Fluids and Electrolytes in the Human Body (week 8)
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Electrolyte
Ion, compound that dissociates in water to ions, conducts electricity.
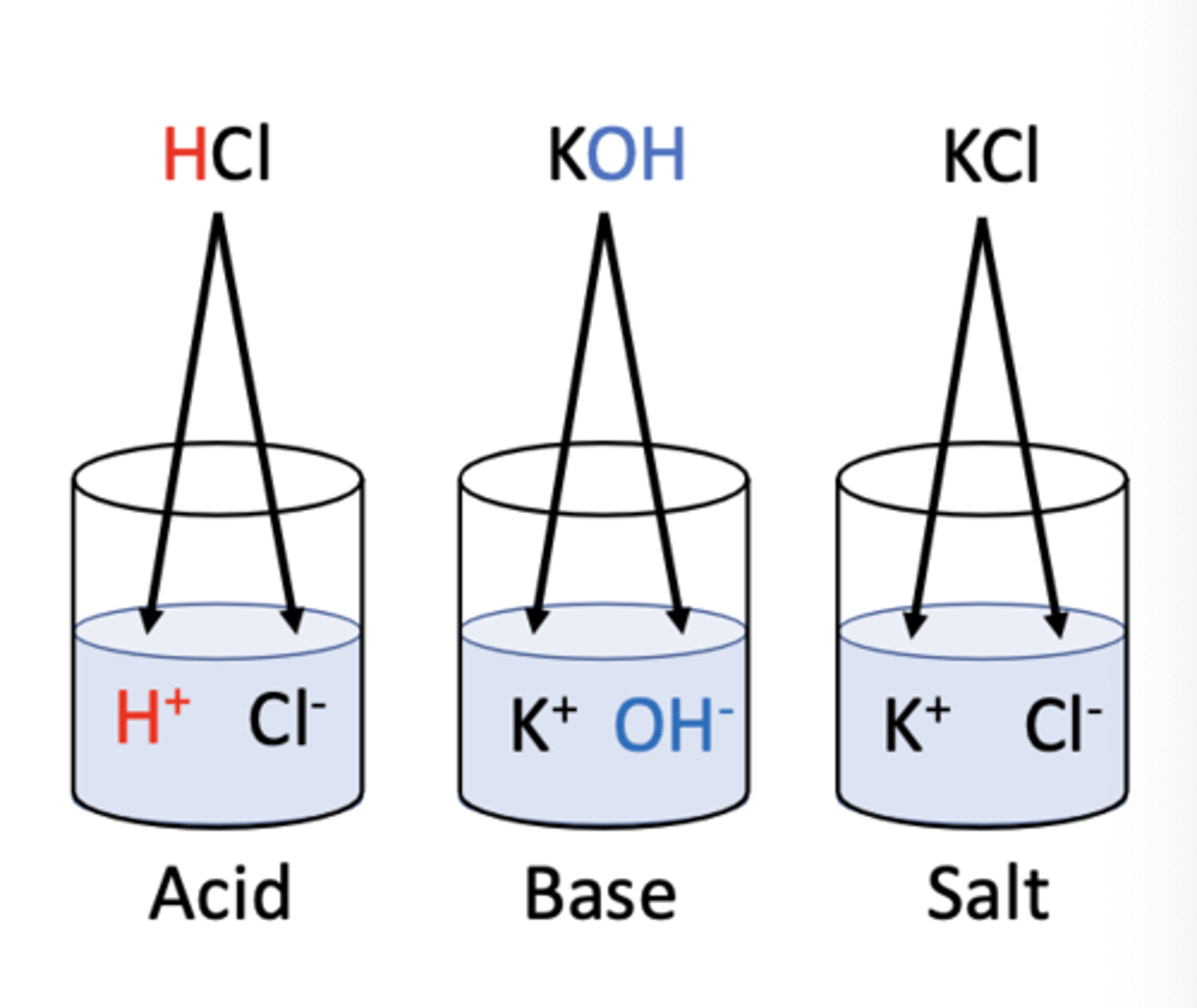
common electrolytes (conduct electricity)
ionic compounds, inorganic acids, inorganic base, salts
Acids
Substances that release H+ ions in water.
Bases
Substances that release OH- ions in water.
Salts
Compounds that dissociate into cations and anions (not H, OH).
Non-electrolytes
Compounds that do not dissociate in water.
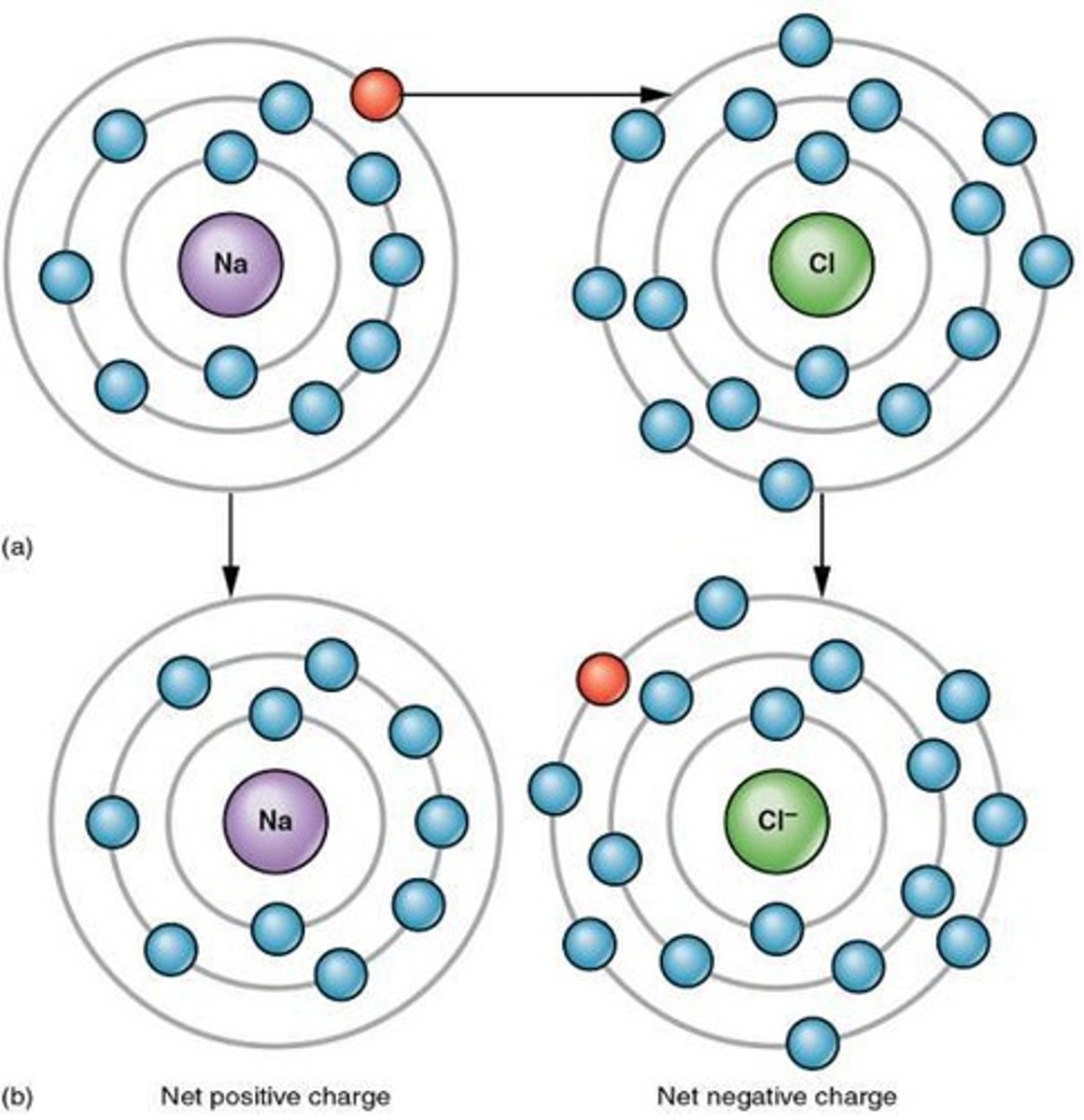
Ionic bonds
Chemical bonds formed by electron transfer of 2 opposing ion charges.
