11 - GRAVIMETRIC ANALYSIS
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
A. 88.21
If a 0.3800 g sample of sodium sulfate yielded 0.55 g of barium sulfate precipitate by gravimetric assay, what would be the percentage purity of sodium sulfate? At.wt.: Ba = 137.3; S = 32.06; Na = 23; O = 16
A. 88.21
B. 99.94
C. 99.15
D. 88.51
D. 113.7%
If a 0.47 g sample of potassium iodide yielded 0.7564 g of silver iodide precipitate by gravimetric assay, compute for the % purity of the potassium iodide. MW KI = 165.90; MW AgI = 234.76
A. 83.7%
B. 93.7%
C. 103.7%
D. 113.7%
B. Physical
In gravimetric analysis, when the process used in extraction to obtain the original constituent, this method belongs to:
A. Chemical
B. Physical
C. Precipitation
D. Any of the above
A. 0.70668
Solve for the gravimetric factor, if a 0.235 g sample of potassium iodide yielded 0.3782 g of silver iodide precipitate by gravimetric assay, compute for the % purity of the potassium iodide.
A. 0.70668
B. 1.41507
C. 0.62136
D. 1.60936
B. Gravimetric
Analysis wherein the constituents of a sample are separated and then the product is weighed:
A. Volumetric
B. Gravimetric
C. Special method
D. Gasometric
C. Gravimetry
Assay of NaCl in table salt by precipitation as AgCl, filtration, drying and weighing the residue is classified as
A. Direct precipitimetry
B. Volhard’s method
C. Gravimetry
D. Residual precipitimetry
Law of Mass Action
Reversible Reactions
Solubility Product principle
Common Ion Effect
The chemical reactions in gravimetric analysis take place in accordance with the established laws and theories of chemistry:
Gravimetric Methods
The measurement of the weight of a substance in a sample
Calculation of the weight of a substance in a sample from the weight of a chemically equivalent amount of some other substance
Physical Methods
the substance to be measured gravimetrically is separated from other substances composing the sample
by physical methods, purify and weigh without chemical change
Frequently used in pharmaceutical analysis
Chemical Methods
Employed when other components of the sample are such that separation by physical means of the substance being measured is not possible or convenient
Convert the substance to a chemically equivalent amount of some other substance which can be separated, purified and weighed
Gravimetric Factor
the MW weight of the sample proportionate to the MW weight of residue/precipitate obtained from it
Chemical Factor
Gravimetric Factor is also known as
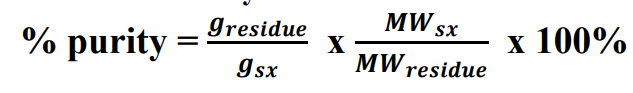
Gravimetric Factor formula
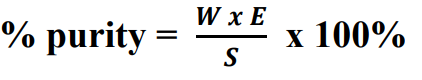
other Gravimetric Factor formula: