Price determination in a competitive market
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Effective demand
Demand backed by the ability to pay
Market demand
Quantity of goods/services that all consumers in the market wish to and are able to buy at different prices
Law of demand
As price falls,demand increases
inverse relationship
Hence downward sloping
What causes a movement along the demand curve?
Price change
Define extension
Fall in price
more goods demanded
Define contraction
Rise in price
Less goods demanded
Define ceteris paribus
All other factors remain constant
What factors cause demand curve to shift?
Price of substitute goods
External factors (economic shocks)
Population
Trends
Income
Complementary goods
Equilibrium price
Price at which demand for goods = supply of goods
Normal good
A good for which demand increases as income increases
Inferior goods
A good for which demand decreases as income increase
Exceptions of the law of demand
Speculative demand
Price as an indicator of quality
Veblen goods
Speculative demand
If housing, shares or foreign currency starts to rise, people speculate that prices will rise even further
So demand increases
Price as indicator of quality
A higher price may signify high quality when info about the good is limited
Veblen goods
A good that is marketed as exclusive
The high price is the selling point
Price elasticity of demand (PED)
Measures the change in demand in response to price change of the good
% change in Q demanded / % change in price
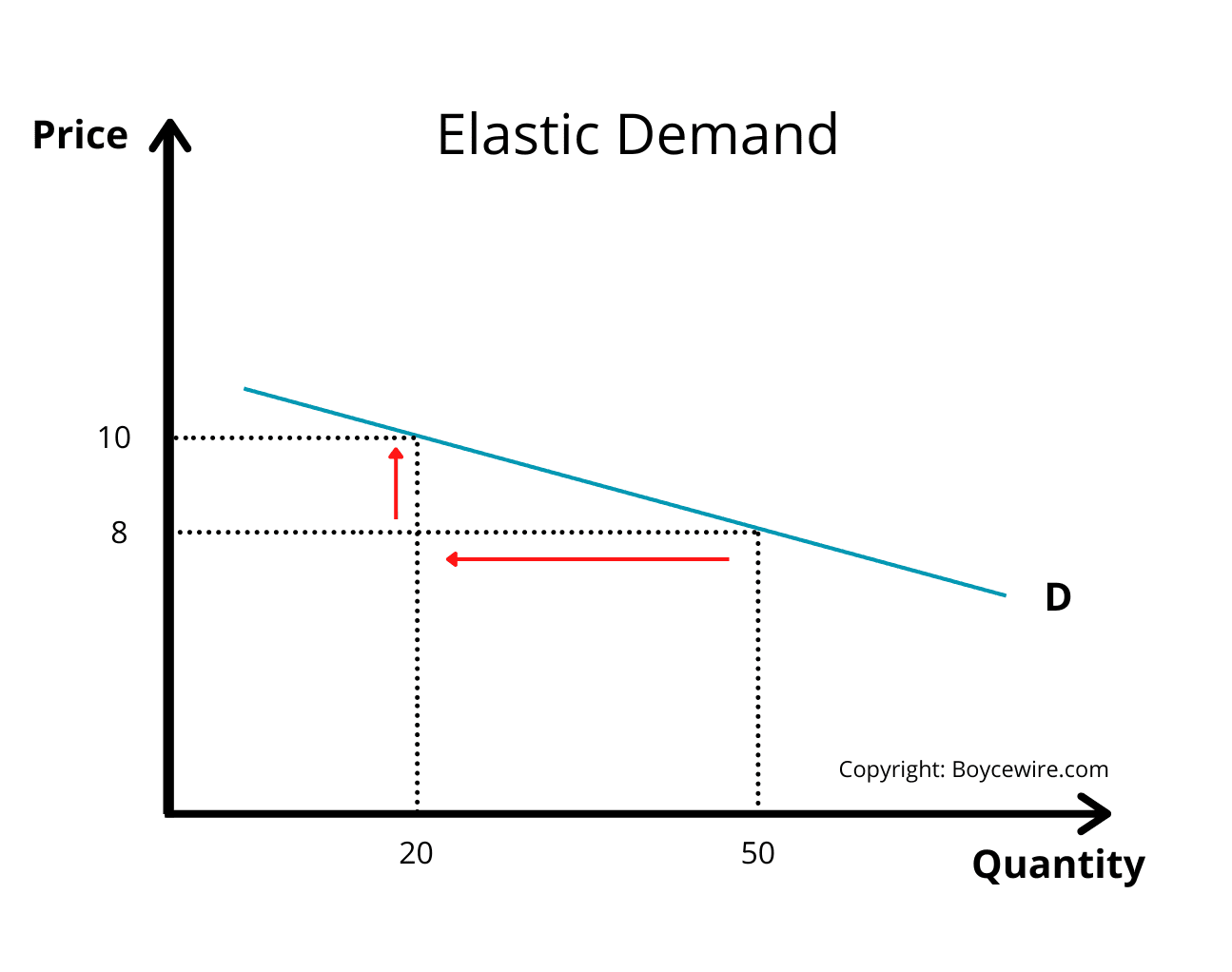
Elastic demand
A change in price leads to a bigger % change in demand
PED> 1
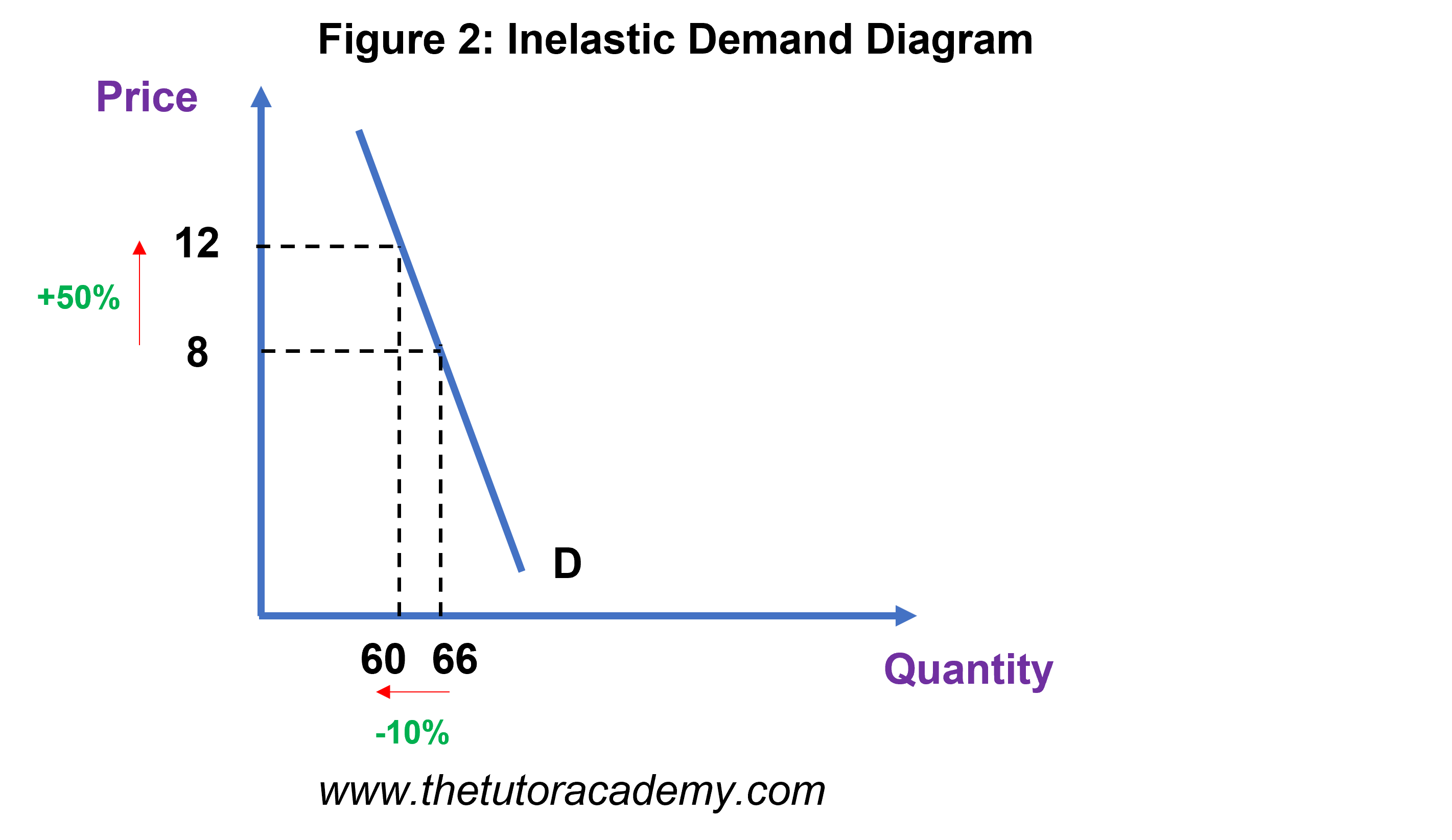
Inelastic demand
Change in price leads to a smaller change in demand
PED< 1
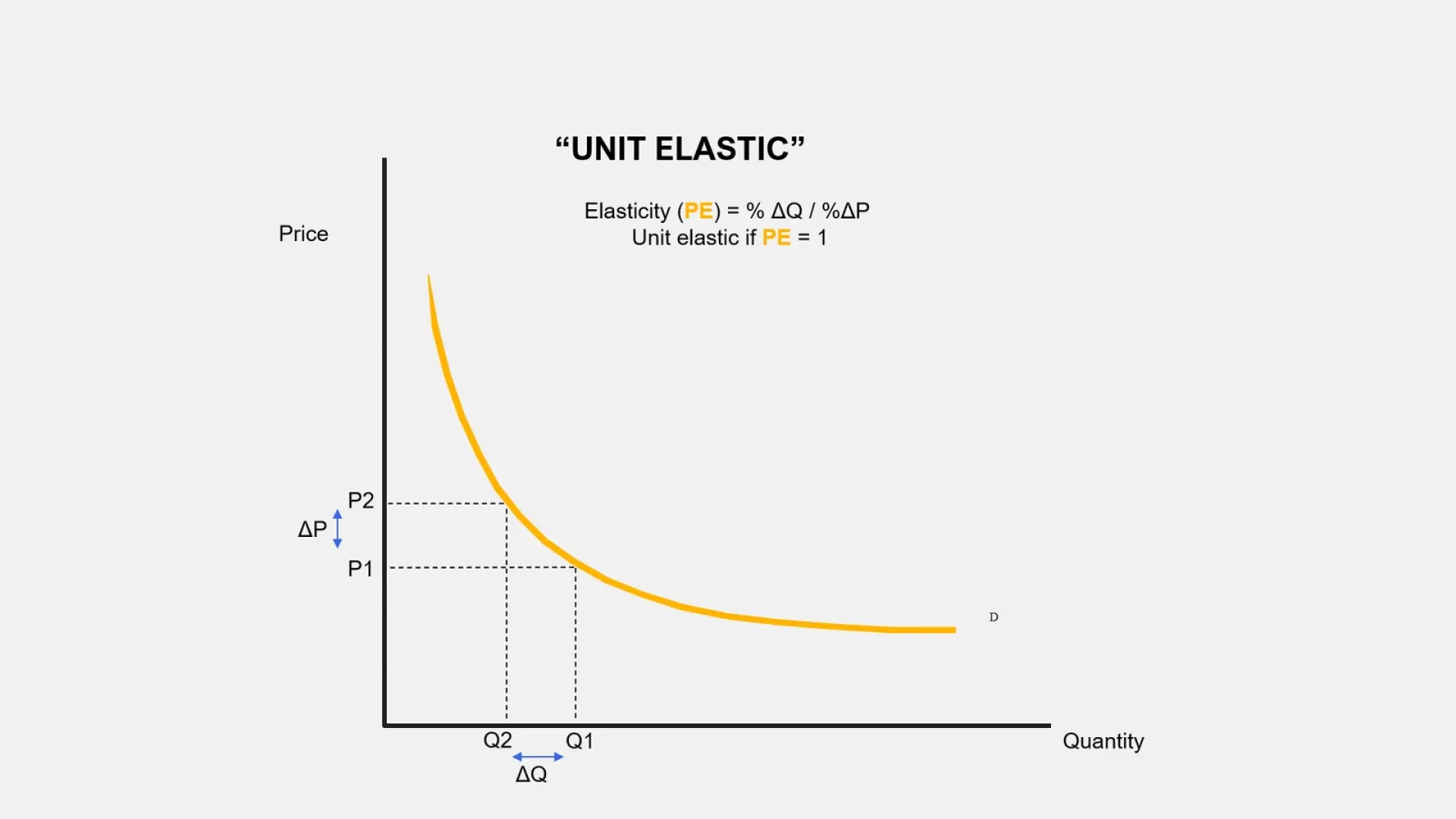
Unit elastic demand
Change in price induces exactly the same change in demand
PED = 1
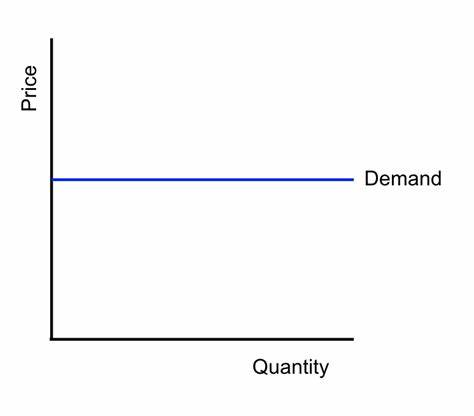
Perfectly elastic demand
Demand is highly sensitive to price change
e.g. A slight decrease in price would lead to an infinite quantity demanded
PED= infinite
Completely inelastic demand
Demand does not change regardless of price change
PED=0