Covalent bonds
Chemical bonds formed by electron sharing, can't be broken except by chem.reactions/intense heat. (Organic compounds: lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids)
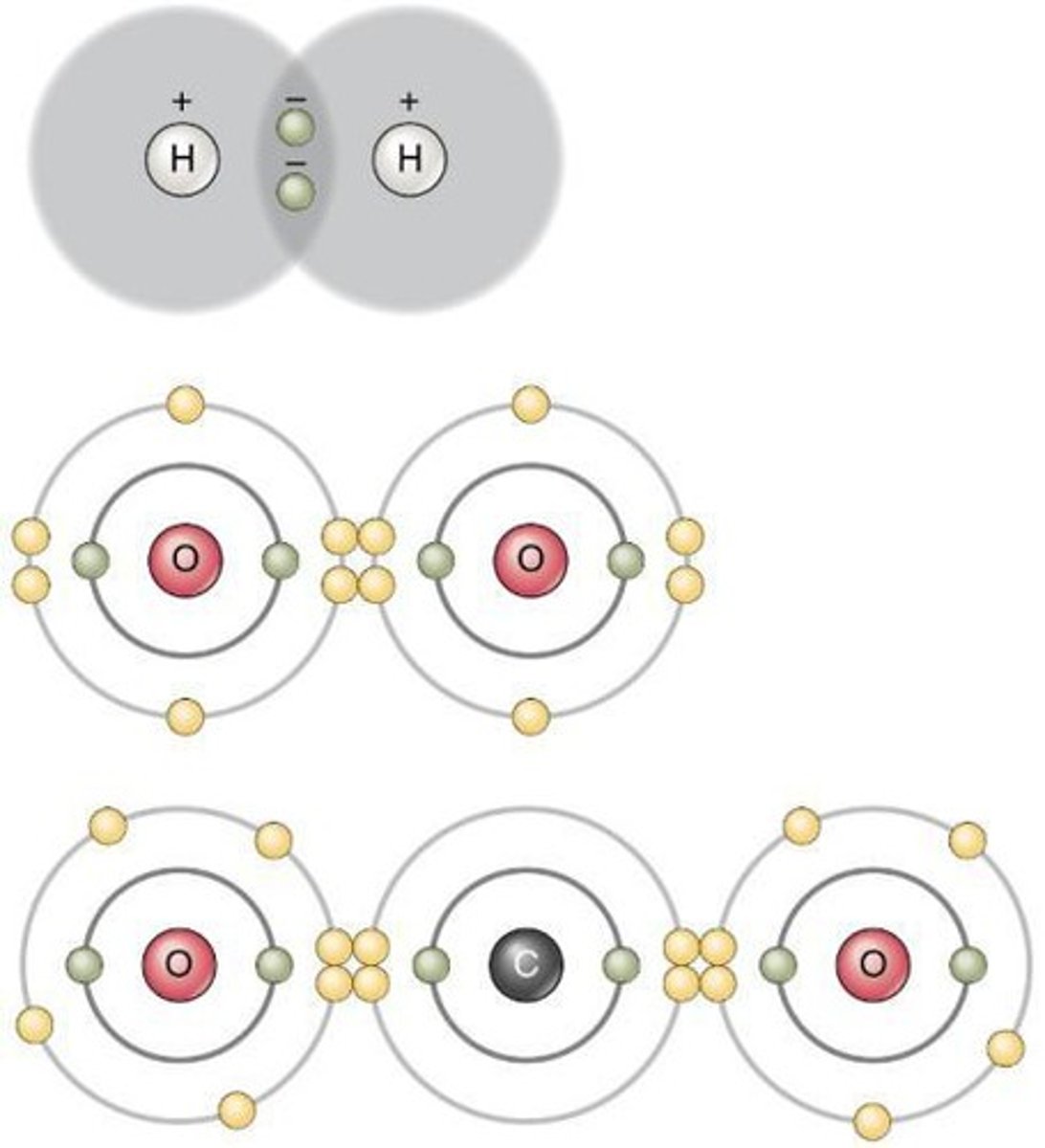
Compounds that don't form ions in water:
non-electrolytes, organic compounds (contain covalent bonds, don't dissociate, shared electron bond can't be broken by water molecules)
functions of electrolytes:
maintain fluid balance & acid-base balance, make electrical currents, be cofactors
Fluid balance
Control of water movement in body compartments.
Acid-base balance
Maintenance of pH levels in the body.
Electrical currents
Generated by electrolytes in muscles and neurons.
Cofactors
Substances that assist enzymes in biochemical reactions.
total body fluid of males, females, infants
60%, 55%, 75%
Intracellular fluid (ICF) (major fluid compartment)
Fluid (cytosol) within cells, comprising 2/3 of body fluids.
