Microbiology Lab Final
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
tears, saliva, mucus, and breast milk contain the enzyme ___ that destroys certain bacteria.
lysozyme
which first-line defense molecules produced by the immune system kill pathogens, and pathogens rarely become resistant to them?
AMPs
which subcategory of first-line defenses does skin belong to?
physical barriers
swollen ___ indicate that a foreign antigen is present, and leukocytes are rapidly multiplying to mount an immune response.
lymph nodes
the thymus and bone marrow are considered ___ lymphoid tissue.
primary
the majority of secondary lymphoid tissue is called ___, and includes Peyer’s patches, tonsils, and the appendix.
MALT
which granulocyte when stained exhibits red-orange granules, is moderately phagocytic, and attacks allergens and parasites?
eosinophils
which granulocyte contains granules packed with histamine, that stain dark purple?
basophils
which agranulocyte has a large horseshoe-shaped nucleus, and matures into either fixed or wandering macrophages?
monocytes
signaling proteins that support cell-to-cell communication and initiate and coordinate immune responses are called ___. examples of these signaling proteins are interleukins and interferons.
cytokines
which complement pathway has complement proteins that are directly activated by interacting with a pathogen?
alternative pathway
which of the following is NOT a hallmark sign of inflammation?
fever
fever-inducing agents released by certain microbes are called ___.
pyrogens
___ cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity and ___ cells are involved in humoral immunity.
T; B
T cells can be classified by certain glycoproteins on their surface called clusters of differentiation (CD). T helper cells are classified as ___, and T cytotoxic are classified as ___.
CD4; CD8
what is the function of activated macrophages in cell-mediated immunity?
enhances phagocytic activity
once T or B cells are activated, they proliferate and differentiate into active immune cells and ___ cells that protect the body from reinfection from the same pathogen.
memory
T helper cells produce cytokines that signal B cells to produce plasma cells, and T ___ cells, that function to destroy infected cells, cancer cells, and transplanted tissues.
cytotoxic
the T helper cell subclass that stimulates B cells to proliferate and differentiate is called ___.
TH2
which of the following is a function of antibodies?
all answers are functions of antibodies
which antibody isotype can be monomeric or dimeric, and is the primary antibody found in breast milk?
IgA
which antibody isotype can be monomeric or pentameric, and is produced early in infection?
IgM
what category of immune deficiencies results from genetic causes?
primary immunodeficiency
what category of autoimmune diseases results in damage to diverse tissues throughout the body?
systemic
the cause of autoimmune diseases is unclear, but genetic predisposition, and exposure to ___ may lead to these disorders.
certain infectious agents
the body’s response to an antigen which is beyond what is considered normal is called a/an ___ response.
hypersensitivity
it is unclear why hypersensitivities develop, but genetics and environmental factors may play a role. another proposed factor suggests that individuals living in developed countries may have weaker immune systems due to accessibility of clean food, and water, antibiotics, and minimized exposure to diseases. this is known as the ___ hypothesis.
hygiene
when an allergen is recognized by the immune system, it mounts a humoral response producing IgE antibodies which bind to mast cells or basophils. upon subsequent exposure, the allergen binds to the IgE located on the mast cell or basophil which causes degranulation of chemical mediators. name the chemical mediator blocked by Benadryl.
histamine
systemic anaphylaxis is also known as ___.
anaphylactic shock
conditions such as asthma and seasonal allergies are caused by what type of hypersensitivity reaction?
type 1
what would likely occur if an individual with type A blood receives type B blood during a transfusion?
hemolysis of RBCs
ABO blood incompatibility reactions are an example of what type of hypersensitivity reaction?
type 2
what would happen the FIRST time an Rh- woman is pregnant with an Rh+ fetus?
antibodies to Rh factor would develop in the mother
when does hemolytic disease of the newborn occur?
when a previously sensitized Rh- woman is pregnant with her second and subsequent Rh+ fetus
name the condition caused by generation of an immune response against administered medications such as antitoxins and penicillin?
serum sickness
what type of hypersensitivity reaction is caused by the complexing of soluble antigens with antibodies that are deposited into tissues?
type 3
what type of hypersensitivity reaction is responsible for autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus?
type 3
___are small molecules that are in-and-of themselves incapable of eliciting an immune response.
haptens
what type of hypersensitivity reaction is associated with transplant rejection?
type 4
what type of hypersensitivity reaction is associated with allergic contact dermatitis?
type 4
what type of hypersensitivity reaction is the only one that isn’t antibody-mediated?
type 4
a patient has been diagnosed with a wart, a type of primary lesion known as a papule. describe the appearance of a papule.
raised solid lesion that isn’t fluid filled
a patient has been diagnosed with psoriasis. psoriasis body lesions are caused by the shedding of the outer layers of the skin, so that the skin surface appears flaky. what is the name of the secondary lesion that the patient is exhibiting?
scale
Fred has developed a large blister on his foot. what is the name of the primary lesion that he is exhibiting?
bulla
Jamie gave birth to her first child after 15 hours of labor. the next day, she looked in the mirror and noticed small, red pinpoint-sized spots on her face. Jamie asked the nurse about the spots and he told her that capillaries had burst under her skin during the strenuous delivery. what is the name of the secondary lesions on Jamie’s face?
petechiae
rubeola is also known as ___ and the etiological agent is ___.
measles; measles virus
what type of pathogen causes rubella and rubeola?
virus
rubella is also known as ___ and the etiological agent is ___.
