(ANAT 612) Lecture 5 - Development of the Heart
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
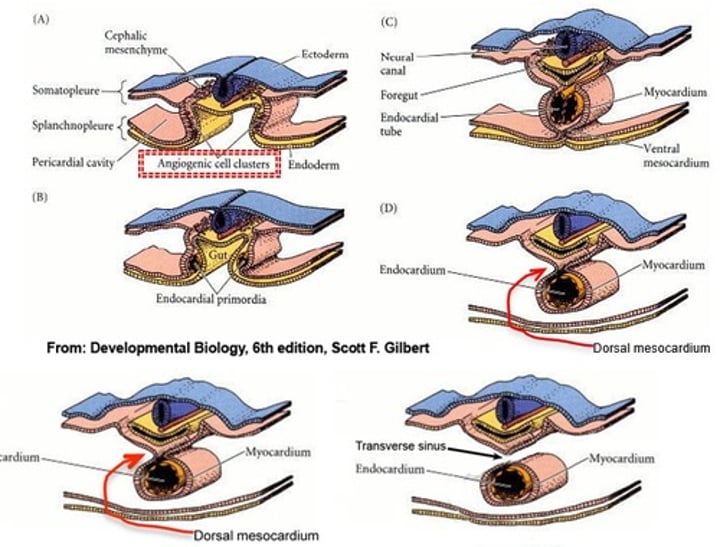
Explain how the primitive heart tube is formed
- angiogenic cell clusters located between the splanchnic mesoderm and yolk sac endoderm make up the initial pericardial cavities
- through lateral folding (head folding) those cavities come together beneath the gut tube (foregut)
- the pericardial cavity's myocardium is attached by the dorsal mesocardium
- dorsal mesocardium degenerates leaving the heart tube freely suspended in the pericardial cavity
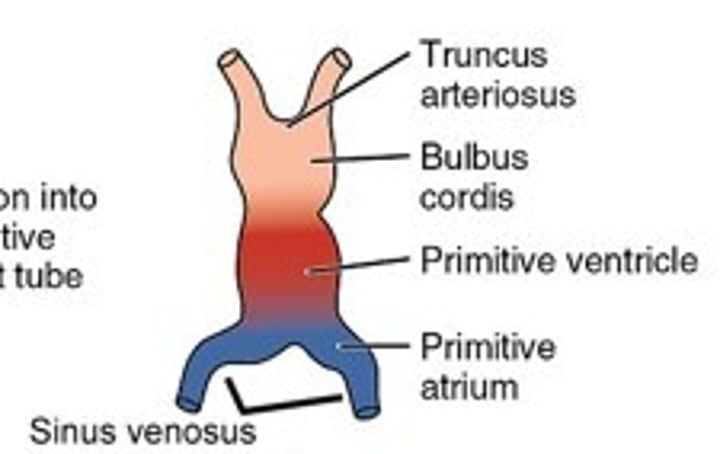
What makes up the primitive heart tube?
- truncus arteriosus
- bulbus cordis
- primitive ventricle
- primitive atrium
- sinus venosus
What structures make up the adult right ventricle?
- bulbus cordis
What structures make up the adult left ventricle?
- primitive ventricle
- some bulbus cordis
What structures make up the adult right atrium?
- primitive atrium
- right sinus venosus
What structures make up the adult left atrium?
- primitive atrium
- pulmonary vein (exstrophied)
True or False: the smooth patches make up more of the atria than the rough portions
True - the smooth portions are larger in both atria
What becomes of the left sinus venosus?
coronary sinus
What 3 types of veins flow into the sinus venosus?