Factors determining PED
Substitutability
Percentage of income= Goods that take up a large amount of income are elastic
Necessities or luxuries
Width of market definition=when a market is narrow(specific) demand is elastic because there are substitutes. Contrastingly a broad markets are inelastic because there are fewer close substitutes)
Time= Demand is elastic in the long run, because it takes time to adjust. But response is greater in the short run because consumers may choose to economise in the first few weeks
Market supply
Quantity of goods and services that all firms plan to sell at different prices
Law of supply
As a goods price increases more is supplied
Why do supply curves slope upward
To illustrate the assumption that the primary objective of all firms are to maximise profit
What causes the supply curve to shift?
Cost of productions
Technical progress
Taxes imposed by gov
Subsidies
What is expenditure tax?
VAT and duties imposed by the government that increase the cost of production
Expenditure tax is known as indirect tax as consumers indirectly pay this tax in the form of a higher price
Define ad valorem tax
It is VAT
The amount of VAT paid depends on the value of the good
e.g. If VAT is 20% tax on gold worth £1 is 20p
Tax on gold worth £2 is 40p
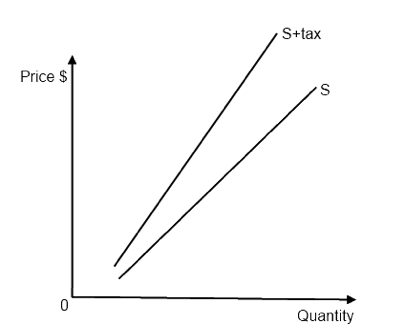
What is specific/unit tax
Tax that does not depend on the price of the good
Define shifted incidence of tax
and unshifted incidence of tax
Part of the tax passed onto consumers
Part of the tax paid by firms
What does a firms ability to pass incidence of tax to consumers depend on?
Ability to pass on tax is highest when demand is inelastic
And non existent when demand is perfectly elastic
Price elasticity of supply (PES)
Measures how the supply of a good responds to a change in the price of a good
% change in Q supplied / %Change in price
Unitary supply curve
Change in price leads to a proportional change in supply
Factors determining PES
Length of production process
Availability of spare capacity
Accumulating stock
Ease of switching between methods of production
Ease of entering the market
Length of production period effect on PES
