Biological Molecules, Nutrition, and Digestion Flashcards
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary terms from the lecture notes on biological molecules, nutrition, and digestion.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Organic molecules
Molecules that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms, often found in living organisms.
1. Carbohydrates; Monomer, main function, food source, energy role, extra
Monomer: Monosaccharides (e.g. glucose)
Main Function:
Primary energy source (quick-release energy)
Some used for structural support (e.g. cellulose in plants)
Food Sources:
Starch: Rice, potatoes, bread, cereals
Sugars: Fruit (natural), soft drinks, desserts (refined)
Energy Role:
Short-term energy
Stored as glycogen in animals, starch in plants
4 kcal/g
Other Notes:
Simple sugars = fast energy, cause spikes
Complex carbs = slow-release energy (healthier)
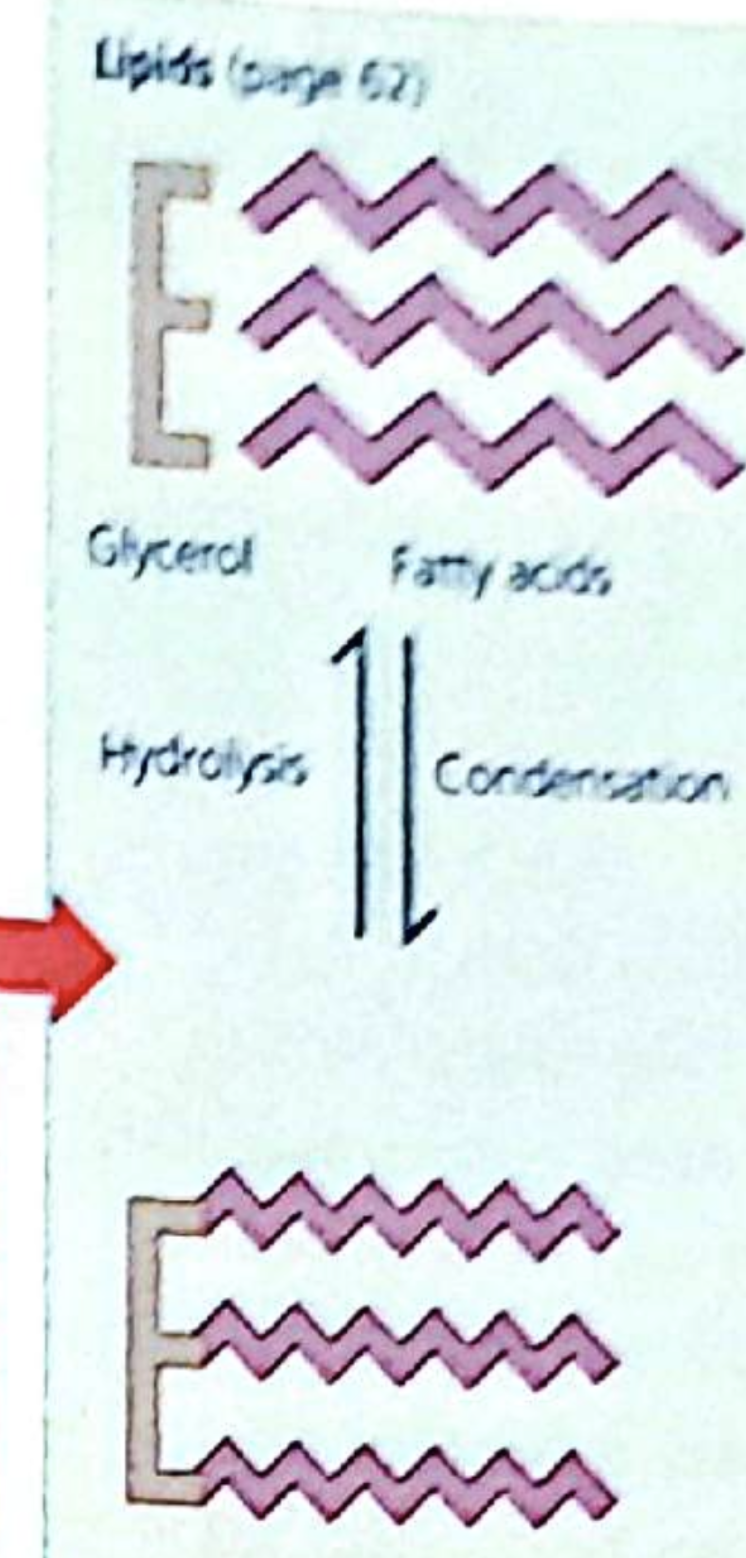
Lipase how made, main function, food source, energy role, other notes
Formed by the condensation of three fatty acid molecules with one glycerol molecule.
Fats (solid at room temperature) and oils (liquid at room temperature) are insoluble in water, excellent for energy storage and forming barriers between watery environments.
