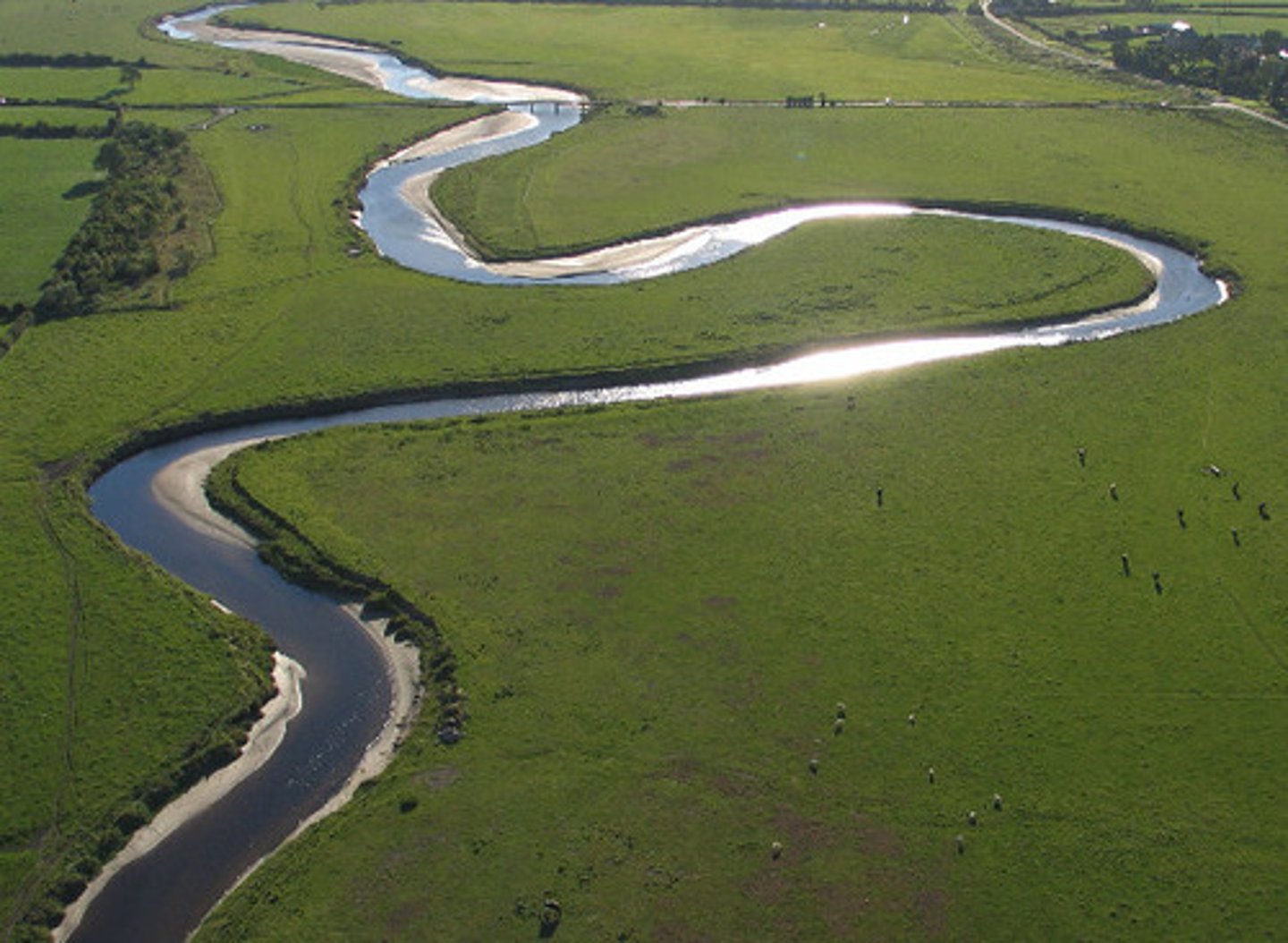

oxbow lake
a lake formed by a cutoff meander

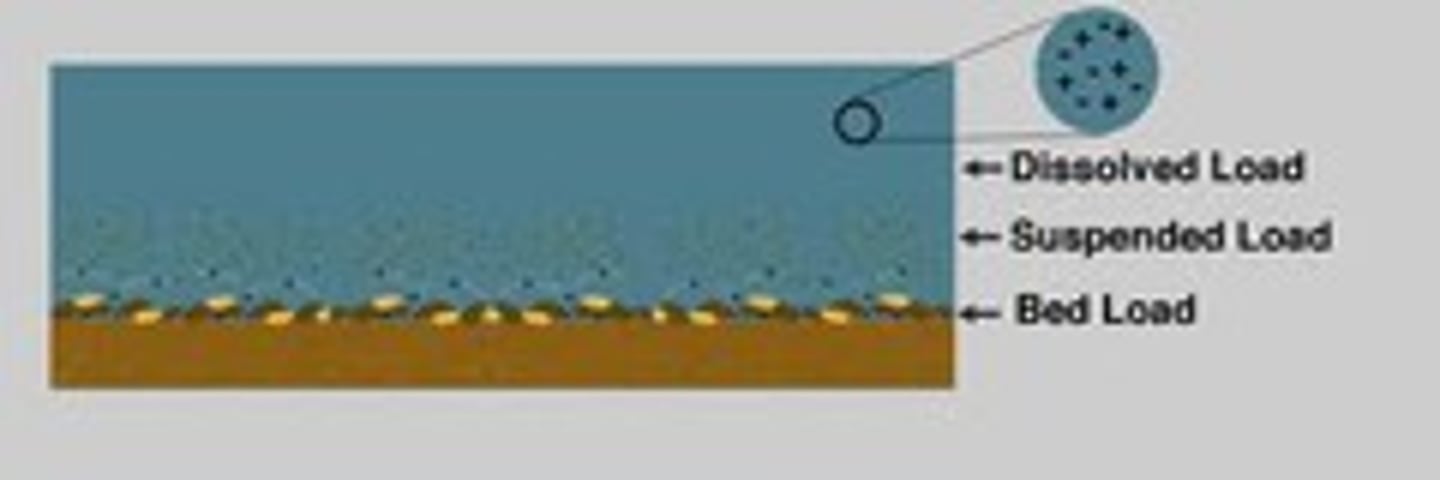
dissolved load
material carried in solution by a stream
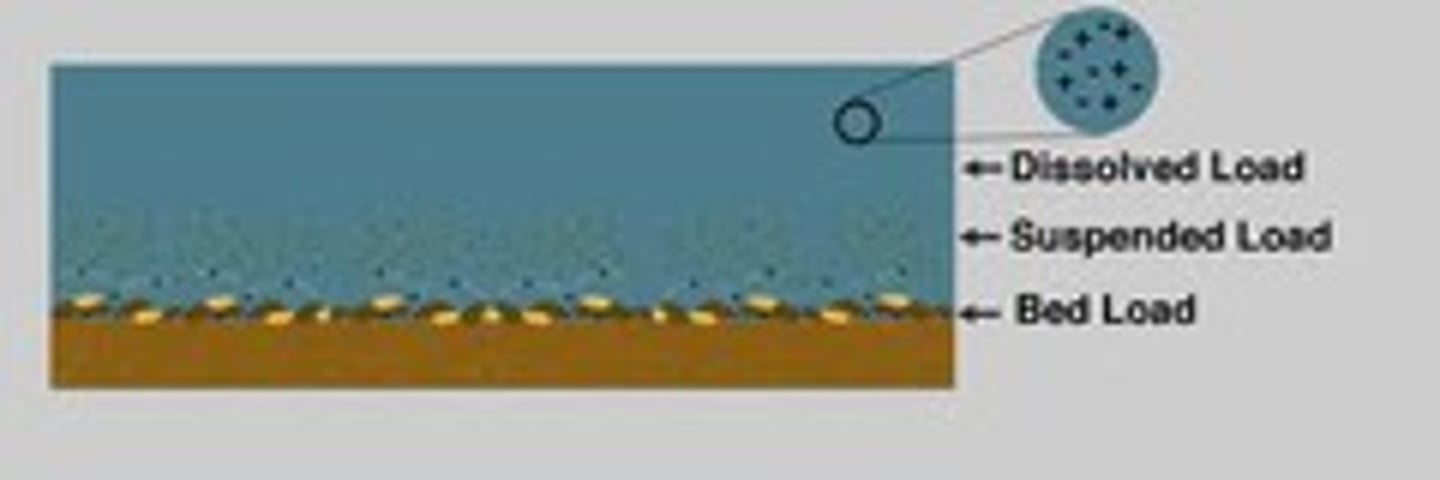
suspended load
undissolved material that is carried by a stream
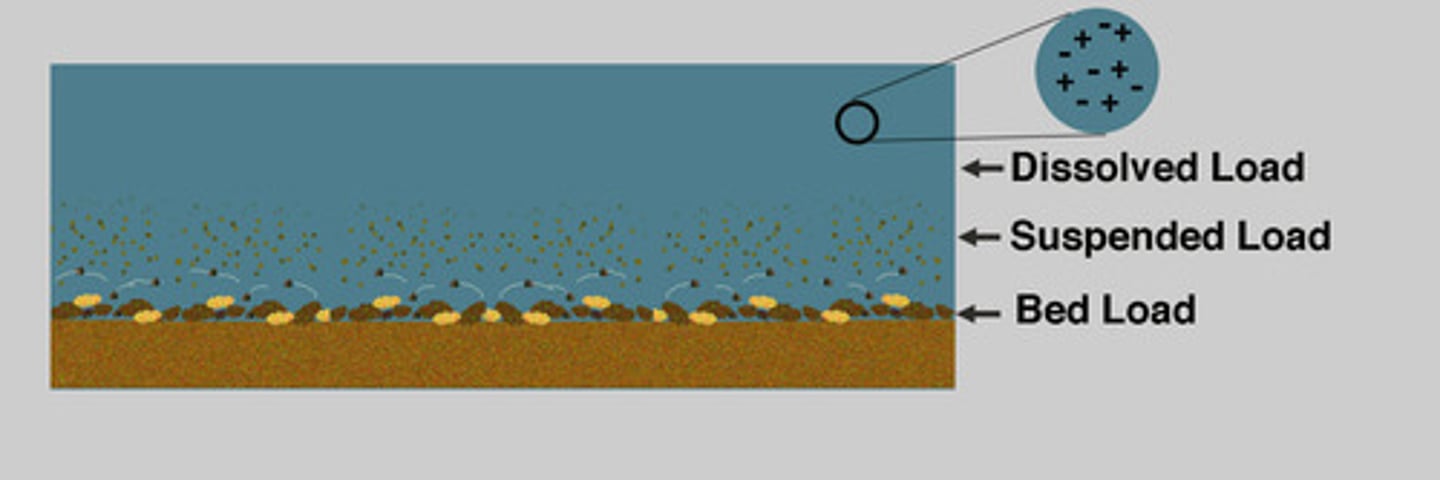
bed load