If raw materials can be converted into finished goods quickly supply will tend to be more elastic
Effect of spare capacity on PES
If spare capacity like labour and raw materials is readily available
Production can be increased quickly
More spare capacity = PES is elastic
Effect of accumulating stock on PES
When stock of unsold finished goods are stored
Firms can responds quickly to price/demand changes
Making PES elastic
(If prices fall, firms can divert production away from sales and into stock accumulation)
Effect of easily switching between methods of production on PES
When firms can efficiently switch between how they produce goods (capital/labour intensive)
Supply is elastic
Effect of easily entering the market on PES
If there are a lot of firms in the market, a new firm can enter easily
Making PES elastic
(*Because with more firms, supply of goods increases)
Income elasticity of demand (YED)
Measures how demand responds to a change in income
% change in Q demanded / % change in come
What is YED for normal and inferior goods?
YED is always positive for normal good and negative for inferior good
As Q demanded of an inferior good falls as income rises and Q demanded for a normal good rises with income
Normal goods
Can be luxury or basic goods
Luxury goods YED is greater than +1
Basic goods YED is between 0-+1
(YED increases more than proportionately for luxury goods)
Cross elasticity of demand (XED)
Measures the extent to which the demand for a good changes in response to a change in price of another good
% change of Q demanded for good A / % change in price of good B
What are the different possibilities of XED
Substitute goods will have a positive XED
Complementary goods will have a negative XED (Because if price of 1 increases, demand for both decreases)
Unrelated goods will have an XED of 0
Close substitutes and their XED
Close substitutes will have a higher XED than weaker substitutes
Strong complements and their XED
Strong complements have a lower XED
XED of -1.6 shows stronger complementary goods than an XED of -0.28
Define market equilibrium
Demand = supply
What can market disequilibrium be caused by?