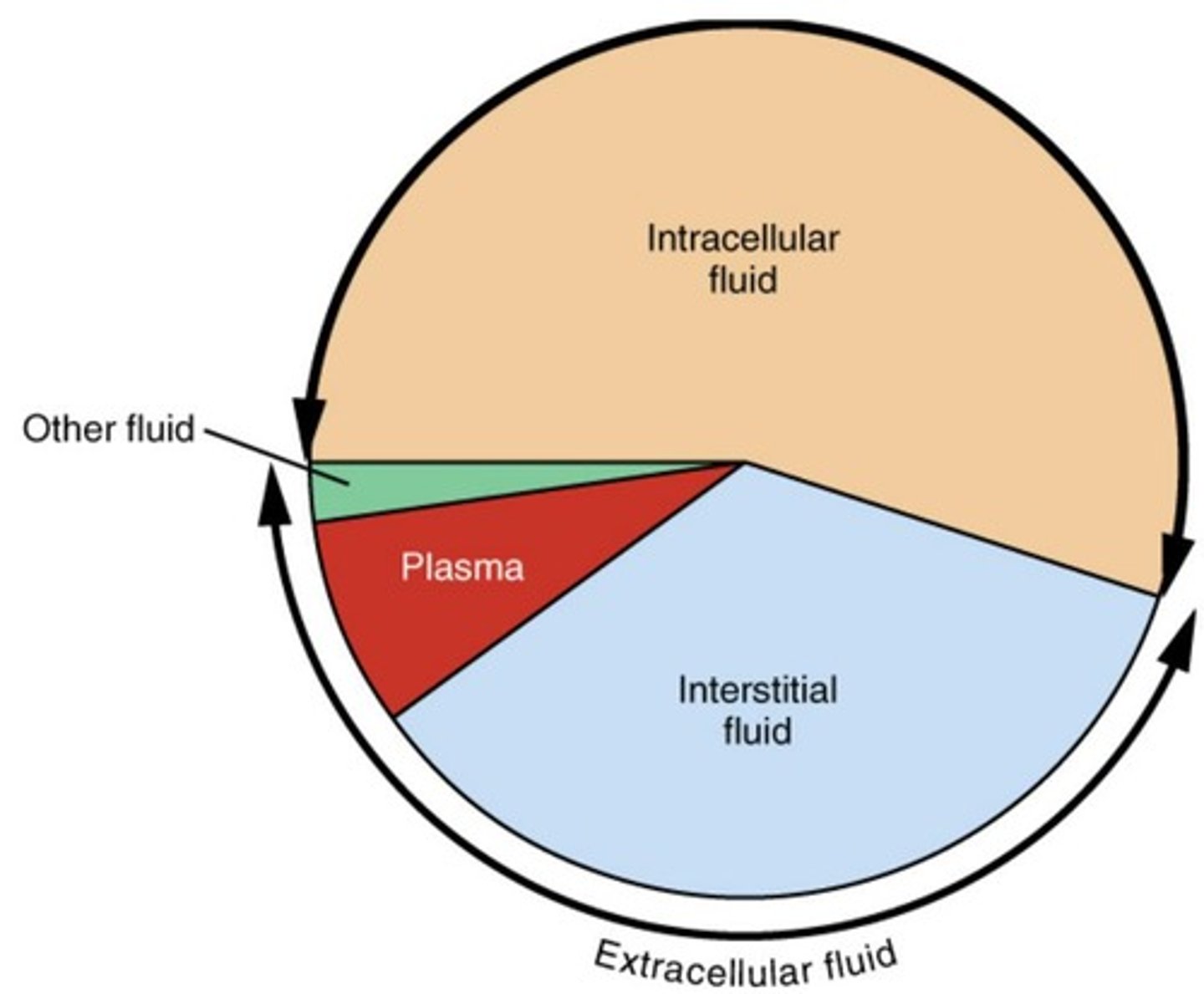
Extracellular fluid (ECF)(major fluid compartment)
Fluid outside cells, comprising 1/3 of body fluids.
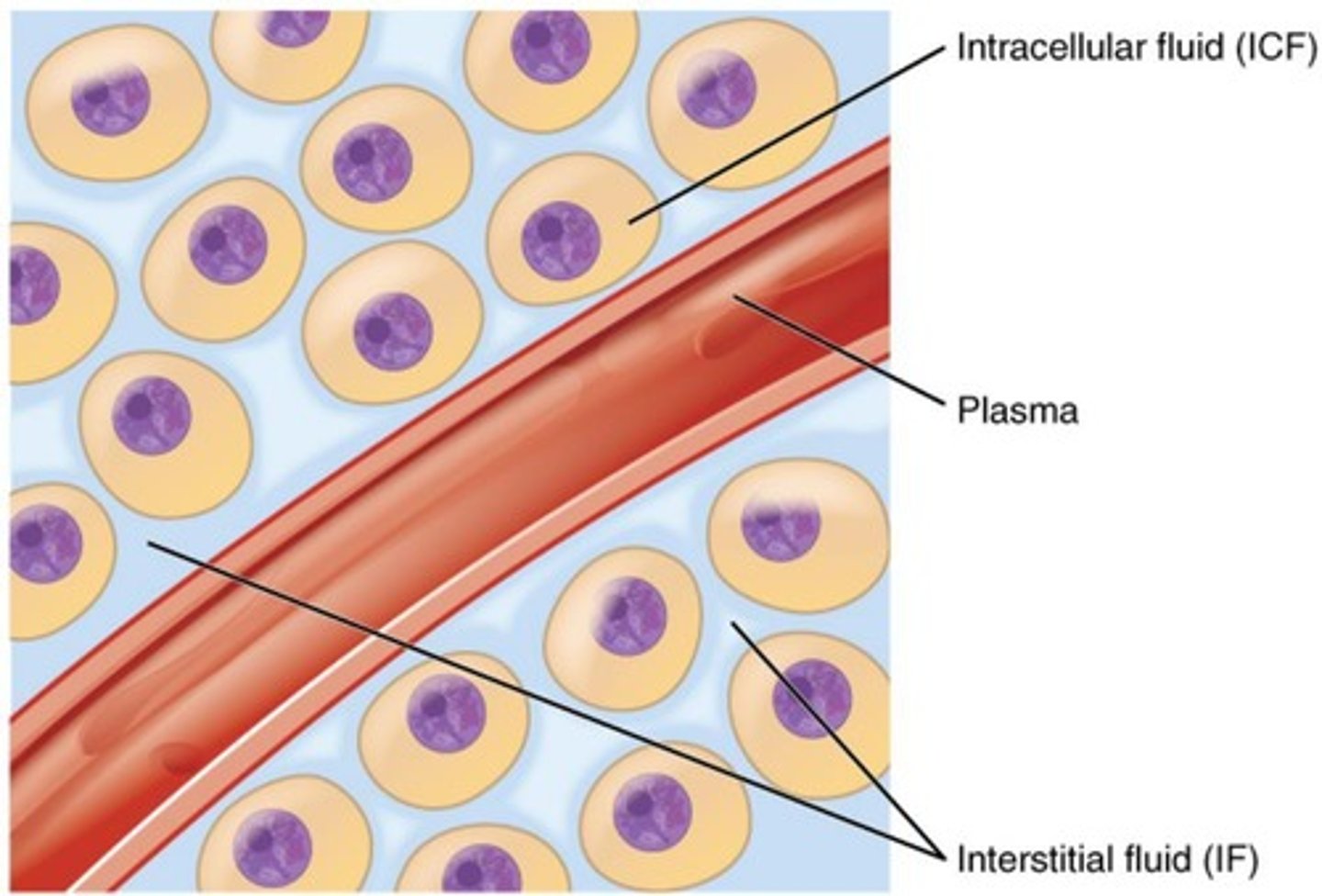
Plasma
Liquid portion of blood, 20% of extracellular fluid.