German measles; rubella virus
fifth disease is sometimes called ___ syndrome, because of the appearance of the rash.
slapped cheek
which maculopapular rash-producing disease is caused by human parvovirus B19?
fifth disease
what etiological agent causes roseola?
human herpes virus 6 and 7
Coxsackievirus 16 and enterovirus 71 are the main viruses that cause ___ disease.
hand, foot, and mouth
what is the etiological agent of smallpox?
variola virus
which is the etiological agent of chickenpox?
varicella-zoster virus
reactivation of latent (dormant) viruses cause shingles and reoccurring cold sores. name these two viruses.
varicella and HSV-1
fever blisters are vesicular/pustular rashes that usually occur around the mouth area. what is the etiological agent of fever blisters?
HSV-1
what is the etiological agent of necrotizing fasciitis?
Streptococcus pyogenes
what is the etiological agent of scalded skin syndrome and impetigo?
Staphylococcus aureus
You diagnose your patient with cellulitis but do not know if the causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. You run the following tests and obtain these results:
Blood agar: beta hemolytic
Gram stain: Gram-positive cocci
Catalase: positive
Coagulase: positive
Which is the likely organism that is causing your patient’s cellulitis?
Staphylococcus aureus
Clostridium perfringens is the etiological agent of ___.
gas gangrene
MRSA and VRSA are antibiotic resistant forms of which bacteria?
Staphylococcus aureus
cutaneous anthrax is caused by what type of microbe?
bacteria
otitis externa is caused when the ear is infected with ___.
Pseudomonas
the genus of the etiological agent of acne is ___.
Propionibacterium
Tinea corporis means ringworm of the ___.
body
what type of microbe causes cutaneous candidiasis?
yeast
tinea infections are caused by what type of microbe?
fungus
conjunctivitis can be caused by bacterial and viral pathogens. what microbe is the main cause of viral conjunctivitis?
adenovirus
what is the etiological agent of ophthalmia neonatorum?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
what microbe is the etiological agent of the eye disease, trachoma?
Chlamydia trachomatis
what eye disease is the leading cause of preventable microbial blindness?
trachoma
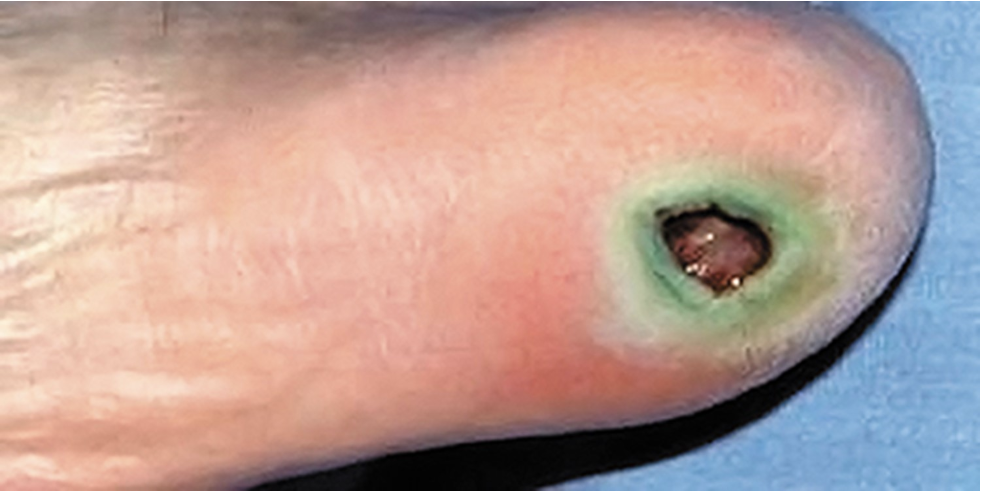
what genus of bacteria likely caused this greenish-colored lesion?