- cardinal veins (anterior and posterior cardinal veins collect into the common cardinal vein before reaching sinus venosus)
- vitelline veins
- umbilical veins
The atriums have both smooth and rough patches. Explain what makes up these patches.
rough patches = primitive atrium
smooth patches = veins
- left atrium = pulmonary veins
- right atrium = right sinus venosus
Explain the formation of the atrial septum
- septum primum grows from the roof towards the endocardial cushion
- the opening between the septum primum and endocardial cushion is called the foramen primum
- the septum primum grows until it fuses to the endocardial cushion
- some of the middle piece of the septum primum has degraded leaving two pieces with a hole in the middle, called foramen secundum
- septum secundum starts to grow from the right side of the original septum primum on the roof
- the valley between the septum secundum and septum primum is called foramen ovale
- after birth, the pressure change, causes the septum primum and septum secundum to fuse, closing the foramen ovale
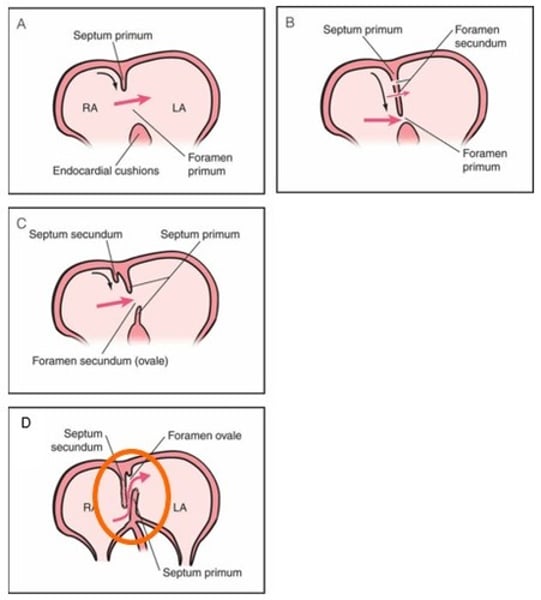
What type of defect is patent foramen ovale? What is it?
- Atrial septal defect (ASD)
- when the foramen ovale doesn't close
What can happen when there's premature closure of foramen ovale?
- heart muscle hypertrophy
