ZOO 4513C - Exam 2 Study Guide
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Made by jordanstrunk248 on Quizlet :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
What is Umwelt?
An individual's or species' perception of their surroundings. Each species has a unique sensory system that affects how they perceive and respond to the world
How does cone arrangement affect color discrimination?
Widely spaced cones provide the broadest range of color detection but less discrimination. Closely spaced cones allow for finer color discrimination but narrower range
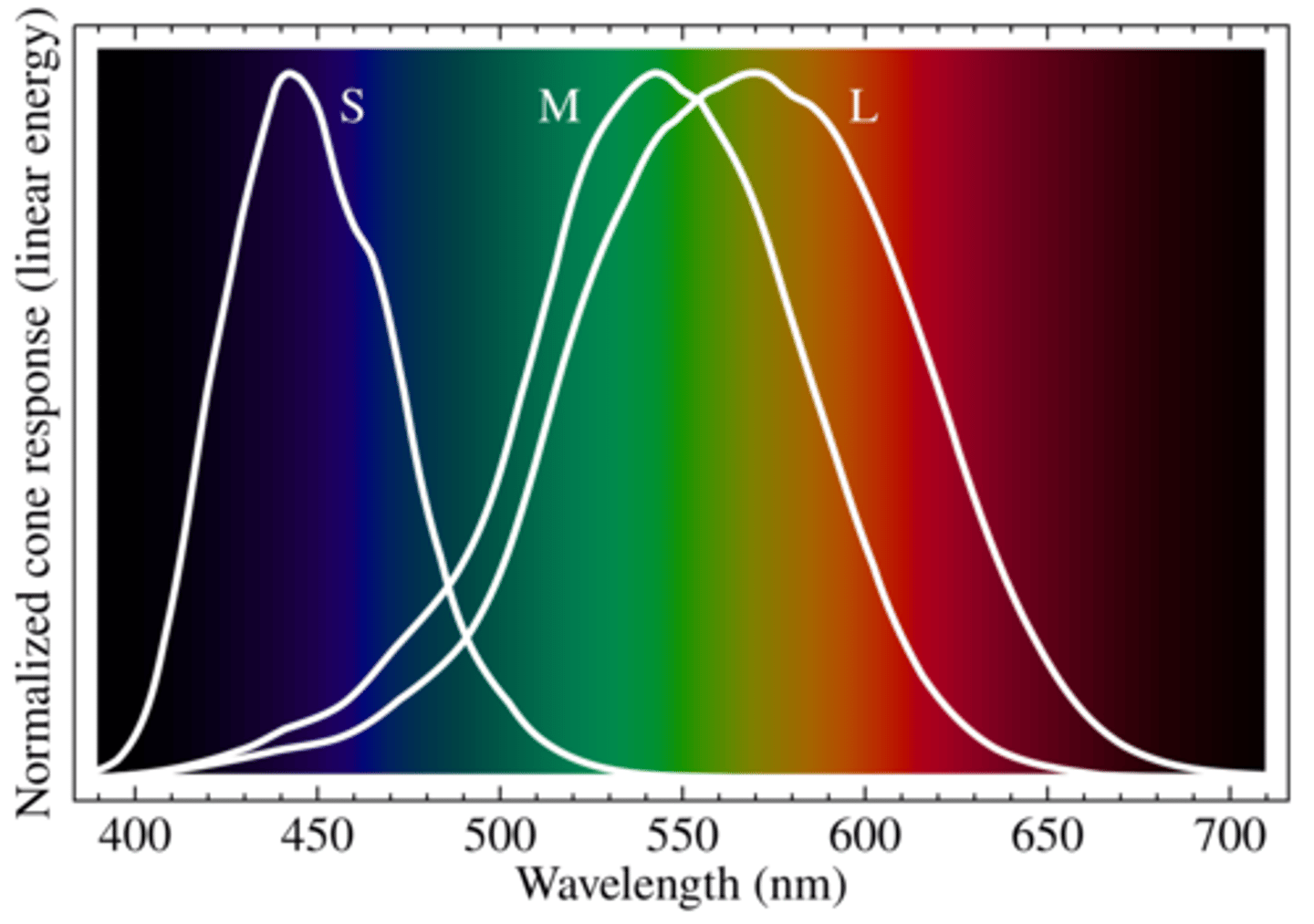
What is unique about the visual system of dogs compared to humans?
Dogs are dichromatic (two types of cones), allowing better peripheral vision and movement detection
How did Donald Griffin discover echolocation in bats?
Through sensory deprivation experiments in the 1940s.
Took place in a sound proof room with wires connected to the ceiling. He would plug/cover the bat's eyes, ears, and mouth to determine what they were using to navigate.
What is the range of ultrasonic calls emitted by bats? What is the range of human hearing?
Bats emit ultrasonic calls of 30-150 kHz. Humans can hear between 20 Hz-20 kHz
What are the two main types of echolocation calls?
Frequency Modulated (FM): short pulses with a downward sweep in frequency, broad rand detection, better for cluttered environments (forests), used by Big Brown Bats
Combined Signal (CF-FM): long constant tone followed by a downward frequency, better for open environments (grasslands), used by Greater Horseshoe Bats
What are the call phases during hunting for bats?
Search phase: 10-20 second calls, breathing between calls
Approach phase: increasing call rate, still breathing between pulses
Terminal buzz: ~200 calls/second, energetically demanding
What happens to the rate of calls as a bat approaches its prey?
The call rate increases
How does frequency affect the precision of echolocation?
Higher frequency calls (shorter wavelengths) provide more precise information. They also attenuate more quickly (lose energy).
Shorter wavelengths reflect better off of smaller objects.
How do bats avoid deafness from their own loud calls?
By closing ears with each pulse, inhibiting brain activity during pulse, and tuning ears to returning sounds rather than outgoing calls
How do tiger moths defend themselves against bats?
They produce ultrasonic calls that jam bat sonar, creating a "flash bomb" effect that disorients the bat
How do bats recognize water?
By its mirror-like echo reflection properties
What sensory input is most important for bats to capture prey efficiently?
Mouth and ears
When do bats rely on vision rather than echolocation?
When echolocation is ineffective, like at sunset in a cave when a lot of bats are calling at once
What is a key element of the umwelt concept?
Understanding that we cannot assume non-human animals perceive the world as humans do
How do human medium and long cones support social interactions?
They have significant overlap, allowing discrimination of subtle differences in facial coloration to help detect health, attraction, and emotional states in other humans
How do Brazilian Free-tailed Bats differ from most bats in terms of vocalization?
Unlike most bats, they vocalize in the audible range for humans
What evidence suggests that water recognition in bats is innate?
Experiments showed that even juvenile bats with no prior experience recognize water surfaces
What is the function of the tympanum in tiger moths?
It is a structure used to produce ultrasonic calls that jam bat sonar
What are some major threats to bat populations?
Wind turbines, habitat loss, invasive fungal disease, and declining insect populations
What is communication in a biological context?
Communication occurs when the behavior of one animal (signaler) affects the behavior of another animal (receiver)
Give an example of a signaler/receiver system.
Offspring acting as signalers and adults as receivers in birds
What is a pseudopenis?
A modified clitoris found in female hyenas
What are the problems associated with the pseudopenis in hyenas?
10% of first-time mothers die during birth through the clitoris
High androgen levels associated with pseudopenis development can cause sterility
What is the By-product Hypothesis regarding the pseudopenis?
Increased androgens may have made female hyenas more aggressive, as a by-product of selection within female social groups
What observations support the By-product Hypothesis?
Female hyenas are more aggressive than males, daughters inherit rank, and high-ranking daughters grow faster and survive longer
What is a problem with the By-product Hypothesis?
The pseudopenis is actively used, suggesting it has a function, whereas the hypothesis suggests it would have no use
What does the By-product Hypothesis suggest about androgen levels and rank?
More androgen should equal higher rank
What is the Signaling Hypothesis regarding the pseudopenis?
Males present penis in courtship to prevent female attacks; mutant pseudopenis could allow females to benefit from male-female signal subordination
According to the Signaling Hypothesis, which hyenas are more likely to present the signal?
Subordinate females
How does inheriting rank affect daughters in hyena societies?
High-ranking daughters grow faster and survive longer
What methodologies were used in the Atta ant study?
Measured isolated ant behavior, measured attenuation of stridulation, conducted Y-maze choice tests, and performed open arena choice tests
What are the findings of the Atta ant study?
Communication occurs through social signaling
Calls are highly localized (disappear within 6cm)
Ants that hear the signals will respond by moving toward them
Define eusociality.
Eusociality is an extreme form of social organization where species socialize and communicate with each other. Key characteristics include progressive parental care, division of labor, multigenerational care, and a caste system
Give examples of social species that are NOT eusocial
Humans, dogs, and cows
Describe primitively eusocial species.
Roles tend to be facultative (can change), and there is no defining characteristic that determines which female becomes queen. Example: Paper wasps
Describe highly eusocial species
Division of labor is not facultative and is associated with sterility of non-reproductive animals
Example: Honey bees and ants
How does sex determination work in bees, ants, and wasps?