Excess demand or excess supply
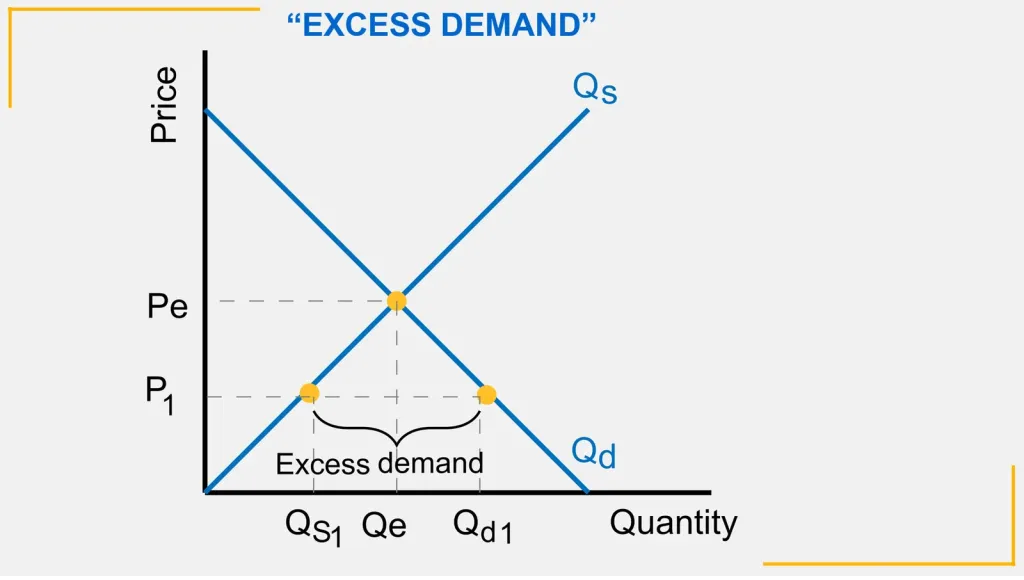
Disequilibrium caused by excess demand
Excess demand can be caused by price being below market equilibrium.P1 is below Pe
Excess demand causes disequilibrium as supply does not increase at the same rate
Prices must rise to ration demand and achieve equilibrium .Higher prices reduce demand and incentivise firms to produce more
There will be an extension of supply and contraction of demand
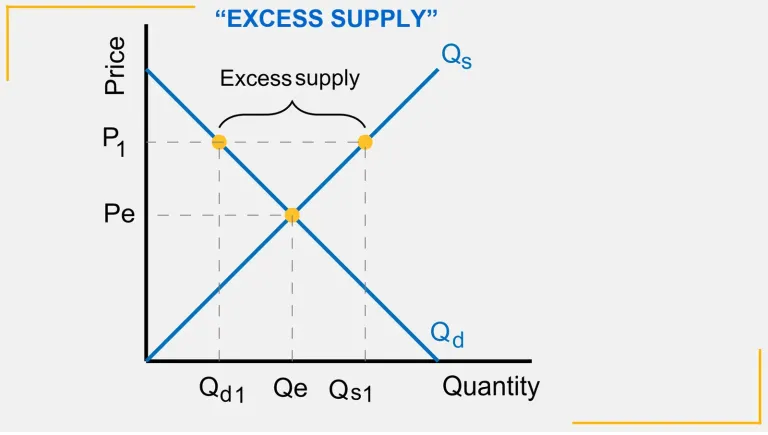
Disequilibrium caused by excess supply
At P1 prices are above market equilibrium. Firms are supplying more
This causes disequilibrium as there is excess supply and not enough demand
Prices must be reduced to stimulate demand and for firms to produce less
There will be an extension of demand and a contraction of supply
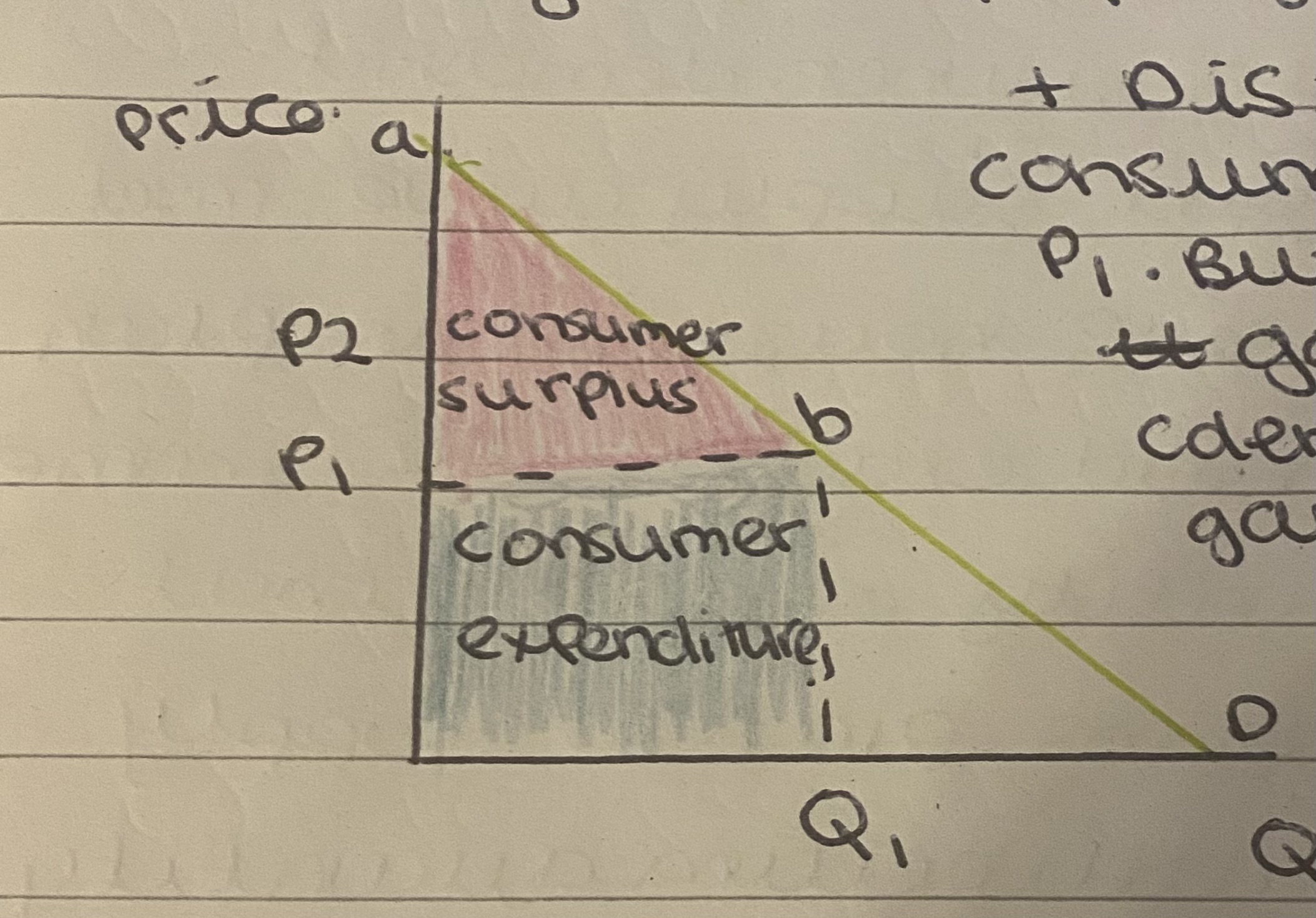
What is consumer surplus?