What causes secundum ASDs?
- abnormally short septum secundum prevents the closure of the foramen ovale
Which ASDs is the most common?
A. premature closure of foramen ovale
B. patent foramen ovale
C. secundum ASDs
D. cor triculare biventriculare
B. patent foramen ovale
Which is the worst ASD?
A. premature closure of foramen ovale
B. overriding aorta
C. secundum ASDs
D. cor triculare biventriculare
E. transposition of the great vessels
D. cor triculare biventriculare (one atrium, two ventricles)
*B and E are VSDs
Explain the formation of the aortico-pulmonary septum and how it relates to the formation of the ventricular septum
- when the truncus arteriosus and bulbus cordis become the aorta and pulmonary trunk creating one outflow tract in each ventricle
- the membranous septum spirals within the tube until it reaches the outgrowth endocardial cushion (muscular) at the base (floor) of the ventricles (aka ventricular septum)
- coincides with the division of the ventricles
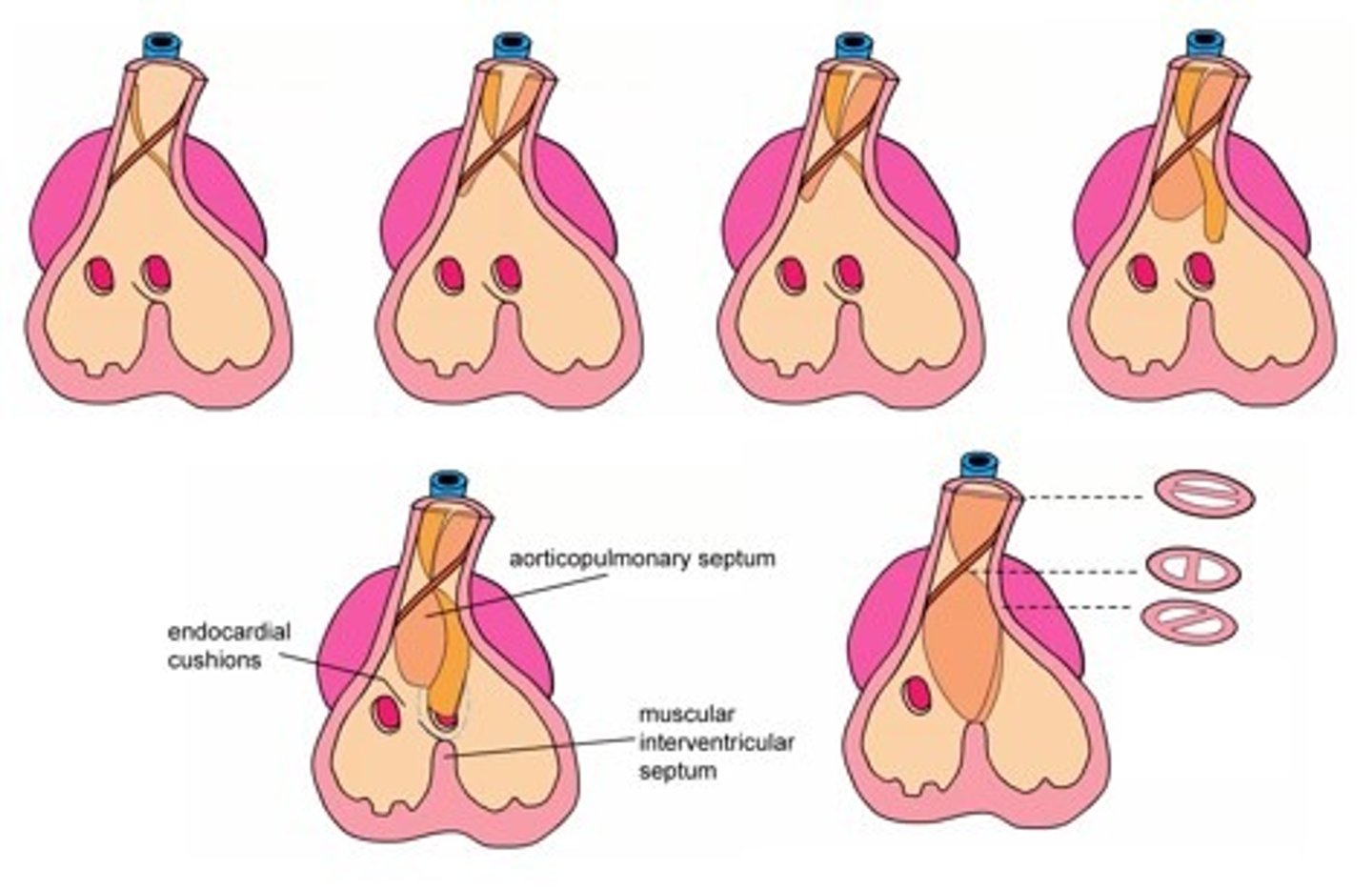
True or False: the membraneous portion is larger than the muscular portion of the aorticopulmonary septum/ventricular septum
False - the muscular portion is larger
What cells make up a large portion of the aorticopulmonary septum?
neural crest cells
Which one of these is NOT a ventricular septal defect (VSD)?