material that is transported by bouncing or rolling on the bottom
capacity
the maximum load a stream can carry. The combination of dissolved load, suspended load, and bed load
alluvium
material deposited by a stream
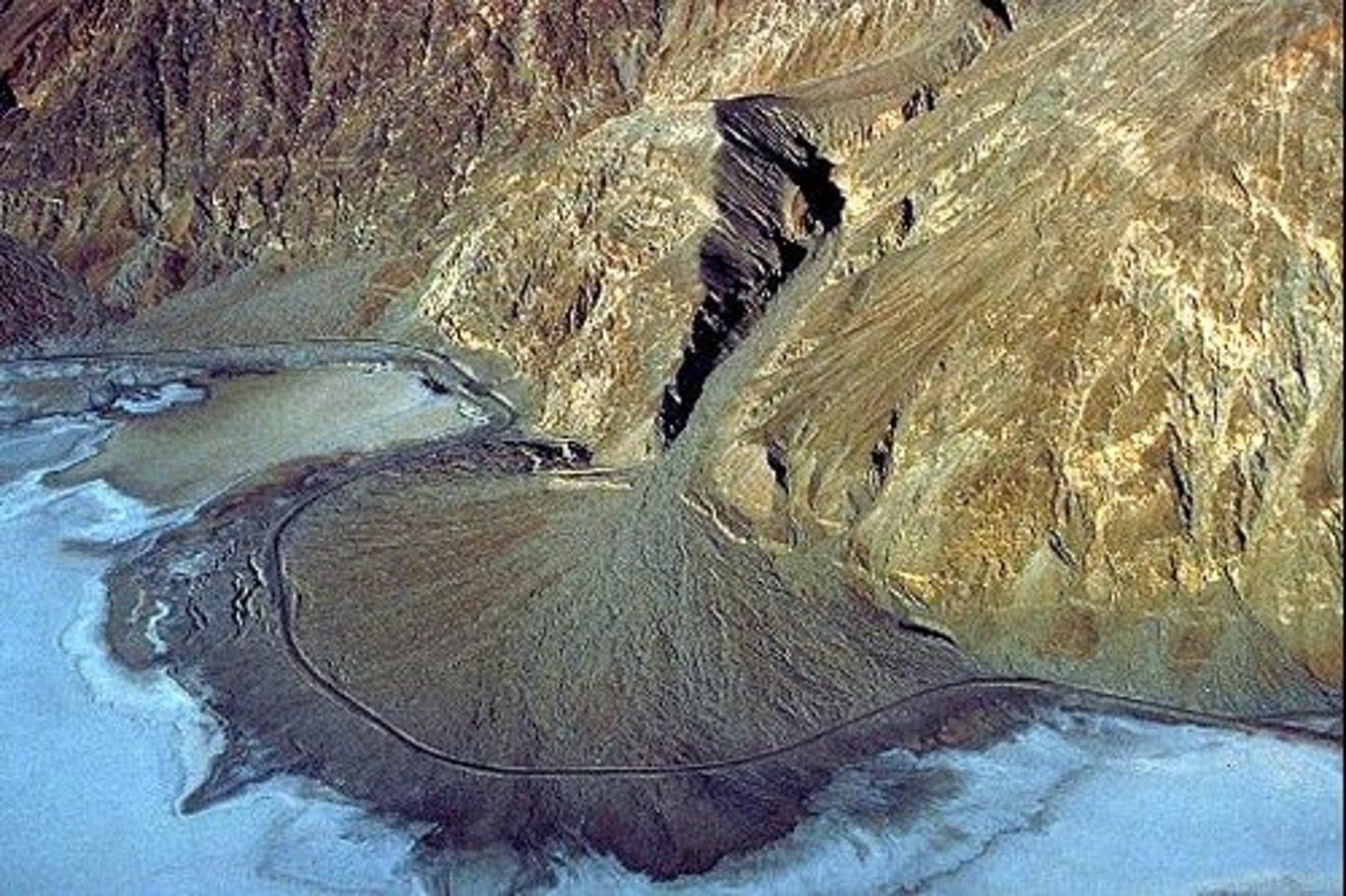

delta
accumulation of sediment deposited where a stream enters a lake or ocean
natural levee