Pseudomonas
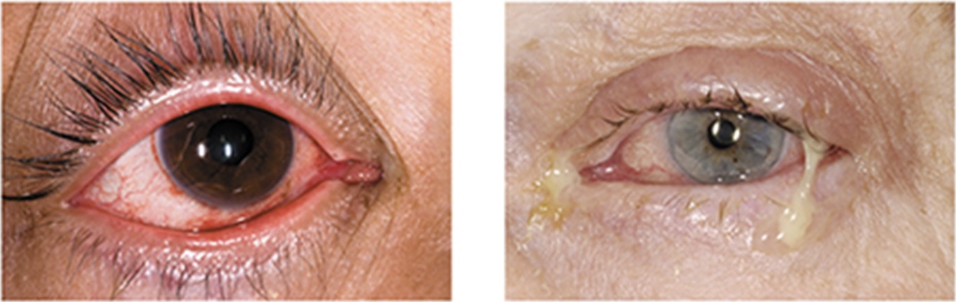
which picture likely represents viral conjunctivitis?
left hand side image
what disease does this vesicular/pustular rash depict?
smallpox
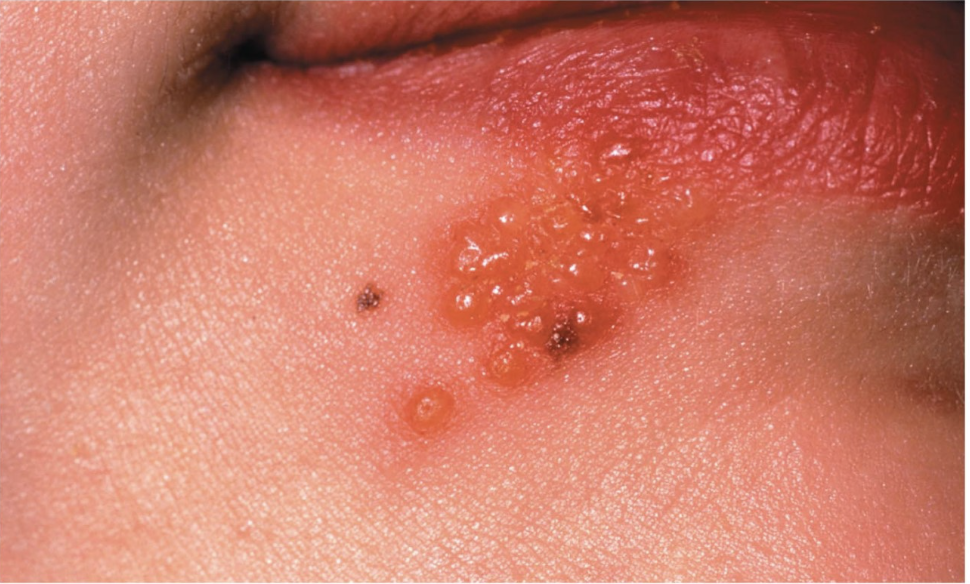
this image depicts an individual who has cold sores. what type of microbe causes cold sores?
virus