Interstitial fluid (IF) (part of ECF)
Fluid between tissue cells (lymph, eye fluid, etc.), 80% of extracellular fluid.
Major cation in extracellular fluid
Sodium (Na+) is the primary cation, similar in plasma & interstitial fluid
Major anion in extracellular fluid
Chloride (Cl-) is the primary anion followed by bicarbonate ion (HCO3-).
protein anion concentration..
intracellular fluid>>plasma>interstitial fluid
Major cation in intracellular fluid
Potassium (K+) is the primary cation, Mg2+ also important.
Major anion in intracellular fluid
Phosphate is the primary anion.
Sodium-Potassium conc.
very low is ICF, reflect activity of cellular ATP dependant on Na+/K+ pumps
electrolyte composition of ICF
potassium, magnesium, phosphate, protein anions, sulphate
electrolyte composition of ECF
interstitial fluid: Sodium, calcium, chloride, bicarbonate.
blood plasma: sodium, calcium, chloride, bicarbonate, protein anions
Resting membrane potential
Negative charge inside plasma membrane relative to outside in all cells.
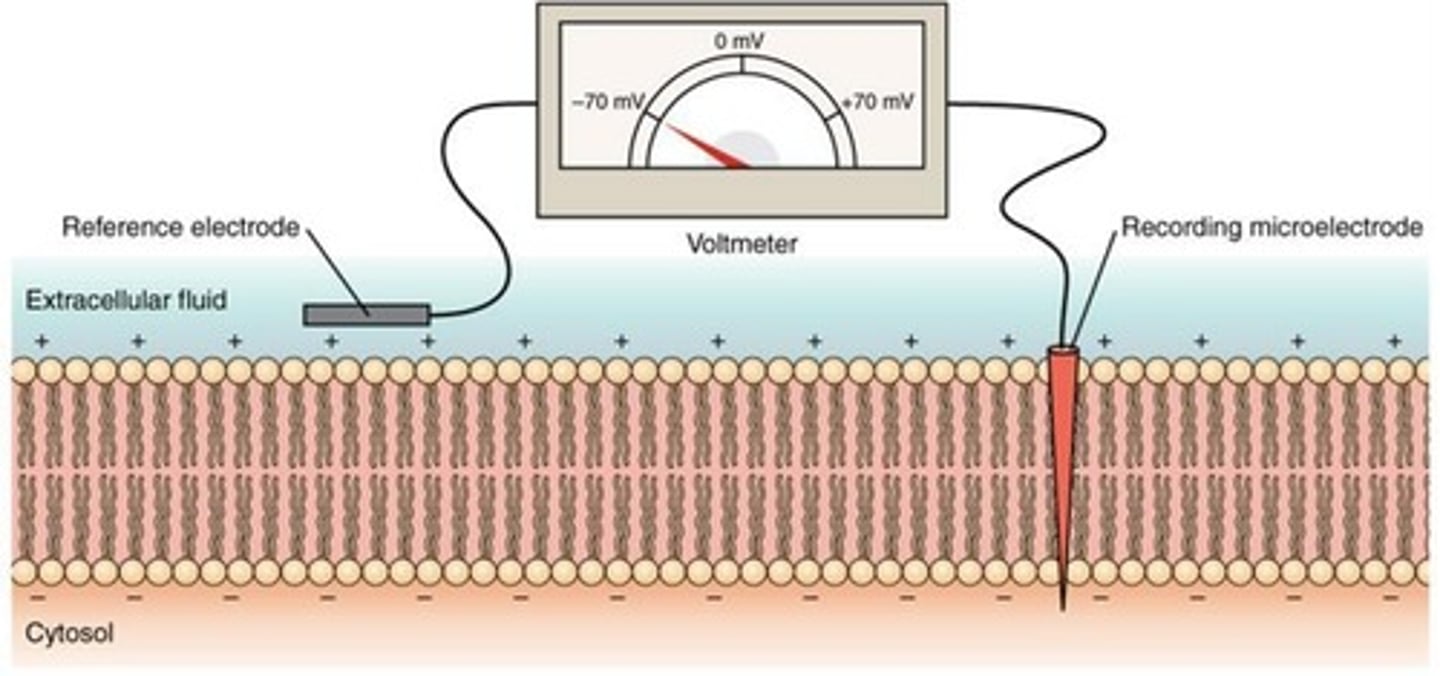
Resting membrane potential is due to three key factors:
1. Action of Sodium-Potassium Pump: 3 Na+ pumped out for every 2 K+ pumped in
2.Intracellular protein anions are trapped
3. Plasma membrane is more permeable to potassium than to sodium
Acid (special type of electrolyte)
Substance dissociate & releases hydrogen ions (protons) in water.
Strong acid
Completely dissociates, releasing many of H+ ions. ex. HCl
Weak acid
Partially dissociates, releasing few H+ ions. ex. carbon acid HCO3-
Example of strong acid
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) dissociates fully.
Example of weak acid
Carbonic acid (H2CO3) dissociates partially.