ridge of sediment on the banks of a stream, deposited by periodic floods
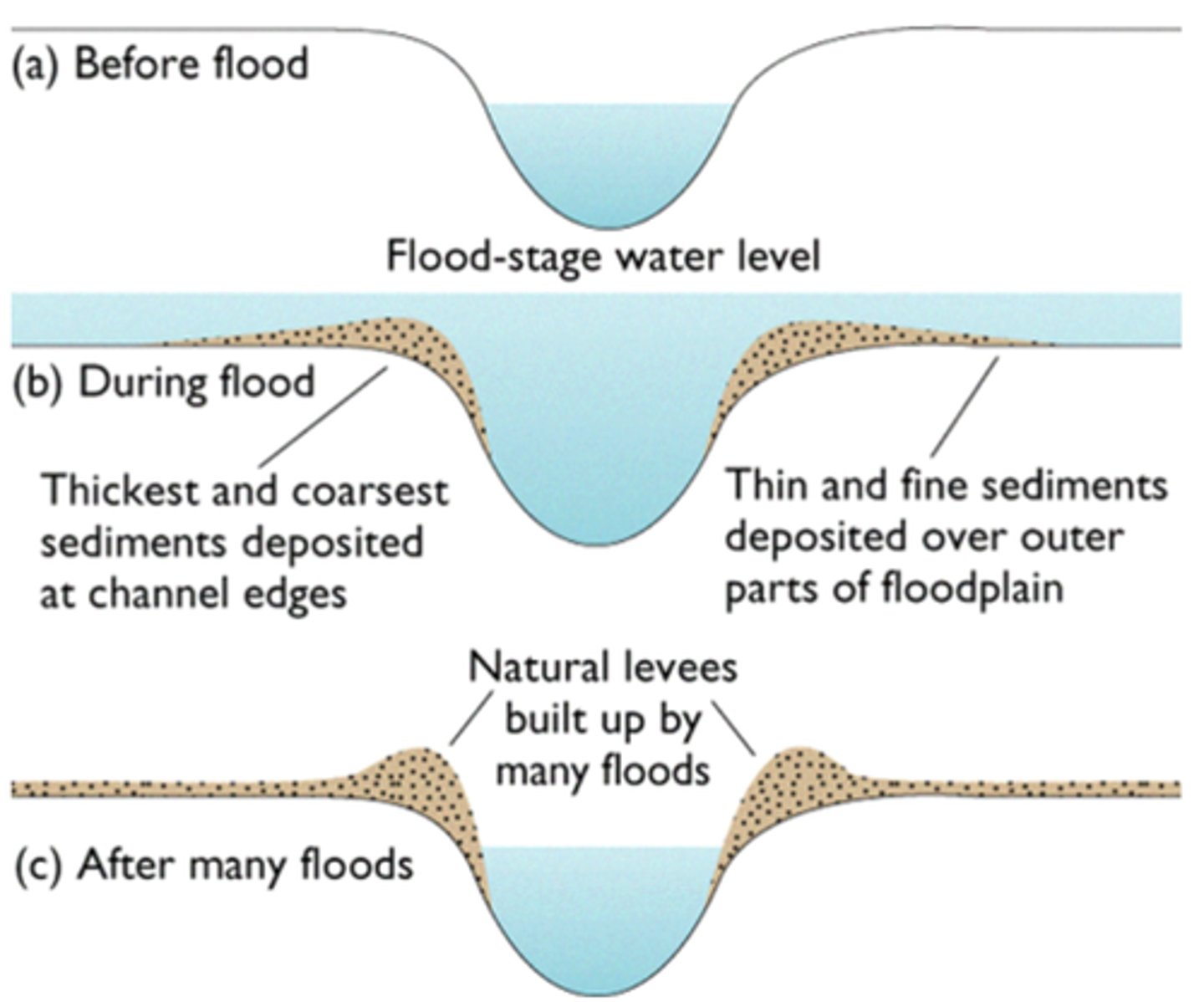
floodplain
flat, low-lying portion of a stream valley subjected to periodic flooding
drainage basin
also called a watershed, it is the land area that contributes to a particular stream
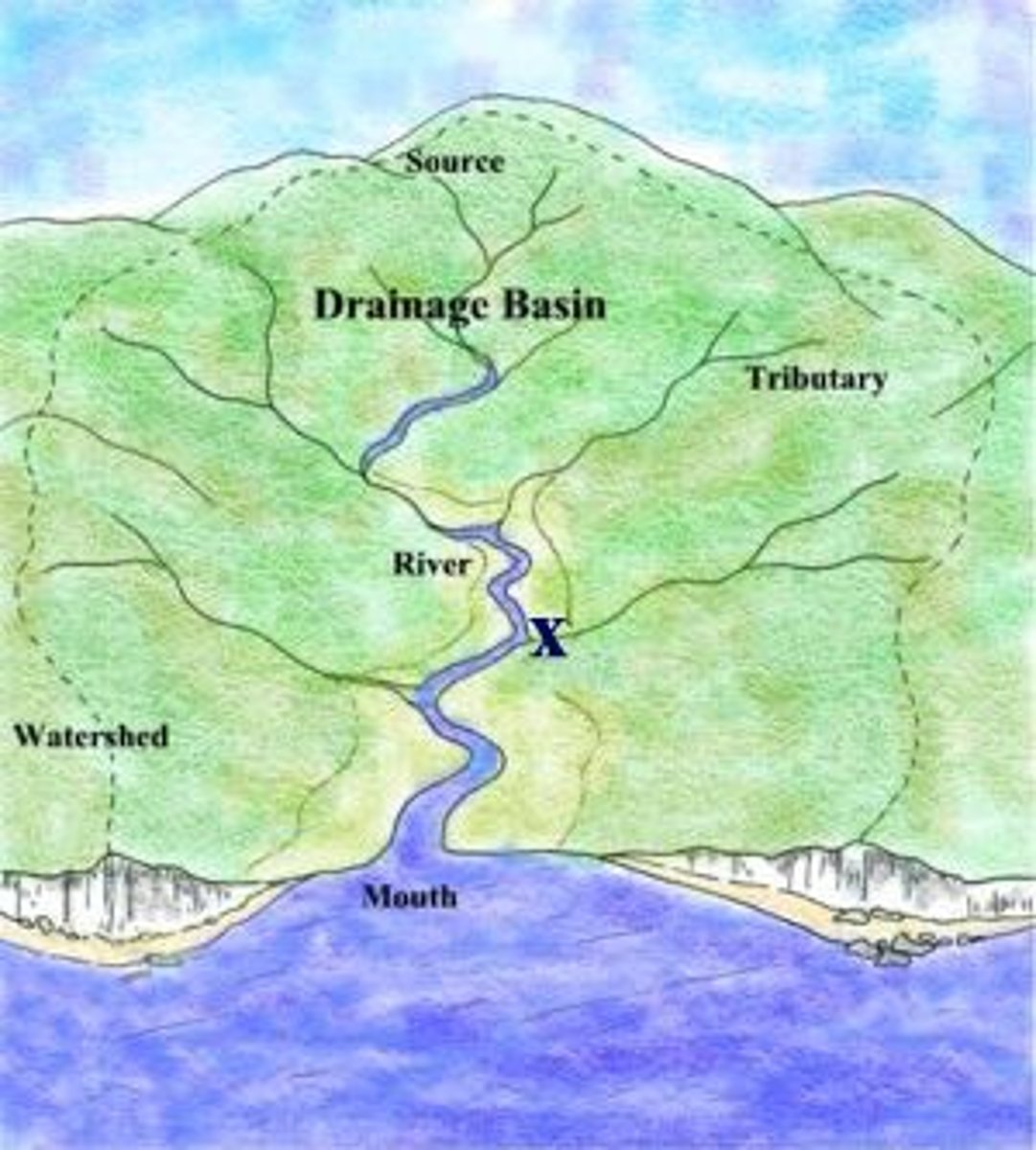
divide
area of high land that separates one drainage basin from another