A. transposition of the great vessels
B. patent foramen ovale
C. overriding aorta
D. persistent truncus arteriosis
B. patent foramen ovale
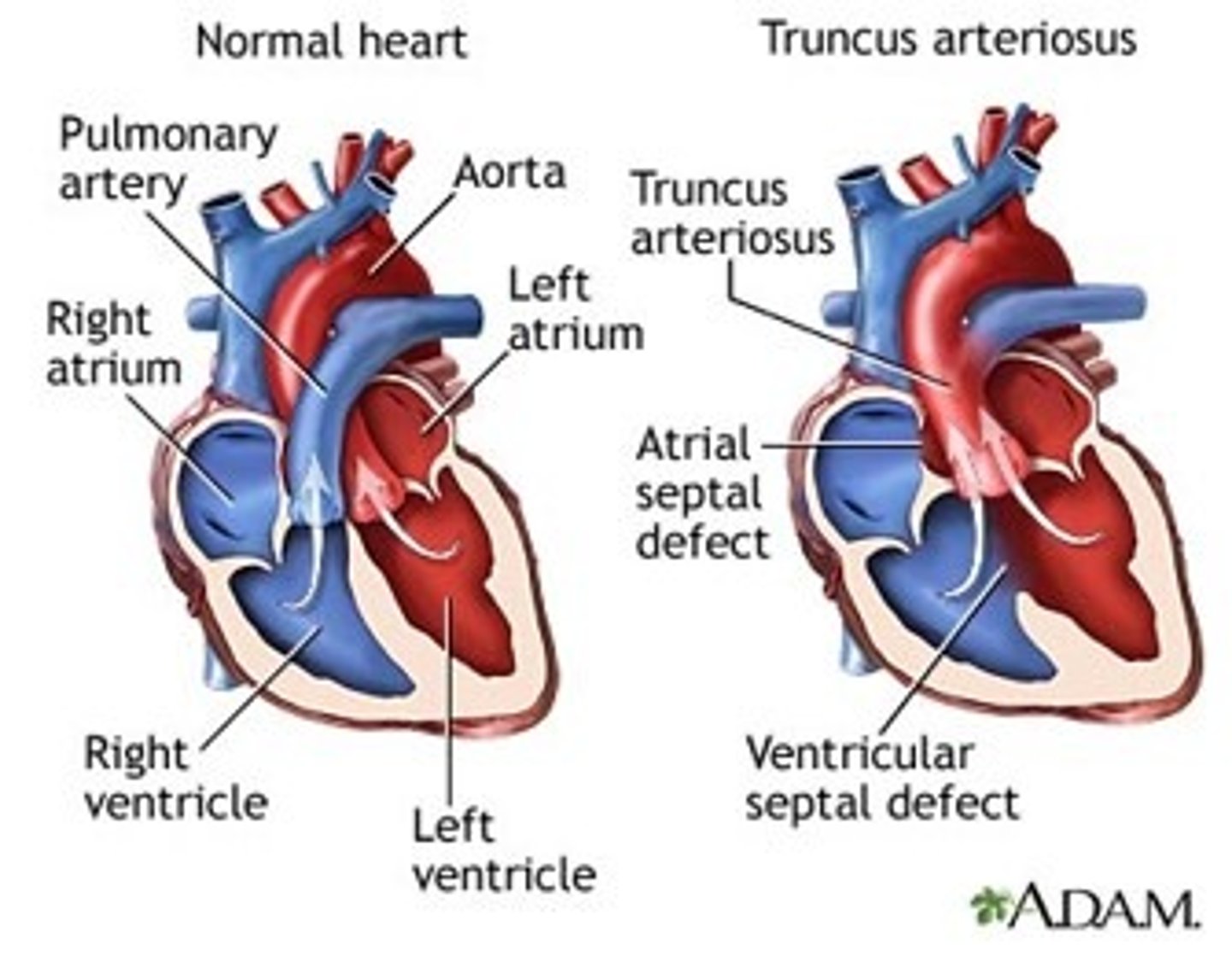
Explain persistent truncus arteriosus
- when the truncus arteriosus fails to divide into the aorta and pulmonary trunk due to a defect in the development of the bulbar/conotruncal ridges
- causes a VSD because the ventricular septum has nothing to attach to so there is a hole
- both ventricles flow into the common artery (truncus arteriosus) so oxygenated and deoxygenated flow out