Base (special electrolyte)
Substance that accepts hydrogen ions from solution.
Strong base
Completely dissociates, removing H+ from solution. (ex. OH- + H+ = H2O)
Weak base
Partially accepts H+ ions in solution. (ex. H2CO3 = H+ + HCO3)
pH
Measure of H+ concentration per litre of solution.
pH scale
Ranges from 0 (acidic) to 14 (basic).
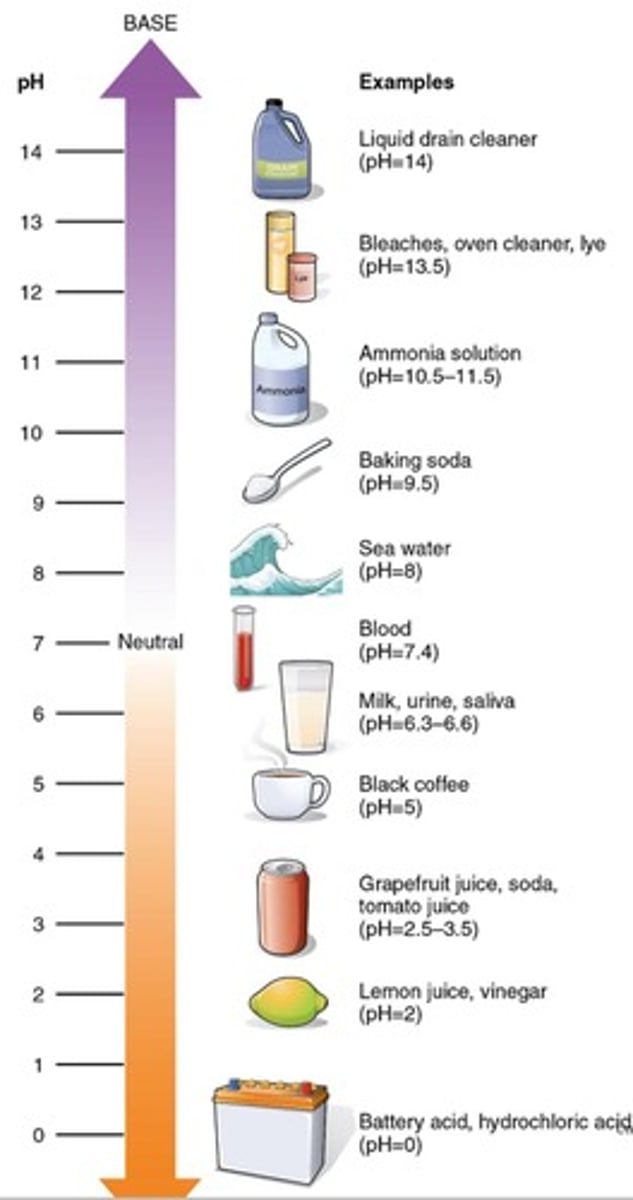
Neutral solution
pH of 7 indicates equal H+ and OH-.
Acidic solution
pH below 7 indicates higher H+ concentration less OH
Basic solution
pH above 7 indicates lower H+ concentration more OH.
pH change significance
Each 1 pH change equals 10-fold H+ change.
Salt
Electrolyte, ionic bonds, ions other than H+ & OH-, ex. NaCl
Salt formation
Acids and bases react to form salts and water (neutralization reaction).
Neutralization reaction
Reaction that prevents pH changes from acids/bases (not H+ donor or acceptor)
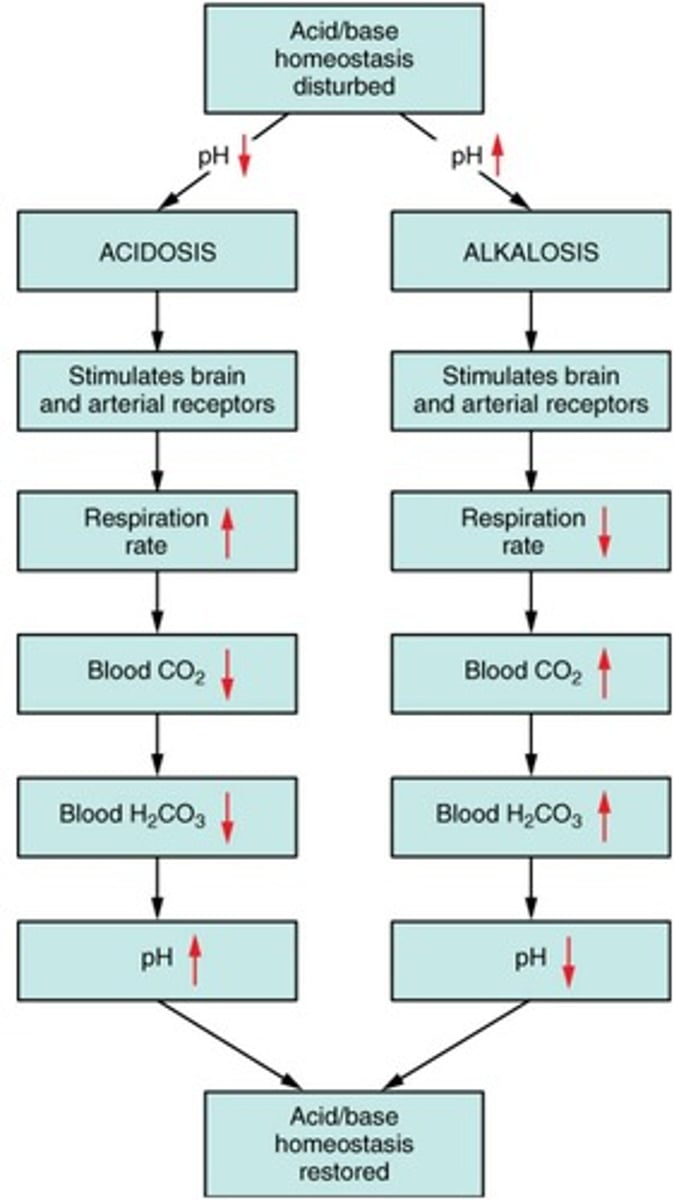
pH homeostasis importance
Big pH changes harm metabolic processes because they interfere with protein shape &
functions,
normal blood pH
7.35 - 7.45
Buffer
Solution resisting pH changes from added acids/bases.