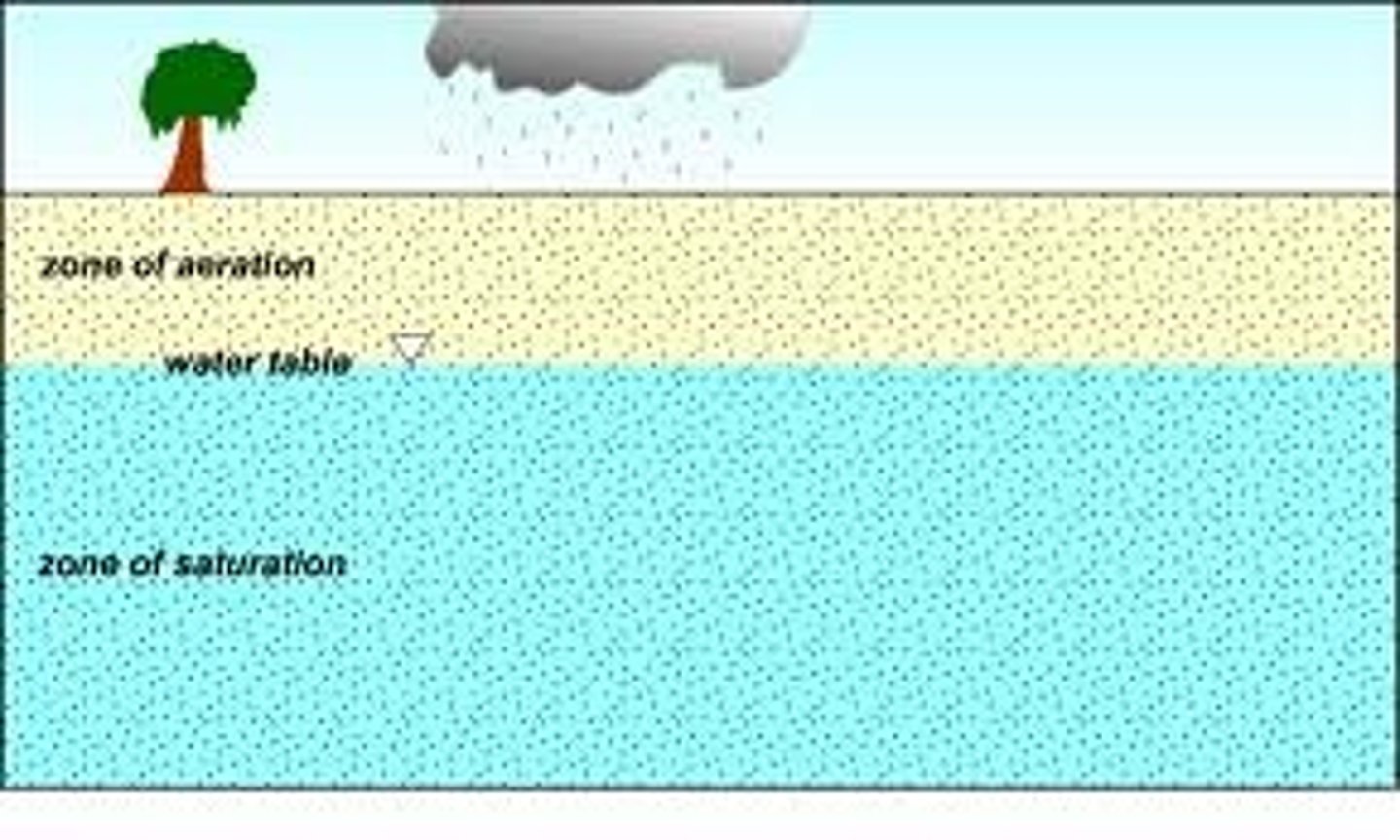
zone of saturation
depth at which all pore space between sediments is filled with water
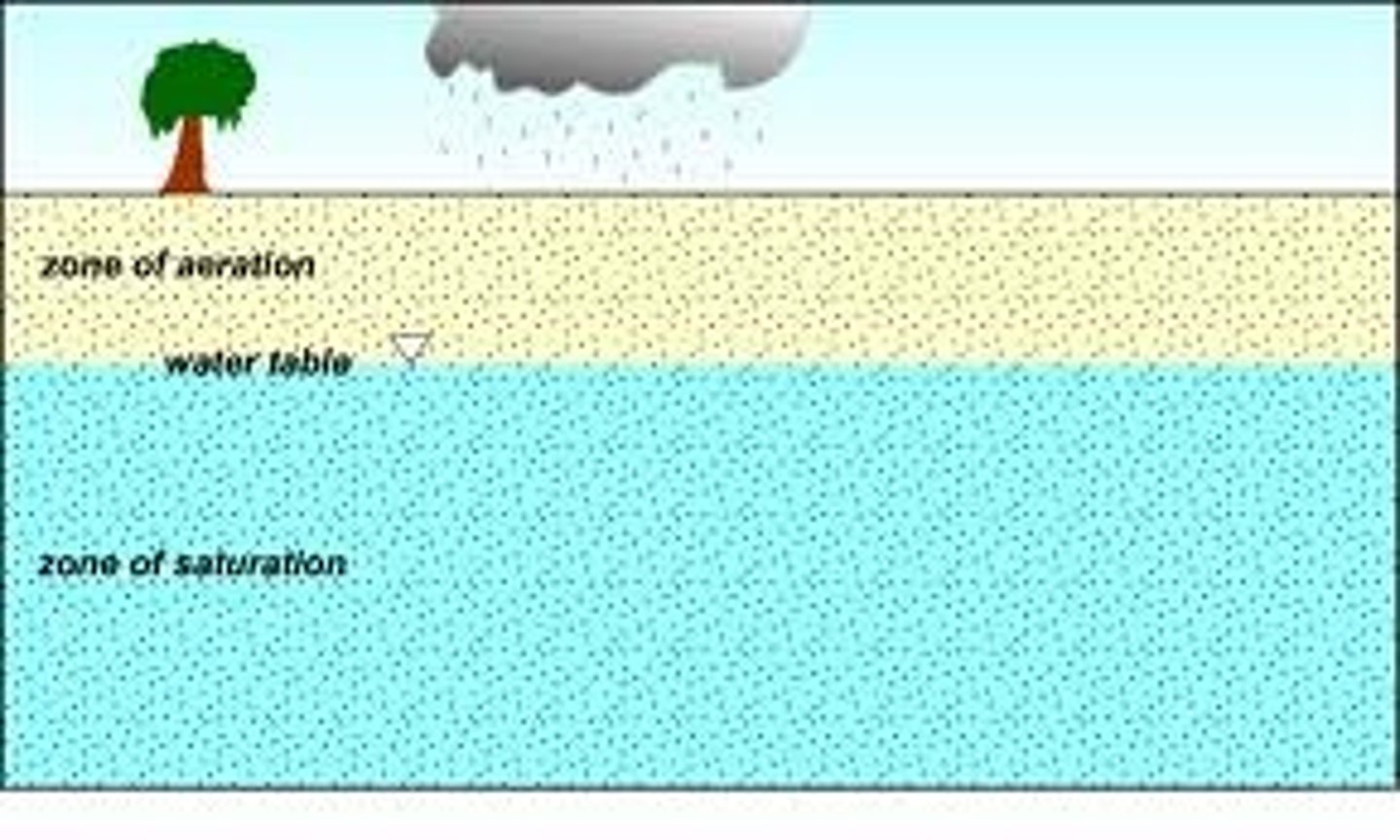
water table
the upper boundary of the zone of saturation
porosity
the percentage of pore space in rock or sediment
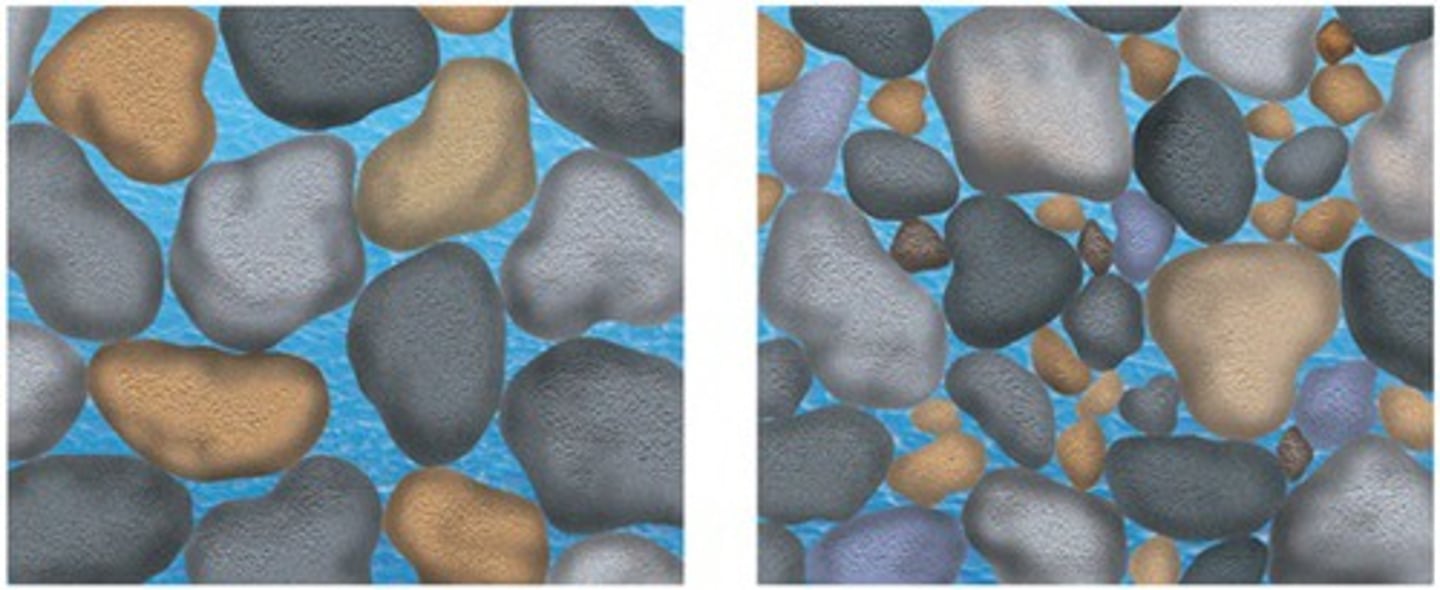
permeability