Main Function:
Long-term energy storage
Insulation (electrical & thermal)
Cell membranes (phospholipids)
Hormones (e.g. sex hormones from cholesterol)
Food Sources:
Saturated fats: Meat, cheese, butter
Unsaturated fats: Nuts, sunflower seeds, plant oils
Energy Role:
Long-term energy storage
Very energy-rich (9 kcal/g)
Other Notes:
Too much saturated fat → high cholesterol → heart risk
Unsaturated fats = healthier for heart
3. Proteins Monomer, main function, food source, energy role, extra
Monomers: Amino acids (20 types, 9 essential)
Main Function:
Build and repair body tissues
Enzymes (speed up reactions)
Transport (e.g. haemoglobin)
Hormones (e.g. insulin)
Immunity (antibodies)
Food Sources:
Meat, fish, eggs
Legumes, beans, soy, mycoprotein
Energy Role:
Not main source of energy
Used only if carbs/fats are low
4 kcal/g
Other Notes:
Animal proteins = complete
Plant proteins = may lack some essential amino acids
Deficiency diseases: marasmus, kwashiorkor
4. Nucleic Acids (DNA & RNA)
Monomers: Nucleotides (sugar + phosphate + nitrogen base)
Main Function:
Store and transmit genetic information
DNA: Blueprint for making proteins
RNA: Helps build proteins
ATP (a nucleotide): Main energy carrier in cells
Food Sources:
Found in all living cells (e.g. from meat, plants, anything with DNA)
Energy Role:
Not used as energy source
But ATP stores energy for cellular use
Other Notes:
Not broken down for fuel like carbs or fats
Metabolism
The sum of all the chemical reactions in living organisms.
Hydrolysis
Large organic molecules are broken down to smaller ones by the addition of water.
Condensation
Large molecules are built up from smaller ones by the removal of water.
Water
The most important biological solvent.
Diet
A total of the molecules or nutrients that we need.
Balanced diet vs Malnutrition
A balanced diet provides all nutrients in the correct amounts, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins, minerals, water, and dietary fiber.
Malnutrition occurs if the diet lacks nutrients in correct proportions.
Nutrition
Nutrition is the taking in of nutrients (organic substances and mineral ions), then absorbing and assimilating them.
Alimentary canal
Specialized tube running from mouth to anus (also called gut).
Mouth: Mechanical digestion (chewing) and chemical digestion (salivary amylase).
Oesophagus: Muscular tube that moves food to the stomach by peristalsis.
Stomach: Stores food, mixes food with acidic digestive juices (hydrochloric acid and pepsin).
Small Intestine (Duodenum, Ileum):
Duodenum: Mixes food with pancreatic juice (amylase, trypsin, lipase) and bile.
Ileum: Absorption of digested food molecules.
Liver: Produces bile, important in assimilation.
Gall bladder: Stores bile.
Pancreas: Produces pancreatic juice.
Large Intestine (Colon, Rectum):
Colon: Reabsorbs water from gut contents.
Rectum: Stores faeces before expulsion.
Anus: Exit for faeces.
Ingestion
Taking food and drink into the body through the mouth.
Mechanical Digestion
Breaking food into smaller pieces without a chemical change to the food molecules.
Chemical Digestion
Enzymes break down large, insoluble molecules in the food to small, water-soluble molecules.
Absorption
Small digested food molecules and ions cross the wall of the intestine into the bloodstream or lymph.
Assimilation
Digested food is moved into the cells of the body, where they become part of the cells and are used for energy, growth, and repair.
Egestion
Dietary fiber and other indigestible substances pass out through the anus.
Oesophagus
a muscular tube which helps food move to the stomach by peristalsis.
Liver
produces bile, which helps to neutralise acidic chyme and also emulsifies fats. Important in assimilation.
Duodenum
first part of the small intestine, where semi-liquid food is mixed with pancreatic juice and bile.
Bolus
ball of food
Mastication
cutting and mixing food
Digestion
Digestion converts large, insoluble molecules into smaller, soluble molecules via hydrolysis, catalyzed by enzymes.
Carbohydrate Digestion:
Salivary amylase (in mouth): starch→maltosestarch→maltose
Pancreatic amylase (in small intestine): starch→maltosestarch→maltose
Maltase (on small intestine wall): maltose→glucosemaltose→glucose
Protein Digestion:
Pepsin (in stomach): protein→amino acidsprotein→aminoacids
Trypsin (in small intestine): protein→amino acidsprotein→aminoacids
Fat Digestion:
Lipase (in small intestine): fats→fatty acids+glycerolfats→fattyacids+glycerol
Bile (from liver): Emulsifies fats to increase surface area for lipase.
Peristalsis
Waves of muscular contraction push the bolus down towards the stomach.
Salivary amylase
Enzyme that secreted in the mouth that catalyses the conversion of starch to maltose
Chyme
It is formed by the mixing of partially digested food with gastric juices. Chyme is then gradually released into the duodenum for further digestion and absorption. c
Water
Is absorbed from the gut contents that remain and indigestible food is then expelled.