How buffers work?
buffers has a weak acid & its salt (weak base), don't react with each other but with an added base/acid
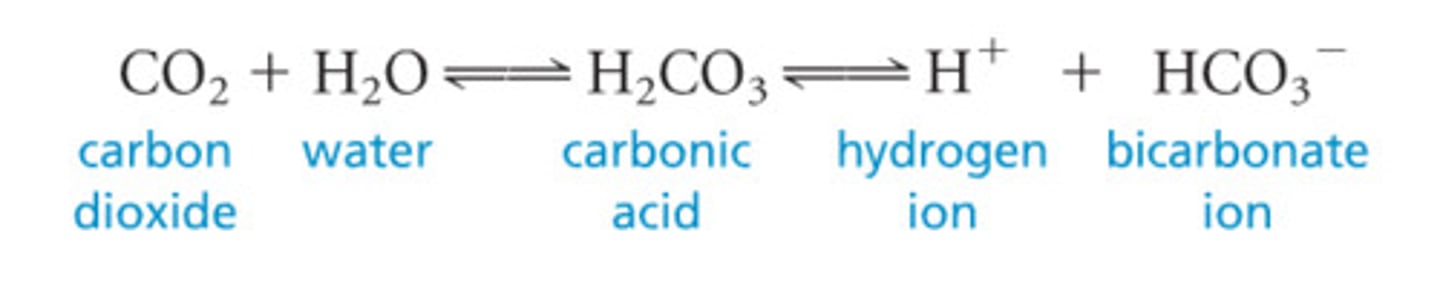
Carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer
Buffer system reacting to maintain pH balance. (H2CO3 HCO3- = + H+)
Acid component of buffer reacts when
base added by releasing H+ ions
Base component of buffer react when
acid is added by absorbing H+ ions
Chemical buffers (pH mechanism)
Immediate mechanism for short-term pH maintenance.
Respiratory system (lungs, pH mechanism)
Regulates carbon dioxide levels in body, works in 1-3 mins
Renal system (kidneys, pH mechanism)
Controls acid-base balance by excreting ions into urine, hours-days to affect pH
most abundant chemical buffer in ECF
regulator of blood pH bicarbonate to carbonic acid (HCO3- basic = H2CO3 acidic)
most effect buffer in urine & intracellular fluid:
phosphate buffer system, hydrogen phosphate to dihydrogen phosphate (HPO4 basic = H2PO4 acidic)
Add an acid to buffer (HCl)
Hydrogen ions released by the strong acid combine with the bicarbonate ions and form carbonic acid (a weak acid)
• The strong acid has been converted to a weak acid
• The pH of the solution decreases only slightly
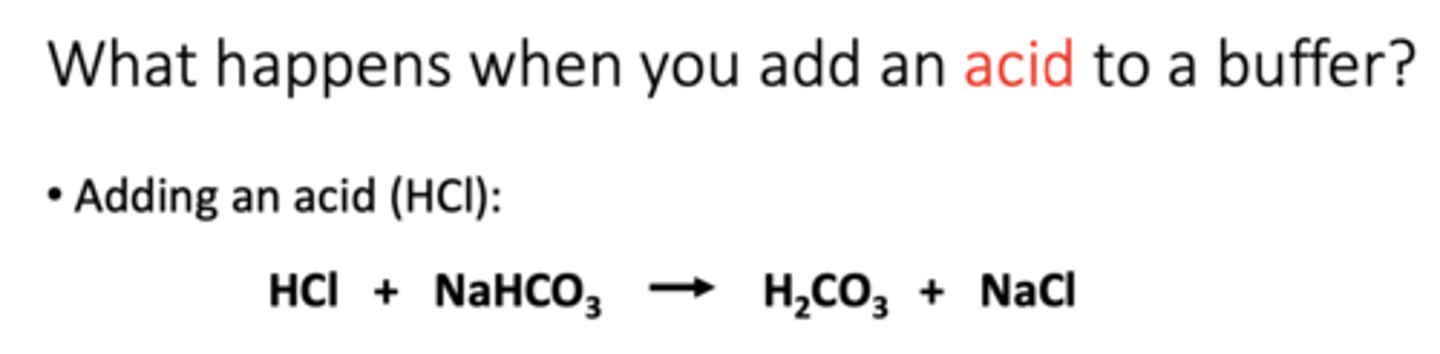