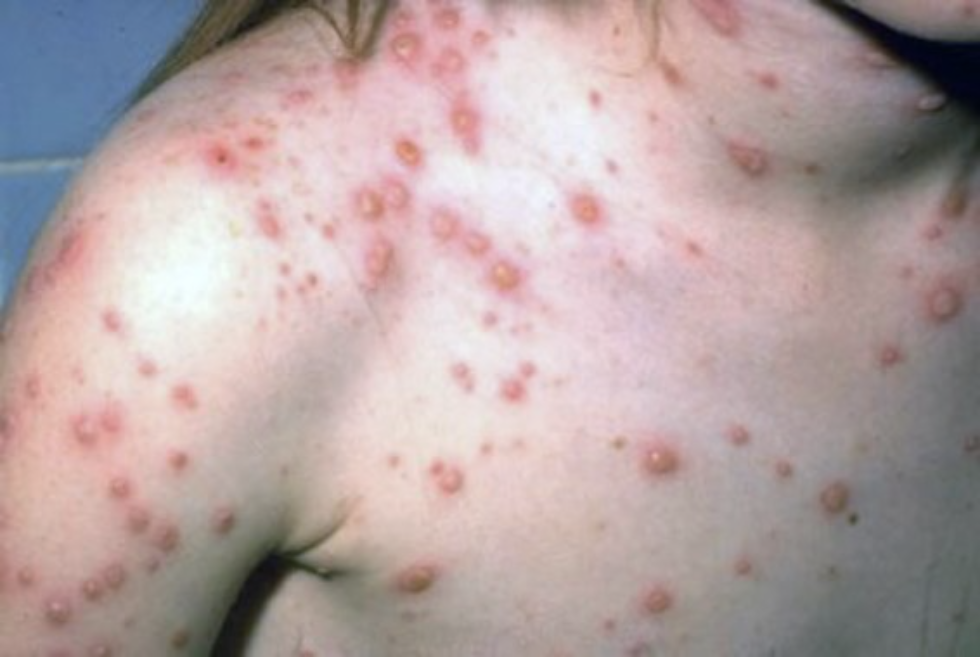
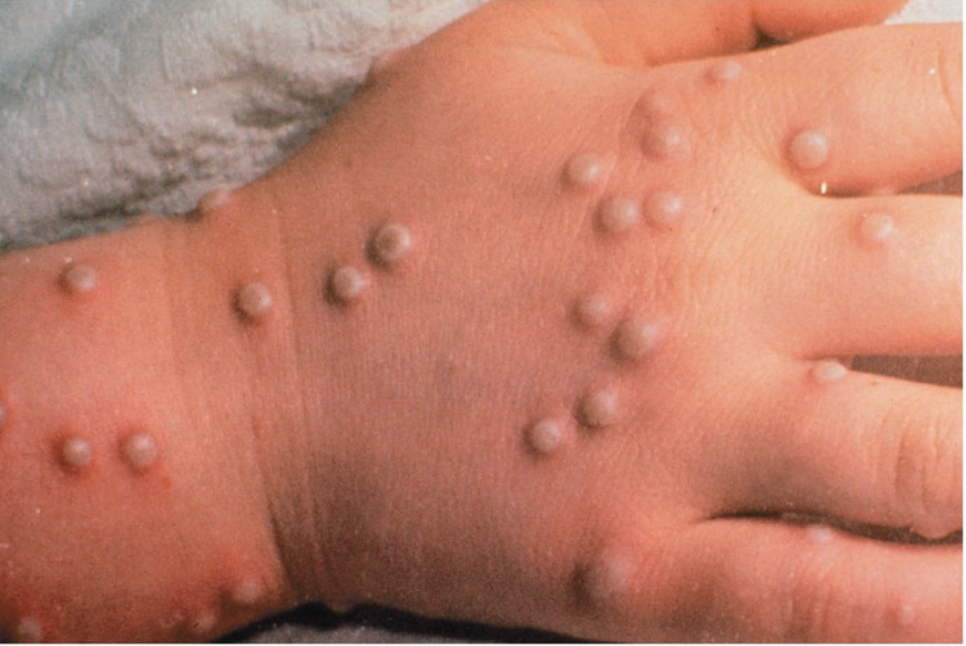
the image is of a child who has the chickenpox. what type of rash does chickenpox present with?
vesicular/pustular rash
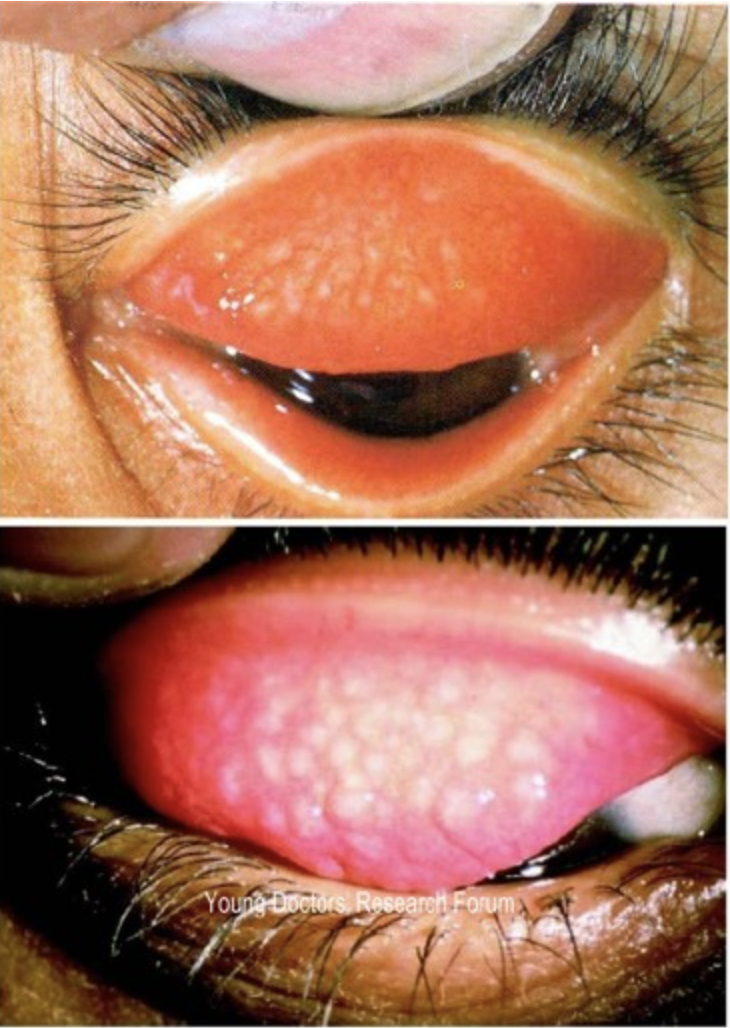
what bacterial eye infection that can cause irreversible blindness is depicted in this image?