Difference between the price consumers are willing to pay and the price they actually end up paying (for a good/service)
Consumer surplus diagram
Distance from a to b shows that consumers were willing to pay more than P1
But because they were able to buy the good for less, utility gained which is demonstrated by the consumer surplus is high
If prices were to rise consumer surplus would decrease.
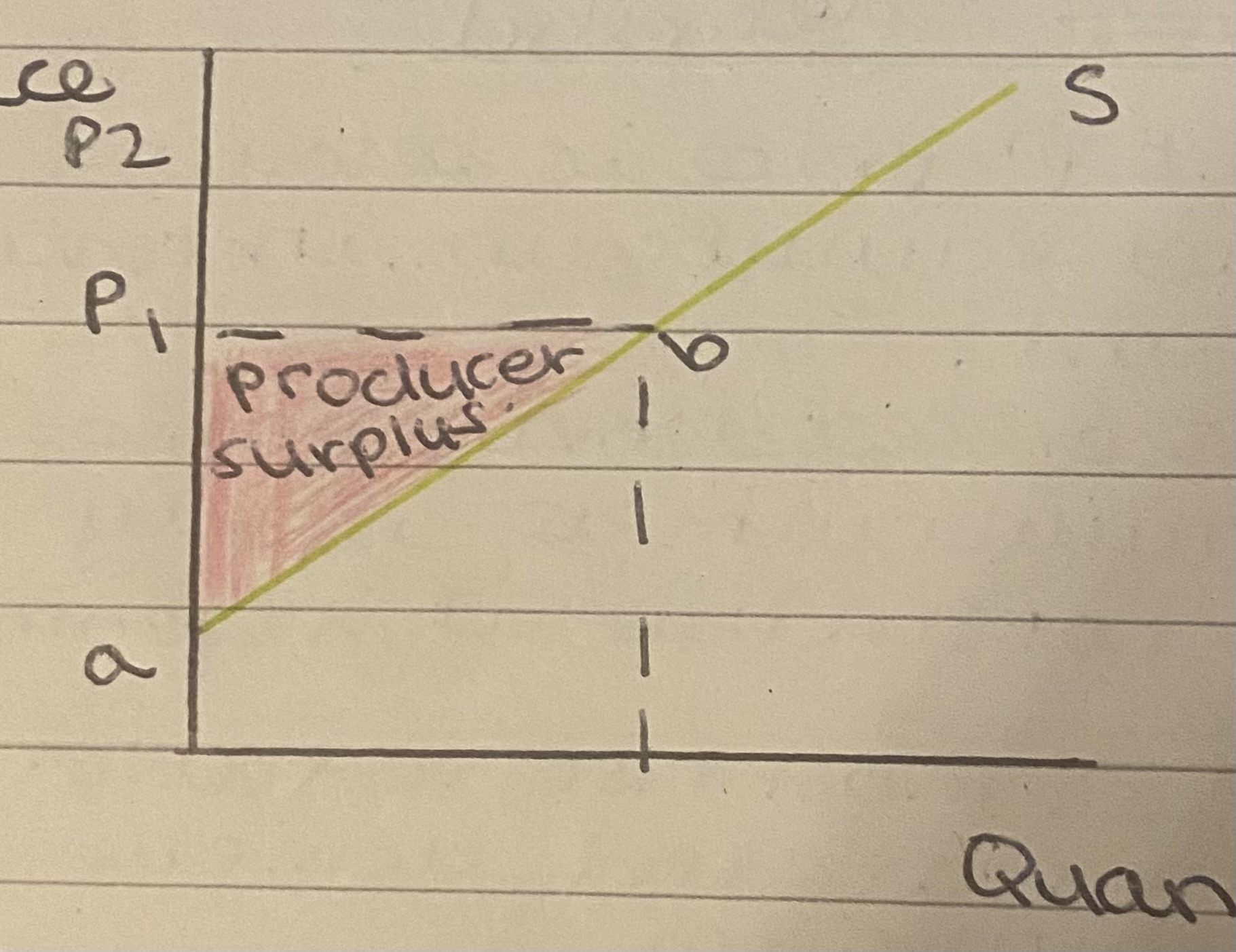
Define producer surplus
The difference between the price producers are willing to supply a good for and the market price.
Producer surplus diagram
The distance between a and b shows that producers were willing to supply goods below market price (P1)
But as they are able to sell it at a higher price, they gain profit and thus gain producer surplus
If prices rise, surplus rises.