the ease with which water moves through connected pore spaces
aquifer
permeable rock or sediment layer that can store and transmit water easily
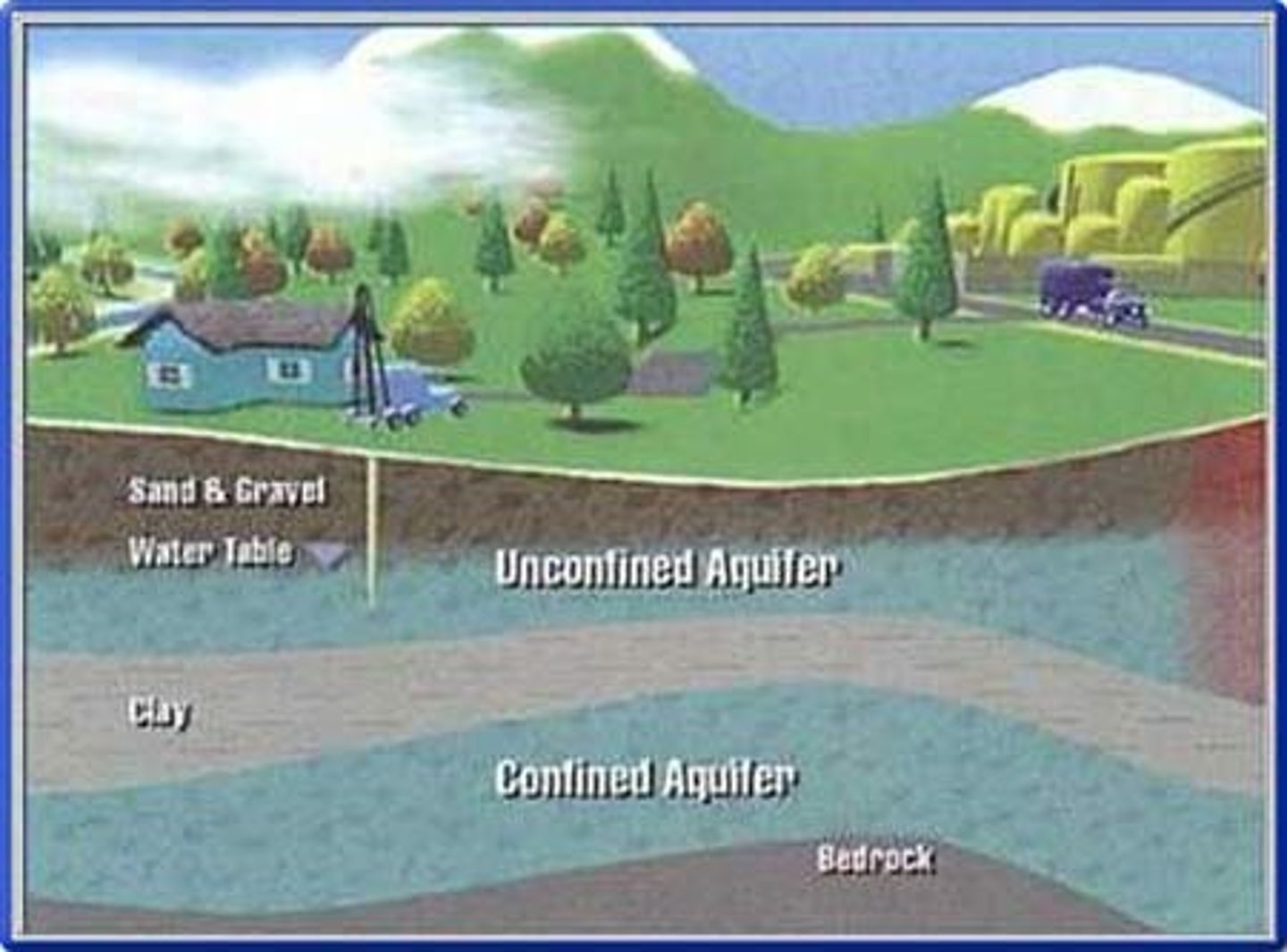
spring
an area where the surface intersects with the water table. Groundwater comes to the surface at these areas
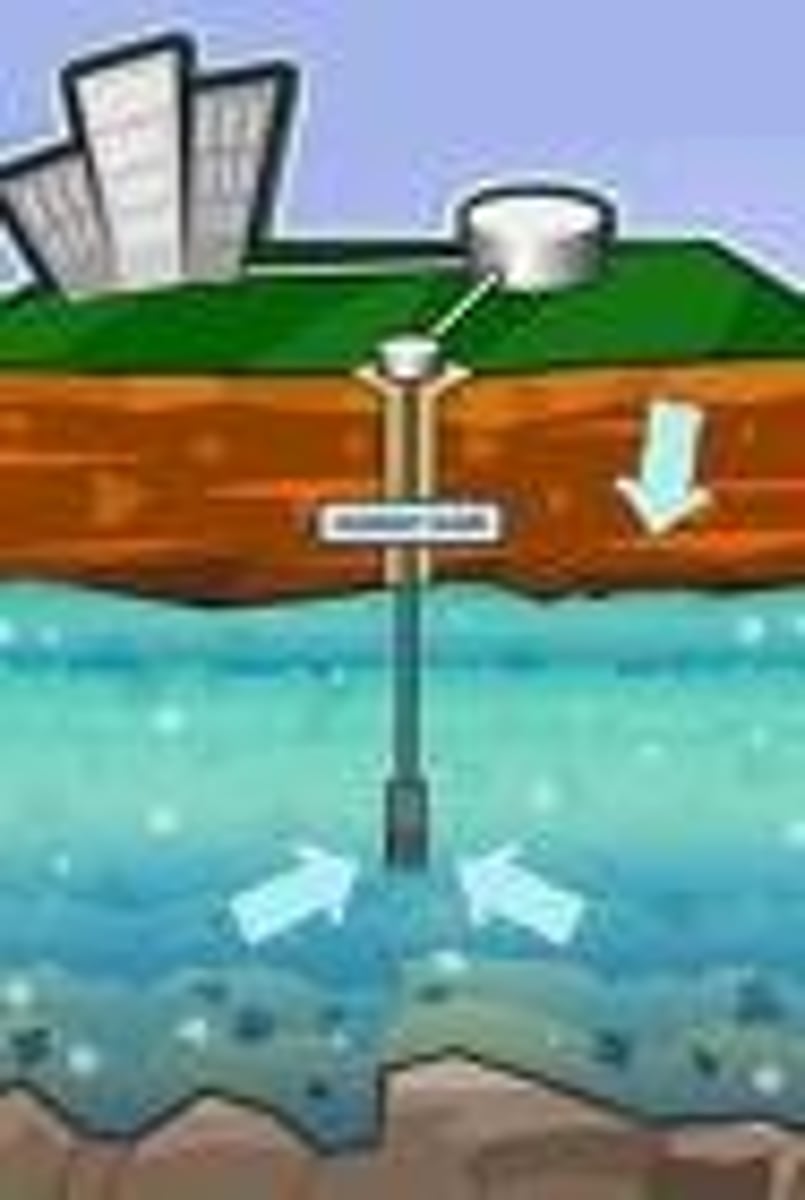
well