trachoma
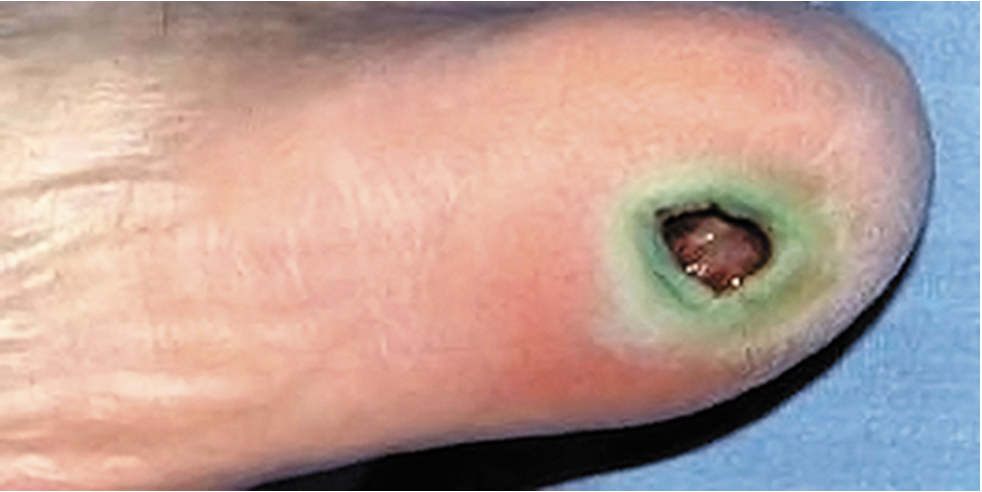
this greenish lesion is caused by a bacterial virulence factor called ___.
pyocyanin
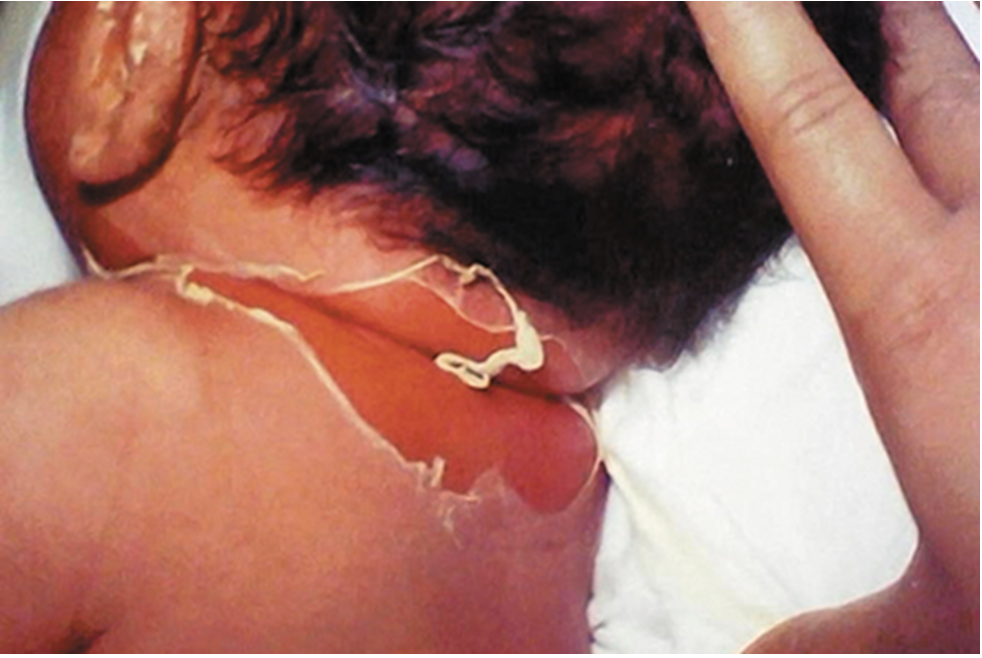
what is the name of the infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus that is depicted in the image?