- may or may not have a pulmonary artery coming of the common artery
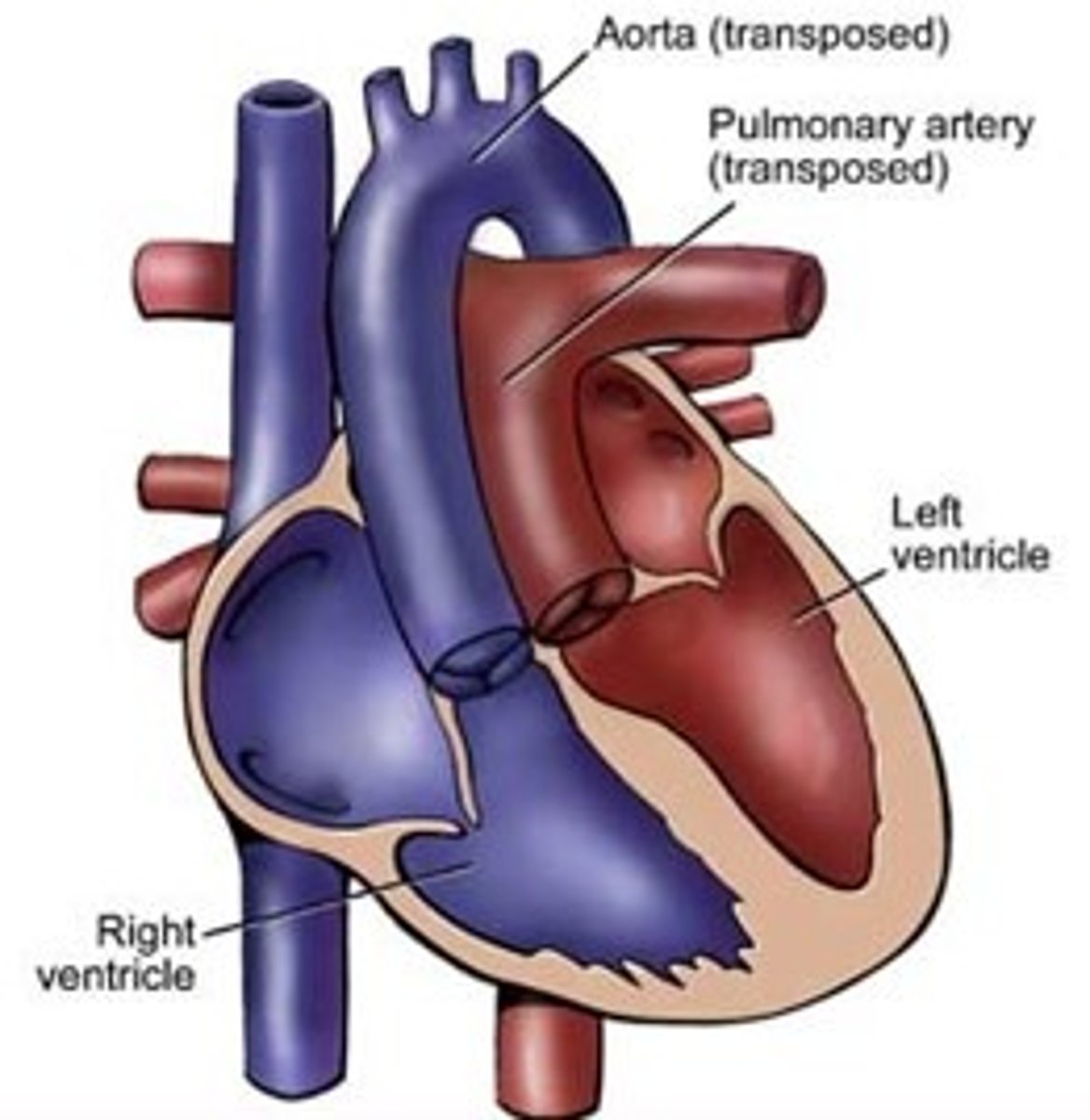
Explain transposition of the great vessels
- when the spiral of the aorticopulmonary septum doesn't occur so the aorta comes out of the right ventricle and pulmonary trunk comes out of the left ventricle
- oxygenated blood goes to lungs, deoxygenated blood goes to body
- may not involve a VSD because the aorticopulmonary septum can still attach to the ventricular septum
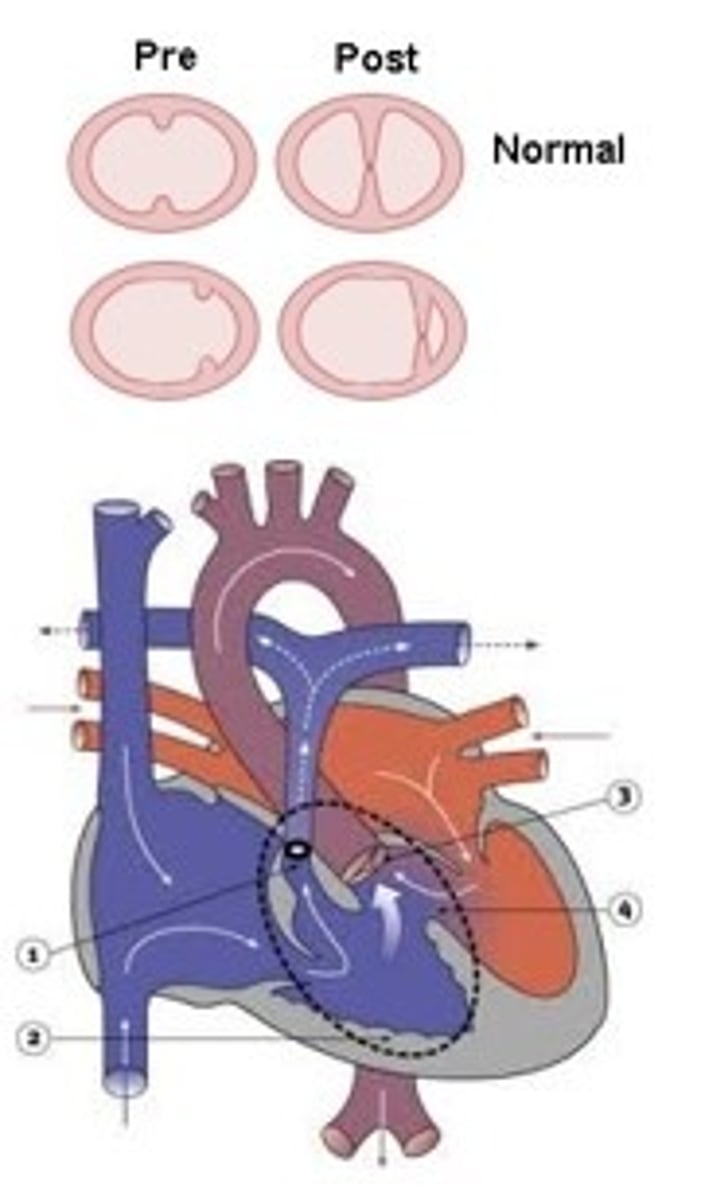
Explain overriding aorta or pulmonary trunk