add base to buffer (NaOH)
The released OH- group reacts with the H+ released from carbonic acid to form water and bicarbonate ion (a weak base)
• The strong base has been converted to a weak base
• The pH of the solution increases only slightly2. Respiratory system
• Negative feedback loop regulates
blood pH by altering respiration rate
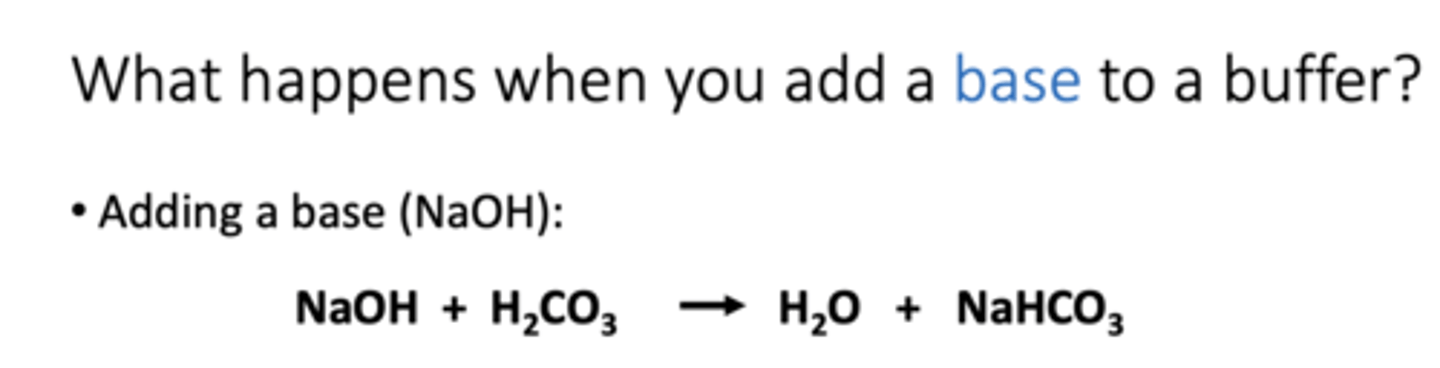
respiratory pH regulation:
Negative feedback loop regulate blood pH by altering respiration rate (ventilation rate). CO2 + H2O = H2CO3 = H+ + HCO3
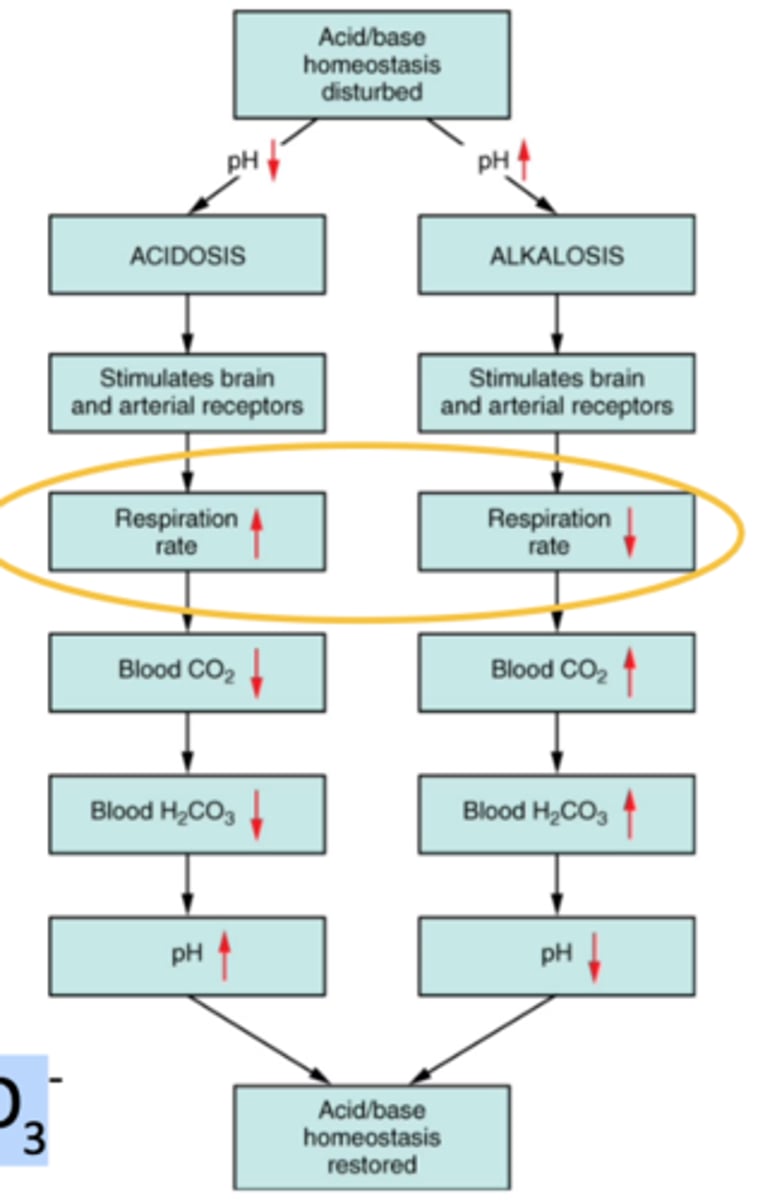
increase acidity of blood
increase acidity = increased H+, they'll combine with bicarbonate to make more carbonic acid which forms more CO2 & H2O. increased ventilation rate to remove excess CO2 to decrease H+
decrease acidic of blood
decrease acidity = decreased H+. Carbonic acid breaks down to make more hydrogen ions & bicarbonate, to do this lungs must retain more CO2 to make more carbonic acid (decreased ventilation), result in more H+ in blood
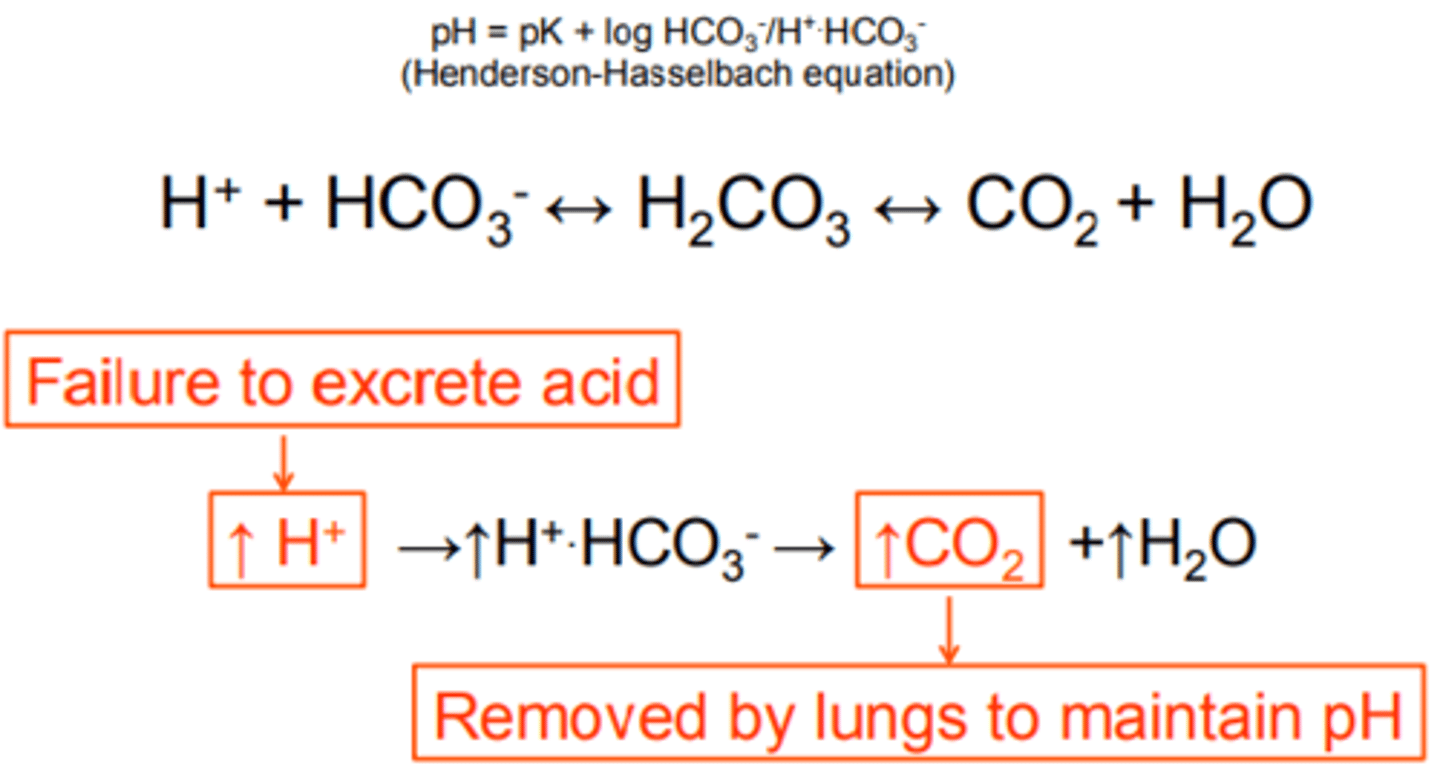
acidosis control in kidney
low blood pH:
1. H+ are secreted (from blood) into urine (proton pumps)
2. Bicarbonate ions are reabsorbed into the blood.
Urine pH Range
Normal urine pH varies from 4.5 to 8.