scalded skin syndrome
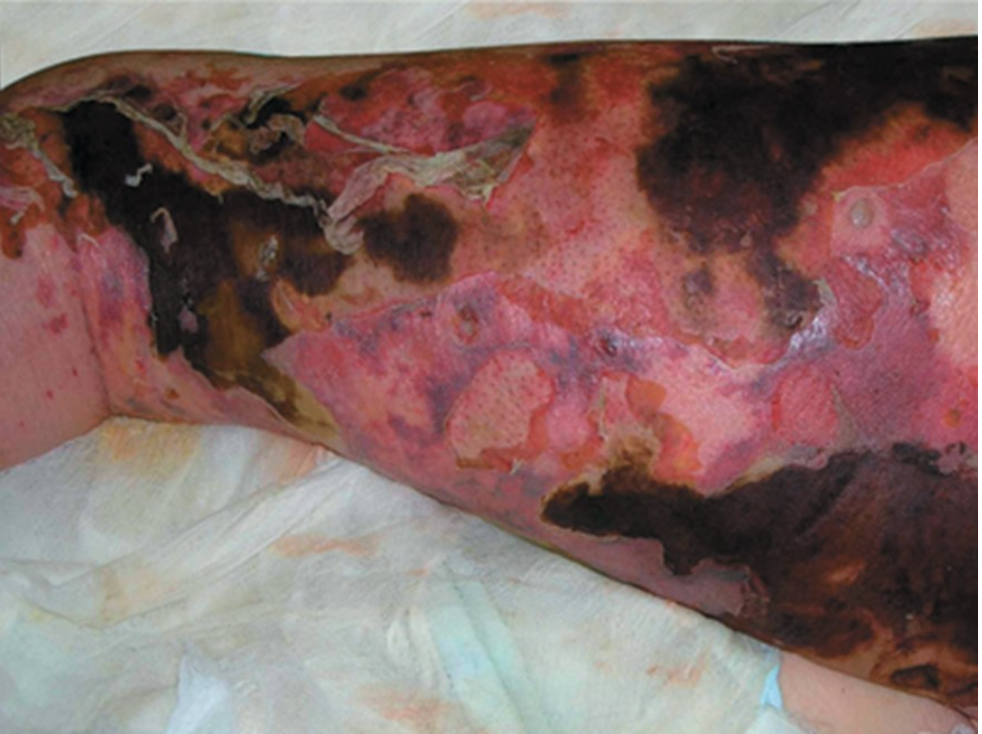
what is the name of the infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes that is depicted in the image?
necrotizing fasciitis
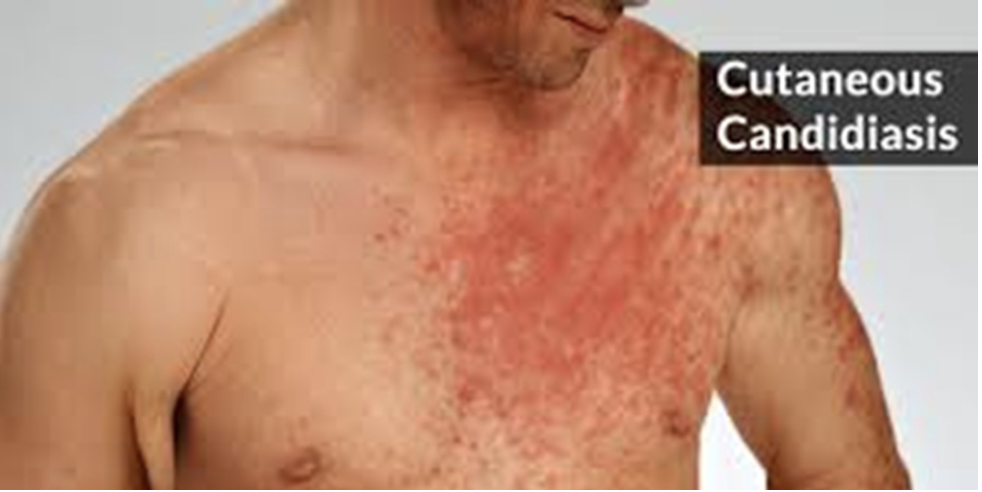
what is the microbe that mainly causes cutaneous candidiasis?
Candida albicans
the glycolipid substance that forms an insulating sheath around certain CNS and PNS nerve axons is called ___.
myelin
the nervous system is divided into the ___ nervous system and the ___ nervous system.
central; peripheral
the suffix “-itis” means ___.
inflammation of
what type of pathogen causes poliomyelitis?
virus
what infection’s diagnostic indicator is the presence of Negri bodies within a neuron?