a hole bored down below the water table, into the zone of saturation
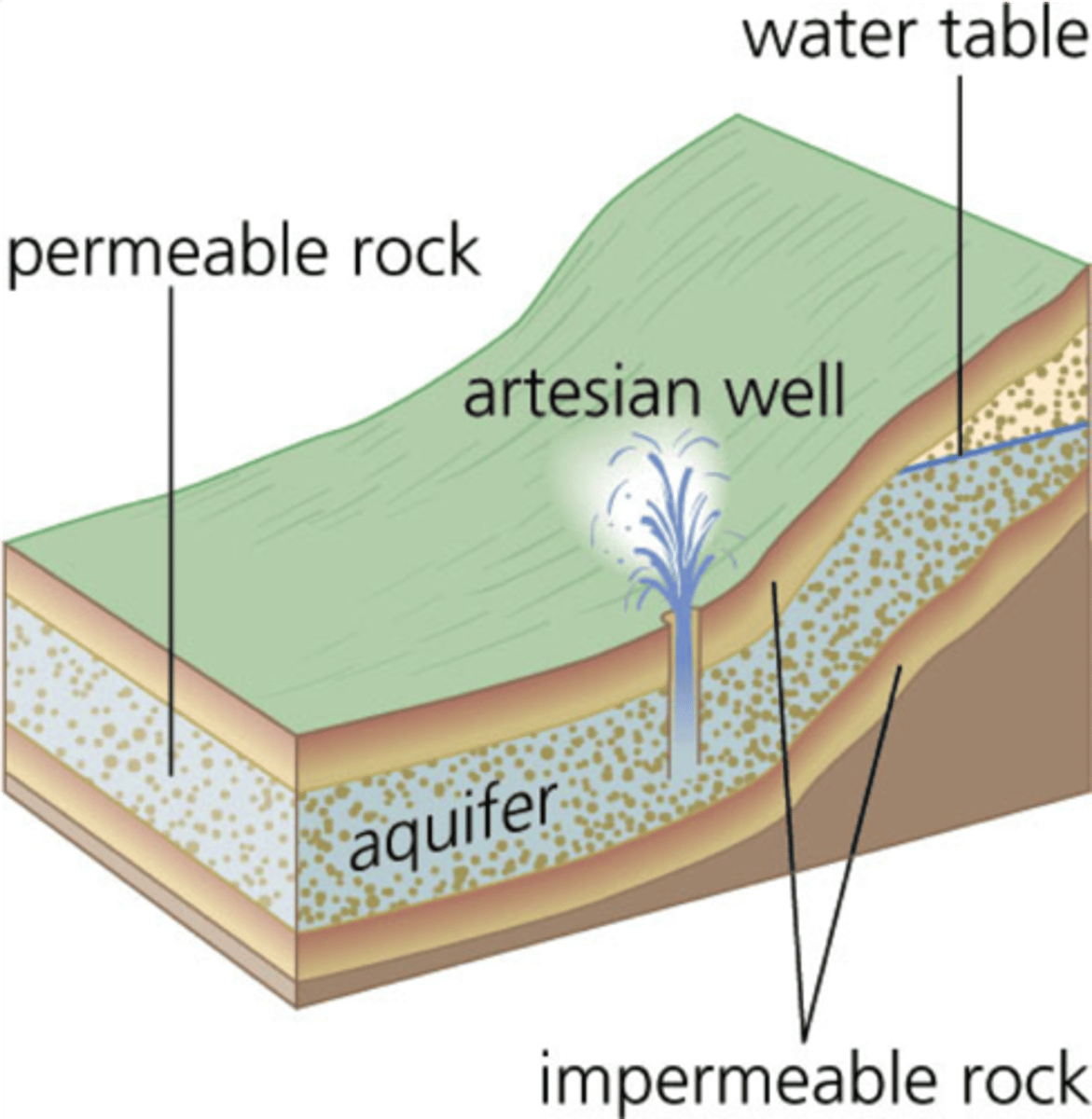
artesian well
a well where groundwater comes out under its own pressure
drawdown
lowering of the water table as a result of water removal by a well
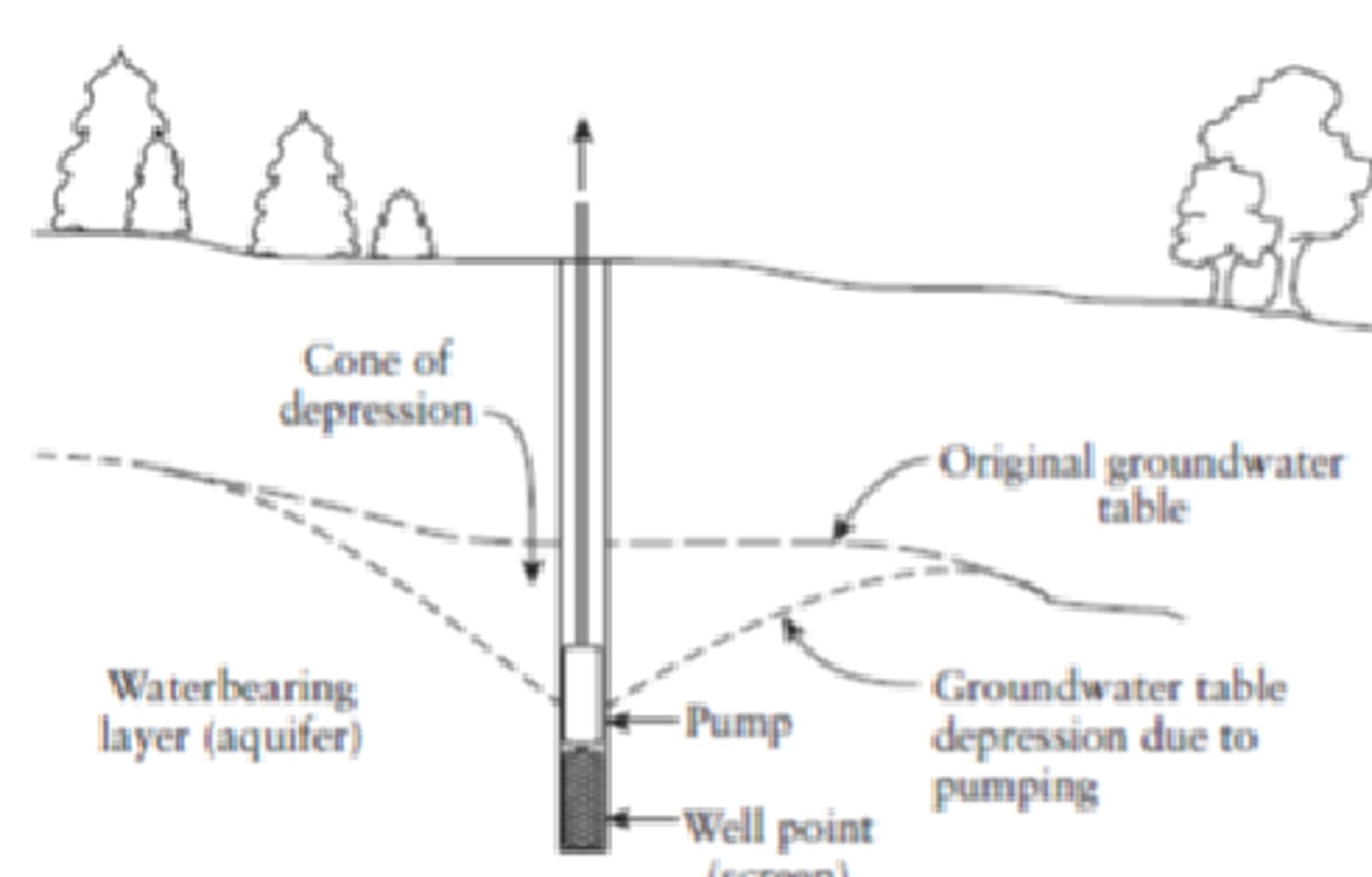
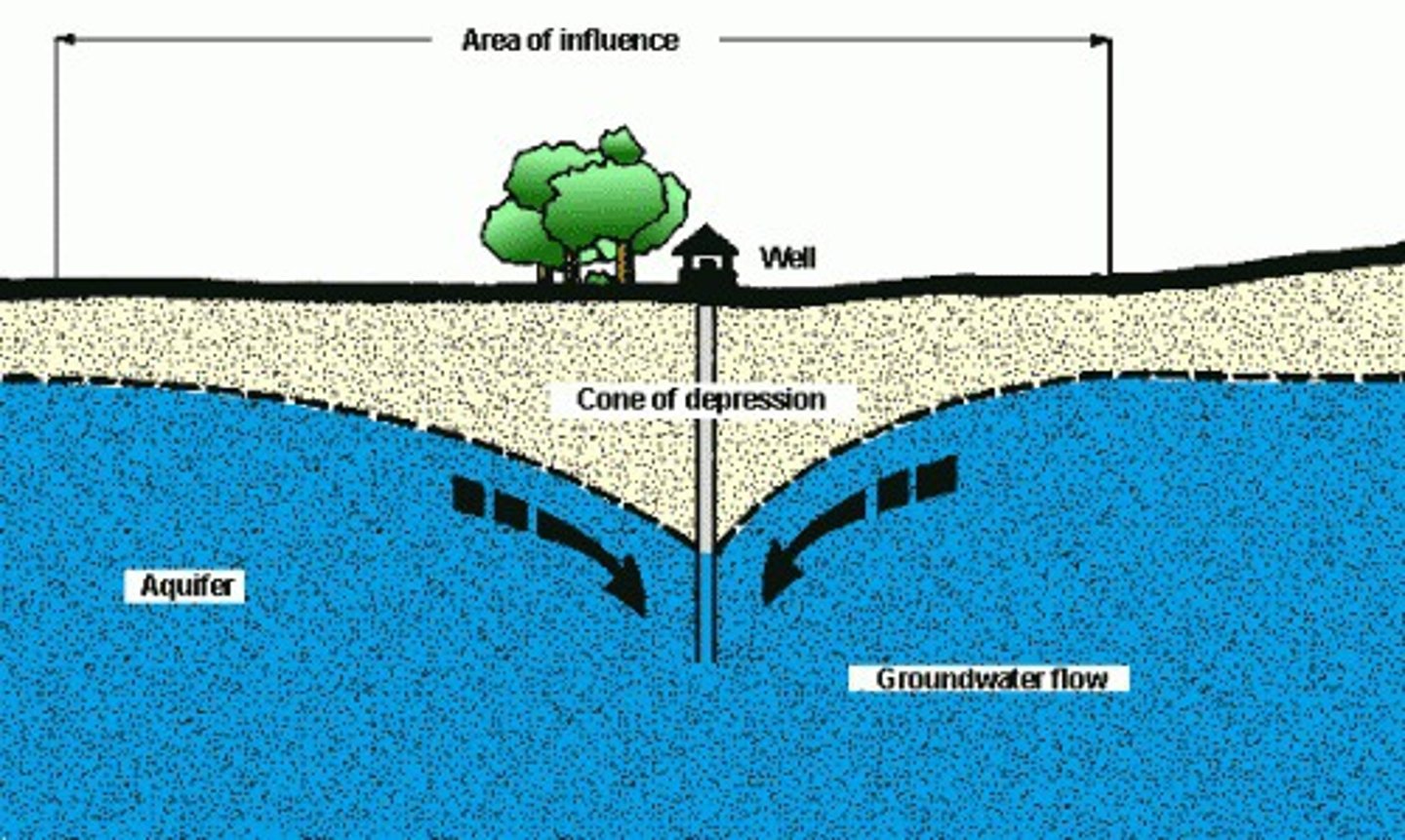
cone of depression