Haplodiploidy. Males are haploid (receive only one gamete from the mother), and females are diploid (receive genetic material from both parents)
What is the genetic condition created by haplodiploidy thought to encourage?
Sociality through kin selection. Individuals can pass on their alleles indirectly when close siblings reproduce
How many of the same genes change each time eusociality evolves? (From the paper)
The same suite of about 200+ genes
What other biological trait shows similar genetic patterns to eusociality?
Echolocation. Genes associated with echolocation in bats are more similar to those in dolphins than to non-echolocating bats
What does the repeated use of the same genetic pathways for complex traits like eusociality and echolocation demonstrate?
There may be limited ways to achieve certain biological innovations at the genetic level, even when they evolve independently multiple times
What is a signal/receiver system?
Signal/receiver systems are prevalent throughout biology. Communication occurs when the behavior of one animal (signaler) affects the behavior of another animal (receiver)
Define communication in a biological context.
Communication is defined when the behavior of one animal (signaler) affects the behavior of another animal (receiver). Communication is also considered universal across organisms
What is a pseudopenis and in which animal is it discussed in the sources?
A pseudopenis is a modified clitoris found in female hyenas
Describe the By-product Hypothesis regarding the hyena pseudopenis.
The By-product Hypothesis suggests that increased androgen levels in female hyenas may have made them more aggressive, and the pseudopenis is a non-adaptive by-product of this selection for aggression within female social groups
What are some problems with the By-product Hypothesis for the hyena pseudopenis?
Problems with this hypothesis include that the pseudopenis is actively used, all females display the trait, selection should be directional (more androgen = higher rank) but evidence suggests stabilizing selection
Explain the Signaling Hypothesis for the hyena pseudopenis.
The Signaling Hypothesis suggests that a mutant pseudopenis could allow female hyenas to benefit from a male-female signal of subordination, increasing cooperation between subordinate females. Males present their penis in courtship to prevent female attacks, and females with a pseudopenis could mimic this signal
How do small Atta ants coordinate nest evacuation?
Small Atta ants coordinate nest evacuation through social signaling via highly localized calls (disappearing within 6mm). Ants that hear these signals respond by moving toward them
What is stridulation in the context of the Atta ant study?
Stridulation refers to sound production by the Atta ants, the attenuation (decrease in intensity) of which was measured in the study
How is language defined as a specialized form of communication?
Language is a specialized form of communication that requires abstraction, uses symbolic meaning, involves syntax, and provides symbolic representation
Describe the round dance performed by honeybees.
The round dance is used by honeybees for food sources close to the hive (within 50 meters). Bees circle in a circular pattern, indicating a nearby food source
Describe the waggle dance performed by honeybees.
The waggle dance is used by honeybees for food sources further from the hive and is a complex communication method with multiple information layers
What information does the orientation of the waggle dance convey?
The orientation of the waggle dance uses gravity and the sun as reference points to communicate the precise direction of a food source. This is considered a highly abstract communication system
What information does the length of the waggle in the waggle dance convey?
The length of the waggle in the waggle dance indicates the metabolic energy required to reach the food source, with approximately one second of dance per kilometer, considering two-dimensional space only
What information does the intensity of the waggle in the waggle dance convey?
The intensity of the waggle reflects the food source value, with the relative intensity changing based on environmental conditions
Describe the strategy of cuckoo chicks related to brood parasitism.
Cuckoo chicks lay eggs in other species' nests and mimic the begging call of the host species, producing a call suggesting a large brood to manipulate the host parents into providing more food
What are some key characteristics of bat communication calls, and what factors influence their variation?
Bat communication calls have species-specific characteristics and discernible differences between family groups. The structure of these calls can be analyzed by their frequency range, call length, and number of harmonic notes. Social groups influence call similarities more than genetic relationships, and environmental factors play a stronger role in communication patterns. This is analogous to regional accents in human communication
Describe the communication dynamic between frogs and bats, and what evolutionary trade-off does it illustrate?
Frogs produce mating calls that attract mates, but these same calls attract predatory bats. This illustrates an evolutionary trade-off between sexual selection and predation risk. Interestingly, females may prefer calls that increase predation vulnerability
What are two examples of unique communication phenomena involving fireflies?
Male fireflies use light signals for sexual selection. Additionally, there are femme fatale fireflies that produce signals to attract males of different species, which they then lure and consume
What is the central idea of the nature vs. nurture debate in behavioral development?
The central idea of the nature vs. nurture debate is not an either/or scenario, but an interaction between genetics and environment. While genes are fixed, the environment can change how they are expressed
How do genes and the environment interact in behavioral development?
While genes are fixed, the environment can change how they are expressed
How do birds typically learn their songs, according to the Mahler paper?