- when the bulbar/conotruncal ridge development doesn't occur in the middle of the truncus arteriosus so the aorticoventricular septum does not equally divide the truncus arteriosus into two tubes
- causes VSD b/c aorticoventricular septum does not align with ventricular septum and attach
- whichever artery (aorta or pulmonary trunk) overrides receives the mixed blood
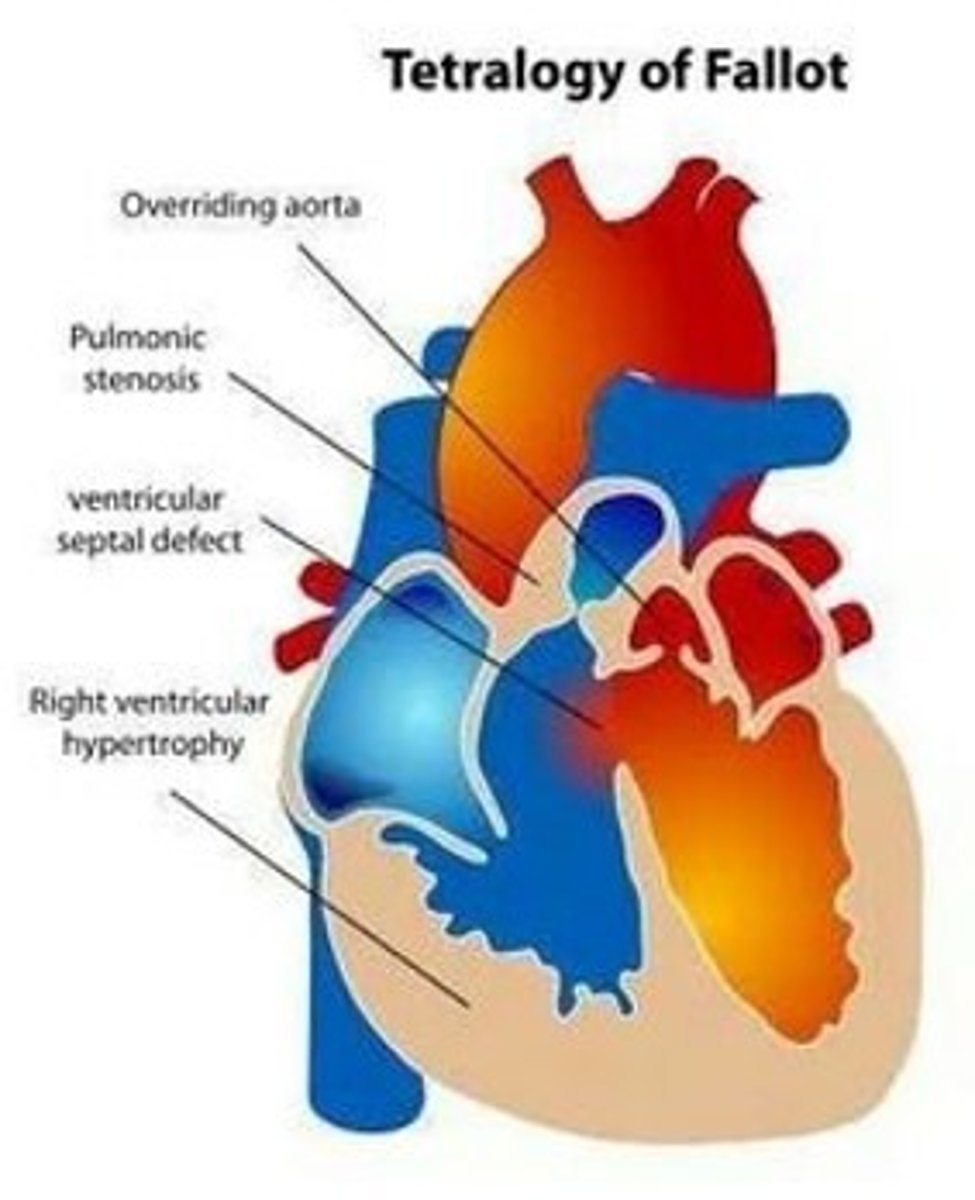
Explain Tetralogy of Fallot
- made up of 4 defects
1) overriding aorta
2) ventricular septal defect (VSD)
3) pulmonary stenosis
4) right ventricular hypertrophy
Which VSD may not actually have a VSD?
A. Tetralogy of Fallot
B. Persistent truncus arteriosus
C. Transposition of the great arteries/vessels
D. Overriding aorta or pulmonary trunk
C. Transposition of the great arteries/vessels
- because the aorticopulmonary septum may still align with the ventricular septum to divide the two ventricles
True or False: prenatal diagnosis of transposition of the great vessels is fatal
False - transposition of the great vessels is not immediately fatal because the foramen ovale is still open
Due to neural crest cell involvement, we typically see ____________ along with congenital heart defects.
cranio-facial abnormalities