cone shaped area of drawdown around a well that is heavily pumping
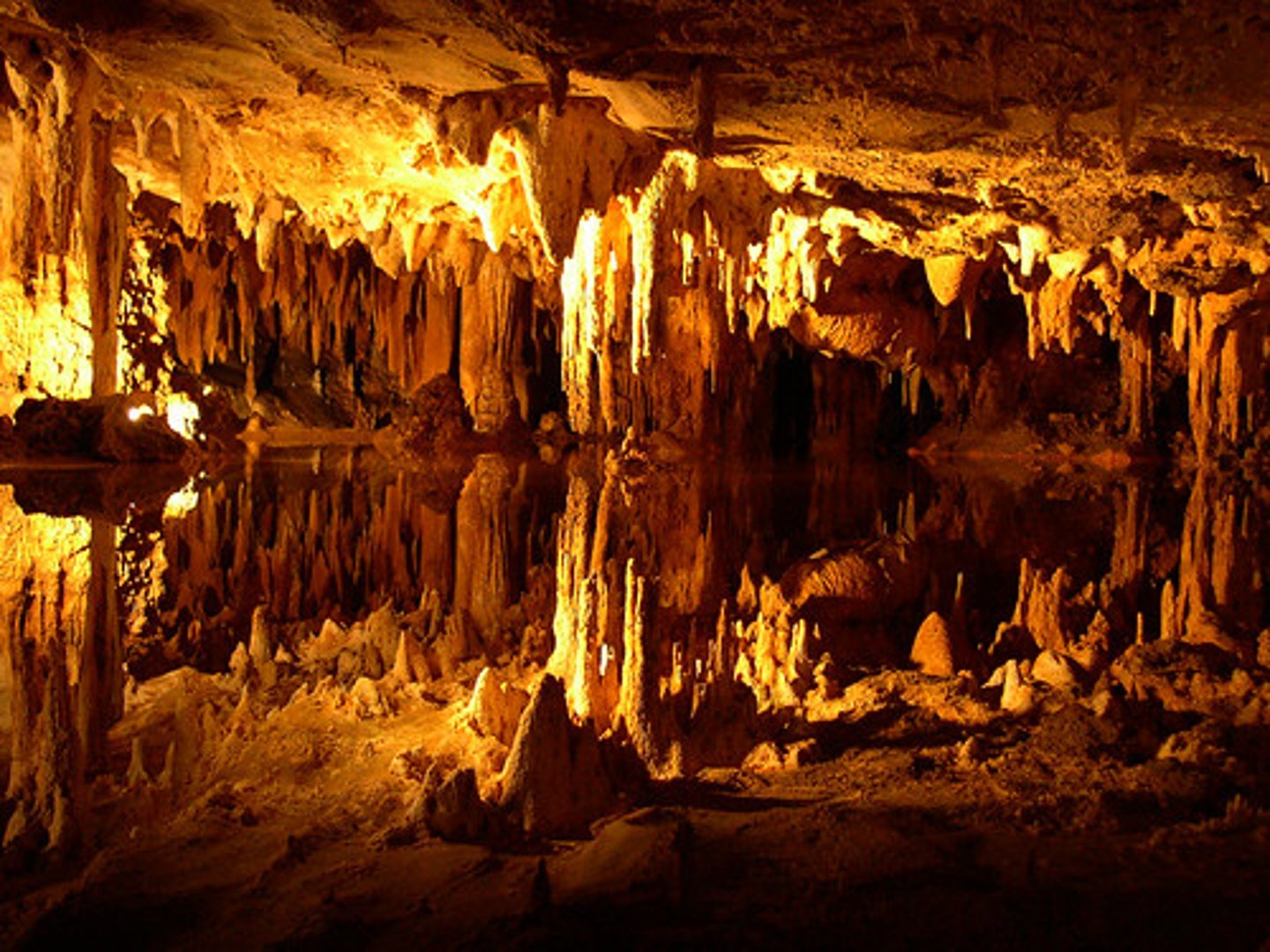
cavern
naturally formed underground chamber that forms in the zone of saturation

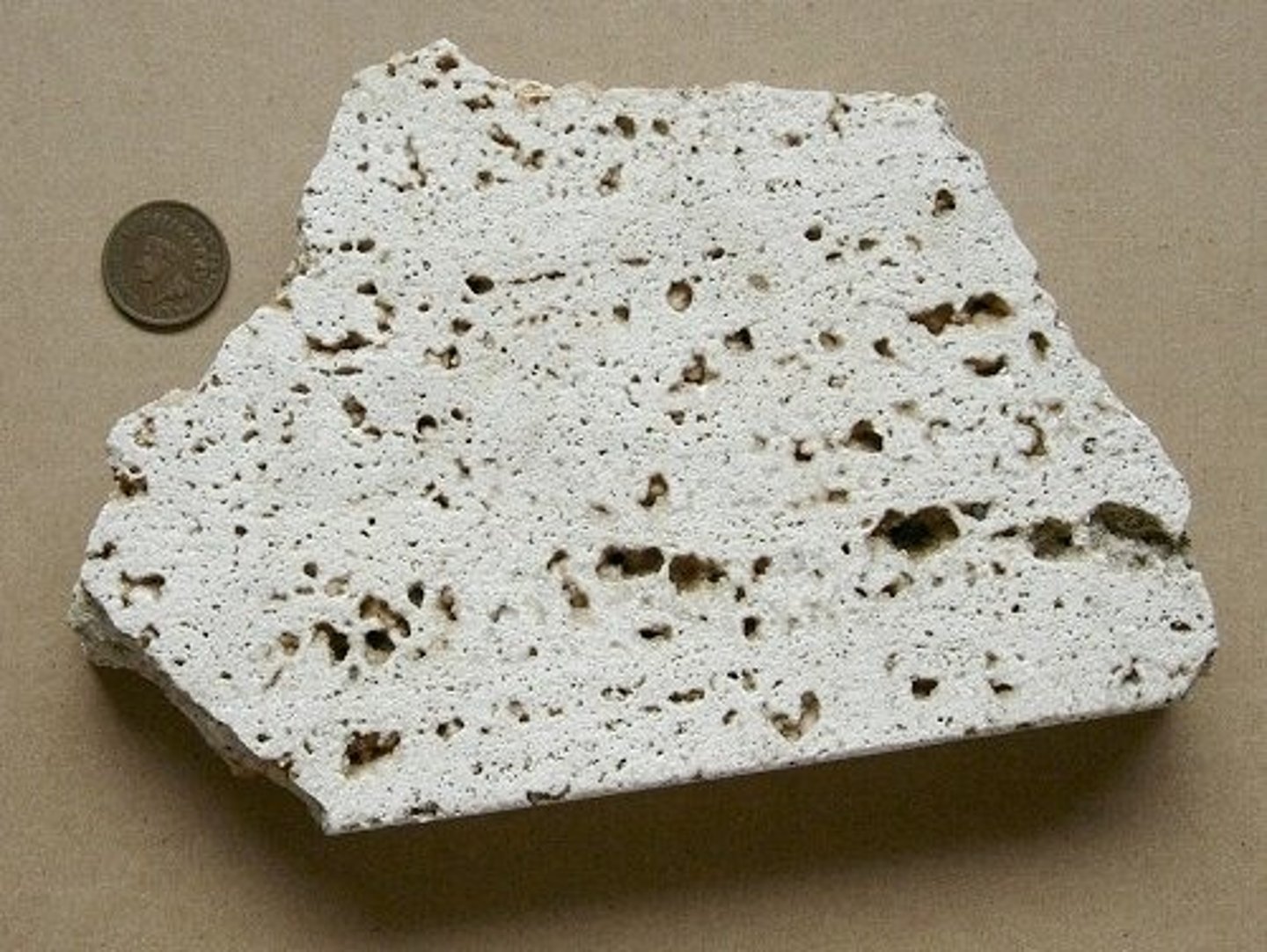
travertine
form of limestone that is formed as a chemical sedimentary rock

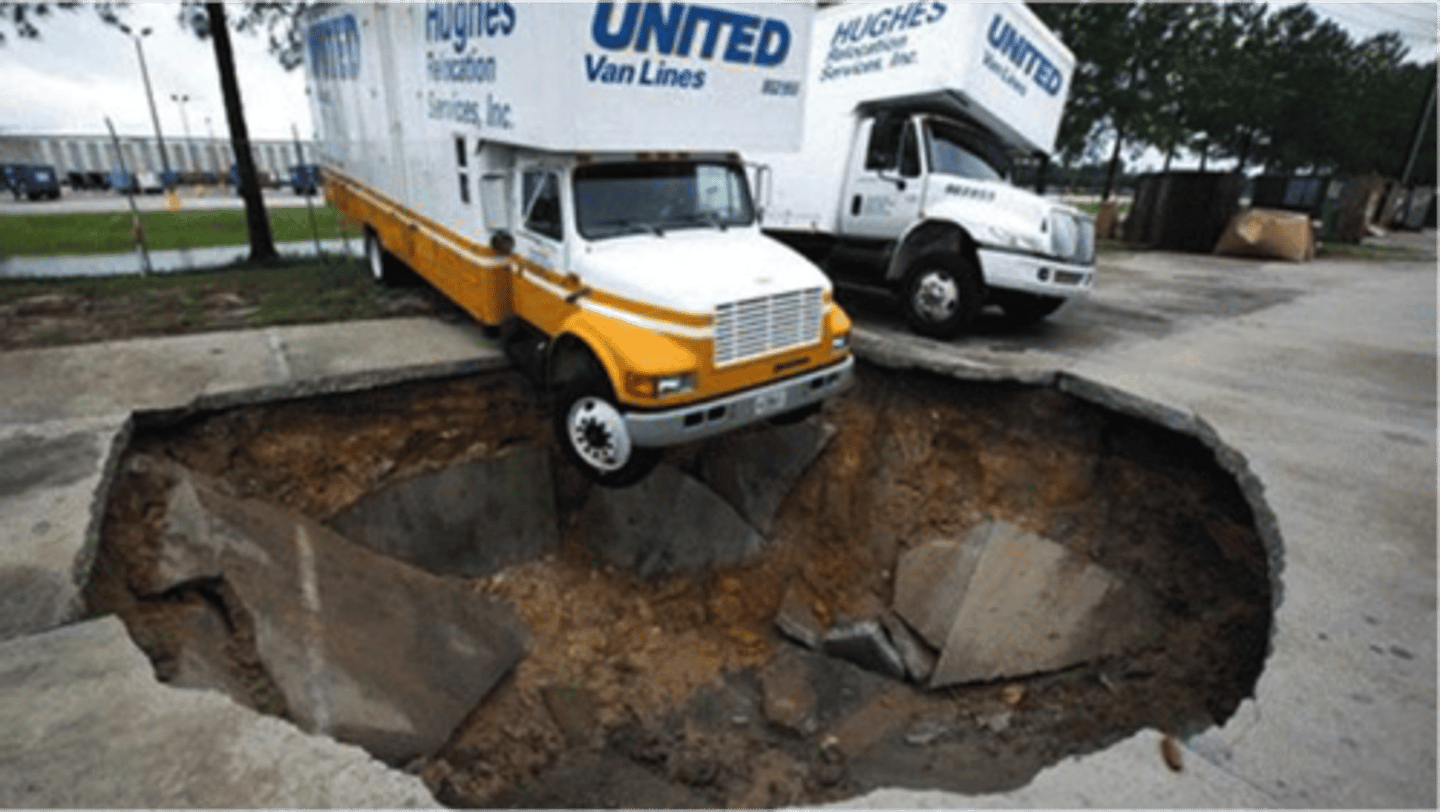
sinkhole