alkalosis control in kidney
high blood pH: The mechanisms to deal with
acidosis decrease
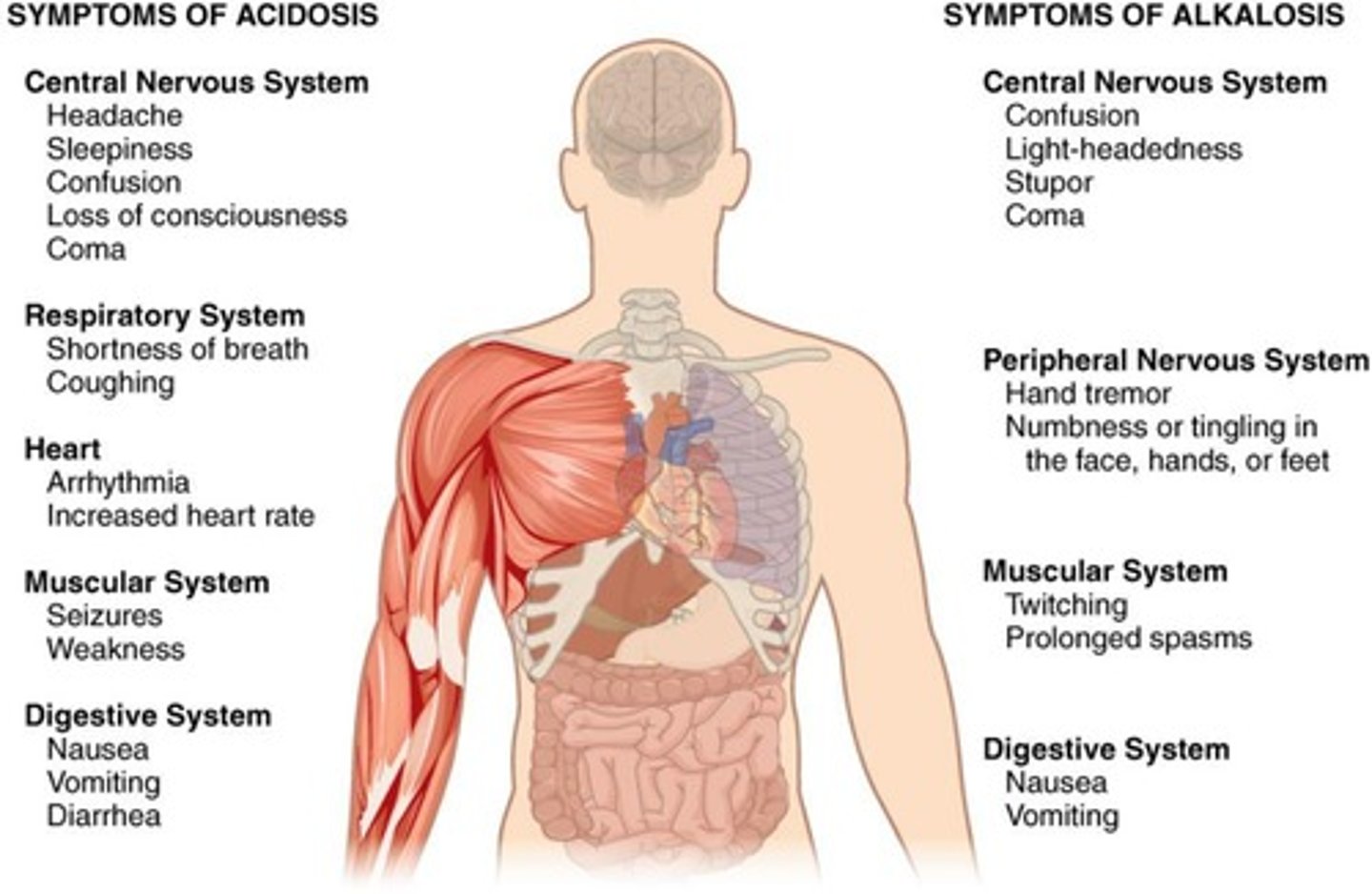
Acidosis
Condition with blood pH<7.35 (CNS depression → coma → death). blood may be alkaline, but still considered acidosis.
respiratory acidosis
Increased pCO2 in blood.
Impaired ventilation of the lungs (thus removal of CO2):
• Asthma
• Emphysema
• Barbiturate poisoning
• Damage of the brain stem
• Damage to respiratory muscles
metabolic acidosis
Increase in acids (increased H +/reduced bicarbonate ions in blood): Lactic acidosis, Ketoacidosis, Severe bicarbonate loss, Decreased renal excretion of H+
Lactic Acidosis
increased production of acids. Acidosis from strenuous exercise or hypoxia.
Ketoacidosis
Acidosis from uncontrolled diabetes mellitus or starvation.
severe bicarbonate loss
increases acids, caused from chronic diarrhea
decreased renal excretion of H+
increases acids, caused from kidney diseases
Alkalosis
Condition with blood pH greater than 7.45. Overexcitability of CNS → convulsions → death.
Respiratory Alkalosis
Decreased pCO2 due to hyperventilation: high altitudes, anxiety/stress, pain, aspirin OD.
hyperventilation decreases CO2:
cause reaction to shift and make more CO2 (HCO3- + H+ = H2CO3 = CO2 + H2O)
Metabolic Alkalosis
Increased bicarbonate ions in blood: loss of acids (excessive vomit, loose gastric HCl). too much alkaline drugs (antacid)
Proton Pumps
Transport proteins secreting H+ into urine.
CNS Depression
Reduced central nervous system activity, can lead to coma.
Overexcitability of CNS
Increased CNS activity, can lead to convulsions.
Bicarbonate Reabsorption
Kidneys reclaim bicarbonate ions into the blood.