What can be understood by “interrelationship between markets”
Refers to how different markets influence and interact with each other
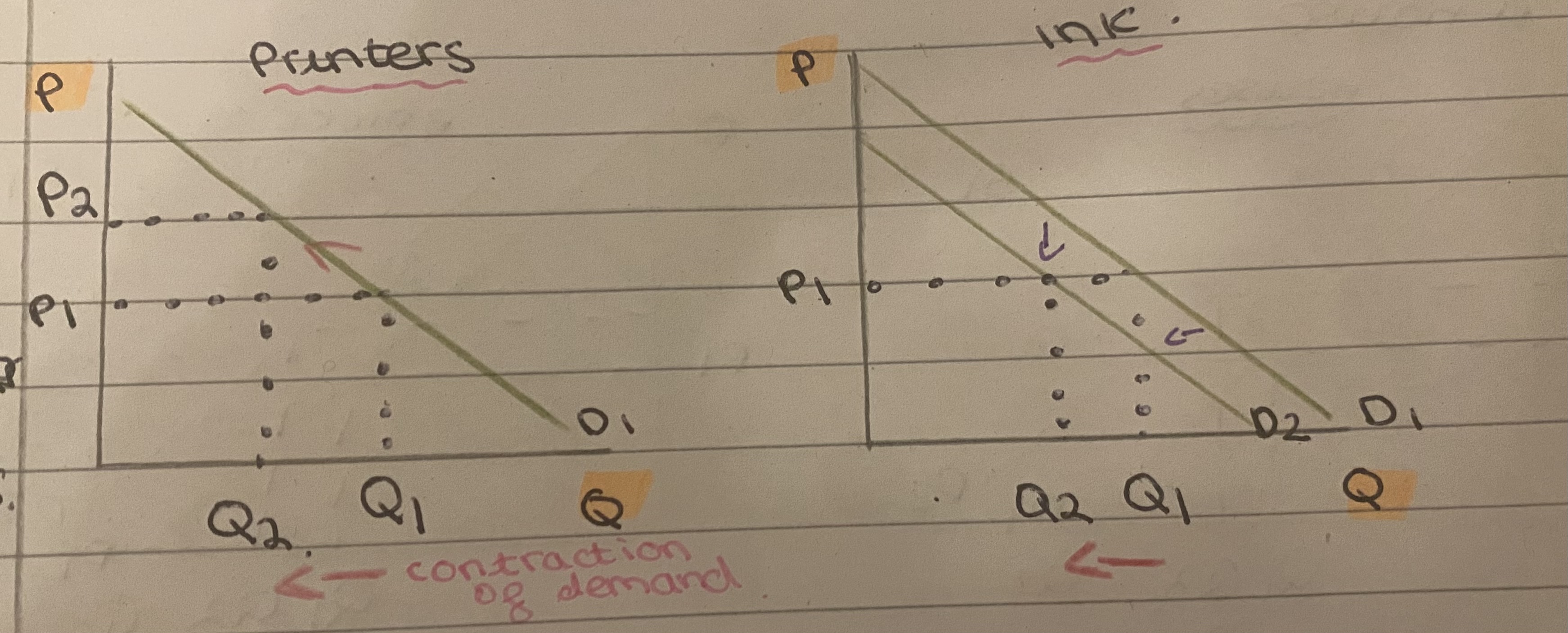
What is joint demand?
Goods that are bought in conjunction (complements) e.g. Printer and ink
If the price of printers increase, Q demanded is lower. So demand for ink experiences a leftward shift
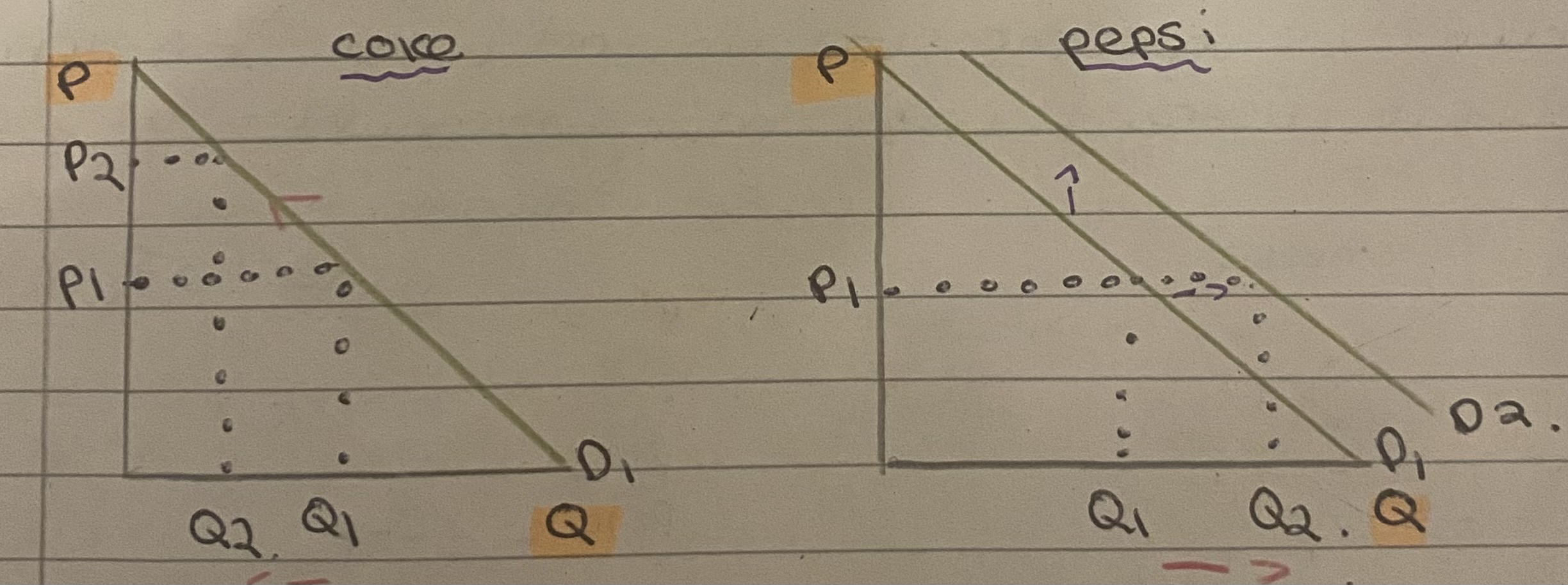
Define competitive demand
Goods that can be interchanged (substitutes)
E.g coke and Pepsi
If price for coke increases, there will be a contraction of demand. But Pepsi will see a rightward shift in the demand curve
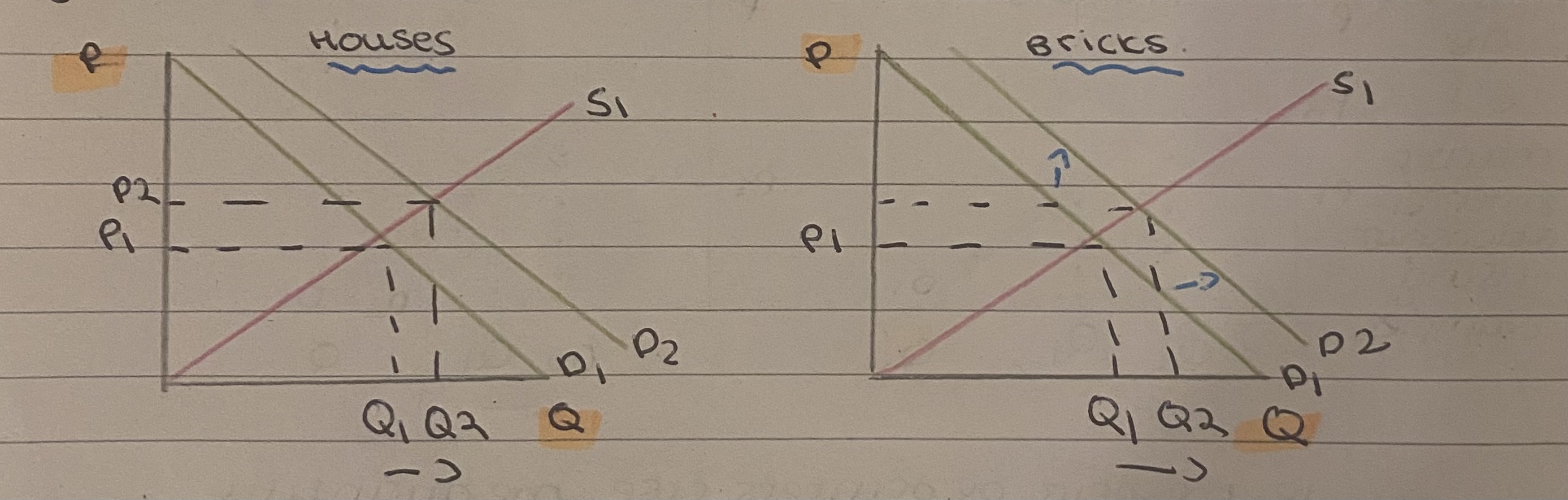
Define derived demand
Some goods/services are demanded because they are needed for the production of another good. E.g house and bricks