rabies
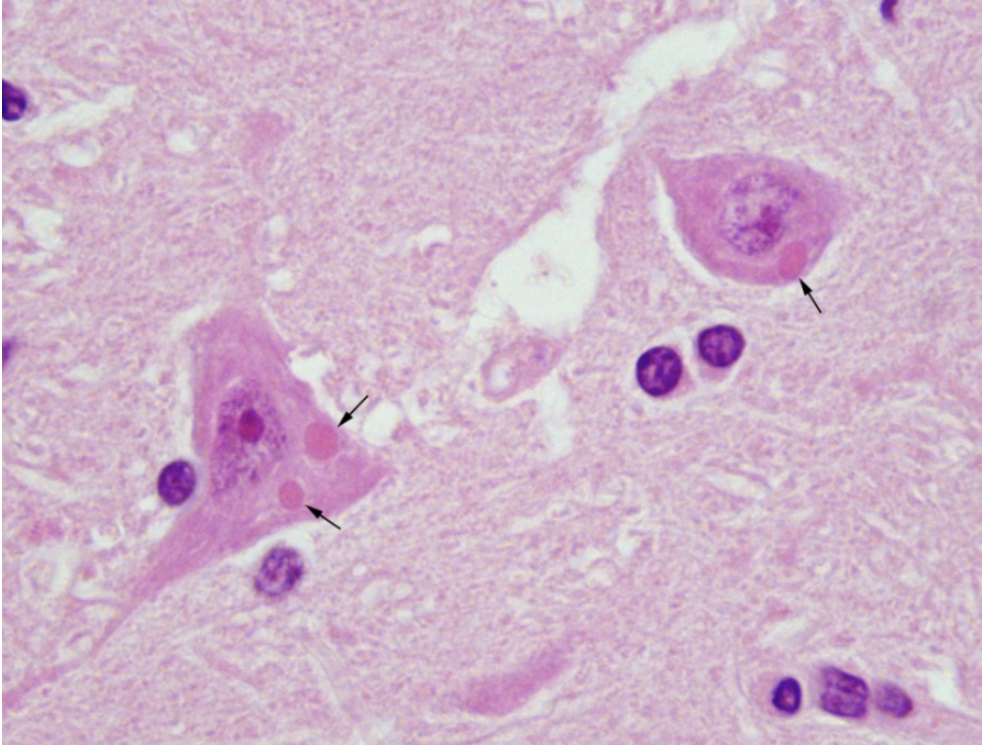
a patient with a suspected case of rabies died in the hospital last night. to confirm the diagnosis, a histological section of brain tissue was stained, and the following was observed. based on these results, was the diagnosis of rabies confirmed? why or why not?
yes; there is the presence of Negri bodies
what is the vector that spreads West Nile Virus and La Cross Virus to humans?
mosquitos
the word ___ is derived from the shortened form of “arthropod borne” virus.
arbovirus
in most cases, bacterial meningitis is diagnosed by the presence of bacteria in what body fluid?
cerebrospinal fluid
a child presents with a fever, headache, and a stiff neck. the pediatrician suspects pneumococcal meningitis. what is the etiological agent of this form of meningitis?
Streptococcus pneumoniae
a college student presents with a fever, headache, and a stiff neck. the doctor suspects meningococcal meningitis. what is the etiological agent of this form of meningitis?
Neisseria meningitidis
a patient is suspected of having bacterial meningitis. upon analysis, the doctor observes encapsulated gram-negative diplococci in her cerebrospinal fluid. what is the likely etiological agent of the patient’s meningitis?
Neisseria meningitidis
the common name for Hansen’s disease is ___.
leprosy
a powerful toxin called tetanospasmin causes the symptoms of what nervous system infection?
lock jaw
why does infection with Mycobacterium leprae usually effect body extremities such as the fingers and toes?
M. leprae preferentially grows at temperatures between 30-35C
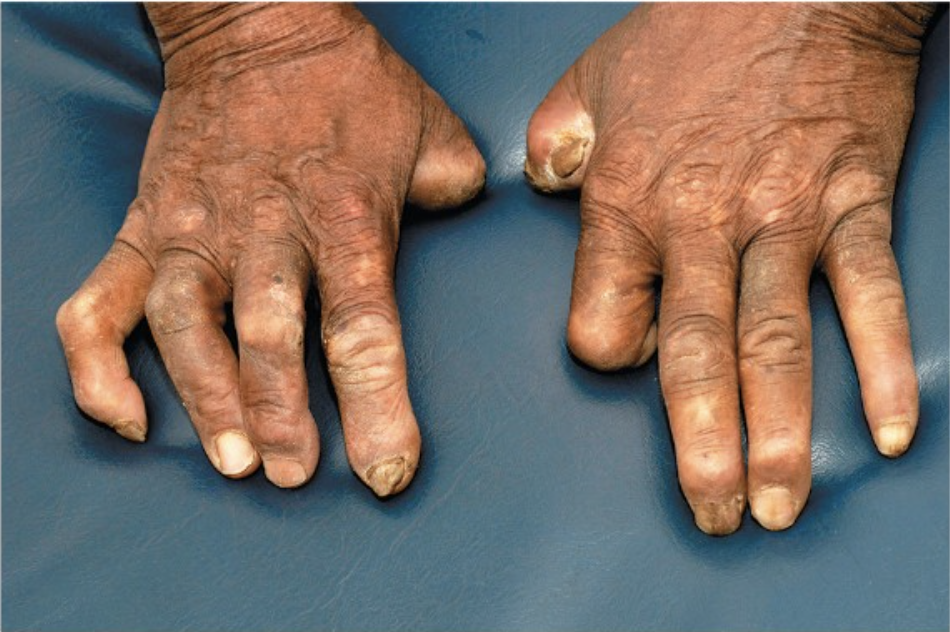
this patient has a disease caused by an acid-fast positive bacterium that grows best between 30-35*C. what bacteria causes this disease and what form of the disease is it?