surface depression formed when a cavern collapses

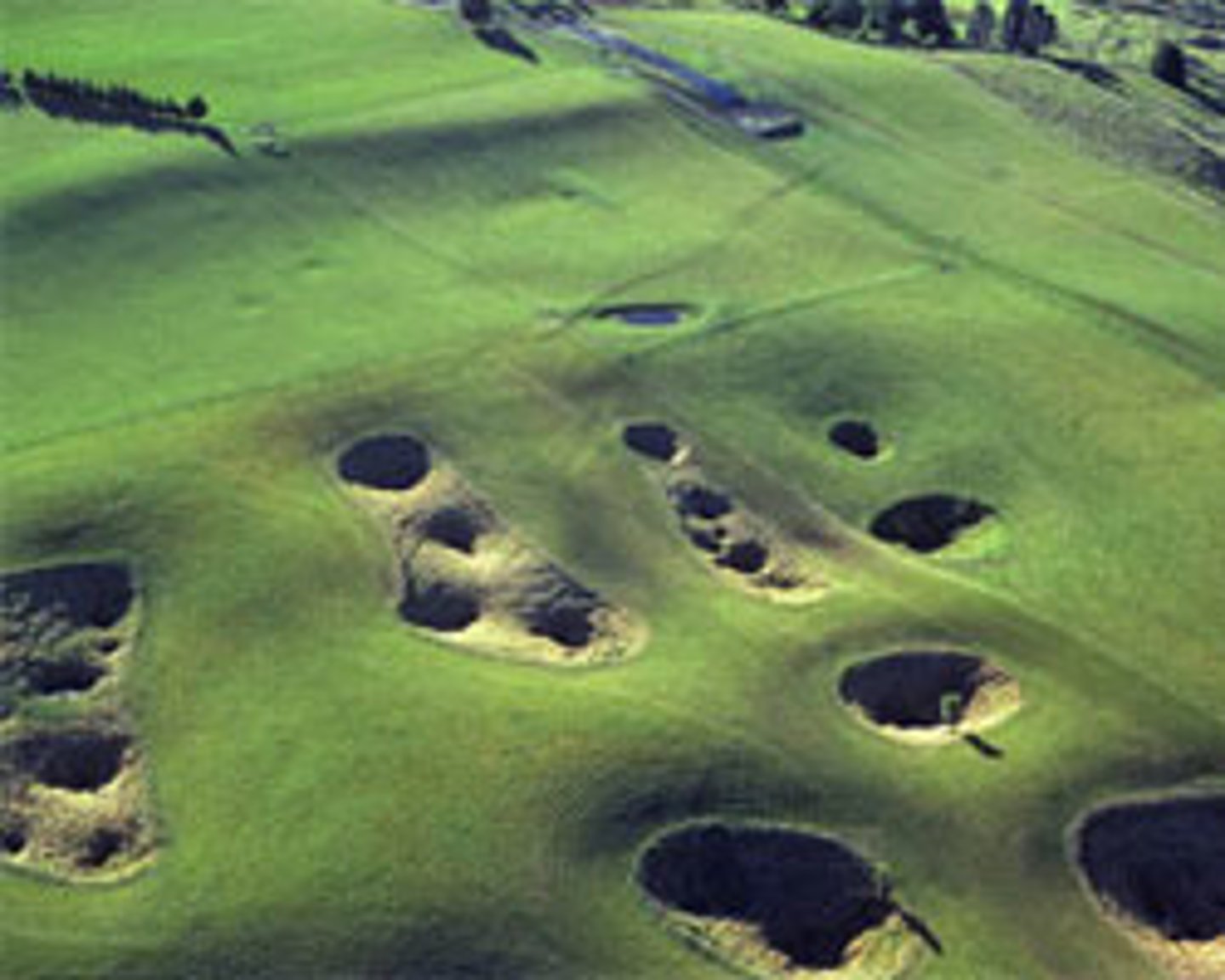
Karst topography
surface landscape formed by rock dissolving at or near the surface. Includes sinkholes, sinking streams, caverns, towers, fissures and other landforms

Geyser
an intermittent hot spring or fountain in which a column of water shoots up with great force at regular intervals