If the demand for houses increases, so does the demand for bricks. The demand for bricks is derived from the demand of houses.
Define composite demand
A product is in composite demand when it is demanded for several different uses.
E.g. Milk → Cheese and Butter
If demand for cheese increases, more of it will be produced. More milk is used in the production of cheese.
Therefore supply for butter will shift left as there is not enough milk to produce butter
Diagram for composite demand
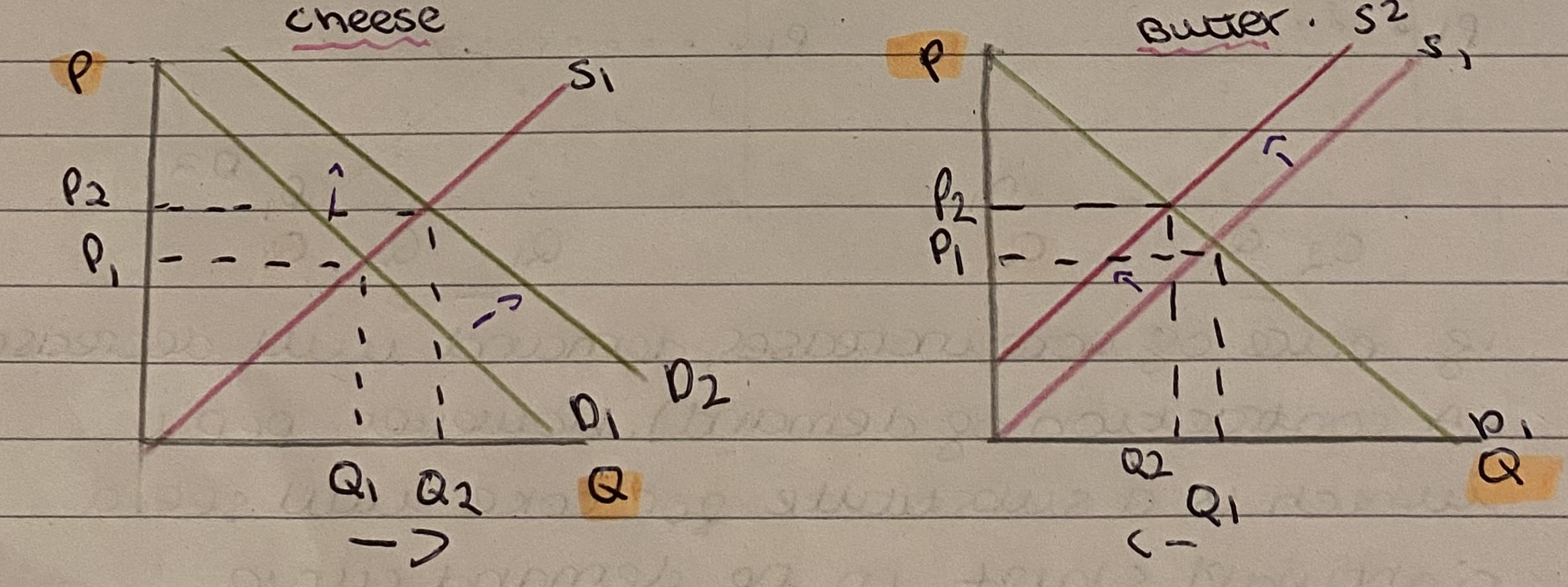
Define joint supply
An increase/decrease in the supply of one good leads to an increase/decrease in the supply of a by product
E.g. Honey → Beeswax
If demand for honey increases. Production of it will increase. As there is more quantity of honey produced, supply of beeswax increases as it is a by product of the honey.