Mycobacterium leprae; lepromatous form
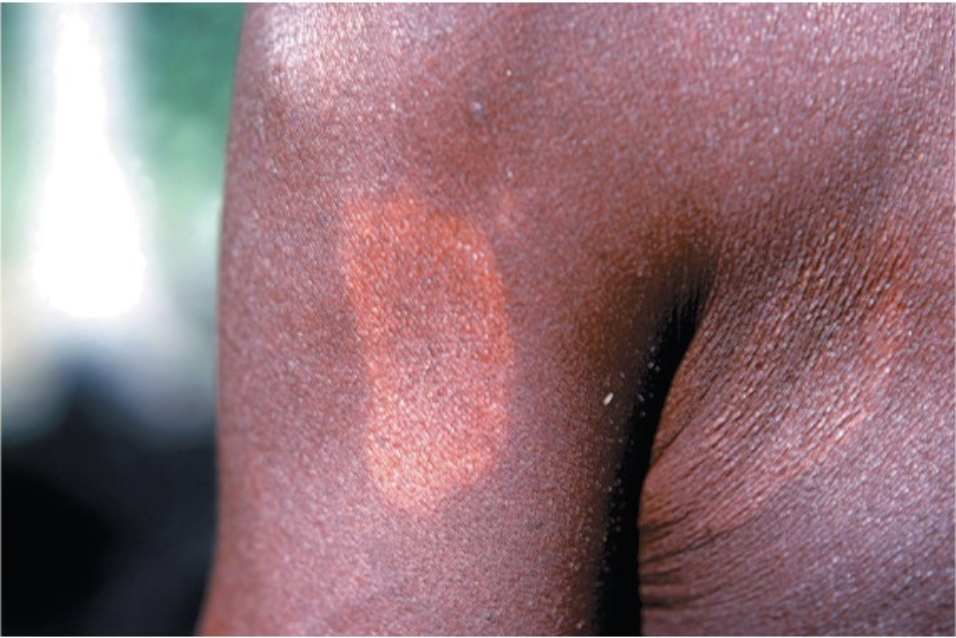
this patient has a disease caused by an acid-fast positive bacterium that grows best just below core body temperature. what is the disease and what form of the disease is it?
Hansen’s disease; tuberculoid form
botulism and tetanus are caused by toxins produced by which genus of bacteria?
Clostridium
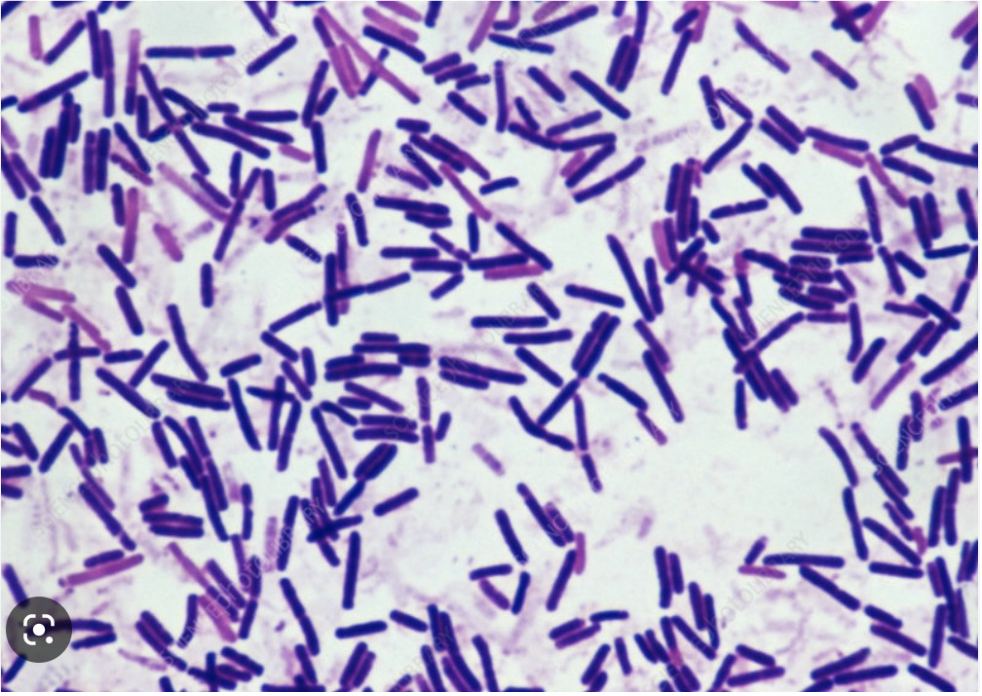
this image depicts the Gram staining result of an organism that causes flaccid paralysis due to the production of an exotoxin that can be produced in contaminated canned vegetables. name this organism
Clostridium botulinum