Birds learn songs by hearing adult birds, and this ability is species-specific
What happens to the song of a bird that is deafened?
Deafened birds can sing, but not accurately reproduce songs
How does selection pressure differ between young and adult animals?
Selection pressure acts more strongly on younger/adolescent individuals, and selective pressure decreases with age. After reproductive maturity, organisms begin to decay
Is behavioral development always a linear progression from young to adult behavior?
No, it is not always a linear progression from young to adult behavior. The importance of understanding developmental stages is a broader scientific insight
What are some key characteristics of play behavior in animals?
Play behavior is spontaneous, voluntary, and pleasurable. It occurs when an animal is fed, safe, and healthy
What are some key attributes that define play behavior?
Play is not fully functional, differs from mature behavior, is repeatable, and not stereotyped
What does the surplus resources hypothesis suggest about play behavior?
The surplus resources hypothesis suggests that play occurs when an animal has sufficient metabolic energy
How does developmental stability relate to bilateral traits and health?
Bilateral traits can vary during development, and more healthy organisms tend to show greater symmetry
What are critical learning periods in development?
Critical learning periods are specific windows for learning skills. Learning sensitivity varies by species, specific trait, and developmental stage
How is learning defined?
Learning is defined as a long-term change in behavior resulting from practice and experience. It is not necessarily permanent and occurs through individual and external experiences
What are the two primary types of learning?
The two primary types of learning discussed are non-associative learning and associative learning
What is non-associative learning?
Non-associative learning is learning that occurs from repeated exposure to stimuli
What are the two primary forms of non-associative learning?
The two primary forms of non-associative learning are habituation and sensitization
Define habituation.
Habituation is when a response declines with repeated exposure to a stimulus
Define sensitization.
Sensitization is when a response increases with repeated exposure to a stimulus
What is associative learning?
Associative learning is when a new behavior becomes connected to secondary stimuli. It involves connecting primary and secondary stimuli
What is classical conditioning?
Classical conditioning involves connecting a neutral stimulus with a biological response
Who developed classical conditioning and in what decade?
Ivan Pavlov developed classical conditioning in the 1890s
Name the key components of classical conditioning.
The key components of classical conditioning are Unconditioned Stimulus, Conditioned Stimulus, and Conditioned Response
What is an unconditioned stimulus?
An unconditioned stimulus is something that naturally triggers a response
What is a conditioned stimulus?
A conditioned stimulus is a neutral stimulus that becomes associated with an unconditioned stimulus
What is a conditioned response?
A conditioned response is a learned response to the previously neutral stimulus
What is operant conditioning focused on?
Operant conditioning focuses on modifying behavior through reinforcement
What is the difference between positive and negative reinforcement in operant conditioning?
Positive reinforcement increases the frequency of a behavior, while negative reinforcement decreases the frequency of a behavior
What is involved in social learning?
Social learning involves learning through observation and interaction. It includes types such as individual learning, social facilitation, observational learning, and local enhancement
What is required for an animal behavior to be considered 'teaching' according to these notes?
Teaching in non-human animals requires an actor to change their behavior to facilitate learning in another individual
What is cultural transmission, and can you provide an example from the notes?
Cultural transmission refers to population-specific behavioral patterns that are transmitted through social learning. An example from the notes is Japanese snow monkeys washing sweet potatoes
What is imprinting, and what are some of its critical roles?
Imprinting is described as developmental sensitive learning. It is critical for species recognition, parental bonding, and the development of survival skills
What is one way action potentials are similar to binary language communication?
The pattern of on and off signals can create variation and determine meaning
What is a key characteristic of an electrical synapse in terms of speed?
Electrical synapses provide a fast response with no delay in the action potential from one neuron to another
How can the "gates" in electrical synapses regulate the continuation of an action potential?
Closing the gates in electrical synapses will stop the action potential from carrying on
What is released at a chemical synapse?
Neurotransmitters are released at a chemical synapse
Where is a lot of the variation created in a chemical synapse, if it's not primarily the neurotransmitters?
The variation in chemical synapses is created in the receptors
What was the key factor determining the behavior of prairie voles versus montane voles, even though they had the same neurotransmitters (oxytocin and vasopressin)?
The key factor was where within the brain the receptors were located
What is the name of the very large neuron found in squids that is easily visible?
giant axon
How does the diameter of an axon affect the speed of an action potential?
A wide axon will have a faster action potential compared to a thin axon
What is the function of the stellate ganglion in the squid escape response?
The stellate ganglion receives signals from the giant axon and then radiates out other neurons to contract the mantle
Which type of synapse is faster, electrical or chemical?
Electrical