Diagram for joint supply
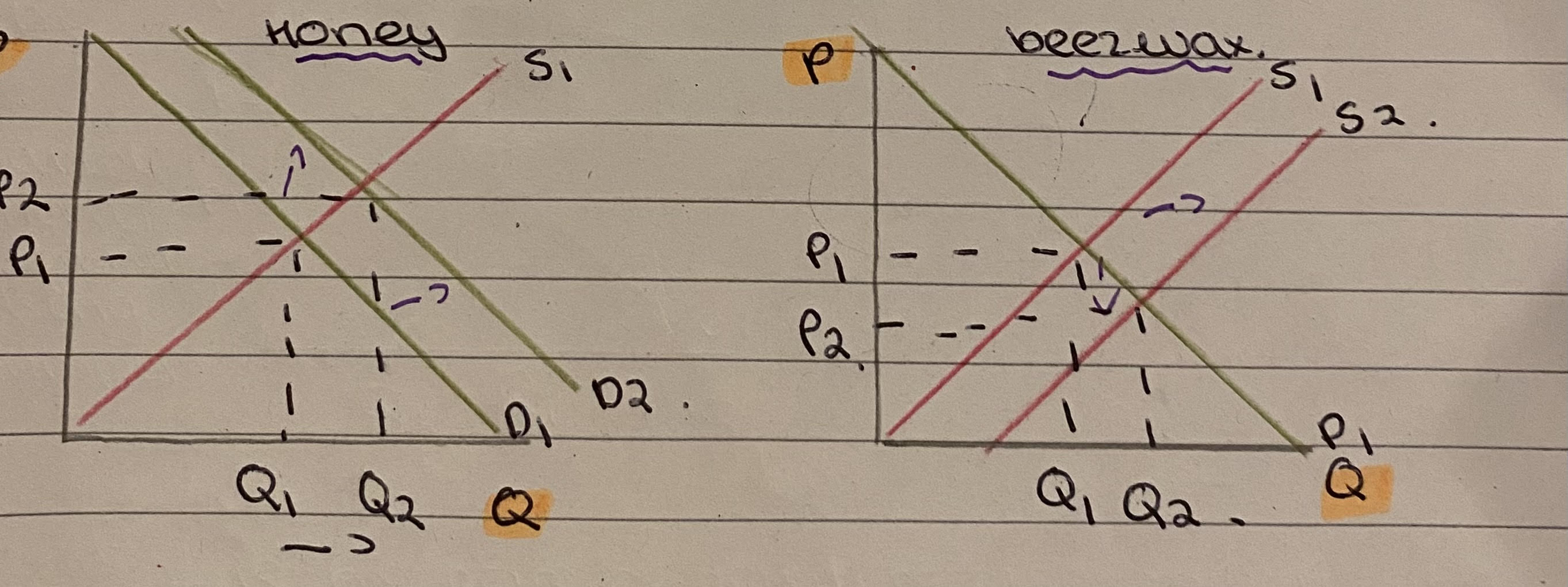
Define competitive supply
Goods are in competitive supply when raw materials that are used to produce one good can’t be used to produce another
E.g. Timber and paper both need wood
If demand for timber increases, more of it will be produced and there will be less wood available to produce paper so supply shifts left
Diagram for competitive supply
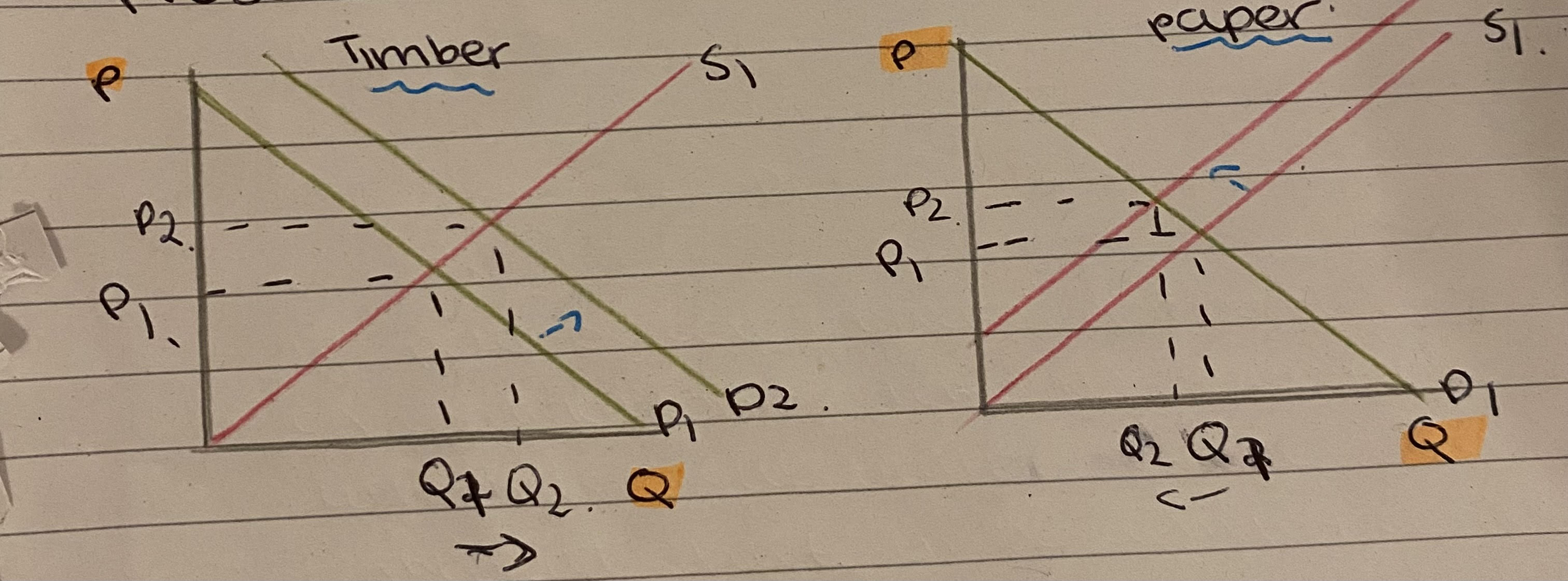
Why are agricultural markets prone to disequilibrium?
The supply curve can shift randomly due to climatic factors. Drought can reduce crop yield